In accounting, an advance is an advance payment in the form of a sum of money that is transferred from the buyer to the supplier as payment for services not yet provided, work not performed, or goods not shipped.
The advance payment is not income for the organization that received it until certain services are provided to the customer (or the previously paid goods arrive at the warehouse). From this article you will learn about the specifics of reflecting advances issued and received, as well as about the documents on the basis of which entries are made in accounting for advances.
Accounting for settlements with customers during sales
Revenue from the sale of goods (work, services) is recognized as income from an ordinary type of activity and is reflected in the credit of account 90 “Sales”.
If the sale is one-time and is not a regular activity of the enterprise (for example, the sale of a fixed asset), then the proceeds are reflected as part of other income under the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”.
These two accounts 90 and 91 will be discussed in detail a little later; they are interesting and unlike other accounts, they have their own characteristics. It is necessary to calculate VAT on the sale price of goods (works, services) and send it for payment.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8000 books purchased |
Postings to account 62 during regular sales: (click to expand)
| Debit | Credit | Operation name |
| 62 | 90/1 | Revenue from the sale of goods (works, services) is reflected |
| 90/3 | 68 | VAT accrued on goods sold (work, services) |
| 62 | 91/1 | Revenue from the sale of fixed assets, intangible assets, materials is reflected |
| 91/2 | 68 | VAT accrued on sold assets |
| 51 | 62 | Payment received from buyer |
Other transactions - the supplier’s invoice for materials, work, services has been paid
The current account, the transactions with which we examined in the previous section, is most often used in settlements between economic entities. However, payment can be made not only from it; there are other ways to make it. Account correspondence can take the following form:
- Dt 60 Kt 50 - paid to the supplier in cash; the supplier's cash receipt must be attached to the receipt documents if he is required to use a cash register.
- Dt 60 Kt 52, 55 - if payment is made by bank transfer from a foreign currency or specialized account in a banking institution.
The choice of subaccount for account 60 in the proposed entries will also depend on when the payment occurred - before or after the receipt of products, works, services, etc.
If the buyer transfers his own bill of exchange as a guarantee of payment for goods, works, services, then accounts payable from account 60 are not written off, but are reflected in a separate sub-account intended for accounting for bills of exchange. Posting - the supplier's invoice is paid with its own bill of exchange - may look like this:
Dt 60.1 Kt 60 “Settlements on bills issued.”
When repaying his own bill, the buyer will write:
Dt 60 “Settlements on bills issued” Kt 50, 51, 52, 55.
Read about how to create a balance sheet for account 60, taking into account all the entries made in accounting.
Accounting for advances received in settlements with customers
If the buyer pays for the goods in advance and makes an advance payment, then to account for settlements with buyers, in this case, subaccount 2 “advance received” is opened on account 62, while subaccount 1 will reflect settlements with buyers in the general case.
VAT is considered and payable on advances received. Then, when goods, works or services are transferred to the buyer, VAT is charged again, this time on the proceeds. The accrued amount of VAT on the advance received is restored, and then an entry is made to offset the advance. You can read more about accounting for VAT on advance payments in the article: “Accounting for VAT on advance payments and gratuitous transfers.”
Postings for accounting for advances received (account 62)
| Debit | Credit | Operation name |
| 51 | 62. Advance received | An advance was received from the buyer to the bank account |
| 76.VAT on advances received | 68 | VAT is charged on the advance received |
| 62/1 | 90/1 | Revenue from sales of goods is reflected |
| 90/3 | 68 | VAT accrued on goods sold |
| 62. Advance received | 62/1 | Offset of advance against debt repayment |
| 68 | 76.VAT on advances received | Accepted for deduction of VAT in connection with the sale of goods paid in advance |
Postings for advances issued in favor of the supplier
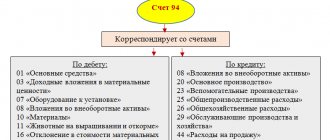
To account for advances transferred by the enterprise to pay for services, work and finished products, account 60 is used. The organization carries out settlements with accountable persons using account 71.
Reflection of the prepayment transferred to the seller for raw materials and materials
Let's consider an example: I ordered raw materials for the production of products from the Atlet enterprise and paid 48,000 rubles in advance on 04/2015. 06/01/2015 Atlet supplied raw materials to the Sigma warehouse.
The customer’s accounting must reflect the following accounting entries for the advance:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Base |
| 60.02 | The advance payment issued to the Atlet enterprise was transferred | 48,000 rub. | invoice | |
| 10/1 | 60.01 | Atlet supplied raw materials and materials in full | RUB 39,360 | waybill |
| 19/3 | 60.01 | VAT (18% of the cost of the goods received) | RUB 8,640 | waybill |
| 60.01 | 60.02 | Crediting the supplier's advance upon delivery of goods | 48,000 rub. | waybill |
| 68.02 | 19.03 | VAT credit upon delivery of goods | RUB 8,640 | waybill |
How to reflect an advance to an employee for business needs
Inter LLC issued to its employee Sviridov V.P. advance payment in the amount of 5,200 rubles for the purchase of stationery. Sviridov purchased office supplies in the amount of 4,850 rubles, and returned the remaining unused funds of 350 rubles to the cash desk of Inter LLC.
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Base |
| 71 | Sviridov received an advance on his card account | 5,200 rub. | application for funds | |
| 10 | 71 | Reflection of purchased goods | 4,850 rub. | expense report |
| 50 | 71 | Sviridov returned unspent funds to the cash register | 350 rub. | expense report |
Accounting for bills received from the buyer:
If the buyer issued a promissory note to the seller, it must be accounted for in subaccount 3 “Bill of note received” of account 62. After the sale of the product, posting D51 K62. Bill of exchange received - this bill is repaid.
If the nominal value of a bill of exchange received exceeds the sale price, then the excess amount is reflected in entry D62. Bill of exchange received K 90/1.
Postings to account 62 when paying by bill of exchange:
| Debit | Credit | Operation name |
| 62 | 90/1 | Revenue from the sale of goods is reflected. Accounting for a bill received from the buyer. |
| 62.Bill received | 62/1 | The bill received from the buyer was taken into account |
| 51 | 62.Bill received | The received bill is repaid |
| 62.Bill received | 90/1 | The excess of the nominal value of the bill over the sale price is reflected |
Step-by-step instruction
The organization entered into an agreement with Avtopark LLC for the supply of a Ford Mondeo car worth RUB 792,960. (including VAT 18%).
On March 19, 100% prepayment was transferred to the supplier.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | |
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| Transfer of advance payment to the supplier | |||||||
| March 19 | 60.02 | 51 | 792 960 | 792 960 | Transfer of advance payment to the supplier | Debiting from the current account - Payment to the supplier | |
For the beginning of the example, see the publication:
- Payment order to pay the supplier
An example of accounting for settlements with buyers and customers. Postings
| The organization Alpha LLC received an advance payment from the Beta LLC company for the shipment of finished products in the amount of 236,000 rubles. A week later, I shipped part of the finished products worth 47,200 rubles. (including VAT RUB 7,200) How to account for these transactions? |
In fact, account 62 “Settlements with buyers” reflects the buyer’s debt to the seller, that is, accounts receivable. Postings to account 62 are made at the time the sale is made, that is, at the time the goods are shipped.
Thus, account 62 reflects settlements with customers and 3 sub-accounts can be opened on it: (click to expand)
- subaccount 1 – to reflect settlements for regular sales;
- subaccount 2 – to account for the advance received;
- subaccount 3 – for accounting for bills received.
In the next article we will look at how to carry out accounting of accounts payable: “Accounting for short-term and long-term loans and borrowings (accounts 66 and 67)“.
Postings for state employees
Advance reports (accounting entries) are also compiled depending on the direction of movement of these funds. BU are compiled in form 0504053 in accordance with the provisions of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 123n dated September 23, 2005.
Typical accounting entries for account 206 00 000:
Dt 206 00 000 Kt 201 01 610, 304 05 000 - advance payment to the supplier (posting), advance payments to financial authorities;
Dt 302 00 000 Kt 206 00 000 - receipt of goods and materials or consumption of services against the previously listed prepayment.
The crediting of received proceeds for advance payment to buyers (customers) will be reflected in account 0 205 00 000 “Calculations for income”.
An advance payment has been received from the buyer, the wiring for the control unit will be as follows:
Dt 2,201 11,510 Kt 2,205 31,660 (account “Advances received”).
In commercial and non-profit organizations, to reflect mutual settlements on prepayments, account 61 “Settlements on advances issued” is used (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 94n dated October 31, 2000). Analytical accounting is carried out on the basis of the turnover sheet and balance at the beginning and end of the reporting period. On the debit of the account. 61 reflects the listed advance, the loan reflects the return of previously issued amounts and the offset of money upon actual receipt of goods, work or services.
Typical accounting entries for accounts. 61:
Dt 61 Kt 50, 51 - an advance was issued to the supplier, posting (basis - cash settlement, payment, etc.);
Dt 60 Kt 61 - offset of a previously issued prepayment (basis - invoice, act, etc.).
Related topics:
- When is VAT paid? Organizations that combine UTII and general taxation tax In the event that a company combines UTII and the general taxation regime, income,...
- VAT declaration filing deadline What are the features of the declaration? The updated VAT report from 2021 is not limited to the fact that...
- Including VAT February 17, 2016How to calculate VAT including March 27, 2021 The employee provided services unofficially:…
How to organize accounting
Accounting is organized according to separate accounts in the context of the purpose for which the prepayment was issued. This allows specialists to maintain proper analytical records and control the effective and appropriate spending of money in the organization. Accounting for a budgetary institution is regulated by Instruction No. 162n (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 6, 2010) and Instruction No. 157n (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010).
All advance transactions in budgetary institutions are reflected in accounts 0 208 00 000 “Settlements with accountable persons” and 0 206 00 000 “Settlements for advances issued” (Instruction approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 25n dated 02/10/2006). To receive an advance payment, the employee must write a corresponding statement, which will reflect the purpose and deadline for issuing the money (clause 155 of Instruction No. 25n).
When is it issued?
An advance is the issuance of a partial amount of money to achieve certain goals. In budgetary institutions, an advance payment, the transactions for which we will consider in the article, is issued for the following operations:
- payment of wages;
- transport and utilities;
- general business expenses;
- acquisition of inventory, fixed assets and fuels and lubricants;
- travel expenses.
The issuance of advanced funds is reflected through cash outgoing orders; the advance payment (entries will be presented in our article) is offset through incoming cash orders. All actions are recorded in the Journal of settlements with accountable persons.
General points ↑
What is the essence of the advance and when can it be issued? These are the first questions that are worth understanding. Let's turn to the legislation and highlight the basic information.
Concepts
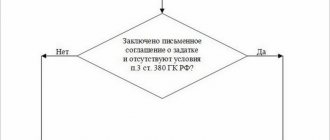
An advance is money or other valuables of a material nature that are transferred from one party to another to fulfill their obligations before the start of fulfillment of counter obligations.
But there is no exact definition in the legislation. Advance payment is an advance payment that should not be confused with a deposit. What is the main difference?
If a party fails to fulfill its obligations, the deposit is not returned to it. This does not happen with an advance payment - it will be returned. An advance is not a form of securing an agreement.
An advance is proof that the terms of the contract will be fulfilled. Any preliminary payments are considered advances, unless otherwise provided by the contract.
Who is issuing?
Advance is issued:
- management of the company as partial payment for employees;
- by the customer when concluding construction contracts until the provision of services or performance of work;
- by the buyer to the supplier as a form of crediting supplies until the products are shipped;
- by the buyer of real estate as a guarantee of the transaction.
Legal regulation
The advance payment is discussed in the following articles of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation:
- 380;
- 711;
- 735;
- 823.
The issues of payment of advances are also considered in Federal Law No. 311-FZ of Russia (Section 2, Chapter 11, Article 121 - transfer of advance customs amounts).
Payment of advance income tax is discussed in Art. 286 of the Tax Code of Russia. Operations for payment of advances are carried out in accordance with the norms of PBU 9/99 and PBU 10/99.