Can an individual entrepreneur pay his own wages?
According to the law, entrepreneurs have the right to hire people and pay them wages.
There is also no direct prohibition on paying your own salary, but there is one very important point - payments can only be made in accordance with the employment contract. Article 56 of the Labor Code clearly states that it is impossible to conclude an employment agreement with oneself, since in this case there is no other party to the transaction. That is, an entrepreneur is both an employer and an employee. In addition, it is prohibited to accrue other expenses, the payment of which is provided for by labor law, namely: travel allowances, compensation, social benefits. However, this does not mean that an individual entrepreneur cannot independently manage the income from his business. All financial resources that remain with him after paying taxes and other payments belong to him, and he is free to dispose of them as he wants.
Is it possible to make an entry in your work book that a citizen is engaged in entrepreneurial activity? No, because an individual entrepreneur cannot hire himself, and, accordingly, he does not have the right to make a note in the employment record.
Authorized capital as the basis of financial security
An individual entrepreneur is liable for his obligations with all the property that belongs to him by law, excluding property that cannot be recovered by law. The current law does not oblige an individual entrepreneur to have an authorized capital, but creating an analogue of such capital on his own is desirable for any serious entrepreneur.
Financial reserve capital can be used only for specific needs, for example, to compensate for losses that may arise in the process of doing business or to purchase fixed assets. There is no such order by law, but every entrepreneur has the right to decide to establish his own reserve capital; in the future, such steps may allow him to work successfully even in difficult economic periods.
Thus, the finances of an individual entrepreneur are a system of interrelated indicators of profit, expenses and taxation. An individual entrepreneur, unlike an LLC, is not required to have an authorized capital. But creating a reserve of financial resources will allow it to “stay afloat” in any economic conditions.
How can an individual entrepreneur pay himself a salary?
An individual entrepreneur can receive earned funds legally in one of the following ways:
- Take cash from the cashier. The Central Bank allows working according to a simplified cash management scheme. This means that you don’t have to record incoming and outgoing orders, and you don’t have to fill out the cash book at all. Some entrepreneurs still keep cash records; this is not prohibited. When withdrawing money from the cash register, you must simply indicate in the “Base” column that the money was issued to the entrepreneur for personal needs.
- Withdraw money from your current account. Funds can be obtained by transferring the required amount to a bank card and withdrawing it from an ATM, or using a checkbook. In both cases, in the line “Base” you should write “Transfer of own funds for personal needs of the individual entrepreneur.”
Regardless of how the business owner collects his money, he needs to report on his actions to regulatory authorities.
Types of tax audits
Tax audits are divided into two types: office and on-site.
The difference lies in the way the test is carried out. A desk tax audit is carried out at the location of the tax authority, that is, tax officers do not go to the entrepreneur. This is a regular check that is carried out every time an entrepreneur has submitted tax returns. It can last up to 3 months after the end of the reporting period.
During the camera meeting, inspectors check the very fact of submission or failure to submit reports, the correctness of its completion, the accuracy of calculations and the reliability of the information presented. If you fill out the reports correctly and submit them on time, the tax authorities will not make any claims.
Keep records and prepare reports according to the simplified tax system for free
Therefore, you may never know about a desk tax audit—the tax authorities do not inform you about its start and completion.
However, if necessary, tax authorities may request clarification on tax calculation or additional documents confirming your expenses. Such information will need to be provided to inspectors within five days. This will happen if your mistakes led to underpayment of taxes. If you cannot clearly answer the tax authorities’ request for clarification or provide documents on expenses, then within 10 days after the end of the “camera chamber” the inspectors will issue a decision to hold you accountable. And subsequently they will send you a demand for payment of arrears, penalties and fines. Receive requirements from the Federal Tax Service and send requested documents via the Internet
An on-site tax audit is carried out on the territory (premises) of an entrepreneur based on the decision of the head or deputy head of the tax authority. An on-site inspection can only cover the last three years of the entrepreneur’s activity. Repeated audits for the same tax during the year are not allowed. The inspection should last no more than two months, with the exception of several cases:
- when an individual entrepreneur has a separate division;
- when during the inspection other violations are revealed that require additional verification;
- when the taxpayer delays the submission of documents necessary for conducting an on-site audit;
- in the event of force majeure circumstances.
During an on-site inspection, inspectors check the correctness of calculation and payment of one or more taxes. At the same time, the entrepreneur is obliged to provide access to accounting documents for these taxes. In addition, during an on-site audit, inspectors can assign various control activities, such as calling a witness, inspecting the premises, seizing documents and objects, examination, etc. Each of these events has its own characteristics (see “Waiting for an on-site inspection: what to prepare for and how to protect yourself”).
Determine the likelihood of an on-site tax audit and receive recommendations on the tax burden
Upon completion of the inspection, the inspector must draw up a special certificate indicating the subject of the inspection and its timing. Based on the certificate, the inspection will draw up an inspection report in two copies, which will indicate all the identified violations and proposals for their elimination. Then within two weeks you can appeal the results of the inspection.
How often can you borrow money and in what quantity?
There are no restrictions regarding taking funds for your own needs, that is, the business owner can do this at any time and at any frequency. Also, the legislative framework does not specify restrictions on the amount of funds withdrawn; you can take at least all the money that is currently in the cash register. From a legal point of view, for an individual entrepreneur there is no difference between personal money and company funds.
Novice businessmen, out of ignorance, can confuse income and profit, so they take and spend all the funds that come into the account. This is a serious mistake that can lead to business ruin in the future. It is recommended to take for personal use only those funds that remain after paying all taxes and fees. You should also invest some of your profits in business development.
Expense part of the business
Expenses of an individual entrepreneur are expenses that are actually paid, documented and directly related to the extraction of profit from business activities. Existing legislation obliges an entrepreneur to take into account his income and expenses to verify compliance with impeccable taxation. This is also convenient for an entrepreneur who needs this check to monitor the company's performance.
A year after opening a business, it will not be amiss to assess the financial situation of an individual entrepreneur. Such an assessment is an alternative to audit control of a legal entity. It is best to carry out such an analysis every year. Such frequency will allow you to identify business problems in advance and take the necessary actions to resolve them, and thanks to the analysis, it will help you determine the exact areas that require a quick response and clear control in the current situation.
Accounting and taxes
The individual entrepreneur must pay taxes on all income received. Their size depends on which taxation system the entrepreneur has chosen.
As already stated, a business owner does not have to keep books. But if he nevertheless decided to additionally control his income, then the accounting entries will look like this:
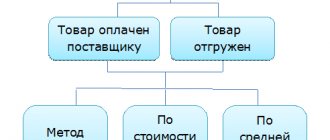
- debit 76, subaccount “Settlements with individual entrepreneurs”, credit 50 - funds from the cash register for personal purposes;
- debit 76, credit 51 - personal income was accrued to the entrepreneur from the current account;
- debit 91, credit 76 - amounts issued for the citizen’s purposes are included in other expenses.
You should also pay insurance premiums to the state in the amount established by law. In 2021, the amount of insurance payments is fixed at 40,874 rubles. Of these:
- 32,448 rubles for compulsory pension insurance (pension insurance);
- 8,426 rubles for compulsory medical insurance (medical insurance).
If the enterprise is large, with income exceeding 300 thousand rubles, then an additional tax of 1% is introduced. You do not need to pay any taxes when withdrawing funds from the cash register.
How to find out the taxation system of an LLC by TIN: 4 ways
- Look at the company's constituent documents - if it did not remain on the OSN during registration, but switched to another regime, then you will find copies of papers there indicating this fact.
- It is easy to determine the reporting regime for past periods.
Having correct information about the taxation system of your organization is a necessary condition for the work of every accountant. In addition, this information is extremely useful when concluding agreements with counterparties. In this article, we will tell you whether it is possible to find out the taxation system using the TIN (individual tax number - a special code for any taxpayer in Russia - both an individual and a legal entity, which is issued to him upon registration at the tax office) and how to do it. Let's start by defining such systems that exist today.
How to issue an income certificate for an individual entrepreneur
When applying for social benefits, a visa to travel abroad, taking out a loan and in other similar situations, you cannot do without a certificate of income. If an individual entrepreneur needs such a document, he can draw it up himself. The certificate can be drawn up in free form, but some information must be indicated:
- Full Name;
- taxpayer number (TIN);
- place of residence;
- the amount of income for the period of interest (for example, for the last 3 months and so on).
Is it possible to find out the taxation system by TIN?
Sometimes a company seeks to find out the taxation system in force not only of their business partners, but also of its own tax collection regime. This is especially true when a company moves from one system to another.
It is similar to the simplified version, but can only be applied to enterprises engaged in the production, processing and sale of agricultural products. In this case, the company must carry out all three processes independently (Chapter 26. 1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Is it possible for an individual entrepreneur to work for hire in another company?
There are no restrictions on this issue in the legislative framework, so a business owner can combine running it with work in another organization. There are some restrictions associated with employment in government positions.
For example, military personnel, employees of state corporations, employees of law enforcement agencies and other government agencies are prohibited from registering a business.
In addition, some institutions do not allow their employees working under a contract to engage in entrepreneurial activities in addition to their work. You need to carefully study your employment contract to know for sure about the possibility of such a combination.
Gross revenue
Gross revenue will show whether all expenses incurred in the past period were recouped. To do this, you need to subtract operating expenses and depreciation from the company's revenue.
Evgeniy counted the money taking into account his new knowledge and was delighted:
200,000 – (150,000 + 100,000: 36) = 47,200 rubles
Almost 50,000 rubles! You can buy another refrigerator and cook around the clock to flood the shelves of all stores with delicious dumplings. You just need to remember about your obligations and make sure that the business can handle the expansion.
How to pay wages to individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system (USN) 15%
Funds spent on the personal needs of an entrepreneur are not considered expenses under the “Income minus expenses” tax regime.
A business owner needs to take the following points into account:
- An entrepreneur cannot pay his own wages, since he does not have the right to draw up an employment contract with himself.
- Individual entrepreneurs can withdraw funds from their current account at any time, in any quantity. Money spent on a citizen’s personal needs is not reflected in tax reports.
- The money that an individual entrepreneur withdrew from his current account and spent on his needs is not subject to any additional taxes.
Other employees must be accounted for and all applicable fees and taxes must be paid.
The procedure for recognizing income under the simplified tax system
Under the simplified tax system, income is recognized (Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) at the moment:
- receiving payment from the buyer to a bank account or to the cash register;
See also “What date should the principal recognize income on the simplified tax system?” .
- receipt (free of charge or as payment) of property (or rights to it), work, services;
- receiving advances for the subsequent transfer of goods;
- payment by bill of exchange;
- payment by check;
- payments through electronic payment systems.
The day the money is received is the date for recording the income received. Moreover, it does not matter whether the goods have been shipped, the work has been completed or not. Receipt can be payment of both debt and advance payment.
Income is also recognized as the offset of debts of organizations among themselves for the amount of the repaid obligation (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated September 23, 2013 No. 03-11-06/2/39230).
When paying for goods with a bill of exchange, the date of receipt of income will depend on the method of its sale. When submitting a bill of exchange for payment to the bank, the receipt of money in the company's current account will be considered the day the income is received.
You can also pay with a bill of exchange with another supplier. In this case, a transfer signature (endorsement) is filled in on the bill, i.e. the right to the bill passes to another person. The date of transfer of the bill will be the day the income is received on it (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 20, 2016 No. 03-11-06/2/9917).
If an organization using the simplified tax system received a check from the buyer as payment, it can count the income on it if the following conditions are met:
- crediting money to the seller's account when submitting the check to the bank;
- receiving cash by check;
- transfer of a check to a third party.
The date of receipt of income on the check will be the day the money is received in the current account or cash register. When transferring a check under a deed to a third party, the day the income is credited will be the date of the executed transfer deed.
When making payments through electronic payment systems (Clause 10, Article 7 of the Law “On the National Payment System” dated June 27, 2011 No. 161-FZ), the date of payment is considered to be the simultaneous performance of the actions of the system operator:
- acceptance of electronic funds from the client;
- reduction of balances on his account;
- increasing them in the recipient's account by the same amount.
The supporting document in this case is an extract or message from the payment system operator.
Let's consider the payment method through ATMs. If the housing management company (HMC) collects fees for utilities using the simplified tax system, then payment for them can be made through ATMs. In this case, the UZhK enters into an agreement with the payment agent to accept payments and their subsequent crediting to the UZhK's current account for a fee. The date of receipt of income from the UZHK will be the day the money is received from an individual to the paying agent (clause 3 of Article 3 of the Law “On activities for accepting payments from individuals carried out by payment agents” dated 06/03/2009 No. 103-FZ). This date can be determined based on the payment register compiled by the payment agent.