A unit of equity participation in a company can be with or without par value. If the capital is expressed in shares with a par value (par value), then the corporation's charter establishes the par value (par value) that is indicated on the shares when they are printed. The face value can be equal to 10, 1, 5, 100 or any other amount determined by the founders of the corporation. The par value of an ordinary share is usually less than the par value of a preferred share.
In most countries, the par value (face value) of a share is the amount of each share that is reflected in the share capital accounts and constitutes the authorized capital of the corporation. A corporation cannot declare dividends that would cause its shareholders' equity to be less than its authorized capital stock. Therefore, par (face value) is the minimum part of capital that guarantees payment to creditors. Amounts received from issuing shares in excess of their par value are called share premium and form part of the company's share capital.
Shares without par value are shares of a company that do not have a par value (par value). There are several reasons for issuing such shares. The first is that investors sometimes confuse the market value of a stock with its par value, which is essentially an arbitrary value. Another reason is that most countries do not allow the initial issue of shares below their par value, which deprives the company of a certain amount of flexibility in raising capital.
Shares without par value may be issued with or without a stated value. In most countries, the law obliges the board of directors of a corporation to set a stated price for such shares when issuing shares without par value. The declared value can be any number set by the board of directors, although some countries impose a minimum declared value. The declared value may be assigned before or after the issue of shares, unless otherwise provided by law.
If a corporation issues shares of stock without par value without a stated value, the proceeds from the issue are recorded in the Stockholders' Equity account. This amount is included in the authorized capital of the corporation, unless the legislation of the country provides otherwise. Since additional shares can be issued at different values, the amount of credit to the Share Capital account will not always be constant. This is one of the differences in accounting for the issue of shares with a par value from shares without a par value with a declared value.
When shares without par value but with stated value are issued, the shares are recorded in the share capital account at stated value. Any amounts received in excess of the declared value are recorded in the share premium account. The excess over the stated value represents a portion of the company's share capital. As a rule, the declared value of the shares is considered in this case as the authorized capital of the corporation.
What is an additional issue of FPO shares (additional issue)
To understand what an additional share issue is, let’s remember the very concept of an issue. An issue is the release of securities. If a company issues bonds, this is one of the types of lending: the company borrows funds from buyers of securities, pledging to subsequently repurchase the bonds with interest. By placing shares, the company attracts sources of free financing - investor funds. However, it is not entirely free: investors need to pay dividends provided that the company makes a profit at the end of the year.
Primary issue (English IPO - Initial Public Offering - initial public offering) is the process of the initial placement of securities on the stock exchange. Shares can be sold either openly (to everyone) or closed (for a certain circle of people).
An additional issue (FPO – Follow-on Public Offering – next public offering) is the issue of securities in addition to those already available.
For example, the authorized capital of a joint stock company consists of 1000 shares with a par value of 100 rubles. each. Thus, the size of the authorized capital is 100,000 rubles. The Board of Directors decides to increase the authorized capital by 20% through an additional issue. After this, the number of securities will be 1,200, and the size of the authorized capital will be 120,000 rubles.
If a shareholder owns 10 securities, before the procedure his share was 1%. After the additional issue, its share will decrease to 0.833% (10/1200). Of course, this will negatively affect his income and will also likely reduce the market value of the security.
In order to protect the interests of investors, the process of carrying out an additional issue is controlled by the state represented by the Federal Securities Commission (Federal Securities Commission) through an audit, during which the economic justification for the additional issue must be confirmed.
The question immediately arises: is the additional issue of shares good or bad? The answer suggests itself: it’s good for the company, because The procedure will allow you to attract free sources of financing, but for the investor it will be rather bad. Is this so clear? We’ll look into it further.
Kinds
Emissions are classified into several types according to certain criteria:
| Criterion | View | Description |
| By timing of implementation | Primary | An issue occurs when a legal entity is created or securities of a certain type are issued for the first time. For example, a company has passed state registration and issues shares. The placement will be considered primary if the current JSC previously placed only ordinary shares, and has now issued preferred securities |
| Secondary | This is an issue that is carried out by an operating company for the second, third, and so on time. | |
| In order | Distribution | Securities are distributed between pre-designated persons, and there is no requirement to sign a purchase and sale agreement |
| Subscription | Papers are placed among pre-designated buyers or an unlimited number of persons. A purchase and sale agreement is signed with buyers | |
| Conversion | Securities of a certain type are placed with the condition of further replacement with others. Conversion conditions are pre-agreed by authorized employees |
Procedure for additional issue of shares
Additional issue of shares is a process that takes place in several stages. Let's look at each one separately.
Deciding on additional release
The decision is made in one of the following ways:
- board of directors;
- by holding a general meeting of participants.
The method of making a decision is fixed in the company's charter. Based on the voting results, a protocol is drawn up, which indicates the following parameters:
- number of securities;
- price;
- placement method;
- payment method.
If the decision on an additional issue is made by the board of directors, then the placement price is determined at market value. For these purposes, appraisal companies are involved.
Approval of the decision made
The decision is approved within six months after adoption. At the same time, an issue prospectus is created. This document contains the characteristics of the securities listed above. The preparation of an additional share issue prospectus is mandatory in the following cases:
- open placement;
- closed subscription with more than 500 participants;
- the amount of the additional issue exceeds 50,000 minimum wages.
The decision approved by the board of directors, as well as the issue prospectus, are sent for state registration.
Registration of the solution
The registration of the additional issue prospectus is carried out by the Central Bank within up to one month. It is possible to submit documents electronically and receive an electronic registration mark.
In preparation for registering an additional share issue, a package of documents is collected, including constituent documents, financial statements, certificates from the Federal Tax Service, etc. In order to save time, you can entrust the procedure to specialized organizations, whose employees will fill out all the necessary forms.
Placement of newly issued shares
The placement occurs in this way: existing investors have a pre-emptive right to purchase; in case of refusal, the securities are sold to everyone.
The placement price is determined according to the following criteria:
- not lower than the book value;
- no higher than the price on the secondary market.
These requirements are established to protect the rights of shareholders. To understand how this works, let's return to our example with conditions:
- total number of papers – 1000 pcs.;
- book value of one share – 100 rubles;
- According to the additional issue, 200 shares with a par value of 100 rubles were issued.
So, the par value of the share is 100 rubles. On the market, papers are sold for 600 rubles. The price of the additional issue should be in this range. Suppose the shares were placed at 550 rubles. for each. Then an investor who owns a block of 20% (200 shares), in order to keep his share unchanged as a percentage, must purchase 40 securities at 200 rubles each, which will cost 22,000 rubles:
1200*20%=240 pcs.
(240-200)*550=22000 rub.
If the securities were placed at a price below par, then the meaning of the additional issue would be lost: the authorized capital would then have no sources of financing. If the placement price is higher than the market price, it will be more profitable for existing shareholders to repurchase shares traded on the stock exchange than to purchase them through an additional issue. This will directly lead to speculation, and as a result, the gap between the offering price and the market value will increase.
Registration of a report on an additional release
After the securities are placed, the Central Bank registers the results of the additional issue. Next you should perform a series of procedures:
- Amendments to the charter.
- Announcement of the closure of the additional share issue.
- Reflection of results in accounting: entries for changes in the amount of authorized capital and the status of settlements with the founders.
Amendments to the charter of the issuing company and their registration
Changes to the charter are also registered in accordance with the established procedure. The issuer applies to the registration authority (FTS), which makes changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities (USRLE). After this, the issuer receives a new extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, which reflects the changes made to the charter: the size and structure of capital, the composition of the founders.
Increase the authorized capital
Placement decision
Before placing the next shares, you need to make sure that the constituent document contains a provision on declared ones. The latter, in their essence, are not some special type of securities. This is just an opportunity, fixed in the Charter, to place a certain number of additional shares. As well as specifying their number, the articles of incorporation may contain information about their type, value and the rights they provide.
If the constituent document does not mention such securities, then the legal entity does not have the right to issue new ones. Only shareholders at the meeting can add a phrase about declared shares to the Charter. In a similar way, the owners seem to control their Board of Directors. The latter distributes shares in a quantity not exceeding the number of declared shares specified in the Charter.
Therefore, before issuing further securities, the meeting must fix in the Charter the provision on declared shares. After state registration of these changes, you should proceed to the issue of placing securities. Such a decision can be made both by the Board of Directors (hereinafter referred to as the Board of Directors) and by the owners at a meeting. In both cases, it takes the form of a protocol. In this case, the Board of Directors (or the supervisory board) can simply initiate the issue of issuing additional shares and submit it for consideration by the owners (Minutes of the Board of Directors of PJSC Kubanenergo No. 247/2016 dated July 29, 2016), or independently make such a decision (Minutes of the Board of Directors of OJSC " FGC UES" No. 179 dated November 19, 2012).
How does the additional issue affect the price of shares?
Since the additional issue of shares leads to an increase in their quantity, the supply accordingly increases, causing the price to fall.
Thus, the additional issue of shares of the company leads to a decrease in quotes on the stock exchange. There are two reasons - an increase in supply and a decrease in the yield per security.
The additional issue has the most negative impact on small shareholders. In this regard, the process is controlled by the state.
Postings to account 83 accounting
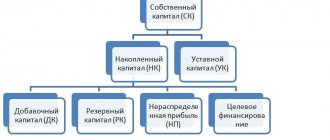
Account 83 is used in accounting practice quite often and includes many operations and activities. After all, the increase in the active part of the enterprise may be reflected within the structure of additional capital.
It acts as part of the organization’s total fund and is subject to reflection in passive account 83. It is an element of the total capital along with the reserve fund.
Legislative regulation
- The decision to conduct an additional share issue is made by the board of directors or the general meeting of shareholders.
- Existing shareholders have a preemptive right to purchase.
- The placement price should be above the face value and slightly below the market value.
- The issuer's obligation to pay dividends on preferred shares issued under an additional issue remains regardless of the financial results of the company.
These norms are contained in the Laws:
- 208-FZ of December 26, 1995 “On joint stock companies” (latest edition);
- 39-FZ of April 22, 1996 “On the securities market” (as amended).
Account composition
To form additional capital, the arbitrary desire of the enterprise management is not enough. The reason for creating this asset can be a limited number of cases.
Additional capital includes:
- the amount of increase in the value of assets as a result of revaluation;
- income from the issue of securities (shares);
- positive exchange rate differences on founders' contributions;
- additional contributions from the founders.
The increase in additional capital is a credit to the account. Decrease - debit.
The amount of additional capital may decrease in the following cases:
- transfer of part of the additional capital into account of the authorized capital;
- repayment of losses for the reporting year;
- its distribution among the founders (participants) of the organization.
All these cases can be described by the following diagram:
What does an additional issue of shares lead to?
Let us formulate the consequences of the additional share issue in the table. Positive changes are highlighted in green, negative changes in red:
| For the issuer | For large shareholders | For small shareholders (without voting rights) |
| Raising funds | Dilution of shares in the authorized capital | |
| Increase the authorized capital | Decline in earnings per share | |
| Fall in market value of securities | Opportunity to purchase securities at a price below the market | |
| Decrease in investment attractiveness | Have the opportunity to influence the process by setting the placement price | They have no ability to influence the price |
Organization
In most cases, when issuing shares, professional stock market participants, the so-called underwriters, are involved. For a certain fee, they undertake obligations to issue and place securities of the issuing company. The underwriter handles all stages of the issue: foundation, selection of indicators, collection of the necessary package of documents, registration with government agencies, placement between investors, etc.
There are three possible options for obligations when placing an issue, one of which is assumed by the underwriter:
- The full issue is purchased from the issuer and placed at market value. The risks of the possibility of under-placement of the issue in full lie with the underwriter or intermediary.
- The underwriter purchases only the under-allocated part of the issue (actual or fixed). In such a situation, the risks concern only this part.
- The underwriter performs all intermediary functions and undertakes obligations to provide assistance in placing the issue, however, he does not take responsibility for under-placement of the issue. Full risks fall on the issuer.
What does an additional share issue mean for a private investor?
We have already found out that an additional issue of shares is rather a plus for a large shareholder and a minus for a small one. What should a new investor do who has not previously owned shares of this company and is thinking about buying?
First of all, the obvious should be taken into account: if a company has decided to issue an additional issue, this most likely indicates financial difficulties. And the reason for increasing the authorized capital is not so important - business development or state requirements. If a company attracts funds from outside, it means that at the moment there is not much of its own money.
I would not recommend purchasing securities immediately after placement on the stock exchange. It is known that first you need to calculate earnings per share. To do this, net profit must be divided by the total number of securities. Thanks to this, you will have an approximate idea of how much you are entitled to.
But in order to find out the amount of net profit, you must wait until the financial statements are published. That is, until the beginning of the year following the one in which the additional issue was carried out.
Amendment of the Charter
The applicant makes appropriate amendments to the Charter of the legal entity only after completion of the distribution of new shares. This decision is made by the meeting (or the BoD, if, of course, it has such powers).
Having received the release report, the responsible person must fill out form P13001, prepare a sheet of changes, or even a new version of the Charter and have it certified by a notary. You should also pay a state fee in the amount of 800 rubles and receive a receipt.
Further, all the protocols, as well as a report on the results of the issue with the mark of the Central Bank, must be attached to the above-mentioned papers.
The applicant submits the completed package to the Federal Tax Service, which is responsible for registering legal entities and individual entrepreneurs in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, or to the nearest MFC. If the applicant has an electronic signature, he can send documents through the State Services website.
It must be said that some business entities believe that when submitting documents to the tax office, they may not attach an emission report. In their opinion, this is against the law. But in such situations, the Federal Tax Service always refuses to representatives of the joint-stock company and does not register changes. Then the company lawyers go to court and lose the case. Arbitration, as a rule, sides with the fiscal authorities and confirms that they are right (Decision of the Arbitration Court of the Sverdlovsk Region in case No. A60-6370/2016 dated May 13, 2016). Therefore, we recommend that readers still attach this report to their application to the Federal Tax Service.
Advantages and disadvantages of an additional share issue
An additional issue of shares is one of the financing methods that has both advantages and disadvantages. How can it be useful?
- Free money that can be used to purchase assets, pay off debts, buy shares in a business, and other purposes.
- An increase in the authorized capital, which may be dictated by both changes in legislation and other needs, for example, improving reporting indicators for investors.
- Influx of new shareholders. With the increase in the number of securities, new persons appear claiming a stake in the company. However, this can also have negative consequences.
Negative consequences include:
- Decrease in the price of shares on the stock exchange: an additional issue interrupts the period of holding shares, as they become cheaper.
- The decision to issue additional shares is often made by the majority of majority shareholders, who pursue their own personal interests, which do not always coincide with the interests of the business.
- The appearance of random persons in the management structure of a joint stock company.
- Costs of issuing and registering additional shares.
- The issuer's obligation to pay dividends on preferred shares continues regardless of whether the company operates at a profit.
An example of an additional share issue and its consequences
In 2010, PJSC Rosseti decided to raise capital through an additional issue of shares. Subsequently, several additional issues were carried out. Let us collect in a table data on how the market value of shares changed as a result of additional issues.
| Denomination, rub. | Total number of securities taking into account additional issues, pcs. | Placement price, rub. | Market value, rub. | |
| Before the additional issue (December 2008) | 1,00 | 41 041 753 984 | — | 1,55 |
| May 2010 | 1,00 | 42 964 067 081 | 4,14 | 4,14 |
| November 2011 | 1,00 | 47 871 694 416 | 3,08 | 2,91 |
| December 2012 | 1,00 | 57 247 302 465 | 2,16 | 1,98 |
| June 2013 | 1,00 | 161 078 853 310 | 2,79 | 1,07 |
| October 2015 | 1,00 | 195 995 579 707 | 1,00 | 0,45 |
As you can see, over 7 years the price of securities has decreased by more than 70%. At the same time, the state owns almost 90% of the shares (data for 2021). Thus, the shares of Rosseti PJSC are not of particular interest to private investors.
Are there subaccounts?
The following subaccounts are used for this account, detailing the main accounting transactions:
- 83-1 – fund of revaluations, in the process of which the entry Dt 01 (4, 7, 8, 10, 16, 41, 43, 45) Kt 83-1 is compiled.
- 83-2 – issue proceeds. Within the framework of this account, actions appear when the shares of a joint-stock company are sold at a cost that exceeds the nominal value.
- 83-3 – exchange rate differences that appear during the formation of the authorized capital.
- 83-4 – the entry reflects the fund for replenishing one’s own fixed assets, which are formed through deductions of 6% of gross income. In this case, the wiring Dt 90 Kt 83-4 is often recorded.
- 83-5 – accumulation fund. Its formation is carried out when the funds of the fund are used in the activities of the organization. The contents of the operation are as follows: Dt 84 Kt 83-5.
- 83-6 – fund of used target funds. In this case, there is correspondence Dt 86 Kt 83-6.
The account, as you can see, has a rich and varied structure, and therefore implies the possibility of compiling a large number of entries.