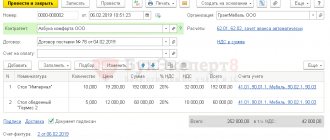
As you know, an integral part of VAT reporting is information from books of purchases and sales , and in some cases - a log of received and issued invoices . The task of the Federal Tax Service is to compare the data of sellers and buyers. If they match, the test will be successful. Otherwise, the operation will be classified as suspicious, and the declaration control system will require clarification.
Judging by the number of errors and questions that the Federal Tax Service receives, not all taxpayers have yet figured out how to correctly record various transactions in the books of purchases and sales.
Most of the difficulties are associated with the use of transaction type codes. We will talk further about how to fill out the mentioned registers when selling goods to organizations (entrepreneurs) and individuals.
We will also discuss issues related to processing the return of goods.
Rules for returning goods between legal entities
The possibility of returning goods is usually determined by an agreement concluded between organizations. If the parties have not agreed on a special procedure for terminating the transaction, then the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation are applied.
Returning goods of proper quality
Unlike the Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights, which applies to transactions made by citizens for household purposes, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for legal entities the right to return quality goods. This is only possible if the parties have included a special condition in the contract.
Important! Part 1 of Article 454 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes the direct obligation of the buyer to accept and pay for the goods if they fully comply with the terms of the contract. In case of refusal of its obligations, the client risks receiving a claim from the seller. In addition, the contract may provide for the payment of a penalty for late acceptance of goods.
Example from judicial practice 1. Diesel-TS LLC purchased a fan, vibration isolator and air vent from Industrial Ventilation LLC. The buyer paid for the goods in full, after which the seller delivered it and installed it. In the process of checking the functionality of the equipment, it turned out that it did not provide ventilation to the room. In this regard, Diesel-TS LLC sent a claim to the seller demanding a refund for the low-quality product. Industrial Ventilation LLC refused to satisfy the claim, so the buyer was forced to go to court to protect its interests.
During the consideration of the case, the judge found that the parties entered into a purchase and sale transaction without a contract . The supply of ventilation equipment was carried out based on the buyer’s request. The plaintiff did not provide evidence that the parties agreed on the terms of the quality of the goods. The case file included an expert opinion, from whose conclusions it does not follow that the ventilation equipment was of poor quality. In this regard, the court refused to satisfy the claim of Diesel-TS LLC (Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Volga-Vyatka District dated March 29, 2019 No. F01-985/20190).
Return of low-quality goods
With a low-quality product, the issue is much easier to resolve, since the law directly provides for the possibility of its replacement and return.
Thus, in accordance with Articles 475, 518 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a buyer who has received low-quality products from the seller has the right to demand:
- proportionate reduction in cost;
- elimination of defects at the expense of the seller within a reasonable time;
- reimbursement of expenses incurred in connection with the correction of product defects.
The buyer may also ask to replace the product with a similar one of adequate quality.
If the product has significant defects, the buyer has the right:
- refuse the transaction and demand a refund;
- request a replacement product.
Additionally, the seller can be required to pay a penalty for failure to fulfill the terms of the contract.
Example from judicial practice 2. NPP Marat LLC purchased a muffle furnace from Votkinsk Repair Plant LLC under a supply agreement. Under the terms of the contract, the seller guaranteed that if the buyer complies with the temperature operating conditions in accordance with GOST 977-88, the guarantee for hidden defects will remain. After accepting the goods, it turned out that the company had transferred the goods to the buyer of inadequate quality, and therefore the company filed a claim with the seller.
The claim was not fulfilled, so NPP Marat LLC filed a claim in court for a refund of the money for the goods. When considering the case, a forensic examination was carried out, the results of which revealed that the muffle furnace had a defect in the form of a burn through the lower part and cracks in the material. The reason for the disadvantage is the uneven wall thickness of the product. The defect is hidden and cannot be detected during normal acceptance of the goods. Due to the fact that the seller’s guilt was established, the plaintiff’s demands were satisfied (Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Volga-Vyatka District dated June 28, 2019 No. F01-2749/2019).
Terms for returning goods
Defects may be identified upon acceptance or subsequently during operation. In accordance with Article 477 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the return period is 2 years , unless a different period is established by the agreement. You can also apply for termination of the contract during the shelf life of the product .
After the buyer contacts the seller, he must return the goods within the period specified in the purchase and sale or delivery agreement. If the parties have not determined it, then the refund is made within 30 days .
After the seller agrees with the buyer's claim, he is obliged to return the money within 10 days .
A different period may be determined by the contract.
Essence of the question
Almost any citizen, entrepreneur or organization, purchasing goods, work or services, becomes a payer of a special type of fiscal burden - value added tax.
This payment is a kind of markup on the actual cost of the purchased product or service. Of course, a number of goods are exempt from taxation, but their number is insignificant. Despite the fact that in reality we are all payers of value added tax, its taxpayers, according to the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, recognize only legal entities and individual entrepreneurs using the general taxation system (OSNO), legal entities and individual entrepreneurs under special regimes (USN, UTII, Unified Agricultural Tax, PNS) when performing certain types of transactions.
What does taxpayer status give? This condition gives the economic entity not only the obligations to calculate and transfer funds to the budget, but also gives the right to a VAT refund. Sometimes taxpayer status is not required for this.
The procedure for returning money for goods between legal entities
Typically, the return of goods between legal entities is carried out on the basis of the procedure prescribed in the contract. The parties must comply with the claim procedure and try to resolve the conflict peacefully.
Let's look at the step-by-step instructions that the buyer must follow.
Step 1. Inspection of the goods upon acceptance and drawing up a report on identified deficiencies
One of the ways to accept goods is to follow the terms of the contract drawn up on the basis of Instructions P-6 and P-7 (resolution of the State Arbitration Court under the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated June 15, 1965 and April 25, 2966, respectively).
The buyer signs documents on acceptance of products only if they meet the contract requirements in terms of quantity and quality. It is advisable to create a commission in the organization consisting of different specialists who will weed out defective goods.
If defects are identified, they must be reflected in the acceptance documentation. In practice, the commission created by the buyer draws up an act that records the following information:
- date of acceptance of goods;
- composition of the acceptance committee;
- information about the parties to the agreement, the date of its conclusion;
- description of the goods being accepted;
- list of identified defects;
- decision to return the goods to the seller;
- signatures of the acceptance committee members.
If an expert was involved in the acceptance of the goods, then the name of the expert organization, data on the expert opinion and the results of the study should be indicated.
Step 2. Drawing up and submitting a claim
After drawing up the act, you must write a claim to the seller. The letter of claim must be sent to the legal address, as well as to the address specified in the contract, if it does not coincide with the legal address.
The claim should include information about the contract under which the delivery was made and about the defects identified upon acceptance of the goods. You should also determine a specific period for eliminating deficiencies.
Step 3. Conducting an examination of the quality of the product
If the seller does not agree that the goods supplied by him are of inadequate quality, a quality examination should be carried out. The buyer contacts an expert organization that has been accredited and specializes in the required type of research.
When appointing an examination, the expert involves the seller and the buyer. They have the right to be present during it and ask questions to the specialist.
Based on the results of the study, a conclusion is drawn up, which reflects the reasons for the occurrence of deficiencies, as well as the cost of losses.
Step 4. Submitting a repeated claim
After receiving the expert's opinion, the buyer makes a repeated claim, in which he describes the results of the study. The letter is drawn up according to the same template as given above.
In a repeated claim, it is necessary to set a new deadline for eliminating defects, and also warn the seller that in case of refusal, the buyer will go to court.
If any difficulties arise during the examination and preparation of the claim, we recommend that you contact a qualified lawyer. He will help you select a suitable expert organization and, after receiving the conclusion, issue a letter of claim.
Tax deduction for legal entities and individual entrepreneurs
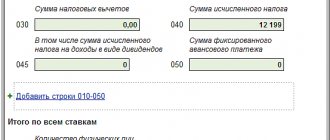
When selling, the tax payer includes obligations in the cost of the goods, work, or service being sold. The rate is 10% or 20% (10/110 or 20/120, respectively) of the sales price. All taxpayers have the right to a tax deduction. It is equal to the amount of tax paid as part of the cost of goods, works, and services purchased for business activities. For example, for the purchase of materials for production.
IMPORTANT!
Individual entrepreneurs and organizations that apply special regimes, but are payers of value added tax, do not have the right to reimburse it from the budget.
Consequently, taxpayers for whom in the reporting period the amount of tax payable to the budget exceeded the amount of tax deductions have the right to a tax deduction. This most often happens during export.
An export deduction for legal entities is also possible when applying a zero tax rate. In this case, the amount payable to the budget is zero. But the company acquired materials, services, and work for the production of export goods. This means you have the right to a tax deduction. As a result, a negative difference arises between the payment to the budget and the deduction amount. This difference accounts for the return.
These conditions are provided exclusively for organizations and individual entrepreneurs.
What to do if a legal entity is refused to return goods?
In the event that it was not possible to issue a refund, the organization has the right to protect its interests in court. Disputes between legal entities are considered by arbitration courts according to the rules of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation.
The buyer must draw up a statement of claim and attach supporting documents to it. We recommend using the claim template below.
The following documents must be attached to the claim:
- purchase and sale (supply) agreement;
- invoices, invoices, delivery notes;
- payment orders for payment for goods;
- expert opinion;
- complaint and response.
Before applying to the arbitration court, one copy of the claim is sent to the defendant. The shipping receipt is attached to other documents.
After filing a claim, the court accepts it and schedules a trial. 3-4 months to resolve the dispute . At the last meeting, the judge makes a decision that is binding on the seller.
Conditions and procedure for compensation
We outlined above in what cases VAT is refunded from the budget. Now let's figure out how to get reimbursement from the budget.
Key conditions for reimbursement:
1. An organization or individual entrepreneur uses OSNO. Let us repeat, subjects under other taxation regimes, even if they pay VAT to the budget, do not have the right to claim reimbursement of value added tax from the budget.
2. The amount of liabilities is less than the tax deduction. Please note that VAT payable is calculated not only on the cost of products sold, but also on a number of other transactions. The full list is enshrined in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
3. The right to compensation is documented. The taxpayer submitted all necessary documents to the Federal Tax Service:
- tax return;
- supply agreement;
- book of purchases and sales;
- invoices;
- stamped customs declarations;
- other documents.
4. An application for a VAT refund has been completed for an LLC, individual entrepreneur, non-profit organization or a taxpayer of another status.
IMPORTANT!
The return application form has been changed! Now you should fill out the form approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 14, 2017 No. ММВ-7-8 / [email protected] (as amended on November 30, 2018).
What purchases can be tax refunded to individuals?
An ordinary citizen cannot return compensation for the purchase of various goods. Only individuals registered as individual entrepreneurs have this right. There is a list of purchases for which VAT can be refunded:
- purchase of real estate for cash and on credit;
- purchasing a car;
- building materials;
- medical services and medicines;
- education;
- purchasing food;
- leasing;
- purchasing goods abroad (cars, equipment, phones, etc.).
A product purchased abroad is a completely different story, which has its own name - Tax Free. This system allows a person to get a tax refund. The only caveat is the list of products that allow for a refund. You should ask the representative providing the services about this (since each country has a different list).
Dear readers!
To solve your problem right now, get a free consultation
- contact the on-duty lawyer in the online chat on the right or call: +7 (499) 938 6124 - Moscow and region.
+7 (812) 425 6761 — St. Petersburg and region. +8 (800) 350 8362 - Other regions of the Russian Federation You will not need to waste your time and nerves
- an experienced lawyer will solve all your problems!