Despite the fact that the concept of an agency agreement appeared relatively recently, this form of civil law relations has become widely used in the modern financial environment. After all, engaging a third party who can provide high-quality services for non-core activities is a reliable tool for optimizing the work process of any enterprise.
In this article we will look at agency agreements in accounting in the form of step-by-step instructions.
How are the terms of an agency agreement and accounting entries related?
The relationship between the parties under an agency agreement is not limited to the direct purchase or sale of goods (work, services). Effective interaction in a principal-agent pair is impossible:
- without competent organization of document flow (including ensuring its completeness and timeliness);
- correct use of accounting accounts when reflecting transactions under an agency agreement (for the formation and presentation of reliable reports to interested users, as well as for the error-free execution of tax obligations).
Features of accounting procedures of the parties to an agency agreement directly depend on its terms. It is from the contract that the accounting staff of the agent and the principal need to learn such important accounting nuances as:
- whether the agent acts on his own behalf or on behalf of the principal;
- whether he participates in the calculations;
- whether goods pass through its warehouses;
- what terms and form of reporting by the agent to the principal are established and within what time frame the report is approved by the principal (or refusal to accept it);
- algorithm for calculating agency remuneration (in percentage, in a fixed amount, etc.);
- nuances of receiving remuneration (through deduction from amounts received from the counterparty or a separate transfer from the principal);
- frequency of agent reporting (as the contract is executed or after its completion);
- other important features that may affect the specifics of accounting and reporting under the agency agreement.
The materials in this section of our website will help you cope with the difficulties of drawing up various business agreements.
Before signing an agency agreement, be sure to check the terms for tax risks. ConsultantPlus experts explained how to do this correctly. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
The intermediary is not involved in settlements
If the intermediary does not participate in the calculations, in accounting, transactions related to the execution of the intermediary agreement are reflected in the following entries (excluding VAT transactions).
As of the date of approval of the report:
Debit 76 subaccount “Settlements with the customer for remuneration” Credit 90-1 - reflects the amount of intermediary remuneration;
Debit 76 subaccount “Settlements with the customer for reimbursement of expenses” Credit 60 (76) - reflects the amount of expenses subject to reimbursement by the customer.
On the date of receipt of funds from the customer:
Debit 50 (51) Credit 76 subaccount “Settlements with the customer for remuneration” - the amount of remuneration was received from the customer;
Debit 50 (51) Credit 76 subaccount “Settlements with the customer for reimbursement of expenses” - the amount of reimbursed expenses was received from the customer.
How to establish document flow between the agent and the principal?
The importance of organizing competent document flow cannot be underestimated, since timely received and correctly compiled documents will allow:
- confirm expenses and legality of VAT deductions;
Find out how to issue invoices when selling goods through an intermediary here. See also our article on re-invoicing under an agency agreement.
- prove the case in court when disputes arise between the agent and counterparties.
In addition to the agency agreement, the set of documents includes:
- originals of the counterparty's documents - contracts, invoices, invoices, acts, etc. (if the agent acts on behalf of the principal);
- copies of the above documents (if the agent acts on his own behalf);
- the agent’s report along with documentary copies confirming his expenses;
- invoices for agency fees;
- other documents (confirming payment of remuneration, other expenses of the agent, etc.).
The types of documents used are agreed upon by the parties to the agency agreement. Including the agent’s report form as a separate appendix to the contract - this document is given the status of a primary document confirming the principal’s expenses in the form of:
- agency fees;
- expenses reimbursed to the agent.
Ready-made solutions from ConsultantPlus will help you check the agency agreement for risks. Get free access and go to the Ready-made solution for the principal. And this link will take you to the Ready Solution for the Agent. If you do not have access to the legal reference system, trial access is available for free.
Purchasing goods and services through an intermediary in 1C: Accounting 8 edition 3.0
This article again focuses on intermediary operations. We will consider in detail, using a specific example, how in the 1C: Accounting 8 edition 3.0 program, transactions for the acquisition of material assets and services through an intermediary are formalized. Let's consider this situation from the side of the buyer (principal) and from the side of the intermediary (agent).
Example. The organization "Principal" for the purchase of goods and services (delivery of goods) uses the services of an intermediary - the organization "Agent". The agent participates in settlements and acts on his own behalf. In accordance with the agreement, his remuneration is 10% of the amount of purchased goods and services. In accordance with the accounting policy, the principal takes into account the costs of delivery of goods and the costs of intermediary services in account 44 “Sales expenses”.
Organizations apply the general taxation regime - the accrual method and Accounting Regulations (PBU) 18/02 “Accounting for calculations of corporate income tax”. Organizations are VAT payers. To maintain accounting and tax records, organizations use the 1C: Accounting 8 edition 3.0 program.
When selling goods and services, the seller issues invoices to the agent. The agent, in accordance with clause 11 of the Rules for maintaining a log of received and issued invoices, registers the invoices received from the seller in part 2 of the log. In this case, invoices are not subject to registration in the purchase book, since the agent does not have the right to deduct VAT (clause 19 of the Rules for maintaining the purchase book).
The agent issues (reissues) invoices to the principal, which reflect the invoices received from the seller. In accordance with clause 7 of the Rules for maintaining a log of received and issued invoices, the agent registers issued invoices in part 1 of the log. In this case, invoices are not registered in the sales book, since the agent does not have the obligation to calculate VAT (clause 20 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book).
The principal, having received reissued invoices from the agent, registers them in the purchase book, since in accordance with clause 2, clause 12 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax amounts presented by the seller to the buyer when selling goods (work, services) are subject to deductions.
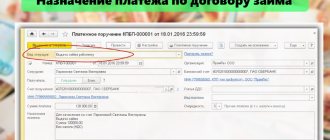
On January 11, 2021, the principal transferred funds for the purchase of goods and their delivery to the agent’s bank account. To reflect this operation in accounting, we will use the document Write-off from current account with the transaction type Payment to supplier. The document indicates the recipient - the agent, the transferred amount and the agreement. The most important thing is to correctly draw up an agreement with an agent in the program. The type of contract must be - With a commission agent (agent) for purchase.
The document Write-off from the current account and the result of its execution are shown in Fig. 1.
Picture 1.
The principal's funds were transferred to the agent's bank account. When a bank statement is received, the agent must create a document Receipt to current account with the transaction type Payment from buyer.
The agent also needs to correctly draw up the contract with the principal. The type of contract must be - With the principal (principal) for the purchase. The contract can specify the option for calculating the agency fee. In our case, this is 10% of the purchase amount. Settlement account 76.09 “Other settlements with various debtors and creditors.” The document Receipt to the current account is shown in Fig. 2.
Figure 2.
The next day, the agent transferred an advance payment to the supplier towards future delivery and delivery of goods.
The program generates a document Write-off from a current account with the transaction type Payment to supplier. The recipient is the supplier. Type of contract - With supplier. The document Write-off from the current account is shown in Fig. 3.
Figure 3.
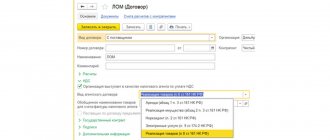
The supplier issued an invoice for the advance in the name of the agent. The agent received an invoice for the advance payment.
It is convenient to create the document Invoice received for an advance payment issued on the basis of the document Write-off from the current account (in which the advance was paid). In the created document, you need to change the invoice type From advance to the type To advance payment from the principal for the purchase, indicate the principal and the agreement with him. Transaction type code – 05 Advances for goods, works, services of the principal.
The document Invoice received with the type For an advance payment from the principal for the purchase does not deduct VAT and, accordingly, is not registered in the purchase book. But such an invoice is registered in the invoice journal. The document Invoice received is shown in Fig. 4.
Figure 4.
The agent must re-issue the advance invoice received from the supplier in the name of the principal.
The document Invoice issued for the advance payment of the principal for the purchase (reissued invoice) is created in the program on the basis of the document Invoice received. In the created document, you must indicate the details of the principal’s payment document and fill out the tabular section. Transaction type code 05. When posted, the document does not charge VAT and is not registered in the sales book. The invoice is recorded only in the invoice journal. The document Invoice issued is shown in Fig. 5.
Figure 5.
The principal, having received from the agent a re-issued invoice for the advance, on the basis of the document Write-off from the current account, with the help of which he recorded the transfer of funds to the agent, creates the document Invoice received.
In the created document, it is necessary to indicate that the invoice was drawn up on behalf of the supplier counterparty. Type of invoice For advance payment. Transaction type code 02 Advances issued.
Principal, in accordance with clause 12 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, has the right to deduct VAT. Therefore, when posting the document, the amount of VAT to be deducted will be taken into account in accounting (Dt 68.02 - Kt 76.VA) and will be registered in the purchase book (VAT purchase register). The document Invoice received for the advance payment issued and the result of its implementation are shown in Fig. 6.
Figure 6.
On January 18, the supplier shipped and delivered the goods to the agent. Moreover, the supplier issued one invoice to the agent for the goods and delivery.
To complete this operation, we will use the document Receipt with the transaction type Goods, services, commission.
The header of the document indicates the supplier counterparty and the agreement with him. In the tabular section on the Products tab, select the purchased product (item with the Product type), its quantity, price and VAT rate. Accounting account - 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping.” The principal, the agreement with him and the settlement account 76.09 are selected. In the tabular part, on the Agency services tab, the service provided by the supplier is selected (an item with the type Service), its price and VAT rate, the principal, the agreement with him and the settlement account are indicated. The invoice received from the supplier is recorded in the “footer” of the document. Transaction type code 04 Goods, works, services of the principal. An example of filling out the Receipt document is shown in Fig. 7.
Figure 7.
When posting, the document is entered in accounting as the debit of account 002 of the goods purchased for the principal, for goods and services it will generate entries Dt 76.09 - Kt 60.01 (the agent owes the supplier, the principal must compensate him for the costs), will offset the advance to the supplier and offset the advance of the principal.
Please note that the document did not make an entry in the VAT register presented, since the received invoice is not reflected in the purchase book, but is recorded only in the invoice journal.
The document was recorded in the register of purchased goods of the principals. This register is used to automatically fill out the Report to the Principal document. The result of posting the Receipt document is shown in Fig. 8.
Figure 8.
The agent is obliged to report to the principal on the purchased goods and services and reissue the invoice received from the supplier in his name. The agent claims a reward.
To reflect the above operations in the program, we will use the document Report to the Principal with the transaction type Procurement Report.
On the Main tab, the principal, the agreement with him, and the method of calculating the remuneration are indicated (for automatic filling, you could specify it in the agreement). A remuneration service is selected (an item with the Service type), accounting and analytics accounts (set automatically based on the information register of the Item Accounting Account and the Nomenclature directory).
The tabular parts on the Goods and services tab are filled in automatically using the “Fill” button -> Fill in purchased under the contract.
When recording (posting) a document, an Invoice document issued with transaction type code 04 - Goods, works, services of the principal (reissued invoice) will be automatically created, which will be reflected in the upper tabular part. A reissued invoice is recorded only in the accounting journal.
The document calculated the agency fee (10% of the purchase amount). An invoice for remuneration is issued on the Main tab.
When carried out, the document will accrue revenue (remuneration) to the agent in accounting and tax accounting, will charge VAT on the revenue and make an entry in the sales book (VAT Sales register).
An example of filling out the document Report to the committent and the result of its implementation are shown in Fig. 9.
Figure 9.
To actually transfer purchased goods to the principal, use the document Transfer of goods to the principal. The head of the document indicates the principal and the agreement with him. The tabular part on the Products tab is filled out based on the report to the principal. When posted, the document will write off the goods transferred to the principal from the credit of account 002. The document Transfer of goods to the consignor and its posting are shown in Fig. 10.
Figure 10.
Let's look at the agent's invoice log. The agent received from the supplier an invoice for advance payment (type of transaction code - 05) and an invoice for sales (type of transaction code - 04). Reissued these invoices to the principal. In column 8 the buyer-principal is indicated, in column 10 the seller is indicated, and in column 12, the invoices reissued by the agent refer to the invoices in part 2 of the journal received from the supplier (see Fig. 11).
Figure 11.
The principal, having received the report and invoices from the agent, creates two Receipt documents in his program.
To capitalize goods and services purchased through an agent, a Receipt document is created with the transaction type Goods; the document indicates the agent and the agreement with him. In the tabular section on the Products tab, select the purchased product (item with the Product type), its quantity, price and VAT rate. Accounting account - 41.01 “Goods in warehouses”.
In the tabular section on the Services tab, select the purchased service (item with the Service type), its price and VAT rate. The cost account 44.01 “Distribution costs in organizations engaged in trading activities” and its analytics are indicated - the cost item “Transportation costs”. The reissued invoice received from the agent is registered in the “footer” of the document. Moreover, when registering an invoice, it is necessary to indicate that the invoice was drawn up on behalf of the counterparty supplier. Transaction type code 01 Receipt of goods, works, services. An example of filling out the Receipt document is shown in Fig. 12.
Figure 12.
When carrying out the document, the purchased goods will be credited in accounting and tax accounting on the debit of account 41.01, the delivery costs will be taken into account on the debit of account 44.01, the VAT presented by the supplier will be allocated on the debit of account 19, the debt will be charged on the credit of account 60.01 and the advance will be offset.
The document will make entries in the VAT register presented - the supplier has presented VAT. If there is an invoice, the VAT amount from the VAT register presented goes into the Purchases VAT register (purchase book) and is accepted for deduction. This operation in the program is performed by the document Invoice received (with the “Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book by the date of receipt” checkbox enabled), or by the regulatory document Formation of purchase book entries at the end of the quarter. The result of posting the Receipt document is shown in Fig. 13.
Figure 13.
To reflect the costs of agency remuneration in accounting, you need to create a second document Receipt with the transaction type of the document, indicate the agent and create a new agreement with him - a remuneration agreement. The type of contract must be - With the supplier. In the tabular part of the document, select the purchased service (item with the type Service) - agency fee, its cost and VAT rate. Cost account 44.01 and its analytics are indicated - a cost item with an expense type for tax accounting Other expenses. The invoice for the remuneration received from the agent is registered in the “basement” of the document. Transaction type code 01. When carrying out the document in accounting and tax accounting, it will take into account the expenses for agency fees on the debit of account 44.01, allocate the VAT presented by the agent on the debit of account 19.04, and accrue the debt on the credit of account 60.01. The document will also make an entry in the VAT register presented. An example of filling out the Receipt document and the result of its implementation are shown in Fig. 14.
Figure 14.
Finally, let's look at what is contained in the principal's purchase book. In the purchase book, in the part of our example, there are three entries. An advance invoice was received with transaction type code 02 Advances issued and a sales invoice was received with transaction type code 01 Receipt of goods, works, services (invoices reissued by the agent), the supplier counterparty is indicated in column 9, in column 11 an intermediary is indicated - an agent. An invoice (transaction type code 01) for the agency fee was also received from the agent. The principal's purchase book, in part of our example, is shown in Fig. 15.
Figure 15.
Accounting for agent and principal
To reflect transactions under an agency agreement in accounting, various accounting schemes are used to record the relationship between the parties to an agency agreement in the following situation:
- sales of products (goods, works, services) by an agent;
- purchasing intermediary operations.
Accounting for an agent under an agency agreement and accounting for agency agreements for a principal are presented in the figures:
Agency for sale
Agency for purchase
You can also read about the features of an agency agreement in accounting here.
Reward amount
Payment for agent services lies solely in the contractual area .
The parties themselves decide how much certain services cost. If for some reason it is impossible to establish what amount the parties agreed on, or they simply did not do it, deciding to postpone it until later, then in the event of a dispute, the court applies the provisions of Art. 424 Civil Code. If there is a legal requirement regarding the services provided and their prices, the parties are guided by the tariffs determined by the authorities having the authority to do so.
If the parties have not previously resolved the issue of price, the court will proceed from the cost of similar services in the same area.
A change in the amount of remuneration may be provided for directly in the contract or in an additional agreement to it.
Results
In order not to make mistakes with transactions under an agency agreement, it is necessary to study its terms - on the basis of which documents to reflect transactions in accounting, what algorithms are used to calculate agency fees, etc.
The main account for recording transactions is 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” in correspondence with accounts 51 (for payments), 68/2 (for VAT accounting), 44 (for registering purchased goods), etc. More
complete You can find information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Examples of reflecting transactions
In practice, various options for the above correspondence accounts can be used. Let's look at some examples of such transactions and how transactions are reflected in accounting records.
Example 1 (customer accounting)
produces stone products. attracts clients for it according to the GPC agreement, the remuneration is 6% of sales. At the end of the month, payment for the product amounted to 150,000 rubles, the cost of products was 100,000 rubles.
Agent's remuneration in costs:
- 150,000*6% - (150,000*6% *20%) = 7200.00 rub. D 20 - K 76 - 7200.00.
- 7200 *20% = 1440.00 - VAT is charged on the remuneration. D 19 - K 76 - 1440.00.
- D 68/2 - K 19 - 1440.00 - accepted for deduction of VAT on remuneration.
- D 90 - K 20 - 100,000.00 - written off products (including costs for agency services).
Agency fee in settlements with the agent: 150,000 * 6% = 9,000 rubles. Income minus remuneration: 150,000 - 9000 = 141,000.00 rubles. D 51 - K 62 - 141,000.00 - income received minus remuneration. D 76 - K 62 - 9000.00 - the remuneration is offset against payment from the buyer.
Example 2 (accounting with an agent)
For a fee of 5% of the goods sold (settlement on payment) the company sells products - equipment for animals. During the month, goods worth 100,000 rubles were shipped, including VAT - 16,666.67 rubles.
Goods sold for 75,000 rubles, including VAT - 12,500 rubles. Payment for goods - 70,000 rubles, including VAT - 11,666.67 rubles. Agent costs 250 rub.
Postings:
- D 004 - 100,000.00 - goods accepted for storage.
- D 62 - K 76, K 004 - 75,000.00 - goods sold.
- D 51 - K 62 - 70,000.00 - goods paid for.
- D 76 - K 76 (according to subaccounts) 70,000.00 - report to the customer for goods sold.
- 70000*5% = 3500 rub. D 76 - K 90/1 - 3500.00 - remuneration accrued.
- D 76 - K 76 - 3500.00 - remuneration is withheld from sales income.
- D 90 - K 68/VAT - 583.33 - VAT on remuneration.
- 3500 - 583.33 - 250 = 2666.67 rubles. - agent's profit. D 90 - K 99/9 - 2666.67.
- 70,000 - 3500 = 66,500 rubles. revenue minus remuneration. D 76 - K 51 - 66500.00 transfer of proceeds to the customer of services.
Question: An organization (principal) has entered into an agency agreement with a citizen of the Russian Federation (not an individual entrepreneur), who, on behalf and at the expense of the principal, provides services for searching for buyers in China on the basis of a power of attorney. What is the procedure for taxing agency fees with personal income tax and insurance premiums? View answer
Agent's report
Thus, in an agent’s accounting, the main document on the basis of which income is reflected and the tax bases for VAT and income tax or simplified taxation system are formed is the agent’s report. The report is provided within the time limits established by the contract. The report is considered accepted by the principal if, within the period established in the contract, the latter has not received any objections to the data reflected in the document. Since the deadline for submitting the agent’s report is not established by law, and 30 days are allotted for the principal’s objections under the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, it is advisable to establish by agreement the frequency or deadline for the submission of agency reports, as well as a reasonable period for its consideration by the principal.
The form of such a report is not fixed by law, but it is subject to general requirements for mandatory details for primary accounting documents. To avoid disagreements at the stage of accepting the agent’s services, it is better to agree on the reporting form as an annex to the contract. According to existing business practices, the fact that the agent provides services is additionally documented in an act of provision of services, and this act can also be made part of the report. The condition for signing the act or its combination with the report must be fixed in the contract.
Withholding amounts
Now let’s consider the procedure for recording transactions when the agent withholds remuneration from the amounts received from the buyer of goods (services, works) of the principal:
Debit 62 (76) Credit 90
— 2000 rubles – the agent’s income is recognized at the moment the principal accepts the agent’s report;
Debit 90 Credit 20
— 800 rubles – if there are direct expenses of the transaction agent, they are recognized in the cost price;
Debit 90 Credit 68.2
— 305.08 rubles – VAT is charged on the entire amount of the agent’s remuneration;
Debit 76 Principal Credit 62 (76) Principal
— 2000 rubles – the agent’s remuneration is withheld from funds received from buyers to the principal.
Accordingly, if the agent uses the simplified tax system, then it is necessary to exclude the posting for VAT calculation.
Let's look at the wiring
Let's consider an example: an agent receives payment (remuneration) directly from the principal on the terms of 50 percent advance. The following entries are made in accounting:
Debit 51 Credit 62 (76)
— 1000 rubles – an advance on the agent’s fee was received;
Debit 62 (76) Credit 68.2
— 152.54 rubles – VAT is charged on the advance payment;
Debit 62 (76) Credit 90
— 2000 rubles – the agent’s income is recognized at the moment the principal accepts the agent’s report;
Debit 90 Credit 20
— 800 rubles – if there are direct expenses of the transaction agent, they are recognized in the cost price;
Debit 90 Credit 68.2
— 305.09 rubles – VAT is charged on the entire amount of the agent’s remuneration;
Debit 68.2 Credit 62 (76)
— 152.54 rubles – VAT accrued on the advance payment is accepted for deduction;
Debit 51 Credit 62 (76)
— 1000 rubles – the agent’s services are paid for by the principal.
In the absence of an advance payment, the agent's accounting is limited to entries 3, 4, 5 and 7 (for the entire amount of the remuneration). If the agent uses the simplified tax system, we exclude VAT transactions (2, 5 and 6).