Faced daily with the challenges of the entrepreneurial sphere, learn how to properly plan your day, interact with clients, and also prepare reporting documents to the tax authorities. Let us remind you that even a small business will require transportation of cargo, goods, documents, carrying out the circulation of existing products. In view of this, you need to regularly think about organizing flights, transits, ordering transport, cargo or cars.
Transport costs
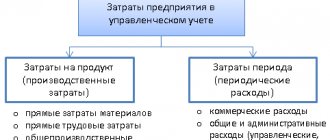
What are direct and indirect costs
Every company incurs costs in the course of its activities.
According to Art. 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, for tax purposes, the taxpayer must indicate in the accounting policy the algorithm for dividing expenses into direct and indirect. Direct costs are included directly in cost, but are recognized only as the product, good or service is sold. And indirect expenses can be taken into account immediately in full in the company’s expenses during the period of their implementation (clause 2 of Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
All companies must allocate expenses by type, but there are 2 exceptions:
- organizations that are allowed to use the cash method in accounting do not separate out direct and indirect expenses, since they recognize all expenses as they are paid (clause 1 of Article 318, Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- firms operating in the service sector have the right to take into account all costs during the period of their implementation (clause 2 of Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 15, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/348).
Read more about the difference between the cash method and the accrual method in the article “Accrual method and cash method: main differences” .
Art. 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains a list of direct expenses of the company:
- material costs;
- labor costs and accrued payments to extra-budgetary funds;
- fixed assets depreciation costs.
This list is not closed and is advisory in nature. This means that the taxpayer can consider the above direct costs as indirect or include in direct costs those that are not directly named in Art. 318 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However, tax authorities require proof of the validity of this approach (Articles 252, 319 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 24, 2011 No. KE-4-3 / [email protected] ). It is possible to take into account production costs as indirect only if the company proves in its accounting policy the impossibility of classifying them as direct, and also presents an algorithm for distributing such expenses taking into account economically justified indicators.
The calculation of income tax depends on the correct classification of costs as direct and indirect. If a company writes off a lot of indirect costs at once, and the tax authorities do not agree with it, additional taxes and a fine will most likely follow. An example where a company included depreciation as part of indirect expenses and defended its position in court is the resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga-Vyatka District dated 02/04/2014 No. A82-12003/2012. However, there is also the opposite example: the Arbitration Court of the Moscow District, in its resolution dated 06/05/2017 No. F05-7067/2017 in case No. A40-136716/2016, agreed with the tax authority, which considered it unlawful to include general construction costs associated with the maintenance of construction as indirect expenses. sites for the construction of low-rise individual housing and village infrastructure (by decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated September 27, 2017 No. 305-KG17-13063, the transfer of case No. A40-136716/2016 to the judicial panel for economic disputes of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation for review in cassation proceedings was refused) .
For more information on how to correctly determine both types of expenses, read the article “How to divide income tax expenses into direct and indirect?” .
If you have access to ConsultantPlus, check whether you correctly divide costs into direct and indirect in tax accounting. If you don't have access, get a free trial of online legal access.
We found out what direct and indirect costs are. Now let’s determine what transportation costs exist and in which cases they are direct costs of the company, and in which cases they are indirect.
What are the features: what costs are fixed and variable?
When a manufacturer has costs, they directly affect the entire cost of the production process, and therefore the cost of the final product (service). It is based on this that this classification is made.
Uninterruptible ones are those that practically do not depend on anything. They are not affected by how big the batch is this month and how big next month. The price tag for them is usually fixed. Payment is made monthly or quarterly, annually - depending on the specific type. And such expenses must be paid in any situation, even if the company has temporarily ceased its activities for some reason.
Fixed costs include:
- Any loans, borrowings and other financial obligations that need to be paid.
- Equipment depreciation. Some believe that the wear and tear of equipment directly depends on the amount of use. But there is such property that is depreciated regardless of actions. For example, a building gradually collapses, cars become obsolete and lose market value, etc.
- Costs for rented space.
- Payment of interest on the company's bonds.
- Most of the employees' salaries. There are people who work seasonally or on a percentage basis, and others who work on a salary basis. These are accounting, lawyers, advertising department and many other positions. Even if there are no orders, the workshops are idle, they need to be paid monthly.
Variable costs, in one way or another, directly depend on the amount of work done (number of goods produced, services provided), as well as on the amount of expenditure on resources. The assortment also influences them. Here's what they can be:
- Supply of raw materials.
- Wages of those employees who receive salaries and bonuses depending on production volumes.
- Transportation of goods means either the cost of fuel together with maintenance of the vehicle fleet, or hiring the services of a transport company.
- Receipts for electricity and other utility resources used in production (water for cooling parts, for example).
- Maintenance and repair of technical equipment, equipment, tools and other things necessary for work.
If you imagine the totality of these expenses as a graph, it will look like this:
That is, costs are expected to increase depending on production. Accordingly, incomes also grow.
An interesting feature is that both a firm's fixed and variable costs (this is from the examples above) are variable in the long term. That is, such a strict distinction can only be made for a few months, or at most years (short-term forecasts). And on a scale of one or more decades, all costs are variable.
Costs for delivery of purchased property
If a trading company purchases goods from another company and exports them on its own or pays for delivery to a transport company or counterparty, such costs will be direct (paragraph 3 of Article 320 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). They are not written off to the cost of goods in full, but are distributed between sold and unsold goods according to the following formulas:
TRNP = OSTtov × average percentage of TR,
Average percentage of TP = (TROst + TPtek) / (Stack + OSTtov) × 100%,
TR to be written off in the current period = TRost + TRtek – TRNP,
where: TR - transportation costs;
TRNP - transportation costs for unsold goods;
TRost - transportation costs for the balance of goods at the beginning of the month;
TRtek - transportation costs for the current month;
Stack - the cost of goods sold in the current month;
OST - the balance of unsold goods at the end of the month.
NOTE! Unlike manufacturing companies, trade organizations do not have the right to establish their own list of direct and indirect costs (paragraph 3, article 320 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When purchasing an OS, the company must include the costs of its delivery as part of the actual costs of acquiring the OS (clause 8 of PBU 6/01). For tax purposes, transportation costs will be taken into account in the same way as in accounting, that is, they will be included in the cost of fixed assets and then written off as expenses through depreciation.
Which document is the basis for capitalization of fixed assets and how to fill it out correctly, read the article “Unified form No. OS-1 - Certificate of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets” .
A manufacturing company includes costs for the delivery of raw materials in the cost of inventories and takes them into account as part of material costs (clause 2 of Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, in this case, TP will be a direct cost to the company. If the delivery cost is fixed as a separate amount, then, in addition to the documents for the raw materials themselves, the supplier provides the buyer with a TTN and an invoice for transport services.
Essence of the term
Any business involves the consumption of various types of resources - these are temporary (human), materials, raw materials, as well as electricity, water and other utilities. Separately, it is also worth noting the depreciation of machinery and production equipment. After going through the entire cycle and turnover, in a good situation, the business should pay off. That is, the revenue received by the company covers the costs incurred during production. This is what determines the two basic rules of a successful enterprise:
- Continuity of activity - one cycle is replaced by another. Either smoothly with gradual replacement of stages, or abruptly. For example, according to the principle: the batch is sold - the revenue is received - we proceed to a new order.
- Receiving income. It is not always possible for an entrepreneur to gain profit from the first turn; it is usually a protracted process. As a rule, monthly costs should be recouped immediately, and the initial one (purchase of equipment) should be recouped over time. But the result and natural goal is to receive revenue that will not only cover the costs, but will also be significantly higher than them.
Let's give a definition: fixed and variable costs of an enterprise are the cost, monetary equivalent for various types of resources in the course of activity.
Economics suggests that at the business level, costs depend on and are based on two parameters:
- Resources are finite and not limitless. Their supply may cease or for other reasons become impossible. This applies not only to material things, for example, raw materials that are out of stock, but also to intangible things – time, labor, technology.
- Alternative uses of the same resource. Assuming that one steel is suitable for making a car body, then most likely it is not used for smelting sewing needles. In other words, if raw materials are used in one direction, they will not be used in another. And purchasing an alternative is not always possible.
But manufacturers are trying their best to minimize costs, which means they are looking for other suppliers, creating a certain resource “safety cushion”, and also considering alternative markets and finding more inexpensive options.
Do you want to implement Warehouse 15? Get all the necessary information from a specialist.
Thank you!
Thank you, your application has been accepted!
Costs of delivering products or goods to the buyer
A trading company takes into account the costs of delivering goods to customers on the basis of paragraph. 3 tbsp. 320 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Such expenses are indirect. Other transportation costs should also be considered indirect (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 29, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/783).
When delivering products to customers, a manufacturing company takes into account the costs of this as material expenses (subclause 6, clause 1, article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Since they are not directly indicated in the list of direct expenses, the company can accept them as indirect (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 13, 2010 No. 03-03-05/251).
To account for TR when delivering property to the buyer, the company must issue a consignment note (TORG-12) and a consignment note (1-T) (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 27, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/105).
Read about the procedure for filling out TORG-12 in the article “Unified form of TORG-12 - form and sample” .
Calculation: what are fixed costs in the given example
In the economic literature, this indicator is written with the letters FC (we have already used this abbreviation above when drawing up the graph). Let's apply it now:
FC = 50*12 + 48 + 84 + 500 = 1,232 thousand per year.
Let us derive the average value depending on the number of units of production:
AFC = 1,232,000 / 5,000 = 246.4 rubles goes for 1 robe.
Now let’s calculate the variable costs (cost of materials, salaries of workshop workers, electricity):
VC = 200 + 360 + 18.5*12 = 782 thousand per year.
Average value (AVC) = 783,000 / 5,000 = 156.4 rubles per 1 USD
TC is the total cost, calculated by addition. As a result, we receive 20,140 thousand per year or 402 rubles 80 kopecks for one robe.
Conclusions based on calculations
If you invest this value in the cost price and add 20-30%, then the enterprise’s income can be called stable. Note that this example does not take into account defects (this is the minimum value) and transportation, that is, it is assumed that delivery and shipment are at the expense of the receiving party.
How to figure out why costs change over time
So far, in this case, fixed costs are higher than variable ones. This is explained by the fact that the business is new, while there is a loan, and also there is still a small turnover. With the release of an increased number of orders, the reverse process will occur - VC will become higher than FC.
To keep track of variables, you need:
- regularly make fresh calculations;
- look for alternative ways of development;
- adjust economic regulation measures.
Only a comprehensive analysis will help determine the real reasons for the decline or increase in costs.
Transport maintenance costs
In the costs of maintaining vehicles, the company includes expenses for fuels and lubricants, repairs and purchase of components for cars, the cost of insurance company services, parking and traffic police fines.
Expenses on gasoline, diesel or other fuel for a car are considered other expenses associated with production and sales (subclause 11, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, the company can also take them into account as direct expenses, based on the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 10, 2011 No. 03-03-06/4/67. For example, if products are delivered to customers by car, spending on fuel and lubricants in this case can be taken into account in material costs. But if the vehicle is intended to transport top managers of the company, the cost of fuel and lubricants is other expenses and indirect expenses. These nuances should be fixed in the accounting policies.
A mandatory document, without which expenses for fuel and lubricants cannot be written off, is a waybill. For more information on how to fill it out, read the article “What is the procedure for filling out travel documents (sample, form)?” .
The purchase of spare parts and vehicle repairs should be classified as indirect expenses and completely written off in the reporting period in which these expenses were incurred (clause 1 of Article 260 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Repair costs are written off based on:
- certificate of completion of work, invoice and payment documents, if the repairs were carried out by a third-party company;
- estimates for repair work, an invoice for the release of spare parts from the warehouse, an act of acceptance of work performed, an act of writing off worn-out spare parts if the repair was carried out on your own.
NOTE! Spending on repairs must be economically justifiable. If, for example, an expensive sound system is installed instead of a broken car radio, the tax authorities will consider this an excess and will remove the costs, since the sound quality does not affect the ability of the car to make a profit.
Any vehicle must be insured and have an OSAGO policy issued for it (Article 4 of the Law “On Compulsory Insurance of Civil Liability of Vehicle Owners” dated April 25, 2002 No. 40-FZ). Expenses for compulsory motor liability insurance are indirect expenses and must be taken into account as part of the company’s other expenses in equal amounts during the term of the contract (clause 1 of article 263, clause 6 of article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition to compulsory motor liability insurance, a company can buy CASCO insurance. This is her right, not her responsibility. CASCO provides an extended insurance guarantee for the car, so it costs more. Expenses for the CASCO policy are considered other expenses of the company (clause 3 of Article 263 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
NOTE! “Simplers” can only take into account the costs of compulsory motor liability insurance, but not CASCO insurance (subclause 7, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
About accounting and tax accounting of transport costs under the simplified tax system, read the article “Transportation costs under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses.”
The cost of paid parking can be taken into account for tax purposes as indirect expenses (subclause 11, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The basis for writing off costs will be a parking receipt, cash receipt and sales receipt, as well as an act of provision of services if a long-term rental agreement for a parking space is concluded.
But if the car ends up in an impound lot or the driver violates traffic rules, then the payment of fines cannot be taken into account in expenses in any case, like any other administrative fines (Clause 2 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Kinds
When classifying all material losses at an enterprise, in economics it is customary to first of all subdivide them into:
- Economic. These are real payments, the actual loss of funds from circulation. You can look at receipts, invoices, calculate with maximum accuracy, and make a report.
- Alternative. Essentially, these are missed opportunities. That is, what could have been obtained if a different solution had been chosen. The calculation is made as an assessment of the potential funds that could be obtained if other resources and technologies were used.
Economic ones, in turn, are divided into:
- Internal. They are also called implicit. They are distinguished like this. A manufacturer, for example, has its own equipment, say a vehicle. He puts it into circulation and uses it with minimal maintenance and fuel costs. But implicit expenses can be considered the amount that would presumably be accrued if the transport were not her own, but hired.
- External. They are explicit, accounting ones. These are the material resources that we talked about above, which are spent on acquiring resources of one order or another.
External costs, in turn, are divided into two main categories. Sometimes the classification is presented like this:
Let us give brief definitions and give examples.
How to define the concept of fixed costs (what are these costs, what are they for)
In short, this is what is spent regardless of production volumes. They have to be paid, even if the workshop is idle, the workers are on strike, and the nearest power plant that supplies your office has cut off power for a day.
Graphically, this expense item will look like a straight line:
Many business consultants insist on turning fixed costs into variable ones. How to do this - instead of a full-time accountant, use the services of an outsourcing company, for example.
Example
Let's assume that a businessman took out a loan from a bank. He undertakes to pay N thousand rubles monthly. And even if product turnover has dropped significantly, the monthly payment remains the same. A way to make this expense item more “convenient” and dependent on production is to consider investment options instead of a loan. Then the investor will invest money in the development of the business and receive a percentage of the income. And if there is no profit, then you don’t need to pay anything.
Variable costs: what are they?
They have a direct dependence (they can either increase or decrease) on production volumes. That is, in order to increase the production of a product, it is necessary to use more raw materials.
It is interesting that at the beginning of a business there is usually a direct relationship - the number of products produced literally dictates the amount of costs. Then this proportion becomes softer (for the manufacturer) because he learns to save and use resources more profitably.
Example
It is interesting to consider this relationship in connection with the current trend towards the introduction of labeling for many product categories. Now it is already actively used to regulate the turnover of alcoholic beverages, tobacco, and medicines. The more cigarette packs a company produces, the more marking codes need to be ordered.
If we consider the issue of labeling goods from a cost point of view, then the constant costs will be those that will be spent at a time on the purchase of equipment (scanners, online cash registers) and software. How to save in this case - contact. We will help you choose an option to solve the problems of your individual enterprise.
Transport rental costs
A company may not have vehicles, but rent them from another company, individual, or pay compensation to employees for using their own cars for business purposes.
For tax purposes, the lessee's payment under a vehicle lease agreement is included in other expenses associated with production and sales (subclause 10, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the car was rented for the main activities of the company (trade or production), rental costs can be taken into account as direct expenses. If the car is used for other purposes (for example, to serve administrative personnel), it is better to take such expenses into account in indirect costs. The company must justify the chosen procedure in its accounting policies.
The lessee, in accordance with the lease agreement, bears the costs of car maintenance (fuels, insurance, repairs, etc.). Such expenses are taken into account in the same way as when a car is owned by a company.
The tenant will write off expenses on the basis of supporting documents: contracts, payment documents, vehicle acceptance certificates, waybills, etc.
If the car is rented with a crew, then the costs of its maintenance are borne by the lessor, and the company can write off the costs of driving the car as part of labor costs (clause 21 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) in accordance with the service acceptance certificate. Whether such costs are direct or indirect depends on the scope of use of the car.
If a company pays an employee compensation for using their own car at work, such expenses can be written off only within the limits established in subparagraph. 11 clause 1 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- for cars with engine capacity up to 2,000 cc. cm - 1,200 rub. per month;
- cars with an engine over 2,000 cc. cm - 1,500 rub. per month (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 02/08/2002 No. 92).
In excess of these amounts, according to officials, the company cannot take into account any expenses on transport owned by an employee (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 23, 2018 No. 03-03-06/1/18366, dated December 4, 2015 No. 03-03-06/ 70852, dated May 16, 2005 No. 03-03-01-02/140).
For arguments from the opposite point of view, see the material “Is it possible to take into account the costs of operating an employee’s vehicles if he is paid compensation for a car?”
Are there any restrictions on recognizing compensation expenses for an employee for using his own truck, see the material “[LIFEHACK] We compensate an employee for expenses for a personal vehicle.”
Compensation to an employee for the use of transport is an indirect expense of the company, since Art. 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation there are no compensations among the amounts that can be attributed to direct expenses.
An example of calculating fixed and variable costs in the table
A small and relatively new textile production received a government order - up to 5,000 units of goods (for example, medical gowns). Working primarily on this project, the company has the following costs:
| What are the funds used for? | What type of consumption is it? | Amount in rubles |
| Renting premises | Post-e | 50 thousand |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | Post-e | 48 thousand |
| Interest on the loan (not the payments themselves) | Post-e | 84 thousand annually |
| Payment of utilities | Per-e | 18.5 thousand |
| Raw materials for sewing - fabric and accessories | Per-e | 200 thousand |
| Seamstress salaries | Per-e | 360 thousand monthly |
| Salaries of administrators and other staff units | Post-e | 135 thousand |
| Purchase of sewing machines and other equipment | Post-e | 500 thousand |
Based on these data, we will conduct further calculations.
Who shares the costs?
The division of expenses is regulated by the Code of the Russian Federation, namely Article 318.
The procedure for distributing and sorting received and spent funds is a very important task, since the amount of tax money paid will depend on this, and if the law is neglected, criminal liability may arise for tax evasion or non-payment.
Not everyone divides income into categories . For organizations that keep track of earnings through a cash register, the need for accounting disappears.
This same category of taxpayers includes organizations that provide services to the population; all income is automatically considered indirect. All others must maintain separation in their accounting policies.
What is included in variable expenses
The most significant are:
- Cost of materials, raw materials.
- Communal payments.
- Transportation.
- Salaries of hired workers.
- Product labeling.
- Energy resources.
Do you want to implement “Store 15”? Get all the necessary information from a specialist.
Thank you!
Thank you, your application has been accepted.
Crisis measures
One of the common ways to minimize costs during a turning point (economic decline, falling purchasing power, emergence of competitors) is to reduce staff. But before resorting to this extreme method, it is worth checking other options. For example, you can change the supplier, find an investor, or transfer part of the staff to a salary based on a percentage of sales.
Analysis and planning
Regardless of the size of your business, it is necessary to plan - for a month, a year or a longer period. This is necessary to:
- rational use of resources;
- make a short-term profit forecast, and on the basis of this make decisions on modernization, expansion of production, etc.;
- find ways to save money to reduce costs and increase competitiveness.
What needs to be done for this? First of all, carry out an analysis - take inventory of all expense items, organize them, analyze the need and possibility of introducing changes.
Remember that the quality of the product (if you save on materials) or its popularity (reducing advertising, for example) may depend on which categories you adjust.