Businessmen are looking for ways to optimize the tax burden, but they forget that there are no legal methods of paying 500 rubles instead of 1000. If you can't pay less, then what is this article about? About how to do everything right and not pay more than you could.
In the article about “black” methods of tax optimization, we talked about what not to do so as not to get into trouble with the law, and today we’ll talk about how to legally reduce taxes.
Find out:
- How are the form of ownership and the amount of taxes related?
- How to optimize income tax
- Optimization tips for VAT payers
No time to read? Check out the article summary
Legal approach
The legislation offers a whole range of tools for tax optimization - special regimes, benefits, zero rates and targeted preferences. For example, small and medium-sized businesses can switch to a simplified system. This will allow them not to pay VAT and pay tax on their income at reduced rates. However, large organizations and many medium-sized businesses cannot apply preferential treatment. They are faced with the question of how to reduce income tax under OSNO.
Tax is imposed on the difference between income received and expenses incurred in the course of business. The Tax Code strictly stipulates what constitutes income and expenses for the purposes of calculating income tax. Any amateur activity is unacceptable here - this is a direct violation of the law.
It is impossible to talk about ways to reduce income taxes without touching on the topic of gray and black optimization. The most obvious illegal practice is to attribute expenses that did not occur or to inflate the amount of expenses incurred. The Tax Service is actively and very successfully combating such violations. Therefore, in no case should you resort to this “optimization” scheme, as well as other illegal methods. Next, we will consider only legal methods.
Free tax consultation
How are the form of ownership and the amount of taxes related?
When registering a business, you need to decide on the form of ownership: to become an individual entrepreneur or a legal entity. If you are going to run a business alone, you can register an individual entrepreneur, if with partners - an LLC. In an LLC, the earnings of each founder depend on the share of participation in the authorized capital; with an individual entrepreneur, everything is simpler: after paying taxes, he can dispose of all the money at his own discretion.
The main differences between individual entrepreneurs and LLCs:
| IP | OOO |
| Freedom and a small tax An entrepreneur pays one tax on the simplified tax system: 6% on income or 5-15% on profit, and spends the rest of the money at his own discretion. | Double tax and reporting In addition to basic taxes, you have to pay personal income tax of 13% on dividends if the founders plan to withdraw money from the account. |
| Not required to keep accounting records. Exempt from maintaining accounting registers (entries) and preparing financial statements (balance sheet, income statement, etc.). | Required to do accounting In most cases, you have to hire an accountant. |
| Pays contributions for itself and employees (if any). The individual entrepreneur will have to report quarterly to the tax, pension fund and social security fund in the same way as an LLC if it has employees. | Reports only for employees. An LLC cannot operate without employees. You will have to pay quarterly insurance contributions from the amount of accrued wages (more than 30%) to extra-budgetary funds: Pension Fund, Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund, Social Insurance Fund. |
| Managing individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system from 3000 rubles [Order] | Managing an LLC on OSN from 8,000 rubles [Order] |
Write-off of losses from previous years
Not every year a company closes with a profit; losses also occur. The legislation allows them to be written off later. When submitting income tax reports, the current period declaration indicates the loss of previous years or part of it. In 2020-2021, the tax base can be reduced in a similar way by up to half. If the loss is greater, it can be carried forward to future years. Previously, there was a restriction that allowed losses to be carried forward in this way for 10 years, but now it has been removed.
It happens that losses from previous years are revealed only in the current year. They can be attributed to non-operating expenses, thereby reducing the tax base, and therefore the tax itself.
Non-operating expenses
If you have committed a fine against a counterparty and paid him a penalty, this is already a non-operating expense.
To non-operating expenses
include interest on loans, bank guarantees, legal costs, fines and penalties for violation of contracts with counterparties. The list of such expenses is also open: it is impossible to foresee all situations that happen in the life of a company.
A separate question is how to take discounts into account for the buyer? Such expenses can be taken into account immediately, or they can be taken into account retroactively. According to the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 23, 2010 No. 03-07-11/267, discounts are allowed to be taken into account in non-operating expenses as a loss of previous tax periods. And in 2012, the department noted that the seller’s costs of paying a premium (discount) to the buyer as a result of his fulfilling certain terms of the contract are taken into account in full as non-operating expenses - subject to their economic justification. That is, a discount for a new client can actually be “defended” as a justified expense. But at the same time, it is advisable to have in hand an agreement concluded with the client, which mentions such a discount.
Creation of reserves
An organization may provide in its accounting policies for the creation of the following reserves:
- for doubtful debts;
- for vacation pay;
- for repairs of fixed assets;
- for warranty repairs and maintenance.
This can be very beneficial for optimizing income taxes. Let us explain using the example of the reserve for doubtful debts. The company shipped the goods to customers but did not receive payment. When accounting for income and expenses using the accrual method, she generated income on the date of shipment. And since there is income, it is also subject to income tax. It turns out that there is no money, but 20% of the theoretical amount of income needs to be paid.
To avoid this, a reserve for doubtful debts is created. At the end of the quarter, you need to determine the duration of the delay. If it is more than 45 days, then half of the debt amount is taken into account. If you are overdue for more than 90 days, you can write off the entire amount.
Of course, when counterparties repay their debts, tax will have to be paid. That is, the creation of a reserve can be used to legally obtain a tax deferment. You will need to pay taxes from what you receive, not from your own funds. The advantage of this method is that during the deferment the company’s money remains in operation and generates income.
How to reduce VAT tax
All entrepreneurs who work on OSN are required to pay VAT. For example, if a company sells goods, marks them up and makes a profit, it must pay VAT.
You can avoid paying VAT in several cases:
A legal entity or individual entrepreneur has small revenue.
If over the previous three months the revenue of a company or individual entrepreneur from the sale of goods or services excluding VAT did not exceed two million rubles, VAT may not be paid. To exercise this right, you need to submit a tax notice with an extract from the balance sheet.
The company's counterparties are VAT payers.
If part of the income is still subject to VAT, you need to try to increase deductions. To do this, we need to cooperate more with those who pay VAT. In this case, the supplier’s VAT amounts can be deducted.
Products with preferential tax rates are used.
There is a list of goods and services that are subject to a zero and reduced tax rate (10%). The full list is attached to. To apply the reduced VAT rate, the product sold or service provided must be in stock. If an entrepreneur mistakenly paid “full” tax instead of reduced tax for several years, he can contact the tax office and get his money back.
Work without advance payment or get rid of it on time.
If the taxpayer has received an advance, he is obliged to transfer VAT on this amount to the budget, in accordance with clause 2 of clause 1. After shipment, you will have to issue an invoice again and pay VAT for the entire amount of goods shipped and services provided. To avoid overpayments on advance payments, you need to immediately transfer them to suppliers. Then it turns out that the seller does not receive money, but spends it, and accordingly there is an opportunity to reduce the tax. VAT works like this: if you received a lot of money and spent little, then the tax amount will be larger, but if, on the contrary, you spent everything, then the tax amount will be small.
Acquisition and liquidation of fixed assets
If you plan to purchase transport, equipment or other similar objects, you can consider leasing. The necessary equipment will be provided by the lessor, and the company will make payments to him. Until the end of payments, the equipment will be owned by the lessor, and the organization will be able to use it in its activities.
Optimization of income tax is as follows: leasing payments are included in the cost of production and reduce the base. If you buy equipment at your own expense, then only the depreciation amount can be taken into account as expenses.
Often new equipment is purchased to replace old equipment that is subject to write-off. The costs associated with its liquidation - dismantling, dismantling, removal - can be written off as non-operating expenses in the period when the liquidation occurs. These costs also include underaccrued depreciation of written-off objects.
Leaseback
To save money, they use leaseback - a completely legal transaction (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated January 16, 2007 No. 9010/06). According to the documents, you sell the equipment to the leasing company and receive a sum of money. After this, you work on the equipment under a financial lease contract and save on taxes - the OS is moved only according to documents.
Keep records and pay taxes in the web service for small and medium-sized businesses Kontur.Accounting. The system itself will calculate the tax based on accounting data and generate reporting. To optimize taxes, the service contains management documents and financial analysis. The first two weeks of work are free for all newbies.
When an accountant does not have enough time for routine tasks, it is time to think about process optimization. You can outsource some of the work or find assistants on staff. But there is an option that will help save the company money and the accountant’s nerves - accounting automation.
Trademark registration
Many organizations today spend money on a trademark. This is another good example of how you can reduce profits absolutely legally, not only by reducing taxes, but also getting benefits for business. After all, a trademark contributes to the recognition of the company, the formation of customer loyalty and protection from unfair competition.
After receiving documents from Rospatent, the trademark is registered as an intangible asset. The costs for it, provided that they amounted to less than 100,000 rubles, are immediately included in expenses and reduce the income tax base. If a trademark is more expensive, it is subject to depreciation, and its cost is reduced by tax gradually.
Decrease in UTII
Among the options on how to legally reduce income tax, one of the interesting solutions may be the use of a single tax on an imputed type of activity, or abbreviated UTII. This tax is a fixed amount that cannot be directly reduced - it is set by the state twice a year.
However, there is a way, using a special option for applying such a regime, to reduce the taxable base of revenue.
Ways to reduce your tax bills
We found out that with UTII it is impossible to reduce payments to the state - they are calculated in advance. But this does not mean that businesses are unable to use the imputation to their advantage. A good option is to combine the tax regimes of the simplified tax system and UTII. The essence of the method is that an entrepreneur works according to several OKVED codes, one or more of which is suitable for imputation, while others are not.
When combined, he pays taxes according to 2 modes at once:
- imputed amount;
- 6% or 15% of income or income less expenses.
In practice, this option is implemented quite easily. The only thing that requires attention is accounting for the taxable base for simplified payments. All accounting will need to be divided into 2 areas in order to clearly justify to the tax office what specific activity code the income was received under and whether it is included in the calculation of taxable profit under the simplified tax system.
Uniform
Continuing the conversation about the trademark, it is worth mentioning another attribute of the corporate identity of the organization - the uniform of the employees. This is especially true in the field of retail trade and services to the public.
The costs of manufacturing the form are included in labor costs on the basis of paragraph 5 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. And they, in turn, lower the tax base. However, for this, 2 conditions must be met:
- uniforms are provided to employees free of charge or at a reduced price;
- the employee receives it as property, that is, after termination of the employment contract there is no need to return it.
Marketing research
Often companies resort to the services of marketers to study the market in order to increase their sales. If such studies have not yet been conducted, it probably makes sense to think about it. Moreover, the costs for them reduce the income tax base as consultation costs.
However, this is true under one condition - such costs are justified, documented and made in order to increase income. Market research should be conducted on the products or services that the company is engaged in. If it is directed to some third-party products, then the expenses may not be recognized. The Federal Tax Service will decide that the study was fictitious and was carried out solely to reduce income tax.
Employee training
If the organization’s specialists periodically improve their professional level, this will only benefit the business. In addition, training expenses can reduce income taxes - they are written off as other production and sales expenses.
To do this, the following conditions must be met:
- employees sent for training are hired under employment contracts;
- The educational institution with which the agreement is concluded has the right to conduct relevant activities.
Preferential rates
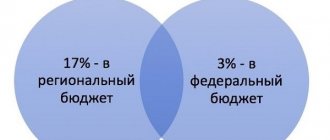
The income tax rate of 20% consists of two parts. In 2021 they are:
- regional - 17%;
- federal - 3%.
For certain categories of taxpayers, federal and regional rates are set at zero. That is, such companies do not actually pay this tax. A 0% rate applies to income received:
- educational and medical organizations;
- organizations providing social services to citizens;
- participants of the Skolkovo project;
- agricultural producers and fisheries organizations.
In addition, the federal portion of income tax is zero for residents:
- free economic zone of Crimea and Sevastopol;
- port of Vladivostok;
- economic zone of the Magadan and Kaliningrad regions;
- tourist and recreational cluster and some other zones.
The regional part of the rate may be lowered by decisions of the authorities of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation for certain categories of payers. Thus, in Moscow for public organizations of disabled people, as well as those who use their labor, the regional rate is set at 12.5%.
When checking an income tax return, the Federal Tax Service may request documents necessary to confirm rights to preferential rates.
Choosing a tax system
The first step to optimizing income tax is choosing a tax system. The tax system is a legally established procedure in which taxes are collected from individuals and legal entities.
Today, three taxation systems are legally defined for use by a wide range of individuals and legal entities, one for peasant farms and one for individual entrepreneurs - patent holders. Each of them carries advantages and disadvantages.
Let's figure out which system is right for you. To do this, let’s get acquainted with them in more detail, considering them in order of growth of the business of the proposed taxpayer.
Unified tax on imputed income (UTII)
This is the name of the preferential tax system, which is fundamentally different from the others. The difference is that the tax base is determined not on the basis of actual performance indicators for the period, but on the basis of the basic “imputed” profitability. To find out the amount of imputed profitability, refer to the Tax Code Art. 346.29 paragraph 3.
Income from the provision of household services is estimated by the state at 7,500 rubles per month. A little, right? There is one caveat - household services can only be provided to individuals.
Other types of activities also have quite reasonable “imputed” income. Veterinarians will have a tax base of 7,500 rubles, car mechanics - 10,000 rubles, sellers - 4,500 rubles, drivers - from 1,000 to 6,000 rubles.
The tax is calculated as 15% of the amount of imputed income multiplied by coefficients K1 and K2. The K1 coefficient is determined once a year by order of the Ministry of Economic Development, the K2 coefficient is determined by local authorities.
UTII is a good choice for individuals and organizations that have large incomes while using few resources. With proper calculation, it may turn out that paying 15% UTII will be less in absolute amount than 13% personal income tax.
Talented programmers, lawyers, doctors, advertisers and other freelancers can use UTII to minimize taxes
But there are also pitfalls here.
Firstly, only a small part of individual entrepreneurs and organizations can work with UTII. Among the permitted sectors of activity:
- passenger and freight transportation;
- catering services (with restrictions)
- maintenance, repair and car wash;
- rental of apartments and commercial premises;
- parking space rental services;
- retail trade (with restrictions);
- veterinary services;
- advertising services (with restrictions);
- certain paid services to individuals and others described in Art. 346 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Article 346.26 limits the possibilities of switching to the Unified Tax Fund even more. You cannot use UTII if:
- you have more than 100 employees;
- You have a share of more than 25% in another legal entity;
- You use simple partnership and trust agreements;
- local laws limit the use of UTII.
Secondly, you must be sure that you will receive sufficient income every month, because the tax is paid regardless of whether you actually worked and whether you earned a profit.
Finally, from January 1, 2021, UTII will be cancelled. Take this point into account when choosing a tax system.
Simplified taxation system (USNO)
The simplified tax system is also a preferential taxation system, but can be used much more widely than UTII. The simplified tax system is called that way because the methodology for calculating the tax base and tax is extremely simple.
In the first option, the tax is calculated as 6% of income. When using this option, you do not need to confirm expenses for the tax office.
In the second option, you pay 15% of the profit, that is, you take into account and confirm income and expenses.
An entrepreneur or organization using the simplified tax system is a single tax payer, which replaces part of the taxes: income tax, VAT, personal income tax (for the business owner), property tax. But other taxes: transport and land, personal income tax for hired personnel and, in special cases, property tax - will need to be paid.
Which taxation method to choose can also be calculated. To do this we use the inequality:
0.06 × Income - Deductible amounts < 0.15 × (Income - Expenses)
If the inequality is satisfied, then it is more profitable to choose a tax of 6% on income, but if not, then it is better to switch to 15% on profit.
However, there are certain restrictions when switching to the simplified tax system. You will not be able to use the benefits of the simplified tax system if:
- Your organization has branches.
- You are engaged in the production of excisable goods.
- You are engaged in pawnshop activities.
- You provide gambling services.
- More than a hundred people work for you.
- There are more than one hundred million fixed assets in your organization.
- You or your organization has a stake of more than 25% in other firms.
- The turnover of your organization over the past nine months has exceeded 45 million rubles, multiplied by the deflator coefficient.
It is worth noting that 6% and 15% are the maximum rates that can be reduced by the territorial laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Minimum rates are 0% and 5% respectively.
On the websites of regional tax services you can find all the necessary information on the legislative framework for reducing income tax.
Basic taxation system (OSNO)
OSNO is the most fiscally and administratively loaded regime. Organizations working in this system maintain full accounting and tax records, calculate and pay all taxes existing in Russian tax legislation.
For 2021, the income tax rate under OSNO is 20%.
Once you have decided on your tax regime, it's time to think about methods to optimize your income tax. Let's take a quick look at the special tax regimes.
Investment deduction
From January 1, 2021, an investment deduction is in effect, which reduces the amount of income tax (not the tax base). The mechanism for its application is prescribed in Article 286.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The conditions are:
- In the entity where the taxpayer is located, a law on investment deduction must be adopted.
- The organization must establish in its accounting policies that it has the right to apply this deduction. In order for this right to appear in 2022, it must be fixed in the accounting policy by the end of this year. In the future, this decision cannot be changed for 3 years.
- The deduction applies to facilities that have been put into operation since the beginning of 2021. Or after this date their cost was revised.
- The deduction applies to all objects that belong to depreciation groups III-VII.
- The regional part of the income tax can be reduced by up to 90% of the costs incurred by the taxpayer in connection with the acquisition, modernization or reconstruction of fixed assets. Moreover, this part of the tax must be at least 5% of the tax base.
- The federal portion of the tax can be reduced by no more than 10% of the amount of costs. There is no minimum tax established.
So, we looked at how to reduce income tax under OSNO within the framework of the law. Most legal methods come down to properly accounting for expenses. Companies should periodically review their costs. It is likely that funds will eventually be freed up, which can be used to develop the business.
Salaries “in envelopes”
With this scheme, the employer specifies a small part of the salary in the employment contract, and pays the rest to the employee. With the help of “shadow” wages, the employer can avoid paying income taxes and save on insurance premiums.
- employee salaries are below the regional average for workers of similar qualifications;
- the salary of ordinary workers is higher than that of management;
- the specialist’s salary is significantly lower than at the previous place of work;
- the employee submitted a document where the amount differs from that indicated in the company’s reports (for example, to the embassy to obtain a visa or to receive benefits).
To identify a violation, tax officials conduct an audit. Payment of wages “in hand” will be confirmed if:
- there is a document confirming the fact of double bookkeeping and payment of “gray” salaries,
- this fact is confirmed by employees.
If the tax authorities prove that the employer issues wages “in an envelope,” he will need to transfer the withheld amount of tax to the budget, in accordance with Art. 108 clause 5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In addition, he faces a fine of 20% of the personal income tax amount, according to Art. 123 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, penalty under Art. 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. He may also be brought to administrative and criminal liability under Art. 15.11 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation and Art. 199.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.