Accounting entries for VAT when importing goods
VAT transactions when importing goods can be presented as follows:
- posting of imported goods – Debit to account 41 “Goods”, Credit to account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”;
- customs VAT was calculated - D 19 “VAT on acquired values”, K 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”;
- the customs duty on imported goods is reflected - D 41 “Goods”, K 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”;
- customs duty is reflected - D 41 “Goods”, K 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”;
- the services of an intermediary/agent (customs representative) for customs clearance of goods are reflected - D 41 “Goods”, K 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”;
- value added tax on the services of an intermediary/agent is taken into account - D 19 “VAT on acquired values”, K 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”;
- accepted for deduction of VAT – D 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, K 19 “VAT on acquired values”;
- the debt for imported goods was paid - D 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, K 52 “Currency accounts”;
- the exchange rate difference in settlements with foreign suppliers is reflected - D 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, K 91 “Other income and expenses” under the subaccount “Other income”.
A person who is not a VAT payer (“simplified”), working without VAT, uses the same transactions upon receipt of imported goods. If an organization (entrepreneur) applies the “income-expenditure” simplified tax system or pays the unified tax system, VAT is taken into account in expenses. Similarly - if goods are purchased by an enterprise on OSNO for activities not subject to indirect taxes. Enterprises and entrepreneurs on UTII and the “income” simplified tax system do not take VAT into account at all.
If the customs authority adjusts the customs value, then the following entries are used in accounting: to reflect the amounts of VAT subject to additional payment under the CTS - D 19, K 68, adjusted VAT - similarly, adjusted VAT previously accepted for deduction - D 68, K 19.
The specified entries are used when paying VAT when importing from any country into Russia, including China, Italy, Turkey, etc. More information about VAT accounting entries for imports can be found here.
How is the cost of imported goods determined?
As you know, goods are accepted for accounting at actual cost (clause 5 of PBU 5/01). It is important to note that when importing goods, as a rule, additional costs arise in the form of customs duties, fees, and other payments paid to intermediaries for customs clearance of goods. All these expenses are also included in the cost of imported goods (clause 6 of PBU 5/01).
No less important is the correct determination of the accounting value of goods under an agreement with a foreign supplier, i.e., the conversion into rubles of the cost of goods expressed in foreign currency. Let us remind you that the cost of goods is reflected in rubles at the exchange rate valid on the date of their acceptance for accounting (clause 6, clause 9 of PBU 3/2006). If goods are purchased against a previously transferred prepayment to the supplier, the cost of the goods is fixed at the rate in effect on the date of the prepayment, and in the part not covered by the prepayment - at the rate at which the goods are accepted for registration. Read a separate article about the peculiarities of forming a ruble valuation of acquired assets under contracts in foreign currency, including on account of a previously issued advance.
VAT on imports
It is levied by government agencies when exporting or importing products across state borders.
The main duties for foreign trade participants include:
Customs fees
Such payments are charged in the following cases:
- as a fee for processing the product at customs;
- for the presence of products in a customs warehouse;
- for customs escort, etc.
Customs duties are paid when exporting or importing goods.
Excise taxes
Such fees are charged when transporting products and consumer goods, the list of which is established by the Legislation of the Russian Federation.
Article 181 of the Tax Code contains all the necessary information about excisable products.
VAT
VAT - value added tax. This payment must be made before the products are released from customs. The following indicators are used to calculate VAT:
- customs value of transported products;
- excise tax;
- current rate;
- the amount of customs duty that is payable.
To calculate value added tax, you need to add up the cost of the product, excise tax and duty. The resulting number must be multiplied by the current bet.
What does not apply to customs duties?
Payments collected from participants in foreign economic activity:
- Special. Some goods imported into the country may negatively affect domestic production, reducing its profitability. This type of duty protects Russian manufacturers from bankruptcy.
- Anti-dumping. They prevent the sale of goods brought from abroad at dumping prices.
- Compensatory. They are levied only when subsidies were used in the production or transportation of products.
Collection of these types of duties is carried out in a special manner in accordance with the current Legislation.
Creating a counterparty Customs
When adding a new position Customs authority to the Counterparties directory, pay attention to filling out the counterparty card:
- Type of counterparty - Government body.
- Government agency - Other.
As a result of selecting such analytics, fields 104-110 will be available in the payment order for the payment of VAT, fees, and duties.
The short name of the customs office can be indicated, for example, as FCS.
Postings and operational accounts for customs duties for exports
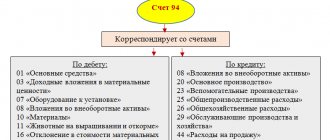
What are wiring? This is an accounting term that means recording various changes in the condition of a particular product in the documentation.
To what account should customs payments be attributed when exporting products? When exporting goods outside the territory of the state, the procedures are written off from account 90, subaccount 5 to account 76. The procedure is documented by posting D90/5 K76.
As a rule, when exporting products, the VAT rate is 0%. In other words, the foreign trade participant receives compensation from the state budget for repayment of this payment. But there are some exceptions for such cases:
- sales and delivery of products are carried out in the Republic of Belarus;
- export of petroleum products.
To receive reimbursement for VAT expenses, you must provide the government agency with the following basic documents:
- a contract concluded between a foreign trade participant and a foreign representative;
- a document from a banking organization confirming a financial transaction;
- cargo customs declaration.
The payer must comply with the deadlines for submitting documents. They are 180 days after drawing up the declaration.
After submitting the required package of documents to the customs authority, VAT refund is carried out within 3 calendar months.
Setting up settlement accounts with customs
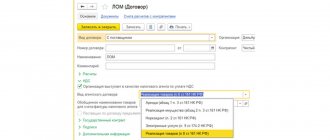
By default, invoice 76.09 is not inserted into the document Write-off from the current account and the customs declaration for import document when making settlements with customs. There are two options for filling out the Settlement account field.
Option #1
Account 76.09 can be filled out in documents manually by selecting from the Chart of Accounts.
This method is suitable if settlement transactions with customs are one-time or very rare.
Option No. 2
Account 76.09 is filled in automatically according to the data in the Account for settlements with counterparties register.
This is a universal option that is best suited for working in 1C for both rare and frequent transactions involving settlements with the customs authority.
The setup can be done by clicking on the Accounts with counterparties link directly:
- from the counterparty's card;
from the Treaty.
In the form that opens, you need to fill out settlement accounts, as shown in the figure below. Then click the Burn and close button.
To which accounts should payments for import transactions be attributed?
The declaration of goods transported to the territory of the state must be carried out within the strictly established time frames established by the Legislation of the Russian Federation. They are 15 days after the day of delivery of products and necessary means of transport.
The following types of payments are charged upon import:
- customs duty;
- excise taxes;
- fees required to cover customs clearance costs;
- value added tax (as opposed to export transactions).
The payer must pay all these payments on time. The deadline for paying customs duties is before drawing up the declaration or simultaneously with its submission. But standard deadlines must be observed - no later than 15 calendar days after the products arrive at the territory of the customs authority.
The import payment account may vary depending on the type of product transported:
- If materials are transported, then the entry for the advance payment for customs is D15 K76.
- If goods are transported, then the wiring is D41 K76.
All customs payments payable by foreign trade participants are expressed in the same currency as the customs value of the imported products.
In order for cargo transportation across the border to go smoothly, it is necessary to calculate customs duties and fees correctly. Foreign trade participants should learn how to calculate payments independently. Information about the types of payments in the customs declaration is in this article. These are mandatory payments for export/import operations.
VAT on import
When accounting for import transactions, special attention should be paid to such payment as value added tax. The main difference between import transactions and export transactions is the taxpayer’s obligation to pay VAT.
The formula for calculating this payment includes the following components:
- excise taxes;
- customs value of transported products;
- customs duty.
All these indicators are added together to obtain value added tax.
Posting for VAT calculation - D19/3 K68/1. In subsequent operations and procedures, the reverse of this wiring is used - D68/1 K 19/3.
In addition, watch the video tutorial “Capitalization of imported goods” in the 1C program:
So, the payment of customs duties is regulated by the Customs Code of the Customs Union. And VAT and excise taxes refer to tax payments. That is why they must be strictly separated in accounting. It allows you to monitor the implementation of payments and compliance with all repayment deadlines established by the Legislation of the Russian Federation.
You can find more information on the topic in the Customs payments section.
Free consultation by phone:
+7 (call is free)
Attention! Due to recent changes in legislation, the legal information in this article may be out of date!
Our specialist will advise you free of charge.
An organization that purchases goods (services) abroad of the Russian Federation must pay VAT when importing the purchased goods (services) at customs. Let's look at how to calculate, charge and receive a deduction for VAT paid at customs when importing, how to reflect import VAT in the purchase book and declaration, as well as transactions generated for VAT when importing goods and services.
Postings for VAT on imports
Standard accounting entries for accounting for VAT when importing goods:
| Debit Account | Credit Account | Wiring Description | Documentation |
| 60 | 52 (55) | Transfer of an advance to the supplier from a foreign currency account (from a letter of credit) | Bank statement (letter of credit 0401063) |
| 76 | 51 | Paid customs duties are reflected | Payment order, bank statement, customs declaration |
| 41 (10;07;08) | 60 (76) | Reflects the transfer of ownership of imported goods (materials, OS requiring installation, OS not requiring installation) according to the terms of the contract | Certificate of acceptance of goods TORG-1, Certificate of acceptance and transfer of goods and materials for storage MX-1, Certificate of acceptance (receipt) of equipment OS-14 |
| 19 | 68 | The amount of VAT paid at customs upon import of purchased imported goods is reflected. | Bank statement, customs declaration, accounting certificate |
| 41 (10;07;08) | 60 | The amount of expenses for the delivery of purchased imported goods on the territory of the Russian Federation is reflected. | Accounting information |
| 19 | 60 | VAT paid for the delivery of imported goods in the Russian Federation is reflected | Invoice received, Accounting certificate |
| 68 | 19 | VAT paid at customs is presented for deduction after the imported goods are accepted for accounting | Invoice received, Accounting certificate |
| 60 | 91.01 | The positive exchange rate difference when importing in foreign currency is reflected | Accounting information |
| 91.02 | 60 | Negative exchange rate difference when importing in foreign currency is reflected | |
| 60 | 52 (55) | Payment was transferred to the supplier from a foreign currency account (letter of credit) | Bank statement (letter of credit 0401063) |
Common Mistakes
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting of foreign trade activities and ruble transactions, taxes, automatic salary calculation and reporting in one service Get free access for 14 days
Control over foreign economic activity by the state is stronger than over internal activities. Therefore, avoid mistakes when maintaining accounting records of import transactions. Check the following points:
- currency conversion - often accountants use the exchange rate on an incorrect date;
- translations of documents - import documents must be in two languages: Russian and the partner’s language, sometimes the partner sends documents only in his own language, then you need to prepare a translation;
- correspondence of accounts - an error typical for internal and external activities; it is eradicated with increasing experience of the accountant.
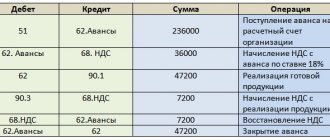
How to take into account VAT when importing in accounting using an example
Let's take a closer look at an example of how to reflect VAT on imports in accounting entries:
Let’s say that VESNA LLC, on December 12, 2016, purchased goods from a foreign company for a total amount of $5,000. According to the terms of the contract, ownership passes upon receipt of the goods, that is, on December 12, 2016. Customs duty - 15%. Customs duty - 7,500 rubles. Services for customs clearance amount to 70,800 rubles, incl. VAT 18% - 10,800 rub.
US dollar rates:
- as of December 12, 2016 equals 63.3028;
- as of December 19, 2016 equals 61.7515.
The accountant of Vesna LLC reflected VAT on imports with the following entries:
| Debit Account | Credit Account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 41 | 60 | 361 514,00 | Purchased imported goods were capitalized (5,000 * 63.3028) | Certificate of acceptance of goods TORG-1 |
| 41 | 76 | 7 500,00 | The amount of customs duty on imported goods is reflected | Accounting information |
| 41 | 76 | 47 439,00 | The amount of customs duty on imported goods is reflected ((5,000 * 61.7515+ 7,500)*15%) | Accounting information |
| 19 | 76 | 64 115,37 | The amount of calculated customs VAT is reflected ((308,757.50 + 47,439.00) *18%) | Invoice received, Accounting certificate |
| 41 | 60 | 60 000,00 | The cost of the service for customs clearance of purchased imported goods is reflected. | Accounting information |
| 19 | 60 | 10 800,00 | The amount of VAT on services is reflected (60,000.00 * 18%) | Invoice received |
| 60 | 52 | 308 757,50 | Payment for purchased imported goods has been transferred (5,000.00 * 61.7515) | Bank statement |
| 60 | 91 | 7 101,50 | The exchange rate difference is reflected (5,000.00 *(61.7515-63.1718)) | Accounting information |
| 68 | 19 | 74 915,37 | Paid VAT is accepted for deduction (64,115.37 + 10,800.00) | Invoice received, Accounting certificate |