According to Art. 487 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, an advance payment is a full or partial payment for goods/services before the actual shipment by the seller. Prepayment is accounted for in special accounting subaccounts and is not the income of the supplier using the accrual method until the organization fulfills its obligations. Let's consider the nuances of reflecting an advance payment as a business transaction, and provide the main entries for advances issued and received.
Note! The legal status of the advance payment is fixed in the terms of the contract, the regulatory regulation of counter-fulfillment of obligations is carried out in accordance with Art. 328 Civil Code.
The difference between an advance and a deposit
An advance is often confused with a deposit. Both the advance and the deposit have one function - advance payment for a product or service, partial or full. There is no clear definition in the legislation to separate these concepts, but according to established practice, an advance payment is considered to be the amount of prepayment for the transfer of which a separate agreement to the contract has not been drawn up:
Results
Settlements with suppliers involve the use of account 60 with the opening of sub-accounts for it, provided for by the working chart of accounts of an economic entity.
In addition to account 60, account 76 may also be involved in such operations. Payments to suppliers are reflected in the debit of these accounts. The choice of the account corresponding to the loan will depend on how the payment was made: non-cash (from a current, foreign currency or specialized bank account) or in cash. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Advances issued
An advance payment is an advance payment to the supplier against future deliveries, work performed or services performed. Transferring an advance payment to a supplier does not mean receiving economic benefits, since the supplier may, for various reasons, fail to fulfill its obligations under the contract: fail to ship goods, fail to provide a service. In this case, the advance payment is returned to the buyer’s account if it was transferred through a bank, or to the cashier if received in cash.
In general, there is no obligation to return the deposit from the supplier.
To account for VAT on advances in the chart of accounts, there is a subaccount on account 76, most often its code is 76.AB.
The buyer can accept VAT as a deduction only if the following conditions are met:
- Presence of an advance payment clause in the contract;
- Documents confirming the transfer of prepayment;
- The supply of goods (services, etc.) is intended for use in activities subject to VAT;
- Availability of a supplier's SF with a dedicated tax.
The buyer does not have the right to accept VAT as a deduction if all of the above conditions are not met. Acceptance of VAT deduction is not an obligation, but a right of the purchasing organization.
If an organization decides to use VAT deduction from an advance issued, then after the provision of the service and the closing of this advance, it will be obliged to restore this VAT to the budget.
Example
Let's say Altavista LLC transfers an advance in the amount of 23,600 rubles. (including VAT). Then Altavista LLC receives goods worth RUB 23,600 from this supplier.
The rate and amount of incoming VAT are indicated in the supplier's invoice.
Advances issued - postings
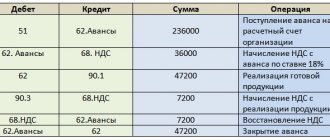
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 60.2 | 51 | Transfer of advance payment | 23 600 | Payment order ref. |
| 19 | 60.2 | VAT on advance | 3 600 | Advance invoice (received) |
| 68 | 76(advances) | VAT deduction from advance payment | 3 600 | Book of purchases |
| 10 | 60.1 | The received goods are registered | 20 000 | Invoice |
| 19 | 60.1 | Incoming VAT reflected | 3 600 | SF supplier |
| 60.1 | 60.2 | Advance offset | 23 600 | Accounting information |
| 60.2 | 68 | Recovered VAT from advance payment | 3 600 | Sales book |
Advance reports - accounting entries
In addition to settlements with counterparties - buyers and suppliers, the company regularly issues funds to its employees. How to correctly make accounting entries for expense reports? And is it true that the amount from the advance report is deducted from profit? Let's look at a specific example.
Example of settlements with accountable persons regarding advances issued:
The Pit Stop enterprise reported to employee E.I. Kovalev. for a business trip 8,000 rubles. Kovalev spent 5,400 rubles, and unused funds amounted to 2,600 rubles. returned to the cashier. The accountant will need to do the following:
- An advance was issued for travel expenses - posting D 71 K 50 for 8000.
- The balance of unspent money was returned - posting D 50 K 71 for 2600.
The accountable person is obliged to report on the expenditure of funds within 3 days after the end of the issuance period, and in the case of being on a business trip - after the employee returns. Specific deadlines are set by the head of the organization. If an employee, without good reason, has spent more than the allocated funds and is unable to account for them, the excess is withheld from his income. Buh. The entries for expense reports in this situation look like this:
- The amount not returned on time is reflected - D 94 K 71.
- The shortfall from the employee’s earnings is withheld - D 70 K 94, but not more than 20% monthly.
Advances received
When an organization sells goods, works or services, the buyer can make an advance payment before the moment of sale.
According to the requirements of the Tax Code, the seller is obliged to charge VAT on the advance received. VAT is calculated using the formula:
VAT on the advance received = Sales amount *18/100
Example
Let's consider the previous example from the point of view of the selling organization, that is. VAT is charged on the advance payment at the time of its receipt; the amount of such VAT is reimbursed to the budget at the end of the tax period - quarter.
VAT on sales is accrued at the time of shipment, that is, at the time the sales transaction is created Dt 62 - Kt 90.1 .
Advances received - postings
When receiving an advance from a buyer, the accountant makes the following entries:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 51 | 62.2 | Advance received from buyer (including VAT) | 23 600 | Payment order in. |
| 76(advances) | 68 | VAT accrual on advance payment | 3 600 | Invoice issued, accounting certificate |
| 62.1 | 90.1 | Sales revenue accrued | 23 600 | Sales certificate, invoice |
| 90(VAT) | 68 | VAT on sales | 3 600 | SF issued, accounting certificate |
| 68 | 76(advances) | Accepted for deduction of VAT on advances (after sale) | 3 600 | Book of purchases |
Other transactions - the supplier’s invoice for materials, work, services has been paid
The current account, the transactions with which we examined in the previous section, is most often used in settlements between economic entities. However, payment can be made not only from it; there are other ways to make it. Account correspondence can take the following form:
- Dt 60 Kt 50 - paid to the supplier in cash, the supplier's cash receipt must be attached to the receipt documents if he is obliged to use a cash register;
Important! Recommendation from ConsultantPlus: How to arrange payment to a supplier for goods in cash If the goods are paid for by an employee of your organization, do the following: 1. Give him cash on account. In RKO, in the line “Base”, indicate the content of the business transaction. For example, for this line you can indicate: …. See K+ for all the details.
- Dt 60 Kt 52, 55 - if payment is made by bank transfer from a foreign currency or specialized account in a banking institution.
The choice of subaccount for account 60 in the proposed entries will also depend on when the payment occurred - before or after the receipt of products, works, services, etc.
If the buyer transfers his own bill of exchange as a guarantee of payment for goods, works, services, then accounts payable from account 60 are not written off, but are reflected in a separate sub-account intended for accounting for bills of exchange. Posting - the supplier's invoice is paid with its own bill of exchange - may look like this:
Dt 60.1 Kt 60 “Settlements on bills issued.”
When repaying his own bill, the buyer will write:
Dt 60 “Settlements on bills issued” Kt 50, 51, 52, 55.
For all the details on recording transactions for the purchase of goods and the transfer of bills of exchange in payment for them in the buyer’s accounting, see the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. Get trial access for free.
Read about how to create a balance sheet for account 60, taking into account all the entries made in accounting.
Invoicing the buyer
Creating an Invoice for the buyer in 1C allows you to automatically track payment and shipment of goods, and also helps:
- quickly and automatically process payment and shipment documents;
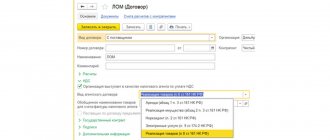
- Correctly fill out the advance invoice: column 1 “Name of goods (description of work performed, services provided), property rights” will reflect specific items of goods indicated in the Buyer’s Invoice .
Study the procedure for filling out advance invoices
An invoice for payment by the buyer is prepared using the document Invoice to buyer in the section Sales – Sales – Invoices to buyers.
The document states:
- from – date of invoice;
- Counterparty – the buyer to whom the invoice is issued;
- Agreement - a document according to which settlements with the buyer will be carried out, Type of agreement - With the buyer ; PDF
- Payment status – Unpaid , set automatically when creating an invoice.
, an Invoice for payment is filled out , then the Payment Status in the Invoice to Buyer will automatically change to Paid or Partially Paid .
Unpaid invoices can be monitored in the section for the Manager - Settlements with customers - Invoices not paid by customers.
- on the Goods and Services , a list of goods, works, services of the proposed supply, their cost and the allocated amount of VAT are indicated.
The document Invoice for payment does not create transactions and movements in registers.
Documenting
The Invoice for payment form can be printed by clicking the Print button - Invoice for payment of the document Buyer's Invoice . PDF
Find out more about additional details of the printed form
Accounting entries for advances from customers and suppliers
At the same time, the group of articles “Accounts receivable” is contained in the “Current assets” section.
In addition, it should be noted that according to paragraph 6 of PBU 4/99, financial statements must give a reliable and complete picture of the financial position of the organization, the financial results of its activities and changes in its financial position. Financial statements prepared on the basis of the rules established by regulatory acts on accounting are considered reliable and complete.
.
If, when preparing financial statements based on the rules of this Regulation
the organization
identifies insufficient
data to form a complete picture of the financial position of the organization, the financial results of its activities and changes in its financial position,
then the organization includes relevant additional indicators and explanations in the financial statements
.
Deviations from these rules can only be made in exceptional cases (for example, nationalization of property).
Also, in accordance with paragraph 73 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, settlements with debtors
and creditors
are reflected by each party in its financial statements in the amounts arising from the accounting records and recognized by it as correct
.
Based on the above paragraph 19 of PBU 4/99, the classification of receivables into long-term and short-term is carried out on the basis of the maturity of such debt (i.e., in this particular case, the delivery time of the corresponding object), and not the operating life of the asset with the acquisition of which related to the transfer of the advance.
Thus, the position expressed in the letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation under consideration is not regulated by regulatory documents on accounting in the Russian Federation; moreover, it currently contradicts them.
Taking into account the above, due to the fact that at present there is no direct prohibition on reflecting the advances in question as part of the group of items “Receivables”, advances, in our opinion, should be reflected in line 1230 “Receivables”
.
In our opinion, the procedure for presenting such advances in the balance sheet should be determined in the accounting policy.
At the same time, in the explanatory note and in the notes to the balance sheet, the Organization may provide more detailed information about the specific composition of the relevant assets (accounts receivable).
Board of Tax Consultants November 26, 2015
Accounting Regulations “Accounting Statements of an Organization” PBU 4/99, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 07/06/99 No. 43n.
“Recommendations for audit organizations, individual auditors, and auditors for conducting an audit of the annual financial statements of organizations for 2010.”
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n
At the same time, in accordance with paragraph 19 of PBU 4/99, it is advisable to distinguish long-term and short-term receivables in this group.
This is interesting: Szi 6 certificate through government services
Disclosure of information about the nature of receivables is usually carried out by introducing additional lines, for example “including long-term” and “including short-term”.
Tax Code of the Russian Federation on advance payments for income tax
The procedure for calculating income tax and advance payments is established by Art.
286 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Income tax during the year involves regular advance transfers to the budget based on the results of reporting periods (clause 2 of Article 286, clause 1 of Article 287 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 2 of Article 285 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Calculation with the budget is carried out:
- or monthly on an accrual basis: 1 month, 2 months, 3 months and so on until the end of the year (for example, January, January - February, January - March, etc.);
- or quarterly: 1st quarter, half year, 9 months.
The calculation of advance payments for income tax is similar to the determination of income tax at the end of the year. It is calculated on an accrual basis during the calendar year as the product of the tax base and the tax rate minus previous advance payments for this year (clause 1 of Article 286, clause 1 of Article 287 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Step-by-step instruction
On September 27, an invoice was issued for payment to the buyer, Architectural Workshop LLC, for office furniture in the total amount of 354,000 rubles. (incl. VAT 18%):
- MIKKE desk – 15 pcs. at a price of 5,900 rubles;
- Chair MARCUS – 15 pcs. at a price of 11,800 rubles;
- File cabinet ERIC – 10 pcs. at a price of 8,850 rubles.
On September 30, the Organization’s bank account received a 100% advance payment from the buyer.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | |
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| Invoicing the buyer | |||||||
| September 27 | — | — | 354 000 | Invoicing the buyer | Buyer's invoice | ||
| Receipt of advance payment from the buyer | |||||||
| September 30th | 51 | 62.02 | 354 000 | 354 000 | Receipt of advance payment from the buyer | Receipt to the bank account - Payment from the buyer | |
Quarterly and monthly advance payments
Companies whose revenue for the previous four quarters on average for each quarter is less than 15 million rubles. (Clause 3 of Article 286 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), advances on NP are transferred quarterly.
The transition to monthly payments based on the profit of the previous quarter is mandatory if the company’s average quarterly income is above the specified limit, and for newly created organizations - if after a full quarter the revenue exceeds 5 million rubles. per month (clause 5 of article 287 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If an organization switches to paying monthly advances under NP based on the profits of the previous quarter (paragraph 2, clause 2, article 286 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), reporting remains quarterly. The company pays once a month 1/3 based on the results of the last quarter, and based on the results of the current quarter it pays additionally to the NP.
On a voluntary basis, you can switch to paying monthly advance payments based on the actual profit received, while during the tax period the taxpayer does not have the right to change the payment method and can switch to it from the new calendar year by submitting an application before December 31 of the current year. This rule does not apply to newly created organizations. Starting from the month of registration, they have the right to calculate and transfer monthly advance payments based on actual profits. The organization must notify the tax office about the use of this method of paying NP in the month of creation, and based on the results of the same month, it is necessary to calculate the first advance payment and submit the first income tax return.