The state's tax system is a necessary tool for performing its most important functions and tasks. The structural organization of the tax system is the main indicator of the economic and social development of the country.
The tax system of the Russian Federation began to operate in 1992 simultaneously with the adoption of the law “On the Fundamentals of the Tax System of the Russian Federation.” The terms income tax, excise tax, and value added tax (VAT) were introduced.
Over the course of 25 years, the Russian tax system has been repeatedly changed and subjected to reforms and innovations.
At the beginning of 1999, the first part of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation came into force. On January 1, 2001, the second part of the law came into force. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation has become the most important legislative and legal act of the Russian Federation, defining the relationship between the state and the taxpayer, the functions, structure and elements of the state taxation system.
The concept of the tax system of the Russian Federation
The tax system in the Russian Federation refers to fees, duties and other various payments that are collected in accordance with the established procedure from taxpayers. The procedure for collection and payment is determined by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Tax includes a huge number of fees, including excise taxes, VAT, and personal income tax. Thanks to the withdrawal of taxes, a budget is formed, and funds are available for the state to fulfill its direct responsibilities.
Functions of taxes
Continuing the conversation about the tax system, types and functions of taxes, it remains to talk about the last point. There are several functions:
- The fiscal function is the most important. It is thanks to it that the state budget is formed.
- Social - redistribution of income in favor of socially disadvantaged groups.
- Regulatory - solving certain problems at the state level with the help of tax policy. It has stimulating, destimulating and reproductive subfunctions.
- Control - state monitoring of the timeliness and completeness of financial traffic to the treasury.
Legislative regulation
Everything related to taxation and withdrawal of duties is regulated by the Tax Code. Articles of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation define regional, federal and local taxes, as well as special tax regimes in the country. The code also regulates inspections of individuals and legal entities for the payment of taxes. Checks are carried out by the Federal Tax Service.
The Federal Tax Service, based on the norms enshrined in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, ensures that taxes are accrued and paid correctly and on time, keeps records of taxpayers, and also monitors the implementation of current legislation.
Important! Taxes are established by the current code, as well as other acts, among which are Federal Laws and government regulations.
Compliance with tax legislation
The issue of monitoring the implementation of tax legislation is set out in detail in Order of the Prosecutor General's Office of the Russian Federation No. 193. In particular, this order established that the legality of tax transactions is entrusted to tax authorities and organizations vested with such rights, and existing violations of the implementation of tax law arise with the connivance of these organizations.
That is why the General Prosecutor's Office of the Russian Federation not only has the right, but also the obligation to carry out monitoring on an ongoing basis to control the implementation of tax law. In addition, it is the Prosecutor General’s Office that is obliged to ensure that both inspections and the process of collecting taxes from payers are non-corrupt.
Article 45 of the Tax Code provides for the payment of all taxes and fees by the payer independently on an ongoing basis without fail. If an organization acts as a payer, then the obligation to pay fees and taxes is transferred to an authorized person.
It is noteworthy that compliance with tax legislation provides for early payment of taxes and fees.
That is, a citizen can pay the fee before the deadline provided by law. However, depositing funds later than the deadline established in each specific case is also not prohibited. In this case, a fine (penalty) is imposed on the late payment payer, which is calculated depending on the type of taxation and the amount of debt.
In addition, a judicial procedure for collecting tax debts may be established in relation to organizations.
In cases where the amount of debt for tax payments exceeds 5 million rubles, as well as in cases where the arrears exceed a period of three calendar months. That is, if, based on the results of an audit by the tax authorities, it was established that the organization did not pay taxes for 3 months, then the collection case can be referred to the court for consideration. Moreover, if there are debts, the tax authority provides monthly notification to the payer in writing.
NS structure
Russia uses a three-tier system, which consists of different types of tax levies. This option has its advantages and disadvantages. Each level of the neural network partially consists of unique elements. The budget into which it will be subsequently credited depends on the level of the tax.
The structure includes tax fees, insurance premiums, taxable entities, government bodies that work in the field of finance and taxation, as well as the legal framework.
Results
The Russian tax system involves a complex interaction of all elements that form its structure. The elements of the tax system of the Russian Federation include: taxes and fees, their payers, the regulatory framework and government authorities in the tax field. The structure of the Russian Federation system in the field of taxation has 3 levels: federal, regional and local. At each of these levels, relevant legislative acts are adopted, which should not contradict the provisions of the Tax Code and the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Federal
Federal taxes include the following:
- VAT;
- excise taxes;
- state duty;
- corporate income tax;
- Personal income tax.
The funds received are sent to the federal budget, which is subsequently used for the provision and functioning of the state.
This type of tax is required to be paid everywhere in Russia. The amount of mandatory federal payments is the same for all regions. It is established by a single legal act or article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Regional
Regional fees are established in individual regions, territories and republics by local legislation. The regional type of tax burden includes:
- transport payments;
- collection on property of organizations;
- gambling taxes.
Control in this area is carried out by the Federal Tax Service of Russia in the constituent entities of the country. Subjects have the right to independently set the rate and terms of payment of regional tax payments. Local authorities determine regulations that detail the timing, rules and procedures for collecting payments.
Classification of taxes on video:
Local
Local types of taxation include land, property and trade taxes. Unlike regional ones, local taxes are collected at the municipal level. A special feature of local taxes is that they are directly credited to the municipality (federal and regional taxes are returned to individual municipalities only in the form of subsidies).
Important! Payment of land tax is required for individuals and legal entities within the time limits established by law. You should carefully study the nuances of paying taxes so as not to face penalties and sanctions in the future.
How the VAT rate has changed in 2021
The VAT rate in 2021 for main categories of goods has not changed. Changes in tax legislation occurred in 2019 and now VAT is 20% instead of the previous 18%.
Thus, there are 3 main VAT rates in the country:
- 0%: for goods intended for sale for export, international transport and operations for the transportation of refined petroleum products;
- 10%: for food products, goods for children, printed materials and periodicals in the field of culture and education, medicines and medical products;
- 20%: for all other product categories.
How the cadastral value for tax calculation has changed
In 2018-2019, tax authorities at all levels set a course to bring the cadastral value of land and real estate to their market value. The new law 269-FZ of July 31, 2020, which came into force on August 11, allows us to prevent excesses on the ground. It strengthens supervision over regional cadastral valuation authorities, not allowing cadastral values to be set above the market average.
Industry fees and charges
There are a number of taxes that are specific only to specific industries. Accordingly, only those legal entities and individuals who are engaged in work in a certain area must pay such fees. Industry payments include:
- fees for the use of wildlife;
- payments for the use of subsoil;
- payments for the use of aquatic biological resources.
These taxes are established and regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Rates for fees and charges are also set by separate articles of the code.
To find out exactly who should pay industry fees and how, you need to carefully study the regulations.
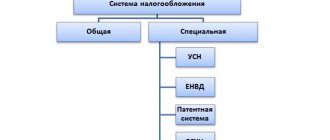
Types of taxation systems
There are several NS available for taxpayers and fee payers to choose from. A person who wants to start working as an entrepreneur or organization can choose one of the following taxation options:
- BASIC (general). A common option that is offered to most entrepreneurs. The regime acts as the main one and is chosen by businesses that do not claim a special preferential tax regime.
- USNO (simplified). Organizations and individual entrepreneurs that meet the requirements (income less than the established value and a number of other conditions) can apply for the simplified tax system. The advantage of the simplified version is a lower tax rate.
- PSN (patent). A special type of taxation that is used only by individual entrepreneurs. The advantage of this option is the low cost of the patent, the absence of the need to file a tax return, and the choice of the patent validity period.
- Unified agricultural system (rural). Entrepreneurs who are engaged in work in agriculture, if they meet the requirements, choose the Unified Agricultural Tax regime. The advantage is the low tax rate, which is only 6%. Thanks to the simplified regime, it is easier for entrepreneurs to develop their agricultural business.
Even before starting work, you should carefully study the available tax options, as well as their conditions.
Attention! The same tax system offers different conditions for individuals and legal entities. Special attention should be paid to these aspects.
PSN
This type of special taxation can only be applied by individual entrepreneurs. To use it, you must purchase a patent for the relevant type of activity. PSN can be combined with any other taxation system. Purchasing a patent replaces the need to pay VAT and personal income tax.
The cost of a patent will be calculated by the Federal Tax Service upon its issuance. But you can first make a calculation on the official service of the Federal Tax Service.
There are restrictions on the use of PSN:
- number of employees - no more than 15 people;
- annual income from activities on PSN - no more than 60 million rubles.
How to choose a tax system
If a person plans to start working as an individual entrepreneur or legal entity, he needs to decide in advance on the type of taxation. You need to choose the best option. Simplified and preferential types of taxation should be used whenever possible. To make the right choice, it is recommended to adhere to the following tips:
- carefully study the advantages and disadvantages of each option;
- pay attention to the tax rate;
- try to select a regime for a specific type of activity;
- use the help of specialists.
There are many organizations that provide tax advice. If you have difficulty making a choice, the consultant will select a suitable solution taking into account your personal needs and requirements.
How to make a choice, watch the video:
It is worth remembering that the tax service provides the opportunity to switch from one tax regime to another. If the work was initially started using the OSNO, then the transition to the simplified tax system can be made without any problems if it meets the requirements of the Federal Tax Service. To do this, a notification must be sent to the inspectorate.
Knowing how the tax system works in Russia, it is much faster and easier to select the appropriate type of taxation for yourself. By using modern tools, paying taxes becomes much easier.
Top
Write your question in the form below