Let's consider the features of reflecting an advance invoice from a supplier in 1C and accepting VAT for deduction on it.
You will learn:
- what conditions must be met in order to exercise the right to deduct VAT on an advance invoice from a supplier;
- how to register an invoice for an advance payment from a supplier in 1C;
- what document formalizes the acceptance of VAT for deduction from advances issued;
- what transactions and movements in the VAT tax register are formed in the purchase book, what lines of the VAT declaration are filled out.
Registration of SF for advance payment from supplier
Regulatory regulation
The organization has the right to accept for deduction VAT presented by the supplier when transferring an advance payment to him (clause 12 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
VAT on advances issued to suppliers is deductible if the conditions are met (clause 9 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- the contract provides for advance payment;
- payment was made against future supplies for activities subject to VAT;
- a correctly executed advance SF is available;
- Payment documents are available confirming the transfer of the advance to the supplier.
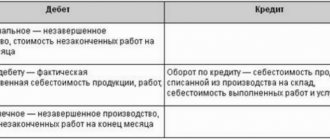
For the amount of input VAT accepted for deduction:
- in the purchase book, a registration entry is made for the advance SF with the transaction type code 02 “Advances issued”;
- In accounting, the entry Dt 68.02 Kt 76.VA “VAT on advances and prepayments issued” is generated.
In this case, it is necessary to take into account the following features associated with the acceptance of VAT for deduction on advance invoices from suppliers:
- accepting VAT for deduction is a right, not an obligation, therefore it is not necessary to accept VAT for deduction for each tax return, especially if the shipment from the supplier occurs in the same tax period;
- transferring the deduction for advance SF for three years is impossible , because it is provided only for VAT deductions when purchasing goods (works, services).
Calculation of VAT on advance payment
The advance payment system provides for the transfer of a certain part of the total cost of goods, works and services against their future delivery or performance.
It is necessary to calculate and pay VAT on advance tranches (AT). The buyer accepts the tax amount as a deduction or refuses it. This is his full right. Each situation has its own nuances.
| Input tax from the vehicle is accepted for deduction by the buyer | The settlement option allows the purchaser of goods to reduce the tax payable to the budget before the actual shipment. To receive a deduction, all three conditions must be met:
Check whether the seller has calculated the tax correctly. After the actual delivery of the goods, the buyer has the opportunity to deduct the entire purchase price. Consequently, the tax on vehicles declared earlier will have to be restored. Report advance invoices on your VAT return in the quarter in which they were paid. Include the amounts in section 3 of the report. |
| The input tax from the vehicle is not accepted for deduction by the buyer | The buyer is not required to deduct the input tax from the AT. It is allowed to reduce the obligation to pay to the budget once - at the time of actual delivery of goods or performance of work or services. The company declares the entire amount of the input fee in the sale without any recovery. This means that the offset of advances issued in the VAT return will not have to be reflected. An application for a benefit is allowed only if three conditions are met: an issued invoice, a supply agreement, and payment documentation for payment. |
How is VAT calculated on an advance payment?
The buyer does not need to calculate the input tax on the advance payment. The seller will do this for him. The tax amount is allocated in the advance invoice. But the buyer should check whether there has been an error in the calculations.
To check, use the formula:
| VAT on advance | = | the amount of AT reflected in the invoice under the supply agreement, contract | × | settlement rate, in accordance with the rate at which the transaction is taxed: 20/120 or 10/110 |
If you find an error in the calculation, contact the seller and clarify the details. An arithmetic error needs to be corrected. Liabilities calculated incorrectly cannot be accepted for deduction.
In accounting, reflect AT in special account 76. For additional analytics, provide subaccounts 76 AB - for tranches received and 76 VA - for amounts issued. Fix the procedure for reflecting accounting transactions in the accounting policy. According to 76 VA, in the VAT return, reflect the amounts of advances issued.
Invoice for advance payment
Those. the deduction for advance SF must be made in the period when the right to it arose (clause 2 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 01/09/2017 N SD-4-3 / [email protected] );
Accounting in 1C
The document Invoice, a received type of transaction for an advance payment, is generated on the basis of the document Write-off from a current account by clicking the Create based on and - Invoice received .
The document Invoice received for advance payment is automatically filled in with the data from the document Write-off from the current account :
- Invoice No. and from – number and date of the invoice received from the supplier;
- Received – the actual date of receipt of the invoice from the supplier;
- Transaction type code - 02 “Advances issued”.
If the document has the Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book , then when it is posted, entries will be made to accept VAT for deduction.
Find out more about Options for accepting VAT for deduction using the document Invoice received .
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 68.02 Kt 76.VA – acceptance of VAT deduction from the advance payment transferred to the supplier.
The document generates movements in the VAT Purchases register :
- registration of advance SF supplier with transaction type code 02 “Advances issued” for the amount of accepted VAT for deduction.
Purchase Book report can be generated from the Reports – VAT – Purchase Book section. PDF
Reporting
When VAT is not paid
You will not always have to pay value added tax on AT. Officials have identified a number of situations where this is not necessary:
- The company applies VAT exemption or is not a taxpayer.
- The company carries out operations that are not subject to value added tax.
- The place of sale of goods for which an advance payment system is provided is outside our country.
- The entity sells goods taxed at an export rate of 0%.
- When selling goods for which the production cycle lasts more than 6 months. The list is fixed by government decree No. 468 of June 28, 2007. Confirmation from the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation is required.
If at least one of the listed conditions is met, then the tax in the AT is not calculated. Therefore, advances are not required to be reflected in the VAT return. For example, an organization in a special regime does not have to submit value added tax reports at all.
Creating an invoice for an advance payment from a sales ledger
IHow to automatically generate a sales book in an advance invoice to obtain the following details: payment document number and the date of its creation? I saw how this topic was discussed and people said that this is completely unnecessary... according to the law of 2002.. but according to the government decree of 02.2004, it is necessary that these invoices have a payment number and date. Please tell me! Maybe someone solved this problem?
Get your work in order using the 1C configuration “IT Department Management 8”
ATTENTION!
If you have lost the message input window, press
Ctrl-F5
or
Ctrl-R
or the Refresh button in your browser.
The thread has been archived. Adding messages is not possible.
But you can create a new thread and they will definitely answer you!
Every hour there are more than 2000
people on the Magic Forum.
Entrepreneurs have been using the opportunity to deduct “input” VAT on preliminary payments for a long time. However, the question of whether an “advance” invoice is needed if the shipment occurred within 5 days after the advance payment still remains open.
An accountant often asks whether it is necessary to draw up an “advance” invoice if goods are shipped within 5 calendar days from the date of receipt of the advance payment.
Sales of goods
The sale of goods and the simultaneous offset of the advance received from the buyer is reflected in the document Sales (act, invoice) transaction type Goods (invoice) in the section Sales – Sales – Sales (acts, invoices) – Goods (invoice).
Find out more about setting up the advance payment method
See also the key points for registering the sale of goods in wholesale trade
Postings according to the document
When posting a document, the advance previously received from the buyer is offset in the amount of the advance payment under the contract, but not more than the total amount under the document:
- Dt 62.02 Kt 62.01 – offset of advance payment.
Doing it right
If the seller receives an advance payment, the VAT tax base must be determined twice: on the day the advance payment is received and on the day the goods are shipped (clauses 1 and 14 of Article 167 of the Tax Code). The invoice is also drawn up twice. Initially, upon receipt of an advance, the seller is obliged to issue the mentioned document no later than 5 days from the date of transfer of money, and also register the paper in the sales book (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Then, as the obligations are fulfilled, the seller deducts the VAT paid on the advance, again records in the purchase book the already issued invoice for the advance (clause 8 of Article 71 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 6 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and issues a new invoice - an invoice upon the sale of goods (works, services) and again registers the paper in the sales book (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Let’s say that the receipt of prepayment and shipment took place in one quarter, and not even 5 days have passed since the receipt of funds. Why, then, use a complex mechanism with “advance” invoices if this does not in any way affect the calculation of the final VAT amount?
And here’s the rub: let’s say the receipt of prepayment and shipment took place in one quarter, and not even 5 days have passed since the receipt of funds. Why, then, use a complex mechanism with “advance” invoices if this does not in any way affect the calculation of the final amount of VAT to be paid to the budget (or reimbursed from the budget)?
How to correctly account for VAT in a purchase ledger
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show an example of the execution of a receipt document and the invoice received from it. An invoice issued in this way will be included in the purchase book.
Fig.1
Fig.2
Pay attention to the registration of the invoice directly from the receipt document (Fig. 1). An invoice is created automatically directly from the “Receipt of goods, services” document if its date and number are filled in (the required fields are located at the bottom of the “Receipt ..." document). What would seem simpler?
Expert opinion
If, within 5 calendar days, counting from the date of receipt of the prepayment, goods are shipped against this payment, then invoices for prepayment should not be issued to the buyer, as representatives of the Ministry of Finance claim, this point of view is reflected, in particular, in Letters from October 12, 2011 No. 03-07-14/99, dated March 6, 2009 No. 03-07-15/39. To justify their position, officials refer to the provisions of paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but they do not provide any additional argumentation.
At the same time, financiers did not fail to note that the organization is still obliged to issue an invoice for the advance payment received, regardless of in which quarter the prepaid goods are shipped. They also indicate the obligation of companies to charge VAT both on the day of receipt of the advance payment and on the date of shipment of goods, if both dates fall within the same quarter. This position is shared by tax officials.
Yana Lazareva, expert at Calculation magazine
« Previous :: Next »
Accounting for invoices when receiving advances
G.L. Malakhova
Chief accountant of the Avanta+ publishing association
Published: Magazine "Calculation" N 10/2002.
Hello, dear editors! I want to tell you about my method of accounting for invoices when receiving advance payments received for upcoming deliveries of goods, performance of work or provision of services. I hope that this method will be useful to my fellow accountants.
For an accountant, an invoice is a very important document. It serves as the basis for the buyer to accept the amounts of value added tax presented to him for deduction or reimbursement in the manner prescribed by Articles 171, 172, 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. According to the provisions of paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the seller is obliged to issue an invoice to the buyer no later than five days, counting from the day of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services), upon their sale. The code does not require an invoice to be issued upon receipt of an advance from a buyer.