Which advances are subject to VAT?
As stated in Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1, the object of VAT taxation is transactions involving the sale of services, work or goods in Russia. Therefore, an organization that has received an advance payment in any amount to secure future obligations must calculate VAT on the amount received.
It must be remembered that not all advances without exception are subject to VAT.
1. Advances made for transactions for which VAT is not legally provided for are not subject to VAT:
- export operations, international transportation and other operations taxed at a zero rate (Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1, subsection 1);
- operations not subject to VAT (Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): insurance, banking, medical, educational services, etc.;
- for the sale of services, goods, and performance of work outside Russia (Articles 147 and 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
2. It is not obligatory to pay VAT on advances credited towards the subsequent supply of services, goods or production of work, for which the manufacturing production cycle lasts longer than six months (according to the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 28, 2006 No. 468) (Article 154, paragraph 1, paragraph 3; article 167, paragraph 13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Results
VAT is reflected in the balance sheet as follows:
- in the asset - in two lines (1220 and 1230),
- in the passive - in one line (1520).
The Russian Ministry of Finance advises including in lines 1230 and 1520 receivables and payables for advances minus VAT. Note that the taxpayer has the right to act differently and not deduct the amount of tax from the debt. However, in this case you need to be prepared to argue your position.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- PBU 4/99, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 6, 1999 N 43n
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How to account for VAT on advances received?
The seller, having received an advance payment (partially or for the entire amount of the contract), in accordance with Article 168, paragraph 3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, must draw up and issue an invoice to the customer within 5 calendar days after transfer of the advance payment. The letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation “On the application of tax deductions for advance payments” No. 03-07-15/39 explains that an invoice may not be sent if the supplier fulfilled its obligations before 5 days have passed since the advance payment was received .
The VAT rate on advances is calculated by dividing the tax rate by the tax base, which is increased by the same percentage of the tax rate. At a VAT rate of 10%, it is equal to 10/110; if a rate of 18% is used, it is 18/118 (Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 4).
The invoice is prepared in 2 copies: the 1st is sent to the buyer, the 2nd is entered by the supplier in his sales book.
VAT on advances received: postings
Example 1. Accounting for the advance received and VAT.
In May, Vesna LLC entered into an agreement with the purchasing company Leto LLC for the supply of sun loungers for a total amount of 94,400 rubles, including VAT.
Also in May, Vesna LLC receives an advance in the amount of 50% of the contract volume, or 47,200 rubles.
VAT, included in the amount of the advance payment that must be paid to the budget, is equal to: 47,200 rubles * 18% / 118% = 7,200 rubles.
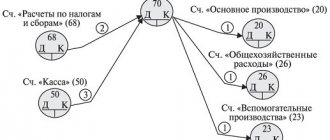
These transactions are recorded using the following transactions: During May:
- Dt 51 “Current account” - Kt 62, s/ac “Advances received”: 47,200 rubles. – the customer’s advance has been credited;
- Dt 76, s/ac “VAT on advances and prepayments” - Kt 68, s/ac “VAT calculations”: 7,200 rub. (RUB 47,200*18% / 118%) – VAT is determined on the cost of the advance received.
When transferring VAT to the budget:
- Dt 68, s/ac "Calculations for VAT" - Kt 51 "Current account": 7,200 rub. – payment of VAT to the budget.
When the goods are shipped, a shipment invoice should be issued, which is also noted in the sales ledger. After this, the invoice for the previously issued advance payment can be included in the purchase book.
The amount of VAT sent to the budget from the amount of the advance received can be included in the deduction amount after one of two events:
- goods, services or work for which the advance was received have been delivered (performed) in full;
- the contract under which the advance was transferred was terminated with the return of the advance to the buyer.
Registration of VAT deduction from the advance received after fulfillment of obligations
After fulfilling the accepted obligations and paying VAT on their amount, the supplier can accept for reimbursement the VAT paid earlier from the advance (Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 8).
Example 2. Registration of VAT deduction from the advance received after fulfillment of obligations
In July, Vesna shipped the sun loungers to the buyer. VAT must be charged on the proceeds received from the sale - 14,400 rubles. (RUB 94,400 * 18% / 118%).
Now there is a reason to accept for reimbursement the amount of VAT transferred to the budget from the advance received from the customer (RUB 7,200). In the declaration for the third quarter: “Spring” will show the remaining 7,200 rubles payable to the budget. (14,400 – 7,200). The indicated operations are recorded by postings: In the month of July:
- Dt 62 - Kt 90, s/ac "Revenue": 94,400 rub. – revenue from the sales of sun loungers;
- Dt 90, sub-account “VAT” - Kt 68, s/ac “Calculations for VAT”: 14,400 rubles. – accrual of VAT on total revenue from the sale of sun loungers;
- Dt 68, s/account “Calculations for VAT” - Kt 76, s/ac “VAT on advances and prepayments”: 200 rubles. – VAT, which was accrued on the advance payment earlier, is accepted for reimbursement;
- Dt 62, s/ac "Advances received" - Kt 62 s/ac "Settlements with buyers and customers": 47,200 rubles. – the advance received in May from the buyer is counted.
When transferring VAT to the budget: Dt 68, s/ac “Calculations for VAT” - Kt 51 “Current account”: 7,200 rubles. – transfer of VAT to the budget.
LLC "Vesna" must issue an invoice to the buyer - LLC "Leto" for 94,400 rubles. and be sure to note it in the sales book.
The accountant notes the invoice issued for the amount of the advance (RUB 47,200) in the purchase book.
Registration of VAT deduction from the amount of advance received after its return
If the seller received an advance, but the contract with the buyer was subsequently terminated, the amount of the advance should be returned.
Example 3. Registration of VAT deduction after termination of a contract with an advance payment previously received by the supplier
Let’s assume that in the situation discussed above, the contract for the supply of sun loungers by Vesna LLC with Leto LLC was terminated in July, but before that, Vesna LLC had already received an advance in May and transferred VAT on it. The VAT then paid to the budget is accepted for reimbursement.
This will require postings: In the month of May:
- Dt 51 - Kt 62 s/sch “Advances received”: 47,200 rubles. – advance payment is transferred from the buyer;
- Dt 76, s/account “VAT on advances and prepayments” - Kt 68, s/account “Calculations for VAT”: 7,200 (RUB 47,200 * 18% / 118%) – VAT is charged on the amount of the advance received;
- Dt 68, s/ac "Calculations for VAT" - Kt 51 "Current account": 7,200 rub. – transfer of VAT to the budget based on the results of the second quarter.
In the month of July:
- Dt 62 subaccount “Advances received” - Kt 51: 47,200 rubles. – on the basis of termination of the contract, the advance payment was returned;
- Dt 68, s/account “Calculations for VAT” - Kt 76, s/ac “VAT on advances and prepayments”: 7,200 rub. – VAT is accepted for reimbursement.
The amount of VAT, which is accrued and payable to the budget based on the results of the third quarter, will be reduced by the amount of VAT accepted for reimbursement on the basis of the return of an advance received earlier.
Write-off of accounts payable with expired statute of limitations
In order to write off identified accounts payable, it must be recognized as overdue.
According to the rules of Art. 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the general statute of limitations is 3 years. Important! This period of time will be recalculated each time when mutual claims are confirmed. The basis document can be a settlement reconciliation act signed by the parties.
If the 3-year period has passed, documentation for write-off is prepared:
- act of conducting a debt inventory;
- director's order on write-off;
- accounting certificate - justification for write-off.
Write-off of accounts payable with an expired statute of limitations is carried out in the reporting period that corresponds to the expired statute of limitations and is formalized on the last day of the period.
Find out what VAT tax consequences arise for the parties to a transaction when debt is forgiven in ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to the system for free and go to the Ready-made solution.
If the debt identified during the inventory should have been written off in an earlier period, then an updated declaration for that period must be submitted. Otherwise, when tax authorities identify amounts of overdue debt, negative consequences may arise, including the discretion of understating the tax base and imposing a fine in accordance with Art. 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
For the position of officials and judges, see our material “In what period are overdue accounts payable included in income?”
It is important to determine the procedure for writing off VAT on accounts payable.
There are 3 possible scenarios for the development of events:
- The buyer received the goods (work, services), but did not make payment. In this case, the buyer accepted the “input” VAT for deduction.
- The buyer received the goods (work, services), but did not make payment. The buyer did NOT accept the “input” VAT for deduction.
- The supplier received an advance payment against future supplies, on which he calculated VAT. However, the shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services) did not occur.
Let's look at each of these situations in more detail.
Have questions about writing off accounts payable? Visit our forum. For example, in this thread, experienced accountants give advice on how to write off an advance payment from a buyer whose statute of limitations has expired.
VAT on advances issued
For the customer-taxpayer who transferred the advance payment, the VAT amounts presented by the seller are subject to deduction (Article 171, paragraph 12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The buyer can refund VAT on advances issued without waiting for the goods to be dispatched. The basis for the deduction are the documents contained in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in Article 172, paragraph 9:
- invoices issued by the seller upon receiving the advance;
- documents confirming the fact of transfer of the advance;
- an agreement in which the transfer of an advance payment must be specified.
The buyer notes the invoice in the purchase book. The seller, after releasing the goods/products (fulfillment of obligations), issues an invoice in full for the entire amount of the contract to the customer. The customer takes this document into account in the purchase book. The invoice for the advance payment previously received must be simultaneously recorded in the sales book.
The buyer accepts the entire amount of tax for reimbursement, but the VAT that he accepted for deduction from the advance payment must be restored to him in the same quarter (Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 3, subclause 3).
VAT on advances issued - postings
Example 4. Registration of VAT from the buyer in the cost of the advance payment
In the same situation described in examples 1, 2, the buyer - Leto LLC - makes the following entries:
- Dt 60, s/ac “Advances issued” - Kt 51: 47,200 rub. – transfer of prepayment to the supplier;
- Dt 68, s/ac "Calculations for VAT" - Kt 76, s/ac "VAT on advances issued": 7,200 rubles. – VAT was accepted for reimbursement from the amount of the advance issued, based on the invoice of Vesna LLC.
After receiving the sun loungers:
- Dt 10 - Kt 60, s/c “Calculations based on received materials”: 80,000 rubles. – receipt and posting of materials (sun loungers) excluding VAT;
- Dt 19 s/ac "VAT on acquired values" - Kt 60 s/ac "Settlements on advances received": 14,400 rubles. – input VAT is taken into account in the price of the sun loungers received;
- Dt 60, s/ac "Calculations for materials received" - Kt 60, s/ac "Advances issued": 47,200 rubles. – repayment of a previously issued advance;
- Dt 76, s/ac “VAT on advances issued” - Kt 68, s/ac “Calculations for VAT”: 7,200 rub. – the amount of VAT previously accepted for deduction from the advance payment has been repaid;
- Dt 68, s/ac: “Calculations for VAT” - Kt 19: “VAT on purchased values”: 7,200 rubles. – VAT has been accepted on the invoice from Vesna LLC on received materials – for reimbursement.
The buyer can restore VAT even if the contract is terminated if the supplier returns the advance payment, in the amount of which VAT was previously accepted for deduction.
Write-off of overdue accounts payable from the buyer: “input” VAT was not accepted for deduction
In this situation, the buyer purchases goods (works, services), but does not make payment for them, and does not accept “input” VAT for deduction. After the expiration of the limitation period, the question arises: is it possible to write off accounts payable along with the VAT amount for tax accounting purposes?
The answer is yes. In this case, the entire amount of VAT can be taken into account in non-operating expenses. The basis for this is paragraphs. 14 clause 1 art. 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which directly states that expenses in the form of taxes on the supply of material and production assets must be written off in the reporting period as accounts payable with an expired statute of limitations - according to clause 18 of Art. 250 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.