Functionality provided by the invoice
An invoice (hereinafter we use the accepted abbreviation сч-ф) is the most important document that is used to account for value added tax.
In general, the seller and buyer apply the common taxation system (CTS). That is, they are VAT payers.
There are several types of invoices:
Our material is devoted to the corrected invoice. Below we will look at the cases in which a correction invoice is used in document flow, and how it differs from a correction invoice.
Results
Changes to the invoice and adjustment invoice not related to amendments to the quantity, cost of goods (work, services) and tax obligations are made accordingly on the form of the invoice, adjustment invoice. When drawing up correction documents, it is necessary to indicate the details of the original document in which the error was made. The procedure for registering a corrective invoice depends on the period in which it was drawn up in relation to the erroneous invoice, and for the buyer also on whether he or she registered an invoice containing errors in the purchase book.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 N 1137
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Differences between corrected and adjusted invoices
The names of the documents are very similar, so an inexperienced accountant may have a question about which invoice to issue in which case. Correction and adjustment - what's the difference?
Thus, we conclude that a corrective invoice is drawn up when erroneous data is identified in the primary account.
Errors can be found both in a regular invoice for shipment or advance payment, and in an adjustable invoice. Therefore, the corrected one can be either a regular sch-f or a corrective one.
In what cases is a corrected ESF issued?
Since the issue does not have a clear legislative regulation, it makes sense to turn to legal practice. Most often the need for changes arises in the following cases:
- A typo in the date of compilation affects the period of work with VAT and may lead to the impossibility of obtaining it;
- Incomplete or unreliable details of the parties, for example, erroneous TIN, name of the counterparty, missing last names - in fact, such an error does not make it possible to identify the parties, accordingly, from the point of view of the law, the transaction is not considered valid, VAT is not refunded;
- There is no name of the sender and recipient of the cargo in cases where they are logistics companies;
- No payment details - such an error makes it impossible to track the payment and verify its authenticity;
- The name of the currency and its code are not indicated or indicated incorrectly;
- The object of payment is incorrectly specified or missing: goods/services;
- Error in the price of a service or quantity of goods;
- The rate is indicated incorrectly, which entails the invalidity of subsequent operations for calculating taxes and the amount of VAT;
- For imported goods, the following information is missing or indicated with errors: country of origin, customs declaration number.
In other situations, an extract of the corrected ESF is not required, since the remaining information does not affect the ability to correctly interpret the information from the document and calculate tax liabilities on it.
You can find detailed explanations on these errors in the letters of the Ministry of Finance dated 08/02/2019 No. 03-07-11/58375, dated 04/19/2017 No. 03-07-09/23491, dated 09/18/2014 No. 03-07-09/46708, dated 04/25/2011 No. 03-07-08/124, dated 03/11/2012 No. 03-07-08/68, as well as in the resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court dated 02/25/2009 No. 13893/08.
Form and sample of a corrected invoice
In order to draw up a corrected invoice, you must use the form of the document that we are correcting . That is, either a regular account form, or a corrective account form. Moreover, they use the form that was in force at the time of drawing up the primary account.
Both forms were approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
You can download official invoice forms on our website. For example, in the article “Samples of filling out invoices in various situations.”
How to correctly enter data into the corrected accounts is also described in detail in the Resolution we mentioned.
Let's look at an example of filling out a corrected invoice.
Example
Let the accountant of Paradox LLC issue an invoice for the shipment of goods on 09/07/2020. However, on 09/22/2020 it turned out that an error was made in the name of the buyer and his INN/KPP (highlighted in red in the figure).
To correct this error, a corrected account has been compiled:
The filling principle is as follows:
- in line 1 – indicate the number and date of the account with an error;
- in line 1a - indicate the correction number and the date of correction;
- In all other respects, we fill out the account in the same way as the original document, but we replace erroneous data with correct ones.
In what cases is an invoice correction required?
So in what cases is a corrected invoice issued? It is needed when it becomes necessary to correct a technical error in the source document. For example, you may need to create a corrected invoice if there is an error:
- in the date, if the original document was mistakenly issued in a different month, year;
- details of the supplier or buyer, if they are written not just with a typo, but do not correspond to them at all (incorrect TIN, address, name, etc.);
- indication of the shipper and consignee, if they do not belong to the persons who actually sent and received the goods;
- details of the document for the transfer of the advance;
- name and currency code of the document;
- indicating the name of the product (work, service);
- indicating an incorrect price or quantity of goods;
- in the rate and, as a consequence, in the amount of VAT and the final amount of the document;
- or in the absence of data required to be filled in for imported goods (country of origin and registration number of the customs declaration).
It should be noted that most taxpayers, if an error is discovered in a timely manner and has not yet been identified by the tax authorities, prefer not to make a corrected invoice, but simply replace the defective document.
For errors that do not require correction, read the article “What errors in filling out an invoice are not critical for VAT deduction?” .
For information about what errors in the invoice should be corrected, read the article “We made a mistake in the invoice - what and how to correct it.”
Reflection in the book of sales and purchases
All invoices are entered into the sales ledger or purchase ledger. At what point and in what order should the corrected account be reflected in these forms? It depends on in which quarter the error was discovered and the corrected account was compiled.
Corrections are made in the same quarter when the primary invoice is drawn up
Let's say the corrected invoice relates to the same quarter as the primary invoice. We register it in the sales book and in the purchase book with the date of correction . In order to prevent doubling the amount of tax to be paid or deducted, the original account is re-registered as the date of correction with negative total values.
Thus, in the sales book and in the purchase book, the total VAT value for this operation will remain in the amount indicated in the corrected invoice.
Corrections are made in the following tax periods
Let's say an error in the primary invoice was discovered in the next tax period, when the VAT return has already been submitted. In this case, fill out an additional sheet of the sales book and purchase book, where 2 lines are entered:
- canceling the primary account;
- corrected sf.
reflected in the sales book or purchase book has been changed a clarifying VAT return.
If an error was made, for example, in the address of the counterparty, which is not reflected in the lines of the sales and purchase books, there is no point in clarification.
Making adjustments
Adjustment invoice
After commented resolution No. 1137 comes into force, taxpayers must use a new (permanent) form for an adjustment invoice.
The main difference from the temporary form* is as follows. Previously, the indicators “before the change”, “after the change”, as well as the difference between “additional payment” and “reduction” had to be indicated in special columns. Now such indicators are allocated not columns, but rows.
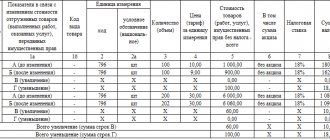
In particular, for each item of the adjustment invoice there are four lines: A (before the change), B (after the change), C (increase) and D (decrease). To calculate the indicators for lines C and D, you need to subtract the figure from line B from the number in line A.
If the resulting value is less than zero, then we are dealing with an increase. It must be reflected in line B with a positive value, that is, without the minus sign. Line D should have a dash.
If the resulting value is greater than zero, we are dealing with a decrease. It must be reflected in line G with a positive value, that is, without the minus sign. There should be a dash in line B.
After filling out all the lines of the adjustment invoice, you need to summarize the following indicators: cost without VAT (column 5), the amount of VAT (column and cost with VAT (column 9). To do this, you need to sum up all the numbers indicated in the line In the data column , as well as all the numbers indicated in line D of the data column.The obtained values will be needed when filling out the purchase book, sales book or additional sheets to them.
and cost with VAT (column 9). To do this, you need to sum up all the numbers indicated in the line In the data column , as well as all the numbers indicated in line D of the data column.The obtained values will be needed when filling out the purchase book, sales book or additional sheets to them.
Let us add that in the “header” of the adjustment invoice there are fields for its number and date, as well as fields for the number and date of the original invoice. Plus, there are fields for the number and date of corrections made to the adjustment and original invoices.
Reducing the cost: actions of the seller
If the original cost decreases, the seller is obliged to issue an adjustment invoice and register it in part 1 of the log of received and issued invoices.
Next, the adjustment invoice must be registered in the purchase ledger. This must be done during the period when the following conditions are met: the seller has an adjustment invoice drawn up no earlier than three years ago, and primary documents for changing the terms of delivery.
The supplier is then entitled to deduct the difference between the VAT amount before and after the adjustment.
Please note that the seller should not record the adjustment invoice in Part 2 of the journal, which deals with invoices received. This nuance is separately specified in the new Journaling Rules.
Cost reduction: buyer actions
If the original cost is reduced, the buyer must register an adjustment invoice in part 2 of the journal of received and issued invoices.
Then the buyer is required to register one of two documents in the sales book: either an adjustment invoice or a contract (agreement, etc.) to change the terms of the transaction. The document that was received earlier is subject to registration. Accordingly, an entry in the sales book must be made for the period in which the registered document was received by the buyer.
After this, the buyer should restore the previously accepted deduction in the amount of the difference between the amount of tax before and after the adjustment.
Increasing value: seller actions
If the original cost increases, the seller must issue an adjustment invoice and register it in part 1 of the log of received and issued invoices.
Also, the adjustment invoice should be recorded either in the sales ledger or in an additional sheet in the sales ledger.
If the shipment and adjustment took place in the same quarter, then registration must be made in the sales book for that quarter.
If the shipment occurred in one quarter, and the adjustment occurred in another, then registration must be made in an additional sheet of the sales book for the quarter when the shipment took place. In this case, recording the data on the adjustment invoice in an additional sheet must be done with a positive value, that is, without the minus sign.
Finally, the seller is required to charge VAT in the amount of the difference between the tax amount before and after the adjustment. The accrual must be dated to the quarter in which the shipment took place.
Increasing value: buyer actions
If the original cost increases, the buyer should register an adjustment invoice in part 2 of the journal of invoices received and issued.
Then you need to make an entry in the purchase book for the period in which the buyer will have both an adjustment invoice drawn up no earlier than three years ago and a primary document for changing the terms of delivery (contract, additional agreement, etc.).
As a result, the buyer receives the right to accept a deduction in the amount of the difference between the VAT amount before and after the adjustment.
How to transfer data from an adjustment invoice to the journal, purchase ledger, and sales ledger
| From which field of the adjustment invoice? | In which column of the accounting journal? | In which column of the purchase book? | In which column of the sales book (additional sheet of the sales book) | |
| In part 1 | In part 2 | |||
| Line 1 | In columns 7 and 8 | In columns 7 and 8 | In column 2b | In column 1b |
| Line 1b | In columns 5 and 6 | In columns 5 and 6 | In columns 2 and 2a | In column 1 and 1a |
| When the original cost decreases | ||||
| Total reduction (sum of rows G) columns 5 | Not transferable | Not transferable | In column 8a (or 9a) | In column 5a (or 6a) |
| Total reduction (sum of rows G) columns 8 | In column 18 | In column 18 | In column 8b (or 9b) | In column 5b (or 6b) |
| Total reduction (sum of rows G) columns 9 | In column 16 | In column 16 | In column 7 | In column 4 |
| When the initial cost increases | ||||
| Total increase (sum of rows B) columns 5 | Not transferable | Not transferable | In column 8a (or 9a) | In column 5a (or 6a) |
| Total increase (sum of rows B) columns 8 | In column 19 | In column 19 | In column 8b (or 9b) | In column 5b (or 6b) |
| Total increase (sum of rows B) columns 9 | In column 17 | In column 17 | In column 7 | In column 4 |
Minor defects in invoices
All other defects that do not interfere with the identification of the above information should not become a reason for the inspectors to remove the VAT deduction. Here are examples of such errors that, according to officials, are not serious.
| Description of the defect | Confirmation letters | Note |
| The invoice was issued late, that is, after the expiration of five calendar days, counting from the day of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services) | Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 25, 2016 No. 03-07-11/2722, dated April 25, 2018 No. 03-07-09/28071 | The day of shipment is included in the five-day period established for issuing an invoice (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 18, 2018 No. 03-07-14/74899) |
| An error was made when filling out line 4 “Consignee and his address” of the invoice | Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 20, 2019 No. 03-07-11/10765 | The officials’ conclusion can be extended to a situation where the error is also contained in line 3 “Consignor and his address” |
| The invoice contains additional information about the actual addresses of the seller or buyer, which differ from the addresses specified in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs | Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 21, 2017 No. 03-07-09/85517 | Information about the actual address is indicated as additional information. That is, the invoice must necessarily contain an address corresponding to the one indicated in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities (USRIP) |
Identification of amounts in the invoice
The cost of goods (works, services), tax rate and VAT amount in the invoice must also be filled out correctly. Errors in them are a serious violation, the consequence of which may be the removal of the VAT deduction by the inspectors.
For example, if the tax rate is in error, the seller must correct the invoice accordingly. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation recalled this in a letter dated November 6, 2018 No. 03-07-11/79611. If there are no corrections, then for the buyer this is fraught with deprivation of the deduction.
What about cost accuracy? For example, from clause 3 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137 follows that the cost indicators of the invoice are indicated in rubles and kopecks. Does this mean that if this order is violated (for example, by rounding), the buyer will lose the deduction?
Let us turn to the explanatory letters of the departments. In a number of letters, officials of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation cite this rule, adding that rounding the amount is unacceptable (letters dated September 27, 2018 No. 03-07-14/69147, dated February 17, 2014 No. 03-07-09/6395 and dated January 29, 2014 No. 03 -02-07/1/3444.). However, the authors of the letters do not draw any conclusion about the consequences of such a violation. We believe that rounding does not make it impossible to identify cost indicators. But we do not exclude the risk of claims from tax authorities.
But on the following situation, officials from different departments do not have a common opinion. We are talking about reflecting the graphic sign of the ruble in the invoice instead of the code and name of the currency. Capital tax officials believe that such filling deprives the buyer of the right to deduction (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated March 22, 2016 No. 16-15/028574), and representatives of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation are more loyal. In their opinion, expressed in letter No. 03-07-11/21095 dated April 13, 2016, such preparation does not prevent the use of the deduction.
We believe this approach is more correct, because such filling does not interfere with identifying the cost indicators of the invoice. If disputes arise with tax authorities, you must refer to this letter from the Ministry of Finance. Most likely, it will convince local inspectors of the legality of the deduction.
What is the purpose of an invoice and what are the consequences of mistakes made in it?
An invoice is the primary tax accounting document for VAT, issued by the seller - a VAT payer when selling products, works, services, etc.
ATTENTION! Invoices are required to be issued by persons exempt from VAT under Art. 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Also, in certain cases (for example, when importing goods from abroad), the document is also required to be drawn up by persons who are not payers of the specified tax, for example, simplifiers or imputators.
The compiler must highlight the amount of VAT payable to the budget on the transaction. The buyer, in turn, if he is a VAT payer, can deduct the amount of tax specified in the received invoice. This is the main purpose of this document (Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Considering that a deduction is an opportunity to reduce VAT payable to the budget, serious requirements are imposed on invoices as documents confirming the right to deduction. By violating them, the seller deprives the buyer of the opportunity to legally reduce the amount of tax. We will talk about all these requirements further.
Canceled and zero invoice - what is the difference
Merchants can issue a zero invoice if they do not apply VAT (for example, simplifiers), at the request of the counterparty.
However, the Tax Code does not provide for the obligation to issue zero invoices for them. Read more about VAT under the simplified tax system in the material “VAT under the simplified tax system: in what cases to pay and how to take into account the tax in 2019-2020” .
The difference between nil and canceled invoices is the tax implications. So, if you register a zero invoice in the book of purchases or sales, there will be no consequences for the merchant. In the case of a canceled invoice, things are not so simple.
How to take corrected ESF?
Making changes to an invoice is not a problem, but each additional ESF involves wasting time and unnecessary entries. Practice shows that accounting books full of corrections are of particular interest to inspection authorities. Also, although these are small, they are still unnecessary expenses. Therefore, when accepting an invoice, especially after corrections, it is recommended to carefully check all document details. Moreover, the information should not only be in its place, but also correspond to reality.
At the same time, no one can work without making a single mistake. With digital document management, it is much easier to make changes to documents. In addition, the speed of data exchange increases significantly. This allows you to quickly identify errors and correct them immediately. Our company specializes in the development and implementation of paperless technologies and the implementation of EDI for the exchange of documents with counterparties. If you are interested in their capabilities, contact us by leaving a request on the website or by phone. We will be happy to advise you and offer the best option for cooperation.
Let's sum it up
It is not always possible to draw up an invoice correctly the first time. This is due both to the characteristics of the specific field of economic activity in which the company operates and to the human factor. Moreover, there are often cases when a seller or supplier makes mistakes due to the fault of the counterparty. For example, the buyer made a mistake when entering bank details or missed a number in the tax ID.
Therefore, the legislator is loyal and gives the opportunity to business entities to make amendments on their own. For this purpose, either an adjustment invoice or a corrected one is used. These two types of documents should not be confused, since their purpose is radically different. It is impossible to reflect a change in the price of a product in the form of a correction if it occurred in connection with the signing of an agreement between the seller and the buyer. To do this, you should use a correction invoice, otherwise it is contrary to current legislation. But if we are talking about real corrections of errors, then it is necessary to prepare a corrected invoice.
In addition to the instructions and recommendations described in the article, remember one more rule: each ESF is signed with a qualified digital signature. No matter how many changes you make to the same document, each time it must be endorsed using the CEP.