One of the key areas of development for 1C:Accounting 8 version 3.0 is its simplification. Starting with version 3.0.65, it has become easier to register the acquisition of a land plot in the program. Now, to reflect this operation in accounting, a special document “Acquisition of land plots” is provided.
It would seem that with the main tools in the 1C: Accounting 8 version 3.0 program, everything has long been clear and simple, why simplify anything else? But accounting for land plots as fixed assets has some peculiarities.
Note
To simplify the accounting of fixed assets in “1C: Accounting 8”, see the article “Simplification of accounting for fixed assets in “1C: Accounting 8”.
The legislative framework
When an organization acquires a plot of land, it is reflected in accounting in accordance with PBU 6/10, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, since this object is a fixed asset, as well as the norms of land and civil legislation.
The Land Code of the Russian Federation contains instructions that you can buy and sell such plots that have been assigned a cadastral number. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that the purchase and sale agreement must necessarily indicate the location of the actual location of the plot, its price, as well as restrictions or encumbrances, if any (
Blitz answers to frequently asked questions
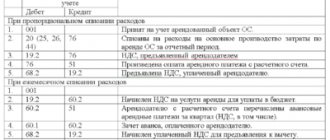
Question No. 1. The organization is building a shopping center on a leased site. To what account are rental payments included?
Payment of rent is accounted for in account 08. These transfers before the start and during the construction process are included in the initial cost of the building under construction.
Question No. 2. How can a business increase the initial cost of land in accounting?
The value of a plot increases when the land is radically improved or when it is revalued.
Question No. 3. How to take into account the payment for notary services when registering a plot? The money was given to the employee on account.
Debit 08-1 Credit 71 - payment for notary services is included in the price of the purchased land.
Question No. 4. The previous accountant of the organization did not register the site. How to do this late?
The land should be reflected at the cost specified in the transfer and acceptance certificate or in the contract. Make a note:
Debit 01 Credit 84 - land is placed on the balance sheet of the enterprise.
So, land accounting has a number of features. It depends on the nature of the acquisition of land, the scope of the enterprise, and the organization of accounting.
Features of land registration
There are several criteria that a piece of land must meet to be recognized as a fixed asset:
- The organization buys land in order to use it in its main activity, or for the purpose of subsequent rental.
- The land use period is more than a year.
- The plot of land is not planned for resale in the future.
- A company that plans to purchase a new site plans to make a profit from its use.
Thus, the site is included in the organization’s fixed assets. If a land plot is necessary for further sale, then its value is not included in non-current assets, but is reflected in the goods account. The value of an object consists of the costs that the company incurred to purchase it. It includes the following amount:
- the cost of the plot under the purchase and sale agreement;
- amounts that were paid to intermediaries (for example, a real estate agency);
- state duty paid upon land registration;
- interest on loans if the purchase of land was made with the use of loan funds (in this case, the cost of the plot, interest on the loan increases only until it is classified as fixed assets);
- other amounts that were paid when purchasing the plot.
A land plot is not subject to depreciation either in accounting or tax accounting, since it does not lose its useful properties . Therefore, the cost of purchasing land will not be included in the cost of production. Only if it is sold will the costs associated with its purchase reduce the profit received.
Important! When exploiting a land plot, it should be remembered that its use must be in accordance with the State Real Estate Cadastre. Thus, it will not be possible to independently decide to build buildings on the site. For example, when production premises are needed, the organization must buy an industrial site.
Accounting for land in construction
A construction company can buy a plot of land or lease it. The most attractive option is to register a lease with subsequent purchase. There are a number of reasons for this:
- There is no need to conduct auctions (Article 30 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Advantage when purchasing state and municipal lands;
- Reducing financial costs and saving time on selling land if a construction permit is refused.
The sale of land is reflected in accounting as follows:
Dt 91-2 Kt 01 - site retired;
Dt 62 Kt 91-1 - revenue is taken into account as other income.
When building a house with the investor's funds, he fully or partially compensates the developer for the cost of the land. The developer shows the cost of the site on the account. 08, and upon completion of construction transfers it to the investor. The following is recorded in accounting:
Dt 76 subaccount “Settlements with investors” Kt 08 - the site is handed over to the investor upon completion of construction work.
In some cases (Article 49 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation), plots may be seized from the owner for the needs of the state or municipalities . The terms are described in the agreement. The compensation amount includes the market value of the land, buildings on it and compensation for losses from the procedure (lost profits).
The land is written off from the register on the day the rights to it are terminated. The cost of the site on the balance sheet is included in other expenses, and compensation is included in income.
When writing off a plot before the transfer of ownership of it is registered, an account is used to record the disposal. 45 subaccount “Transferred real estate”.
Documentation procedure
The legislation does not provide for any special documents intended for recording land plots. The main document is the contract. In this case, you will need to prepare it in 3 copies, one of which is transferred to Rosreestr.
The transfer of land can also be carried out under an agreement, but in this case it must indicate that it is also an act of acceptance and transfer. You can choose the form for reflecting transactions with fixed assets in the company yourself, but such unified documents as OS-1, OS-6 and OS-6b can also be used.
Sometimes a company does not purchase a plot, but receives it as a contribution from the founder as a gift or in exchange for other property. In this case, an objective assessment of the land plot will be required, as well as its acceptance for registration at cadastral value . If a company leases a site, a lease agreement must be drawn up. For a long lease period, such an agreement must be registered with Rosreestr.
Land accounting in a budgetary institution
Before registration, the land is taken into account on the balance sheet of the account. 01 “Property in use.”
Regardless of the source of acquisition, plots should be taken into account as settlements with the founders: account. 210.06.
The nuances of transactions with plots in the budget are regulated by Art. 36, 37, 38 Land Code of the Russian Federation. This includes:
- The sale of land owned by the state or municipality to the owners of structures and buildings erected on the land is carried out at prices approved by the relevant authorities;
- The price of land cannot exceed its value according to the cadastre;
- Lands that have been registered with the cadastral service can be bought and sold;
- The purchase of state land or lease rights is carried out through auctions (tenders).
Example. Reflection of land purchase
Land plot: accounting and tax accounting
To account for a land plot in accounting, an 08 account is provided, to which a corresponding sub-account is opened . It opens for each new object. It reflects the costs that increase the cost of the object. The postings will be as follows:
| Business transactions | D | TO |
| Purchased land | 08.1 | 60 |
| Intermediary services, as well as state duty, are reflected | 08.1 | 76 |
| The land plot is reflected in accounting as fixed assets | 01 | 08.1 |
| If the land plot is purchased for the purpose of resale | 41 | 60 |
| Reflection of proceeds from sales if the plot was purchased for the purpose of resale | 62 | 91(90) |
| Write-off of the cost of the site | 91(90) | 01(41) |
| Reflection of other expenses for the sale of the site | 91(90) | 76,60 |
Important! When financial statements are prepared, land plots are reflected as non-current assets (the first section of the balance sheet).
Accounting for agricultural land: standard entries
Accounting for agricultural land is carried out using the following correspondence accounts:
| Contents of operation | Account correspondence | |
| Debit | Credit | |
| Purchased a plot of land | 08 | 60 |
| State duty for registration and registration is taken into account | 08 | 76 |
| Services for surveying, assessment, etc. are taken into account. | 08 | 76 |
| The site was put into operation | 01-6 | 08 |
| The land was contributed as a contribution to the authorized capital | 08 | 75 |
| Leased land use objects | 001 | – |
| Land rent accrued | 20, 26 | 76 |
| The land was received free of charge | 08 | 98 |
| Payment for land acquisition reflected | 60, 76 | 51 |
| Land tax accrued | 20, 25, 26, 44 | 68 |
| Land tax paid | 68 | 51 |
If a plot of land goes to the authorized capital (CA) of an organization, the following entries are made:
Dt 75 Kt 80 - the founder’s debt on contribution to the management company is taken into account;
Dt 08 Kt 75 - the plot was received from the founder as a contribution to the management company;
Dt 01 Kt 08 - land is accounted for as an asset.
Receipt of land as a gift is reflected in the following records:
Dt 08 Kt 83 - land was received from the founder, the company has no income;
Dt 08 Kt 98 - land donated by third parties;
Dt 08 Kt 01 - the site was put into operation;
Dt 98 Kt 91 - income from land received free of charge is taken into account.
If an organization donates land to another company, the posting takes place:
Dt 91 Kt 01 - reflects the cost of the land donated.
Land revaluation
A land plot is a resource that does not change over time and does not lose its properties. Therefore, the period of effective use is not determined for it. Its cost cannot be recovered through depreciation. Until 2011, there was a ban on the revaluation of land plots recognized by the OS of the organization. But later this ban was lifted. Therefore, organizations have the right to decide to reassess it. This should be reflected in the company's accounting policies. When revaluing land plots, the organization must do this regularly. The company determines the procedure for such a procedure, as well as the rules for conducting it independently.
Cost adjustment occurs when using price indices determined by statistical bodies, or by directly bringing the cost into line with market values on a certain date. After the revaluation, a corresponding act is drawn up, which is signed by all members of the commission and the head of the company. Documents confirming the adequacy of the amount received at which the land will be reflected in accounting are attached to the act.
Important! When revaluing land, you should remember that it is only possible with accounting. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for this possibility.
Acquired and improved land (accounting policies)
Land improvement includes reclamation work, uprooting stumps, drainage, irrigation, soil clearing, etc.
Expenses for improving the enterprise’s own site are recorded in the “Capital investments in non-current assets” account. They are then applied to the increase in the value of the land on which the work was carried out.
When improving land, accounting can be done in two ways. The selected option is fixed in the accounting policy of the organization.
Method number 1 . The enterprise allocates improvement costs as a separate OS inventory item. At the end of the year, the posting is made:
Dt 01 Kt 08 - costs for land improvement are taken into account.
Method number 2 . The cost of radical improvements is added to the original price of the site.
Let's look at accounting for land improvements in the budget using an example.
Capital investments for land improvement are reflected in accounting accounts on the basis of acts of work performed.
Tax accounting under OSNO
When purchase and sale transactions are concluded, the VAT tax base does not arise. The seller does not need to allocate VAT, and the buyer does not need to reimburse it. If the company is located on OSNO, then in the case of calculating income tax, the costs of purchasing the site are not included in the tax base. This can only be done if the plot is sold. An exception is the purchase of land from state or municipal authorities. In this case, the company determines the useful life of the land independently and during this period of time evenly applies the purchase price to taxable expenses. It should be remembered that this period should not exceed 5 years. The company can also include a taxable portion of the costs of purchasing land (30% of the base for the previous year) and continue to do so until the costs are paid in full. In this case, a difference arises between accounting and tax accounting, and hence the emergence of permanent tax differences.
Despite the fact that the land is classified as fixed assets, it is not subject to property tax. According to the clarifications of the Russian Ministry of Finance, an independent tax is provided for land plots, therefore they should not be included in the tax base for property tax. Land tax is calculated in accordance with Ch. 31 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This is a local tax based on the cadastral value of the land. The tax rate is determined by the municipality, which may also provide benefits for it. Companies report land tax every quarter and make advance payments during the tax period.
USN and Unified Agricultural Tax
As for companies using the simplified tax system, the same rules are established for them as for companies using the main tax system. That is, they do not have the right to reduce their income by the amount of expenses associated with the purchase of a plot. However, in the case of resale of a plot, it is regarded as a product and costs can be taken into account when determining the simplified tax system. If a company pays the Unified Agricultural Tax, then it is provided with a special procedure for recognizing costs associated with the purchase of land. For example, a company can determine the period during which costs incurred will be written off. This period must be at least 7 years. However, there are certain requirements for the site. It must be paid for, used only for growing agricultural products, and also be in the process of state registration.