Land is a special type of non-depreciable asset. It can be purchased, sold, resold, sold partially or completely; at the same time appear in accounting as a fixed asset or a product for resale. Land, as an asset, is not subject to depreciation (Article 256-2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), since it does not lose its value during operation.
The plot is accepted for accounting in the amount of all actual costs for it, including state duties for registration of ownership rights (PBU 5/01 r. 2, 6/01 r. 2). Land tax is calculated based on the cadastral value of the plot.
How can an organization register real estate in the form of a land plot ?
Classification of fixed assets
- active - fixed assets that directly affect the subject of labor and affect production;
- passive - fixed assets that provide conditions for the normal flow of the production process.
Similar articles:
The classification of fixed assets according to their physical nature is the basis of their analytical accounting. Grouping of property objects in the OKOF classifier is carried out by assigning codes, the structure of which is built according to the following scheme:
All these are assets consumed in the course of the organization’s activities, which are written off in accounting when they are transferred to production and operation (clause 93 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n).
What applies to fixed assets
In the future, when accepting the purchased formwork for accounting, the manager’s order can indicate that the useful life of the formwork is determined based on the manufacturer’s recommendations, taking into account the needs of creating a specific structure at a specific facility.
Cost limit for accounting as part of OS
If the cost of non-production objects does not exceed 40,000 rubles. (or another limit approved by the organization), they can be reflected as part of the inventory (clause 5 of PBU 6/01). In this case, the organization will not have to charge depreciation on such objects. The cost of non-production objects does not apply to the cost of production, so write it off on account 91 “Other income and expenses.”
Consequently, the initial cost of the building includes RUB 75,000,000. (RUB 120,000,000 x 62.5%), and the initial cost of the land plot is RUB 45,000,000. (RUB 120,000,000 x 37.5%) or (RUB 120,000,000 - RUB 5,600,000).
The cost of the building is repaid through depreciation (clause 17 of PBU 6/01). Depreciation charges under the linear method of calculating depreciation are calculated monthly based on the original cost of the building and the depreciation rate calculated on the basis of the useful life of the building, which is established by the organization when accepting the building for accounting. This follows from clause 18, paragraph. 2, 5 clause 19, clause 20 PBU 6/01.
We recommend reading: Is it possible to buy a ticket using a copy of your passport for a train?
Accounting
The initial cost of an OS is defined as the sum of expenses for its acquisition, construction, manufacturing, delivery and bringing it to a state in which it is suitable for use (paragraph 2, paragraph 1, article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax accounting involves the formation of depreciation deductions linked to depreciation groups. The list of such groups and their features are established by Art. 258 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. A breakdown of classification characteristics and exact service life for each category of fixed assets are given in government decree No. 1 dated January 1, 2002.
Land – depreciation group 7, if the territory belongs to landfill sites. This conclusion can be drawn according to international standards for conducting accounting operations. The areas located under buildings are not included in the depreciation group of assets. The cost of such plots does not affect the amount of depreciation charges for structures located on their surface. The accountant must organize separate accounting of the land and other fixed assets located on it.
Is depreciation charged on a land plot: accounting rules
Which depreciation group does the land plot belong to? This type of asset is not indicated in the classification scheme. Tax accounting rules in relation to land plots coincide with accounting provisions. In paragraph 2 of Art. 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation specifies the list of objects that are considered non-depreciable. These include land resources, subsoil, and water sources.
Resolution No. 7 of the State Statistics Committee
of the Russian Federation
[3] does not contain a special form of the primary document for processing the operation of registering a land plot.
Consequently, organizations have the right to use form No. OS-1 “Act of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets (except for buildings, structures)”
.
At the same time, for organizations of the agro-industrial complex, Order of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation No. 750
[4] approved a specialized form
No. 401-APK “ Act for the registration of land”
.
The act reflects the following information: quantity, type of land, quality of land, book value of the object being registered.
Land depreciation: general procedure
The most popular question among enterprises that have purchased a plot of land as their own is: do we need to take into account the wear and tear of the land?
Tax legislation (Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 2, article 256) gives a clear and unambiguous answer to this question: in tax accounting, depreciation is not calculated on the cost of land, and depreciation on the site is not reflected. That is, the company that owns the land cannot reduce the basis for calculating income tax due to depreciation of the land. The legislation substantiates its position as follows: land refers to environmental management objects (along with water and forest resources, subsoil, etc.), which, in turn, do not lose their properties over time. That is, in general, the consumer value of land is constant and unchanging. The position can be confirmed by the following example: a company that has purchased land for construction can use the site to locate a property for an unlimited amount of time (both after 20 and 50 years a building or other structure can be placed on the land).
Since the useful life of the land from a consumer point of view is not limited, there is no need to charge depreciation on the site. It turns out that in this case the land does not “wear out”, and its book value changes over time only due to improvements and revaluations.
As for accounting, in this case the provisions of PBU completely coincide with tax legislation. The position on non-accrual of depreciation on land in accounting is confirmed by PBU 6/01.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
Accounting and taxation of transactions with land plots
The first option seems to be the riskiest. The costs of acquiring land ownership in full are included in material costs on the basis of paragraphs. 3 p. 1 art. 254 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
:
“Material expenses, in particular, include the following expenses of the taxpayer...
We recommend reading: Subsidy for families with two or more children
Contents of operation
To accept for accounting of land, land shares, including for temporary use, specialized forms of primary accounting documentation for organizations of the agro-industrial complex No. 401 APK, No. 402 APK, No. 403 APK, approved by order of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation dated May 16,
2003, .
No. 750" .
If this type of property assets directly affects the process of producing products, providing services, performing work, determining the result in terms of quantity and quality, then it is classified as active .
IMPORTANT ! In each economic sector, these groups have their own specifications: for example, in agriculture, the composition of fixed assets for the same groups may differ significantly from industrial.
Active and passive fixed assets
- industry of application – means for the production of goods, provision of services or performance of work;
- property – property assets can be divided according to their forms of ownership into public, private, etc.;
- involvement - according to the degree of involvement in the activities of the enterprise, one can distinguish directly used operating systems, backup, spare, repaired, reconstructed, mothballed, etc.;
- source – own property, rented, leased, etc.;
- territory - fixed assets on the balance sheet of a particular enterprise, industry, district, republic, territory, region, city or any other structural territorial unit;
- age – a certain depreciation group, that is, division depending on the maximum useful life;
- form of existence – tangible and intangible funds (according to the all-Russian classifier).
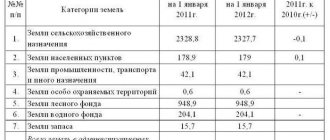
State measures such as recording all land plots, dividing them into categories, establishing restrictions on use, etc., pursue an important goal - the protection of a valuable natural resource , the quantity of which is limited for objective reasons.
- agricultural;
- settlements;
- industrial and other special purposes (transport, various types of communications, defense and security, etc.);
- specially protected natural, historical and cultural sites and territories;
- forest fund;
- water fund;
- reserve lands.
Useful video
- farming itself, all its types;
- personal subsidiary farming of citizens;
- gardening and gardening;
- country house construction (seasonal);
- organization of farming;
- construction of the necessary infrastructure to serve agricultural producers.
Non-agricultural land is occupied by various auxiliary structures. These may include: roads, communications, protective forest belts, reservoirs, buildings that support agricultural production.
Leased land: postings
If a company leases a site, then depreciation on it also does not need to be charged. The value of land received for temporary use should be reflected on the balance sheet. Depreciation must be charged only on fixed assets located on the leased site.
Example.
In April 2021, Focus JSC rented a plot of municipal property for the purpose of constructing a warehouse for its own use:
- book value of the plot – 1,050,704 rubles;
- the cost of the right to conclude an agreement with the municipality is 3,990,407 rubles. (paid in April 2017);
- The amount of state duty for registering a land lease agreement is 14,000 rubles. (paid in April 2017);
- start of construction of the warehouse - May 2021, commissioning of the facility - February 2018;
- useful life of the warehouse is 25 years;
- the period for writing off expenses for concluding an agreement with the municipality is 4 years;
- documents for state registration are dated 05/18/2017.
The following entries are reflected in the Focus accounting:
| date | Debit | Credit | Sum | Description |
| 05.04.17 | 08.3 | 76 | RUR 3,990,407 | The costs of drawing up a lease agreement for municipal land (the right to conclude an agreement) have been taken into account. |
| 05.04.17 | 76 | 51 | RUR 3,990,407 | Paid the cost of the right to conclude an agreement with the municipality |
| 05.04.17 | 08.3 | 68 State duties | 14,000 rub. | The costs of registering a land lease agreement are taken into account |
| 05.04.17 | 68 State duties | 51 | 14,000 rub. | The state fee for registering a land lease agreement has been paid |
| 05.04.17 | 001 | RUB 1,050,704 | The off-balance sheet reflects the cost of the municipal plot |
Until the premises are put into operation, the Focus accountant records monthly expenses for the right to enter into an agreement:
RUR 3,990,407 / 4 years / 12 months = 83.133 rub.
After putting the premises into operation, these expenses are reflected in tax accounting in order to reduce taxable profit.
Detailed overview of land categories and types of permitted use
Please note that Rosreestr sends extracts from the Unified State Register within 3 days (there may be delays). If you want to find out the category of land faster, I recommend ordering extracts directly through the Rosreestr API - this way you will receive the document within a day. The cost is the same - 250 rubles, the official data is from the Unified State Register of Rosreestr and is confirmed by the registrar’s electronic digital signature (EDS).
Differences between the first and second
In addition, the placement of individual buildings should not be confused with settlements. For example, a forester's house, an apiary, industrial and residential premises at mining enterprises cannot be part of a populated area until the land under them changes its category.
We recommend reading: Subsidy for construction for large families in Tagil
First Capital Legal Center Phone, +7 Is a land plot an object of fixed assets? First of all, we will find out whether the land plot is an object of fixed assets for profit tax purposes. According to para. 1 clause 1 art. 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, fixed assets are understood as part of the property used as means of labor for the production and sale of goods (performance of work, provision of services) or for the management of an organization, with an initial cost of more than 40,000 rubles. Moreover, from the title of this article it follows that it establishes the procedure for determining the value of depreciable property.
Land for a quarry or landfill
In certain cases, the company can still charge depreciation on the land and thus reduce taxable profit. According to the law, land depreciation is charged if it is established that the consumer properties of the site have changed over time. Here are the most common options for this situation:
- The land is used as a quarry for mining. If a site is acquired for the purpose of mining, its cost must be depreciated in the general manner. The quarries belong to the 7th OS group with a useful life of 15 to 20 years.
- The site is used to accommodate a waste dump. If land is acquired for use as a municipal waste dump, the site has a limited useful life and is therefore subject to depreciation as required.
In each of the listed cases, the useful life of the site is established by internal regulations (accounting policies). The amount of monthly deductions is determined based on the period of use. The accounting records the monthly posting Dt 02 Kt 01.
What group of fixed assets does the land plot belong to?
- The asphalt pavement was created without attracting targeted funding; its creation complies with legal requirements. For example, according to technical safety requirements, an asphalt site is required on the production site of an enterprise. In this case, the asphalt pavement is recognized as an asset and is depreciated in the general manner.
- It should be noted that the arguments in favor of charging depreciation for asphalt sites are quite ambiguous and are based solely on judicial practice.
Land plots are considered fixed assets
There are no grounds for classifying expenses aimed at acquiring land plots as material or other expenses, which include other expenses of land owners, landowners and land users. And continuation: in relation to fixed assets, it is provided for the inclusion of costs incurred by the organization for the acquisition, construction, delivery and bringing to a state in which these objects are suitable for use in the costs associated with production and sales, only by calculating depreciation amounts. Absence in ch. 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the rules on accounting for expenses for the acquisition of land plots by calculating depreciation amounts deprive the company of the opportunity to reduce the tax base for income tax by the corresponding amounts.
06 Oct 2021 etolaw 66
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Extraordinary Right of a Military Person to Service Housing If the Family Has a Disabled Child
- How to fill out 3 personal income taxes for a minor child to pay tax sample
- Replacement of Passport Due to Unsuitability for Use
- How long does it take to get 13 percent on an apartment purchase?
The legislative framework
When an organization acquires a plot of land, it is reflected in accounting in accordance with PBU 6/10, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, since this object is a fixed asset, as well as the norms of land and civil legislation.
The Land Code of the Russian Federation contains instructions that you can buy and sell such plots that have been assigned a cadastral number. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that the purchase and sale agreement must necessarily indicate the location of the actual location of the plot, its price, as well as restrictions or encumbrances, if any (