According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the category of expenses includes losses and expenses that occurred during the operation of the company and are accompanied by reasonable confirmation.
Question: How to reflect in accounting the distribution of overhead costs between individual types of products? The total amount of general production expenses (expenses for servicing the main production, producing two types of products) for the current month in accounting and tax accounting is 300,000 rubles. According to the accounting policy, overhead production costs in accounting, as well as in tax accounting (as direct expenses) are distributed between types of products in proportion to direct production costs, which form the cost of production according to accounting data. Direct costs for production in the current month were respectively: - for product “A” - 6,000,000 rubles; — for products “B” — 4,000,000 rubles. The organization prepares interim financial statements on the last day of each calendar month. Tax accounting uses the accrual method. Accounting for other costs associated with the production of products, as well as the acceptance of products for accounting, are not considered in this consultation and the corresponding accounting records are not provided. View answer
According to the provisions of PBU 10/99, as expenses of an enterprise, a decrease in the organization’s economic benefits due to the disposal of its assets and the creation of situations affecting the reduction of the company’s capital is taken into account, in addition to a decrease in the amount of deposits by order of the owners of the entity.
Important! In order to be recognized as expenses, expenses must meet certain conditions and purposes for the use of resources. The structure and composition of an enterprise's costs are primarily associated with the nature and conditions of operation, with the ratio of options for present costs (material, labor).
List of LLC expenses for OSNO
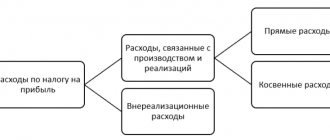
The list of income tax expenses under OSNO, which a limited liability company has the right to take into account when calculating the taxable base, is divided into 2 groups: related to production and sales, and non-sales.
Costs associated with production and sales are given in Art. 253 Tax Code of the Russian Federation . This list includes, in particular, the following types of costs:
- for the production, storage and delivery of products;
- for payment of wages and insurance premiums;
- for the operation and maintenance of fixed assets;
- for R&D;
- others directly related to production and sales.
The list of non-operating expenses that OSNO LLC takes into account when calculating the tax base is given in Art. 265 Tax Code of the Russian Federation . These include, for example:
- leasing payments;
- interest on obligations;
- costs of issuing own securities and servicing purchased ones;
- negative exchange rate differences;
- court fees;
- banking services.
What costs can be included in the costs of OSNO?
There are 3 main criteria that inspectors pay attention to ( clause 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ). Acceptable expenses must be:
- documented;
- economically justified;
- aimed at further profit generation.
Only if all three points are met, an OSNO LLC can take these expenses into account when calculating income tax. In this case, all expenses must be expressed in monetary form.
In addition to the general lists of expenses, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has a separate list of expenses that can be taken into account to reduce the tax base only within established limits . Limitable expenses include:
| Types of costs | Limit | Normative act |
| Certain types of advertising costs | 1% of revenue for the year | pp. 28 clause 1 and clause 4 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Entertainment expenses | 4% of labor costs for the reporting period | pp. 22 clause 1 and clause 2 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Losses | Within the limits of natural loss | pp. 2 clause 7 art. 254 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| VHI, pension insurance | 12% of labor costs | clause 16, part 2, art. 255 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Costs of organizing sanatorium-resort treatment | No more than 50 thousand rubles. for each employee for the tax period | clause 24.2 part 2 art. 255 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Compensation for the use of personal transport | Depending on engine size | Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 02/08/2002 No. 92 |
Limited costs
Save time and money
Accounting services at “My Business” from only 1,667 rubles per month
More details
Indirect or direct: how to determine
The Tax Code gives companies the right to independently decide how to classify expenses; clear rules are prescribed only for trade. For other areas of business, the legislation outlines general distribution criteria.
Art. 320 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
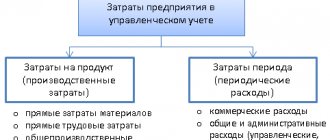
For example, direct costs could be:
- Material . Purchase of raw materials and semi-finished products, costs of packaging and production equipment.
- Salaries. Salary, vacation pay and bonuses of employees who worked on the product.
- Insurance and pension contributions.
- Depreciation . The wear and tear of equipment involved in the production of a product, expressed in money. This also applies to real estate, but only if it is directly related to the company’s work: for example, it is rented out.
- Other expenses. Any other resources that went into producing a specific product or service.
Part 1 art. 318 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Indirect costs include:
- Rental of premises and equipment, utility bills.
- Patent fee.
- Market research and advertising expenses.
- Payments for managers and workers who are not directly involved in production, such as a technical director or accountant. This also includes payment of sick leave for all employees.
- Expenses for the maintenance of equipment or premises that are not directly involved in production, but, for example, generate energy or are intended for the shipment of goods.
- Any other expenses that cannot be attributed to the creation of a specific product. For example, costs for fire safety, advanced training of employees.
- Entertainment expenses.
What costs cannot be taken into account?
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation regularly provides explanations on how to take into account certain types of costs. In particular, LLCs on OSNO cannot take into account the following for calculating income tax:
- The cost of an unfinished construction project in the event of its liquidation. These expenses cannot be taken into account, since such an object is not depreciable property ( letter dated November 23, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/772 ). However, some organizations think differently, and there are court decisions in favor of the taxpayer ( AS NWO of the Russian Federation dated January 22, 2019 No. F07-16106/2018 ).
- Costs paid for another organization ( letter dated 02/08/2019 No. 03-03-07/7618 ).
- Value added tax, which is assessed upon the gratuitous transfer of services or goods. When calculating the tax base, such property, as well as all costs incurred in this regard, are not taken into account ( letter dated November 12, 2018 No. 03-07-11/81021 );
- The organization's loss from debt forgiveness. The Ministry of Finance equates such losses to property transferred free of charge and applies the same approach to them ( letter dated May 22, 2018 No. 03-03-06/1/34203 ).
- Costs for product samples ( letter dated February 22, 2018 No. 03-03-06/1/11485 ).
- Gifts to the company's clients ( letter dated September 18, 2017 No. 03-03-06/1/59819 ).
It will not be possible to take into account in calculating the tax base under OSNO the expenses that are listed in Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation . It contains an extensive list, which includes, for example, dividends, advances and deposits, various excess payments to employees, etc.
Tax authorities will interpret the recognition of such expenses as a deliberate understatement of the taxable base.
Classification
Based on the economic content, the types of budget expenditures are capital and current.
Capital expenditures serve to enable innovation and investment. They include:
- costs of investments made in existing structures or newly created ones;
- funds provided as budget loans to legal entities;
- costs of repair work or expenses associated with modernization or improvement of equipment;
- expenses due to which the property ownership of the Russian Federation or its municipal institutions, as well as other entities, expands;
- other costs that are included in Russia's capital expenditures in accordance with the official economic classification and current legislation.
The development budget is formed as part of capital expenditures.
Current budget expenditures are necessary in order to ensure the current functioning of local governments, state authorities, and any budgetary organizations. They are also intended for government support for entire sectors of the economy. For this purpose, grants, subsidies, subventions, etc. are created. This category also includes some budget expenditures that are not included in the capital category.
Recognition of expenses for basic assets
LLC expenses can be taken into account under the general taxation system in two ways.
The first of these is the accrual method, which in practice is often called “shipment-based” accounting. ( Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ). This is the most common accounting option as it can be used by all organizations without restrictions.
With the accrual method, costs are taken into account in the period in which they are incurred, regardless of the transfer of money.
The second method is the cash method, or “on payment” accounting. On the contrary, it depends on the movement of money , because Expenses are recognized in the period in which actual payment is made.
However, the cash method is not available to all LLCs. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, only those companies that:
- over the past 4 quarters, they received revenue of no more than 1 million rubles. in each;
- do not belong to credit institutions;
- do not engage in hydrocarbon production;
- are not controlling persons of foreign companies.
The difference between the two cost recognition methods is easy to understand using the example of payroll accounting.
Example
The employee's salary accrued for October amounted to 50 thousand rubles. At the same time, an advance payment in the amount of 20 thousand rubles. paid in October, and the final payment (30 thousand rubles) - in November. When using the accrual method, all 50 thousand rubles. will be included in the company's expenses for October. And with the cash method in October, only 20 thousand rubles will be written off as expenses, and the remaining 30 thousand rubles. will be included in November costs.
Reserve Fund
The expenditure side of budgets at all levels of the budget system of the Russian Federation provides for reserve funds. The size of this fund does not exceed 3% of approved federal budget expenditures.
Money from the reserve fund is spent in unforeseen emergencies. These include: emergency restoration work after natural disasters, emergencies at enterprises that entail dire consequences. The procedure for spending this fund is regulated by regulations of the Russian Government.
When new types of expenses appear, they are financed at the beginning of the next financial year and only if they are included in the budget. When establishing sources of financing, the option of increasing the budget deficit is excluded.
Conclusion
Expenses taken into account when calculating the income tax base on the general taxation system must be confirmed, economically justified and aimed at generating income.
Most LLCs must use the accrual method of accounting for expenses, but some microbusinesses have the right to use the cash method.
To correctly calculate the tax base of an LLC on OSNO, you should carefully study the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and the clarifications of the Ministry of Finance to determine whether certain costs can be taken into account. Otherwise, the tax base will be underestimated, which will entail unnecessary attention from the tax inspectorate.
To correctly calculate taxes, fill out reports, and receive expert advice, register in the “My Business” service.
Budget expenses
Budget expenditures are part of the funds that are aimed at financially supporting functions, as well as some tasks that the state or local governments face.
Accounting for budget expenditures at all levels is based on a unified methodological basis, budgetary security standards, as well as monetary costs for the provision of public services, which are established exclusively by the government of the Russian Federation.
Organization expenses
The decrease in economic benefits due to the disposal of assets (in the form of money or other valuable property), as well as the occurrence of liabilities that lead to a decrease in capital, are called expenses of the organization.
Types of enterprise expenses are divided into assets and liabilities. Assets are capable of generating profit in the future, liabilities are not.
The organization's expenses are not:
- non-current and intangible assets;
- purchase of securities;
- financial investment in other organizations;
- repayment of loans;
- advance, deposit for work or services.
Results
The legislative acts of the Russian Federation do not contain a clear list of commercial costs. Based on the established practice of Russian accounting, commercial expenses should be attributed to account 44. Based on this principle, commercial expenses can be recognized as those costs that are listed in the instructions to the Chart of Accounts in the description of account 44.
For more information on how an organization can create its own working chart of accounts and which accounts to include in it, read this publication.
Sources: Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Forms of budget expenditures
The provision of budget funds has the following forms:
- allocations for the maintenance of municipal organizations and budgetary institutions;
- funds to pay for services and work performed by individuals and legal entities under municipal contracts;
- transfers for the population, social payments to citizens;
- appropriations for certain government powers that are transferred to subsequent levels of government;
- allocations to compensate for unplanned costs that arise as a result of government decisions;
- loans to foreign countries;
- funds to pay off state or other municipal debts;
- budget loans for legal entities, including tax credits, installment payments or other obligations;
- subventions, subsidies for legal entities and individuals;
- budget loans, grants, subventions, subsidies for budgets of other levels or state extra-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation.
Selling and administrative expenses are...
The company must disclose information about commercial and administrative expenses in the financial results report:
- line 2210 indicates commercial expenses;
- line 2220 - administrative expenses.
For more information about the procedure for filling out Form 2, read the article “Profit and Loss Statement - Form No. 2 (form and sample)” .
Neither the Tax Code of the Russian Federation nor other regulations contain a clear formulation of what exactly should be classified as commercial expenses and what should be classified as management expenses. In practice, selling and administrative expenses are the company’s expenses reflected in accounts 44 and 26, respectively.