Composition of tangible assets
According to the uniform rules for accounting in Russian organizations, tangible assets are usually divided into two categories.
Some categories are quite rare in practice. For example, these are search assets. But fixed assets, inventories and cash are the most common items. Without such facilities, conducting business is almost impossible.
| Non-negotiable | Negotiable |
| These are all types of assets of an economic entity that are used to carry out activities for more than one calendar year. Examples of objects can be buildings and structures, cars and other equipment, machines and equipment, and software. | These are those objects that are directly involved in the production cycle, but their full turnover (use) period is less than a year. Examples of such objects are raw materials and supplies, fuel and lubricants and spare parts, finished products and goods. |
Composition of non-current assets:
| Composition of current assets:
|
Valuation of assets on the balance sheet
Balance sheet is a document reflecting the presence and condition of the organization’s assets, their itemized and total value (the latter is entered in line 1600). By analyzing the value and structure of assets, one can draw a conclusion about the success of the enterprise, its ability to fulfill its obligations and make a profit.
Many indicators are used for analysis, some of which are discussed below.
Cost and average value of total assets
The cost of resources is an assessment, expressed in monetary terms, of the property of an enterprise that generates income or can generate it in the future. It consists of two positions: the amount of current and non-current assets (in the balance sheet these are lines 1100 and 1200, respectively). Thus, the value of total assets is determined as the sum of lines 1100 and 1200. In other words, this is the balance sheet currency: the total for the assets section, line 1600.
The average value of total resources (ASA) of an organization is found as the arithmetic mean between the value at the beginning of the year (A1) and at the end of the year (A2). This is written as a formula:
SSA=(A1 + A2)/2
To calculate the average annual cost, the same principle is applied: indicators are taken as of one accounting period, but from the balance sheets of different years. The divisor will be equal to the number of years under study (if for two years - 2, if for three - 3, etc.). The average indicators for current and non-current resources are calculated similarly.
Real assets ratio
Real assets include intangible assets, fixed assets, inventories (production) and costs in work in progress - everything that is involved in commercial activities. For analysis, a ratio is usually used - the ratio of the total value of real assets to their total value on the balance sheet. A successful manufacturing company should have a value above 0.5 (50%). Decrease means a drop in production capacity or a transfer of the enterprise to other, non-core activities.
Asset immobilization ratio
Immobilization of assets means their withdrawal from circulation. That is, the share of assets that are not involved in turnover and do not generate income, or are used for other purposes than their intended purpose, is assessed. The immobilization coefficient shows how efficiently the enterprise's resources are used. The indicator reflecting the state of immobilized funds is calculated as the ratio between the permanent (non-current) and current (current) assets of the enterprise.
The lower this indicator, the more liquid resources the enterprise has and, accordingly, the higher its solvency.
How to keep records of tangible assets
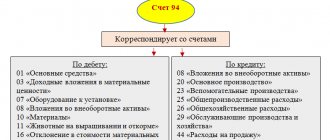
Math assets are reflected in accounting accounts in accordance with their category. For example, fixed assets should be attributed to account 01 of the same name. In the public sector - 0 101 00 000. Inventory in non-profit organizations should be reflected on account 10, and, for example, in a budgetary institution - on account 0 105 00 000. Record the company's cash in the cash register on accounting account 50, on current accounts - 51. State employees register transactions with money in the group of accounts 0 201 00 000.
Accounts for recording tangible assets are active. That is, the receipt of material objects can only be reflected in the debit of the corresponding account. The disposal of objects is reflected in the turnover on the credit of accounting accounts.
IMPORTANT!
Active accounts cannot have a credit balance at the end of the period. The value is either positive or zero!
If, during the formation of accounting registers for one of the accounting accounts for the accounting of physical assets, a credit (negative) balance is identified, then most likely there is an error in the accounting. It is necessary to check whether the postings are made correctly.
Features of accounting for rent
When receiving fixed assets for rent, the company does not acquire ownership of these assets. Consequently, leased properties are not reflected in balance sheet accounts. Such assets should be accounted for in off-balance sheet account 001 “Leased fixed assets”. For example, the receipt of equipment under a lease agreement should be reflected in accounting by a one-sided entry in the debit of account 001.
But there may be exceptions. The rules for accounting for leased property are determined by the terms of the agreement. If the assets are assigned to the balance sheet holder, then the equipment received on lease or rent is reflected in off-balance sheet account 001. If the property is transferred to the recipient’s balance sheet, then reflect the assets on the balance sheet.
How the value of tangible assets is formed
The procedure for forming the value of material objects is fixed by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 34n. The tangible assets of an enterprise should be assessed depending on the method of their receipt by the company. Common methods:
- Acquisition of an object using the organization’s own funds. The cost of material assets is formed as a combination of all types of costs associated with the supply, delivery, setup and installation of the purchased object.
- Free access to property. If a material asset is transferred into the ownership of an organization free of charge, then its value is determined based on market price indicators. Moreover, the market value is assessed as of the date of receipt.
- Independent production of material assets. The cost is formed in this case as the totality of the company’s expenses incurred for the production of valuables. That is, the cost of releasing the finished product is taken into account.
Some companies have the right to use other methods for determining the value of asset assets. For example, determine indicators using the reservation method. But the approach is available if it is permitted by the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
How does registration of real estate of an organization take place?
People in the Russian Federation do not become taxpayers of their own free will. If a company owns any real estate, and also has separate divisions on the territory of the state, it is automatically obliged to register for taxation not only at its location, but also at the location of each existing separate division, as well as real estate and transport. The tax authority assigns the organization an individual taxpayer number.
The obligation to be registered with the tax authority at the location of the real estate forces the business company to write a corresponding application to the tax office at the location of such property within a specific period - 30 days from the date of registration of the property.
However, tax authorities themselves must also take measures to register taxpayers. Thus, after registering ownership of real estate, authorized services provide information to the tax inspectorate at the place of registration, and that, in turn, registers the organization within five days from the date of receipt of the relevant information. The inspection certificate is issued in person or sent by registered mail.
Tax registration at the location of the property subsequently entails the obligation to pay property tax and forces you to provide a calculation using the unified form KND 1152026 (submitted for each separate division and property).
Typical accounting entries
Keep records of material assets in a non-profit organization in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n. Reflect transactions in accounting using the following entries:
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| Equipment for main production was purchased by NPOs for a fee | 08 | 60 |
| VAT is reflected as part of the cost of the purchased fixed asset item | 19 | 60 |
| The initial cost of purchased equipment has been formed | 01 | 08 |
| Reflects the costs of non-profit organizations for the modernization of fixed assets | 08 | 69, 70, 10 |
| The organization purchased raw materials and supplies for a fee | 10 | 60 |
| VAT is allocated from the cost of purchased raw materials | 19 | 60 |
Accounting in public sector institutions should be maintained in accordance with Instruction No. 157. Individual recommendations of the Ministry of Finance must be taken into account depending on the type of institution (budgetary, state-owned or autonomous). Let's define typical entries in the accounting of a budgetary organization using the example of the purchase of raw materials.
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| The inventory supplier has delivered raw materials | 0 105 XX 340 | 0 302 34 730 |
| The amount of input VAT is reflected | 0 210 12 560 | 0 302 34 730 |
| The government agency transferred payment for raw materials to the supplier | 0 302 34 830 | 0 201 11 610 |
| Value added tax was accepted for deduction by the budgetary institution | 0 303 04 831 | 0 210 12 660 |
Sources of formation of property assets
The company's property is formed from specific sources. This can be either the entrepreneur’s or company’s own funds or borrowed assets. Among all sources of formation, there are three main categories:
- The company's own capital. This is not only the authorized capital of the company, which was formed during the creation of an economic entity. Own assets can also include additional capital, as well as reserve funds. These are funds accumulated during the activity of the institution. Also, the company’s profit and targeted financing can be included in equity capital.
- Borrowed capital. It is formed through loans and borrowings received from third parties. For example, loan financing can only be obtained from a licensed company (bank). But a loan can be obtained from both the counterparty and the founder.
- Accounts payable are the amount of debt a company owes to third parties, suppliers and contractors.
Inventory of sources of property formation is an important stage in the financial activity of a company. The procedure allows you to identify unused resources and reduce ineffective expenses of the subject.
Reflection in the balance sheet
To correctly reflect tangible assets on the balance sheet, when preparing the main financial statement, consider the following:
- Data on balances of physical assets at reporting dates are reflected on the left side of the balance sheet. Since this type of object refers to the assets of the enterprise.
- Enter information into reporting form No. 1 based on data from the accounting registers as of the corresponding date. That is, at the beginning and end of the reporting period.
- Detail numerical indicators by asset category. That is, indicate one category of mathematical assets in the corresponding line of the balance sheet:
- p. 1140 - reflect material search objects;
- page 1150 - include information about fixed assets objects formed as of the reporting date;
- page 1160 - include in the balance sheet the amounts allocated to investments in material assets;
- p. 1190 - record other types of SAI;
- page 1210 - disclose information about the cost of goods and materials and inventories as of reporting dates;
- p. 1260 - detail other types of OA.
Results
In accordance with the structure of the balance sheet, assets can be divided into current and non-current - such a division indicates how intensively assets participate in business turnover during the reporting period.
The accounting procedure for various types of assets is established in special accounting provisions. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Generating financial statements using “My Business”
Organizations in special regimes submit financial statements by March 31 of the following reporting year. Accounting statements in a simplified form consist of a balance sheet and a profit and loss statement. Always remember that if you make a mistake at one of the stages of preparing financial statements, you will have to go back and recalculate the indicators, again reconcile the asset with the liability. So that your work does not become similar to similar stories, and the balance converges in a matter of minutes, trust the online accounting “My Business”!
You can generate the organization’s financial statements using the simplified tax system or UTII using the “My Business” online accounting service. The service is updated online, so you will have only the latest forms at hand, and also generate reports that meet all the requirements of current legislation. Go through the Reporting Wizard and generate all the necessary reporting! If you have any questions, you can seek free advice from service specialists.
Debt securities asset or liability
Schmalenbach (1873-1955), the largest German accounting theorist of the 20th century. In fact, the owners invested capital, that is, the enterprise received income from its owner (at the beginning of the business, their own, and during operation they capitalized accounts payable and their income). The funds received must be invested in the business. This means that they should be used to purchase equipment, materials, goods, etc. in order to turn these enterprise incomes into its expenses. The funds received must be invested in the business. In this case, all liabilities can be understood as income of either past and/or future periods. And by and large, the border between own and attracted capital will essentially disappear. The boundary between own and attracted capital is blurred. The peculiarities of this interpretation are that its supporters interpret liability as a cause, and asset as a consequence.
The own funds of an enterprise under any form of ownership (except state) consist of: authorized capital; shares, shares in business companies and partnerships; proceeds from the sale of primary and additional issues of shares; accumulated retained earnings (reserves); realized increase in the market value of securities; public funds with which the enterprise is allocated. Types and properties of liabilities The liability of an investment fund is the short-term obligations of the fund (accounts payable, debt on contributions to the budget, extra-budgetary funds, etc.) and long-term obligations of the fund (loans, borrowed and other borrowed funds). Liability of an investment fund What is a liability? Liabilities are what waste our resources. Monetary liabilities take money away from us, that is, they create a loss.
Assets and liabilities in the personal and family budget
Every family is to some extent similar to an organization, and taking into account the rules of a commercial bank, it is important not only to monitor, but also to plan assets and liabilities in advance. One of the basic rules is that money must work and generate income, but the overwhelming majority of capital cannot be used for work. You don’t have to be a financial genius to understand that it is advisable to strive not so much for an even ratio, but rather for assets to exceed liabilities.
Distribution of family or personal capital, taking into account the security of assets and liabilities
| View | Main methods of investing | Percentage of total income |
| Assets |
| Up to 5% 10-13% 3-5% |
| Liabilities |
| Up to 10% Up to 7% Up to 2-3% |
Of course, this financial report must include expenses for maintaining the family: utility costs, food purchases, transportation. Low liquidity of liabilities may change over time (real estate, land will fall in price), and if funds are systematically set aside for the purchase of different objects, it is possible to comply with the principle of diversification as much as possible.
In a personal budget, assets and liabilities are closely related, since all funds received are used to meet needs, form savings, are used as investments, using the services of a bank or other organizations. And if you haven’t decided where to invest your money, I suggest reading my advice in a ready-made review that offers the most popular and effective ways. Considering assets and liabilities in a family, personal budget or in accounting, a common direction is noticeable: assets are aimed at increasing capital, liabilities are formed from capital and do not generate income, and sometimes require additional “infusions”. Traditionally, I would like to wish everyone that a current asset generates income, allowing them to increase assets and form liabilities with a competent approach.
See also:
- Making money on affiliate programs without a website from scratch: step-by-step recommendations, important tips in choosing a topic and platform and how much you can earn
- The best affiliate programs of different directions, service ratings and how much you can earn on an affiliate program
- What are dividends in simple words? Payment and taxation procedure
Author Ganesa K.
A professional investor with 5 years of experience working with various financial instruments, runs his own blog and advises investors. Own effective methods and information support for investments.
The language of financial literacy
To be financially successful, you need to know financial language and communicate in it as often as possible. You should understand the basic terms, especially if they can be applied in your field of activity. At least when managing a personal and family budget.
For more information on how to manage a family budget, read the article (opens in a new window).
The concepts of Assets and Liabilities are only a small part of financial terms. Let's look at a few more financial concepts.
Income
Income is the money that we, as well as members of our family, if any, receive for our work and knowledge. In this article we will be referring specifically to money, since income can be either in the form of any items or intangible. For example, we did someone a favor, and for this they gave us a mobile phone. We can now sell it and get money.
Thus, income is all the money that comes to us from our activities and assets.
Income can be good and bad. This division is not related to their size