To account for VAT calculations, use account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” and account 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets”. A special subaccount 68.VAT is created for account 68. The credit of this account records accrued VAT, and the debit reflects the tax paid and amounts reimbursed from the budget. Account 19 in accounting is used to reflect input tax received from suppliers, but not yet reimbursed from the budget. Sub-accounts are also opened for account 19 “Value added tax on acquired values” depending on the type of values received.
VAT mechanism
Tax is calculated on all transactions within the framework of core and non-operating activities (entry D/t 90 K/t 68), the accountant records the amount of tax payable to the budget, and the entry D/t 91 K/t 68 reflects the VAT that the company must pay when performing other income-generating transactions.
When purchasing goods, the purchasing company has the right to reimburse from the budget the amount of tax indicated in the invoice by making the following entries:
D/t 19 K/t 60 — VAT on the purchased goods;
D/t 68 K/t 19 - tax is presented for deduction after the values are accepted for accounting. This algorithm allows you to reduce the amount of accrued VAT due to the “input” tax.
Thus, the accrued VAT is accumulated in the credit account. 68, and the reimbursable one is in debit. The difference between debit and credit turnover, calculated at the end of the reporting quarter, is the result that the accountant focuses on when filling out a tax return. If prevails:
- credit turnover - it is necessary to transfer the difference to the budget;
- debit - the amount of the difference is subject to reimbursement from the budget.
Tax recovery
VAT recovery is regulated by subparagraphs 1-4, 6, paragraph 3 of Art. 170 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. There are cases in which an organization has the right to restore tax payable to the budget:
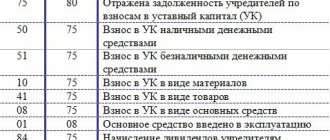
- the organization’s property is transferred as a contribution to the authorized capital of a business company, partnership, target capital of an NPO, or as an investment under a relevant agreement;
- purchased GWS are used for operations that are not subject to VAT (clause 2 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- goods and materials are shipped, property rights are transferred, or the contract is terminated, provided that the supplier has already received an advance payment from the buyer and has accepted the tax from the advance for deduction;
- reduction in the cost of supplied GWS due to a decrease in their price or quantity characteristics;
- subsidies from the federal budget to reimburse the costs of paying for industrial and technical equipment, including VAT.
Accounting for such transactions will be reflected in the following entries:
- Dt 19 Kt 68 - restoration of VAT on goods, works, services;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 19 - accounting for restored VAT as part of other expenses.
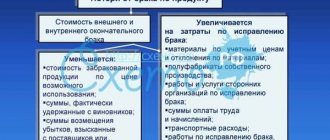
Accounting entries for VAT: valuables purchased
Tax on purchases is taken into account using the following entries:
| Operations | D/t | K/t | Base |
| Reflects the “input” VAT on purchased goods and materials, fixed assets, intangible assets, capital investments, services | 19 | 60 | Invoice |
| Write off VAT on production costs for acquired assets that will be used in non-taxable transactions. | 20, 23, 29 | 19 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| Write-off of VAT on other expenses if it is impossible to deduct the tax, for example, if the supplier fills out the invoice incorrectly, or if it is lost or not received. | 91 | 19 | |
| VAT previously claimed for reimbursement on inventory items and services used in non-taxable transactions has been restored | 20, 23, 29 | 68 | |
| VAT deductible on assets | 68 | 19 |
So, VAT can be reimbursed from the budget only when purchasing assets/services that will be used in transactions subject to VAT. Otherwise (when the property will be used in non-taxable transactions), the amount of tax on these assets is written off as production costs (by analogy with accounting for companies that do not pay VAT).
Attribution of VAT to other expenses, in common usage - write-off of VAT (entry D/t 91 K/t 19) is carried out both in cases of impossibility of obtaining an invoice, and in case of non-production expenses incurred on business trips (for example, for additional services specified in railway tickets), writing off accounts payable, gratuitous transfer of property, expiration of the three-year period allotted for tax refund, etc.
What to do to make a refund happen
However, it won't be easy to get him back. To do this, you need to go through several labor-intensive steps:
- provide a tax return with correct calculations;
- attach to it a purchase book and a sales book in which each invoice is recorded;
- submit an application for a refund to the Federal Tax Service in the prescribed form;
- provide primary documents reflected in the books for desk audit;
- be prepared for the fact that the fiscal authority will require additional documents from other persons.
Almost any materials can be requested, which is confirmed by the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated August 10, 2015 N SD-4-15/ [email protected]
For example, Phoenix LLC sold goods worth 14,123,546 rubles in the 1st quarter, including 18% VAT - 2,154,439.22 rubles. At the same time, the company purchased services in the amount of 16,854,798 rubles. Of these, 1,978,250 rubles were not taxed, since suppliers work under special regimes. Thus, taxable services and goods were received for 14,876,548 rubles, including VAT 18% - 2,269,303.93 rubles.
Accordingly, entries were made in the books of purchases and sales:
- Dt 68.02 Kt 19 - an entry was created in the purchase book in the amount of 2,269,303.93 rubles;
- Dt 90 Kt 68.02 - an entry was created in the sales book in the amount of 2,154,439.22 rubles.
The difference that should be reflected in the VAT return for the 1st quarter will be:
- 2,269,303.93 - 2,154,439.22 = 114,864.71 rubles.
- Dt 68.02 Kt 19 - 114,864.71 rubles were presented to the Federal Tax Service for reimbursement.
For a desk audit, the Federal Tax Service requested documents reflected in both books for the 1st quarter:
- contracts;
- invoices;
- payment orders for advances;
- certificates of work performed, services provided;
- invoices.
As a result of the check, several invoices with facsimile signatures in the amount of 24,000 rubles were discovered. Since this is a violation of the registration rules, but does not indicate fraud by the person being inspected, the Federal Tax Service decided to partially reimburse the tax with the deduction of incorrect documents:
- Dt 51 Kt 68.02 - 90,864.71 rubles were credited to the organization’s current account as a tax refund;
- Dt 19 Kt 68.02 - VAT restored for the amount of rejected invoices of 24,000 rubles;
- Dt 68.02 Kt 51 - arrears of VAT for the 1st quarter were paid to the budget in the amount of 24,000 rubles.
VAT on sales: postings
The sale of assets is accompanied by the accrual of VAT on the debit of account 90/3, on receipts from non-operating transactions - 91/2. Typical transactions for the sale of goods and other transactions with VAT will be as follows:
| Operations | D/t | K/t | Base |
| VAT charged: | |||
| — on sales (upon shipment) | 90/3 | 68 | invoice |
| — upon sale (upon payment) | 76 | 68 | |
| - for non-operating income (shipped or paid) | 91/2 | 68 | |
| — for construction and installation work carried out on a self-propelled basis | 08 | 68 | Accounting certificate |
| - for a gratuitously transferred asset | 91 | 68 | Invoice |
| - for the advance received from the buyer | 76 | 68 | Invoice for advance payment |
| VAT is credited from the advance payment (upon shipment) | 68 | 76 | Issued invoice |
| VAT paid | 68 | 51 | Bank statement |
When is tax allowed to be deducted?
The legislation establishes certain conditions under which VAT can be offset. Let's start with the fact that this is allowed only to organizations and entrepreneurs that are recognized as payers of this tax. All other entities do not deduct input tax even when they are forced to pay it. For example, when issuing an invoice with the tax amount specified as a separate line.
For those entities to whom deductions are allowed, the following conditions must be met:
- goods and services for which tax is deductible must be capitalized, that is, accepted for accounting;
- they are used to carry out activities that are subject to VAT;
- there is an invoice issued by the supplier when purchasing these goods (services), and the VAT amount is highlighted in it.
VAT on reduction of sales value: postings
Often, disputes arise between counterparties after the shipment of goods regarding the value of the assets being sold. Any party can be vulnerable in such a situation, but more often this applies to the supplier. If he agrees to the price change, a sales adjustment is made. Let's consider the option of reducing the price of a product due to additional delivery.
Example:
An agreement was concluded between the two companies for the supply of products in the amount of 100 units for the amount of 500,000 rubles. + VAT 90,000 rub. The price of one product is 5000 rubles. + VAT 900 rub., cost price 3000 rub. After shipment, the supplier additionally supplied 8 products under the additional agreement. The sales adjustment in supplier accounting will be as follows:
Operations D/t K/t Sum Sales proceeds 62 90/1 500 000 VAT on revenue 90/3 68 90 000 The cost of goods sold is written off (3000 x 100) 90/2 43 300 000 The cost of products shipped additionally has been written off (3000 x 44 43 24 000 VAT charged on additional supply (5000 x 8 / 118 x 18) 44 68 6102 Payment received 51 62 500 000 A permanent income tax liability has been created (6102 x 20%)
99 68 1220
Is it necessary to declare a deduction?
It should be taken into account that using a deduction is a taxpayer’s right, but not an obligation. If for some reason he finds it inappropriate to reduce the tax payable, he may not claim the deduction. For example, this is often practiced in order to avoid “negative” tax, that is, the amount to be returned from the budget. The fact is that this process is accompanied by a serious tax audit, and not every company or individual entrepreneur will voluntarily agree to this.
To prevent this, input tax can not be deducted in the current period. This operation can be postponed to any other period within the next three years. Another option is to declare only part of the input tax amount for deduction in the current period, and leave the rest for subsequent periods. This method is also permitted by law.
VAT accounting when returning goods
Failed acquisitions are also reflected in accounting, but they are recorded depending on the reasons for the return.
- If the goods turned out to be defective, and this was discovered after posting, VAT is reflected by postings like this:
| Operations | D/t | K/t |
| From the buyer | ||
| REVERSAL VAT on marriage | 19 | 60 |
| REVERSE previously accepted for deduction of VAT on the amount of marriage | 68 | 19 |
| From the seller | ||
| VAT REVERSE upon acceptance of defects (if shipments and acceptance occur in the same tax period) | 90 | 68 |
| VAT REVERSE upon receipt of a defect in the next period | 91 | 68 |
- if the product is of appropriate quality:
| Operations | D/t | K/t |
| From the buyer | ||
| VAT accrual on returned goods | 90 | 68 |
| From the seller | ||
| Input VAT on return of inventory items | 19 | 60 |
| VAT is deductible on returned goods | 68 | 19 |
If VAT is calculated by tax agents
Example 1. Lease of state property:
Debit 20 (23, 25, 26, 44) Credit 60 (76) - accrual of costs for renting state property.
Debit 60 (76) Credit 68 - VAT accrual from the tax agent.
Debit 19 Credit 60.76 - accrual of input VAT specified in the agreement.
Debit 68 Credit 51 - reflection of VAT transferred to the budget.
Debit 68 Credit 19 - VAT on rent to be refunded at the time of tax payment.
See the material “ Tax agent for VAT in transactions with state property ” for more details.
Example 2. Services provided by a foreign company on the territory of the Russian Federation:
Debit 44 (20, 25, 26) Credit 60 (76) - a reflection of services provided by a foreign company to a Russian organization in the Russian Federation.
Debit 19 Credit 60 (76) - accounting for VAT paid on the income of foreign legal entities.
Debit 60 (76) Credit 68 - VAT withholding from a foreign partner.
Debit 68 Credit 51 - VAT paid by the tax agent.
Debit 68 Credit 19 - VAT of the tax agent to be deducted after its payment.
See also the material “ How can a tax agent deduct VAT when purchasing goods (work, services) from a foreign seller .”
Brief overview of changes
Accounting for VAT in accounting has recently undergone a number of changes. At the beginning of last year, the limit on fixed assets was increased. Therefore, in 2021 the corresponding amount is 100,000 rubles. The increase in limits also affected fixed assets that were put into direct operation after January 1, 2021.
Among other things, those organizations that have allocated the amount of VAT in documents for buyers will not take into account the amount of the corresponding tax as part of their own income. Companies operating under the simplified tax system can now open their own representative offices and branches without the risk of deprivation of their legal rights to use the simplified taxation scheme.
Also, all enterprises are now required to submit reports every quarter using the new Form 6-NDFL. As for form 2-NDFL, it still remains in circulation - it must be submitted at the end of each financial year. It is worth noting that the personal income tax base may be reduced if the authorized capital of an organization is reduced during its liquidation.
Payment of contributions is made within the deadlines established by current legislation. It is worth noting that subsidiaries or branches must pay VAT separately.
Instructions for accruals for dummies
The accrual procedure should be understood even by a “dummie” who does not have even a superficial understanding of this operation, but wants to participate in stable business activities. Therefore, we need to briefly review the main points.
Instructions for selecting accounts:
- To generate information in financial terms about the status of settlements for mandatory payments to the budget of the Russian Federation, account 30300000 is used, which consists of making settlements for payments to budgets. Tax is calculated on the credit of the corresponding account, and tax is paid on the debit.
- In addition to this account, an account for the implementation of VAT tax deductions can be supported, which, in turn, is supplemented by details of other accounts.
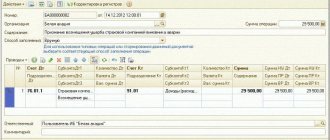
Calculation example
The calculation procedure can be understood based on the following example:
- A certain organization purchased goods from a supplier within 30 days and sold them to its own customers. Within this framework, we can assume a situation where an organization sold the entire batch in one month.
- When purchasing, the cost of the purchased goods in accounting is divided into two components: the cost without VAT and with VAT. After this distribution, the organization can exercise its legal right to reduce tax debt to the budget and submit VAT on products purchased from the loan.
- The company then purchases the product. In this case, to record sales, established account No. 90 is used, on the credit of which the revenue can be fully displayed, and on the debit the cost of the goods and accrued VAT.
Example of calculations in 1C