Personal income tax, or personal income tax, is an abbreviated name for the tax withheld from the income of individuals when they are paid. Personal income tax accounting is carried out on account 68.01 in the context of analytics: tax, penalties, fines for violation of tax legislation on personal income tax (NDFL).
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the calculation and withholding of income tax must be carried out by the person who pays the income to the individual, the so-called source of payment.
From the point of view of tax legislation, the source of payment of income to individuals is the tax agent. His responsibility is to transfer personal income tax to the budget from the amount of remuneration paid no later than the day following the transfer of funds to the employee, with the exception of two cases:
- sick leave payment;
- vacation pay payments.
For these cases, the deadline for paying income tax is the last day of the month in which vacation pay or sick leave benefits were paid.
Salary in accounting: basic operations
Payroll accounting is carried out within the framework of the following main operations:
- payroll;
- personal income tax withholding and salary contributions;
- making other deductions (for example, alimony under writs of execution);
- salary payments (advance, main part);
- payment of taxes and wage contributions to the budget.
These business operations may be supplemented by others, which are determined by the peculiarities of the production process at the enterprise. For example, by depositing salaries.
Each of the noted transactions must be reflected in the accounting registers. They are carried out at different times, which can be determined based on the specifics of tax accounting at the enterprise and the requirements of labor legislation.
Let's study how the timing of the noted transactions for accounting is established, as well as what entries are used when calculating and paying wages.
Personal income tax is withheld from wages.
This scheme works if the tax agent is the source of income for the main taxpayer. In other words, the enterprise withholds personal income tax from the wages of its employees and transfers it to the budget.
- The transaction name column displays the receipt of a short-term loan. The amount in our case is 100,000 rubles. Debit – 50. Credit – 66
- The name of the operation is interest accrued. Amount – 5000. Debit – 91. Credit – 66
- Accrual of personal income tax on interest received on the loan. Amount – 650. Debit – 66. Credit – 68
- Return of funds received as a loan. Amount – 105000. Debit – 66. Credit – 50
- Transfer to the personal income tax budget from interest received on the loan. Amount – 650. Debit – 68. Credit – 51.
Labor compensation accrued: postings
Salaries must be paid at least every half month. For example, until the end of the current month for the first half and until the middle of the next month for the second half. Thus, the generally accepted approach is that the components of salary are:
- An advance paid before the end of the billing month.
Accounting records only reflect the fact of payment of the advance (later in the article we will look at the entries used for such purposes).
- The main part of the salary paid at the end of the payroll month.
If wages are accrued, the posting is as follows: Dt 20 Kt 70 - for the amount of wages for the entire month (regardless of the amount of the advance payment transferred).
In this case, the posting can also be generated by debit of accounts:
- 23 - if the salary is intended for employees of auxiliary production;
- 25 - if salaries are transferred to employees of industrial workshops;
- 26 - if the salary is accrued to management;
- 29 - when calculating wages to employees of service industries;
- 44 - if salaries are paid to employees of trade departments;
- 91 - if the employee is engaged in an activity that is not related to the main one;
- 96 - if the salary is calculated from reserves for future costs;
- 99 - if payments are calculated from net profit.
The salary accrual date is determined based on tax accounting standards, according to which salaries are recognized as income only at the end of the billing month (clause 2 of Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The procedure for calculating personal income tax on material benefits (example)
When receiving a low-interest or interest-free loan from an organization, the employee receives a material benefit in terms of savings on interest.
IMPORTANT! From 2021, new conditions for personal income tax assessment of this type of financial benefit have been introduced. Read more here.
It matters in what currency the loan agreement is drawn up.
If it is issued in rubles, then the threshold rate is 2/3 of the current refinancing rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of receipt of income (clause 2 of Article 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
IMPORTANT! From 2021, the refinancing rate is equal to the key rate (directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated December 11, 2015 No. 3894-U). See its sizes for different periods here.
If the loan is issued in foreign currency, then the established threshold value is 9% per annum (clause 2 of Article 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If interest is less than the threshold values or is not charged at all, personal income tax is withheld from the difference at a rate of 35%.
It is better to consider the postings for calculating personal income tax using a specific example.
The organization issued a loan to employee Ivanov I.I. (resident of the Russian Federation) for a period of 1 year in rubles at a rate of 3% per annum with interest paid at the end of the loan term. Loan size - 500,000 rubles.
Dt 73 “Ivanov I. I.” Kt 50 - 500,000 rub. — the loan amount was issued to Ivanov on January 15, 2021.
Income from the amount of the benefit from 2021, regardless of the date of payment of interest, is determined monthly on the last day of the month. Let's calculate the amount of interest on the loan for January 2021. There was no partial repayment of the loan in January. The number of days for which material benefits are calculated from 01/16/2021 to 01/31/2021 is 16.
500,000 × 0.03 × 16/365 = 657.53 rubles.
Dt 73 “Ivanov I. I.” Kt 91 - 657.53 rub. — interest accrued for using the loan for January 2021.
Let's calculate personal income tax on the amount of material benefit (at a Central Bank rate of 6.25%).
2/3 × 6.25% = 4.17% - threshold, taking into account the current refinancing rate.
4.17 – 3 = 1.17% - interest on material benefits.
500,000 × 0.0117 × 16 / 365 = 256.44 rubles. - material benefit for January 2021. Let's calculate personal income tax (35%) from it: 256.44 × 0.35 = 90 rubles.
If Ivanov were a non-resident of the Russian Federation, then the tax would be withheld at a rate of 30% (clause 3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Dt 70 (73) “Ivanov I. I.” Kt 68 “NDFL” - 166 rubles. — Personal income tax on material benefits for January 2021 is withheld from the employee’s salary (or other income).
Dt 68 “NDFL” Kt 51 - 166 rubles. — Personal income tax from savings on interest for January 2021 is transferred to the budget.
Is it necessary to charge personal income tax if a third party paid the tax for an individual, ConsultantPlus experts explained. Learn the material by getting trial access to the system for free.
Calculation of salary taxes and contributions: accounting features
Immediately after payroll is calculated:
1. Personal income tax
The fact of calculation and withholding of personal income tax is reflected in the accounting registers by posting Dt 70 Kt 68.
If a personal income tax deduction is applied to wages, then it does not need to be reflected in accounting.
2. Insurance premiums.
The fact of their accrual is reflected by posting Dt 20 Kt 69.
As in the case of salary postings, correspondence can also be generated by debits of such accounts as 23, 25, 26, 29, 44 and others that we discussed above.
The accrual of personal income tax and contributions is shown, like the accrual of wages, on the last day of the month.
Personal income tax and contributions are calculated on the total amount of salary without any adjustment for the advance payment.
From November 30, 2020, the cashier is not required to require a passport from the recipient of funds to identify him.
When the salary is issued, the postings will be as follows.
Results
Business entities paying income to individuals become tax agents for personal income tax and are required to withhold and transfer the calculated amount of tax to the budget. Personal income tax accounting is carried out using account 68, the personal income tax subaccount, in correspondence with the accounts corresponding to the transaction being carried out.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Directive of the Bank of Russia dated December 11, 2015 N 3894-U
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Salary issued (reflected on the employee’s personal account): postings
The fact of salary payment is reflected in accounting by posting Dt 70 Kt 51 (or 50).
A similar posting is used when paying an advance.
The date of formation of the above posting for salary or advance payment is determined based on the date of each payment.
In this case, the actual amount of the “basic” labor payment is calculated minus the advance and personal income tax. It turns out that the tax is “withdrawn” from the corresponding amount, although it is charged on the total salary (the summed amount of the “basic” payment and advance payment). This circumstance reflects the specifics of tax accounting.
In accounting, therefore, in any case, the following should be distinguished:
- advance amount;
- the amount of the “basic” payment.
Postings of payment of wages in terms of the advance and its second half are recorded in the accounting registers on the day the funds are issued to employees.
After all the transfers, the employees’ personal payroll accounts are filled out (on Form T-54). Information is entered into them monthly.
Postings to account 68 by accrual
★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased
If you have not found the answer to your question, then you can get an answer to your question by calling the numbers ⇓ Free legal advice Moscow, Moscow region call
One-click call
St. Petersburg, Leningrad region call: +7 (812) 317-60-16
One-click call
From other regions of the Russian Federation call
One-click call
Calculation examples
Calculation of personal income tax from wages
Petrov received a salary for November of 20,000. The employee has two children, and his salary since the beginning of the year has not exceeded 350,000. How to calculate personal income tax from wages?
A 13% rate applies to wages. For each child, Petrov is entitled to a standard deduction in the amount of 1400. Read about tax deductions and rates.
Tax = (20000 – 1400 – 1400) * 13% / 100% = 2236
Postings for accounting for personal income tax from salary:
- D44 K70 – wages accrued for November (20000)
- D70 K68.NDFL – payroll tax withheld (2236)
- D70 K50 – wages paid (20000 – 2236 = 17764)
- D68.NDFL K51 – tax transferred to the budget (2236)
Calculation of personal income tax on dividends
The founder Petrov received income in the form of dividends in the amount of 30,000. How to calculate personal income tax?
Dividend income is taxed at a rate of 9%, no deductions are applied to this rate.
Tax = 30000 * 9% / 100% = 2700.
Postings for accounting for personal income tax on dividends:
- D84 K75 – dividends accrued (30,000)
- D75 K68.NDFL – dividend tax withheld (2700)
- D75 K50 – dividends paid (27300)
- D68.NDFL K51 – tax transferred to the budget (2700)
Calculation of personal income tax on income received from a short-term loan:
The organization received a short-term loan from Petrov in the amount of 100,000. The income Petrov received in the form of interest on the loan amounted to 5,000. How to calculate personal income tax?
Tax = 5000 * 13% / 100% = 650.
Postings:
- D50 K66 – short-term loan received from Petrov (100,000)
- D91 K66 – interest accrued on the loan (5000)
- D66 K68.NDFL - tax withheld from interest received by Petrov on the loan (650)
- D66 K50 – borrowed funds are returned to the employee, taking into account accrued interest minus tax (100000+5000-650=104350)
- D68.NDFL K51 – transfer of tax to the budget.
A sample of filling out 2-NDFL in 2021 can be downloaded, where you will also find the current form.
Payment of taxes and contributions: postings
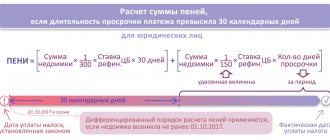
Personal income tax is withheld and transferred from the paid salary (“main” payment) no later than the day following the day the funds are issued.
Contributions are transferred by the 15th day of the month following the month for which the salary was accrued.
Information about this is reflected in the accounting registers when transactions are activated:
- Dt 68 Kt 51 - tax paid;
- Dt 69 Kt 51 - contributions transferred.
In order to reflect in accounting information about other types of labor payments - vacation pay, travel allowances - the same correspondence is used. But you need to keep in mind that in the entries used in payroll and those that characterize the issuance of, for example, vacation pay, the dates of deduction and calculation of personal income tax are determined differently.
The fact is that personal income tax on vacation pay is calculated not at the end of the month, but at the time the vacation is paid. Tax is withheld on the day the funds are issued to the employee. Personal income tax on vacation pay can be transferred on any day before the end of the billing month (clauses 4, 6, article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Accrual of personal income tax on dividends paid
Dividends are the income of the founders. If the founder is an individual, then his income is subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13%. Accounting for paid dividends for founders who are employees of the organization can be kept in both account 70 and account 75, but if the founder is not an employee of the organization, then only account 75 is used.
Dt 84 Kt 75 “F. Acting founder”—dividends accrued.
Dt 75 "F. Acting founder" Kt 68 "Personal income tax" - personal income tax is accrued (withheld) from dividends.
Dt 75 "F. Acting founder" Kt 51 - dividends were paid to the founder minus personal income tax.
Dt 68 “NDFL” Kt 51 - paid by personal income tax to the budget.
Find the KBK for paying personal income tax on dividends paid in this article.
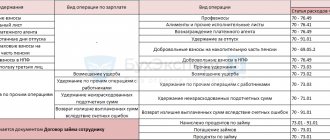
Salary deductions: postings
Common types of salary deductions include:
- Withholding of alimony (based on writs of execution, based on an agreement with the recipient, at the request of the employee).
In the accounting registers it is reflected by posting Dt 70 Kt 76. Subsequent payment of alimony to the recipient is reflected by posting Dt 76 Kt 51 (50).
- Withholding amounts to compensate the employer for damages.
Here, to reflect deductions in accounting, posting Dt 70 Kt 73.2 is used.
- Retention of unconfirmed expenses issued for reporting.
In such cases, posting Dt 70 Kt 94 is used. Previously unreturned accounts are written off using posting Dt 94 Kt 71.
Deductions are made only after personal income tax is withheld from the employee’s salary (clause 1 of article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1 of article 99 of the law “On Enforcement Proceedings” dated October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ).\