Almost all economic entities are required to maintain financial statements. Some are allowed to do this in a simplified form, while others are exempt from this obligation. However, the overwhelming number of business entities regularly prepare reports based on economic indicators from their activities.
One of the main components of accounting is the balance sheet. It is he who allows us to assess the property and economic condition of the company as of a specific date, which is usually called the reporting date. In our article we will take a closer look at one of the elements of the balance sheet and try to answer the question: “What is the balance sheet currency in the balance sheet.” An example will help us figure this out.
How is the balance currency calculated?
The balance sheet currency can be calculated by balance sheet asset and liability.
- formula for calculating the balance sheet currency for an asset (calculated from the balance sheet data):
VB (by asset) = (Intangible assets + OS + DV + FV + ONA + Prvn) + (Z + VAT + DZ + FVl + DS + Proa)
Where:
- Intangible assets - the amount of intangible assets (line 1110)
- OS - residual value of fixed assets (including deduction of depreciation) (line 1150);
- DV - the amount of profitable investments in intangible assets (line 1160);
- FV - financial investments (line 1170);
- ONA - the amount of deferred tax assets (line 1180);
- Prvn - other non-current assets (line 1190);
- Z - the amount of the enterprise's reserves (line 1210);
- VAT - value added tax (line 1220);
- DZ - the amount of debt of debtors (line 1230);
- FVl - financial investments in current assets (line 1240);
- DS - the amount of cash in the cash register and in the current accounts of the enterprise (line 1250);
- Proa - the value of other current assets (line 1260).
Balance sheet currency elements
Thus, you can calculate the balance sheet currency of an enterprise for an asset using lines from the balance sheet:
VB (asset) = line 1110 + line 1150 + line 1160 + line 1170 + line 1180 + line 1190 + line 1210 + line 1220 + line 1230 + line 1240 + line 1250 + line .1260.
If the balance sheet has already calculated the totals of non-current assets (line 1100) and current assets (line 1200), then you can apply a simplified formula for calculating the balance sheet currency for an asset:
VB (by asset) = line 1100 + line 1200
The result should be the same in all cases.
- formula for calculating the balance sheet currency for liabilities (calculated from the balance sheet data):
VB (by liability) = p. 1310 + p. 1320 + p. 1340 + p. 1350 + p. 1360 + p. 1370 + p. 1410 + p. 1420 + p. 1430 + p. 1450 + p. 1510 + page 1520 + page 1530 + page 1540 + page 1550.
If the balance sheet has already calculated the totals of capital and reserves (line 1300), long-term liabilities (line 1400) and short-term liabilities (line 1500), then you can apply a simplified formula for calculating the balance sheet currency for liabilities:
VB (by liability) = line 1300 + line 1400 + line 1500
Note!
Balance sheet currency (by asset) = Balance sheet currency (by liability)
The financial analysis
Financial analysis of an enterprise allows you to obtain a set of indicators that describe the financial condition of the organization. Based on the financial analysis, the manager draws conclusions about the efficiency of the enterprise, makes decisions on how to achieve the desired financial state and creates tasks for structural units and employees.
Our site contains more than 1000 articles on financial analysis and related issues. Using search, you can quickly get the necessary information from all sections of the site.
The section Financial ratios describes more than 100 financial ratios with calculation formulas based on financial statements. The section contains coefficients of profitability, liquidity, turnover, market and financial stability.
In the Library section, publications are grouped by topic:
- financial analysis and financial performance,
- anti-crisis management and diagnostics of the likelihood of bankruptcy,
- enterprise capital management,
- solvency and creditworthiness,
- management and calculation of company value.
You can download books on financial analysis from the library.
The financial dictionary contains more than 1,500 terms on finance and financial analysis.
We have developed a program for financial analysis - FinEkAnalysis, which speeds up and simplifies the process of analysis based on financial statements. The program analyzes financial results, analyzes financial stability and uses other methods of financial analysis. FinEkAnalysis calculates more than 200 financial indicators. To analyze IFRS, additional information from the balance sheet is used. The site contains examples of financial analysis that were created in the FinEkAnalysis program.
The program analyzes the arbitration manager based on financial statements for an arbitrary number of periods in accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 367 of June 25, 2003 “On approval of the Rules for conducting financial analysis by the arbitration manager.”
The FinEkAnalysis program performs a financial analysis of individuals during bankruptcy.
Based on many years of experience in creating the program, we have developed the Online Financial Analysis service, which performs financial analysis via the Internet without installing the program on your computer. Online financial analysis works on Windows, Linux, macOS (Mac OS), Android operating systems.
see also
Financial analysis software
Financial analysis Online
Where is the balance sheet currency shown on the balance sheet?
In the balance sheet, the balance sheet currency is reflected in two places
1.On line 1600 “Balance” in the active part
Balance sheet currency in the asset balance sheet
2. On line 1700 “Balance” in the passive part of the balance sheet
Balance sheet currency in the liabilities side of the balance sheet
[flat_ab id=”5"]
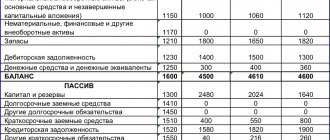
Thus, from the above example, you can see that the balance sheet currency at the end of the reporting period = 171,517 thousand rubles.
Transactions affecting the value of the balance sheet currency
The term BALANCE is of Latin origin. Literally: bis - twice, lanz - scales, i.e. double scales as a symbol of balance.
This is interesting: How to pay the state fee for a passport through Sberbank
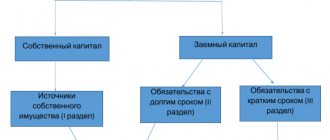
The balance sheet reflects the assets of the enterprise in two aspects: on the one hand, according to their composition and functional role, on the other hand, according to the sources of formation and intended purpose.
All property is grouped and summarized in the balance sheet in a single monetary measure. In order to show the state of assets, the balance sheet is compiled at a certain point, usually on the first day of the month (quarter). Since the balance sheet only shows the state of assets, the balance sheet does not characterize the movement and use of funds.
What does an increase in balance sheet currency mean?
An increase in the balance sheet currency can be either a positive or a negative factor. Let's take a closer look:
Changing the balance sheet currency using own and borrowed funds
As you can see in the balance sheet: line 1700 may increase due to changes in equity or borrowed funds.
- An increase in the balance sheet currency at the expense of own funds is a positive factor for the enterprise, because the enterprise will become more independent and independent.
- An increase in the balance sheet currency due to borrowed funds is a negative factor, because the enterprise will experience an increase in dependence on external creditors, as well as a decrease in the level of financial stability.
Quick step by step guide
So, let's look at the actions that need to be taken.
Step - 1 Enter data in section 1 of the Balance Sheet, which is dedicated to non-current assets. It contains information on balances of intangible assets (line 110), fixed assets (line 120), construction in progress (line 130), profitable investments in tangible assets (line 135), long-term financial assets (line 140), deferred financial assets (line 145) and other non-current assets (line 150). In this case, the calculation is carried out according to the debit and credit of the corresponding accounts at the beginning and end of the reporting period, taking into account depreciation charges. Summarize the total for section 1 and enter the resulting value in line 190. Next, move on to the next step of the recommendation.
How to fill out a company’s balance sheet - balance sheet, balance sheet sections, balance sheet lines, ...
What is the balance sheet currency ratio?
The balance sheet currency ratio shows by how many coefficient points (or percentages) the value of assets or liabilities has changed compared to the previous period.
Formula for calculating the balance sheet currency ratio:
Kvb = (VB1 - VB0) * 100 / VB0
- Kvb - balance sheet currency ratio;
- ВБ1 — balance sheet currency in the reporting period;
- ВБ0 is the balance sheet currency in the base period.
An example of calculating the balance sheet currency ratio (based on the balance sheet presented above):
Kvb = (7598732 - 7640906) * 100 / 7640906 = -0.55
Thus, the balance sheet currency ratio showed that in the reporting period the balance sheet currency decreased by 0.55% relative to the base one.
Asking questions and defining criteria
First, let's talk about what questions are posed to investors when reading a company's balance sheet:
- One of the first questions that should be answered is whether the company has fixed assets (and how related they are to its main type of activity), what happens to the company’s assets, what happens to working capital;
- If sharp changes are detected in any balance sheet items (compared to the dynamics of previous periods), then you should ask yourself a question about their reasons;
- How is the company’s current activities financed – through its own funds or through borrowed funds? Or through a combination of own and borrowed funds (in this case, what is the ratio of both).
- What is the ratio of the dynamics of expenses to the increase in the company's reserves?
- What is the situation with the company’s retained earnings (where is it going and is it there at all). If you expect to receive dividends, you should keep in mind that they are paid only if this parameter (retained earnings) is positive.
We can speak about the investment attractiveness of a company (at least from the point of view of its reliability) when its balance sheet satisfies the following basic criteria:
- For all main items, there is a clear positive trend, that is, the balance sheet currency by the end of the period should increase in comparison with its value at the beginning of the period. Moreover, the rate of its growth should be higher than the inflation rate, but not exceed the rate of revenue growth;
- The shares of receivables and payables should be approximately equal, the same applies to the dynamics of their growth (it should be approximately the same);
- The dynamics of growth of current assets should prevail over the growth of non-current assets of the company;
- The company’s balance sheet should not contain so-called uncovered losses;
- The balance sheet currency must consist of more than 50% of the company's equity.
Before we continue, let's get acquainted with some accounting terms that appear in the above criteria:
The balance sheet currency is the result that is obtained by summing up all balance sheet items (and this result must be the same for both assets and liabilities).
An uncovered loss is a loss that arose as a result of the company’s activities and was not covered by its own sources.
Accounts receivable are all those funds that were transferred to other legal entities and individuals, for example, in the form of loans. That is, this is the amount of money that will return sooner or later.
Accounts payable are all those funds that the company owes to other legal entities and individuals. That is, this is the money that will sooner or later leave the company’s turnover.
A company's current assets are those resources that ensure its continuous operation (usually the time of their use does not exceed one year).
An example of using different balancing approaches
Let's look at how the gross and net approaches differ using the example of one article.
The balance sheet item “Fixed assets” is characterized by the following accounts:
- 01 “Fixed assets” - initial cost of objects (main item) - debit balance;
- 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” - the amount of accumulated depreciation (contrary item) - credit balance.
The gross approach implies the following distribution of items:
The net approach reflects articles differently:
The net balance currency will always be less than the gross balance currency, since it shows the real value of the enterprise’s property as of the reporting date. This is important for owners, potential investors and analysts to take into account, because unscrupulous counterparties can artificially inflate the value of the company by using the gross method, especially in preliminary or internal reporting forms.
Tip: Before completing the balance sheet, identify the items that require cost adjustments. Find counter-accounts to them. Please note that all lines in the asset must be filled out according to the residual value principle. In liabilities, some items are formed at a pre-adjusted cost. But the amount of the counter item “Own shares purchased from shareholders” is indicated in brackets. When calculating the total amount for Section III, its value is taken into account with a “‒” sign.
Balance Sheet Currency Purpose
The balance sheet form is divided into two blocks of indicators - assets and liabilities. For each of them the total is summed up. The data obtained must be identical. If these key values do not match, the balance will be considered incorrect and the report will be invalid. What is the balance sheet currency in the balance sheet - these are the results obtained for all sections of the asset, and the total value of the values of the sections from the liability.
The equality of balance sheet currencies is ensured by the principle of double entry. The key to correctly filling out the report are:
- completeness of recording of business transactions;
- use of standard correspondence when filling out the transaction log for the reporting period;
- compliance with the principle of double entry;
- no arithmetic errors;
- using accounting registers as a basis when filling out a report.
The balance sheet currency – line in the balance sheet 1600 and 1700 helps to check the correctness of the report. In the process of self-checking, it is necessary to focus on the identity of the total lines. Problems solved using this indicator:
- checking that the form is filled out correctly;
- balance sheet analysis (study of its results using vertical and horizontal analysis methods);
- determining the company's performance by calculating a number of financial ratios.
Currency account - asset or liability on the balance sheet
Cash in foreign currency is reflected in active account 52 “Currency accounts”. Analytics is carried out on sub-accounts provided for in the working chart of accounts and accounting policies for each open account.
In accounting, currency is always shown in ruble equivalent. According to the requirements of PBU 3/2006 (clause 7), conversion into national currency is carried out:
- immediately after completing a foreign exchange transaction or operation in order to record this movement in accounting;
- when preparing reports, so that the final documentation shows up-to-date information;
- when the official exchange rate changes to comply with the principle of reliability and objectivity of accounting.
A foreign exchange account is an asset on the balance sheet. For an enterprise, cash expressed in rubles, foreign currency or monetary documents is an element of working capital, which is shown in the reporting as part of assets (the second section of the balance sheet).
Fundamentals of banking analytics. Lesson 3
Continuation. Start: Fundamentals of banking analytics.
There was such a story in my banking practice. This was a long time ago, in 1993, when the information and software of banks was carried out using the most manual methods. The bank where I worked had a large number of branches, and every morning we needed to collect the balance sheets of the branches in order to form a consolidated (single) balance sheet of the bank. When branches, for some reason, were late in providing such information until 10 am, we were forced to call them and ask: “Tell me your balance sheet currency,” in order to at least roughly estimate what would be in the bank’s unified balance sheet. One day the young lady at the other end of the line asked me: “What currency do you need: dollars or rubles?”...
For this reason, when I start talking about the balance sheet and its analysis, I always devote a special place to the concept of “balance sheet currency”.
So, in accounting banking practice, the balance sheet total is called the balance sheet currency. This term is in no way connected with either national or foreign currencies, but implies only one thing - what is the volume of assets or liabilities of the bank’s balance sheet. Since assets and liabilities are equal in the balance sheet (assets = liabilities: liabilities + capital), then the balance sheet currency does not have classifications by asset or liability - it is one!
The equivalence of assets and liabilities follows from the essence of accounting: liabilities reflect funds that are then used in active operations (as a rule, to generate income, and sometimes without income to maintain instant liquidity). Therefore, a liability, by definition, cannot be equal to an asset. Let's imagine that the asset is greater than the liability. In practice, this can be explained as follows: the bank received 100 rubles (liability), and placed 105 rubles (asset). A very reasonable question arises: where did they get the 5 rubles that appeared in the asset? If we imagine that the passive part of the balance sheet is greater than the active part, then it is presented in this way: the bank currently has 100 rubles, and only 95 rubles are reflected in the asset. In this case, I really want to know, where is the money - 5 rubles?
So, the balance sheet currency is a quantitative indicator that allows you to give a primary assessment of the bank’s development and form an opinion about its position in the market. This indicator does not allow us to identify the qualitative aspects of the bank’s activities, i.e. what the bank specializes in, or whether it is more or less reliable.
Rating agencies often use balance sheet currency as a guide to comparing banks with each other. For example, this is what the ranking of Russian banks looked like in the first half of 2005 in terms of balance sheet currency:
| №№ | Commercial Bank | Balance currency |
| 1. | Vnesheconombank | 4 894 376 798 |
| 2. | Sberbank of Russia | 4 562 711 784 |
| 3. | Vneshtorgbank | 602 721 876 |
| 4. | Gazprombank | 434 449 808 |
| 5. | Alfa Bank | 374 945 441 |
As can be seen from the table, the market leader in the first half of the year was Vnesheconombank, which provides the largest volume of services on the market, which is expressed in its balance sheet volume. But, as we have already said, nothing more than the “weight” of the bank, i.e. This indicator does not indicate the volume of transactions performed by him. And the only assessment that we can give to a bank based on its balance sheet currency is its size: large, medium or small.
When mentioning ratings and rankings, I would like to show their difference so that readers do not substitute these concepts. Unlike the ranking, where the bank’s place is determined by one of the financial indicators (for example, “balance sheet currency”), the rating is the most objective multifactor assessment of the bank, where banks are compared according to several indicators, for example, balance sheet currency, equity, working assets, loan portfolio, etc. (an example of a bank rating can be seen at).
If we still talk about the currency in which the balance is formed, then this document is drawn up in Russian rubles, which is regulated by law. Bank operations in foreign currency are revalued at the Bank of Russia exchange rate daily and reflected on balance sheet accounts in ruble equivalent (this can be seen in form No. 102 - each of the main columns contains a subsection “in foreign currency”, which implies the volume of bank operations in foreign currency, but expressed in Russian rubles at the exchange rate on the day of reporting).
Returning to the analysis of the bank's balance sheet currency, we should determine its goals and the methods that we will use.
So, the purpose of analyzing the bank’s balance sheet currency is to determine the development trends of the bank and its place in the market. If the first goal is achieved by us using horizontal analysis, where we will conduct research on changes in the balance sheet currency over time, then we will determine the bank’s place in the market and its size using a comparative analysis of the bank with other banks.
We will analyze a specific bank and, for training purposes, present the text of the research conducted.
So, to analyze the bank’s place in the market, we formed a sample of banks consisting of 6 credit institutions operating in the region.
| Name of the bank | Balance currency |
| Jar | 3 076 123 |
| Bank B | 1 725 122 |
| Bank B | 2 690 149 |
| Bank C (7 branches, of which 4 are non-resident) | 8 942 709 |
| Bank D (6 branches, of which 4 are non-resident) | 6 906 640 |
| Bank E (8 branches, of which 5 are non-resident) | 5 566 258 |
Bank A was selected as the bank being analyzed. The fourth position of the bank in the ranking of selected banks is determined, first of all, by the lack of a branch network of Bank A. The presence of branches is a competitive advantage of the bank, since its regional presence determines its larger customer base, including individuals and legal entities persons from other regions, and this makes it possible to expand the bank’s market sector and increase the volume of services provided to it. Thus, comparing Bank A with banks that have a branch network is not entirely correct, because they are in unequal competitive operating conditions. In order to obtain a more objective assessment, it is necessary to identify groups of homogeneous banks based on the “Branch network” attribute. As a result, Bank A, which we are analyzing, will be compared with Banks B and C, while Banks C, D and E will be cut off from the sample as having branches and belonging to large regional banks.
In the group we have identified, Bank A occupies the first position in terms of balance sheet currency, as a result of which it can be called the leader of medium-sized banks in the region.
To obtain an assessment of the bank's development, it is necessary, using horizontal analysis, to conduct a study of the dynamics of the balance sheet currency, which is presented in the table. To conduct a horizontal analysis, we must have data for several periods, which in practice can be easily obtained from any bank balance sheet [1[1]p>
| Jar | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 |
| Bank balance sheet currency, thousand rubles | 1 264 743 | 1 835 679 | 2 545 208 | 3 076 123 |
Research has shown that the dynamics of the balance sheet currency of Bank A has a steady growing direction, and in general, during the analyzed periods from 2005 to 2008, the balance sheet currency in absolute terms increased by 1,811,380 thousand rubles. This fact allows us to evaluate the bank as growing, but it is not possible to indicate the reasons for growth based only on balance sheet currency data.
So, summarizing the above, I would like to repeat once again that the balance sheet currency, being a quantitative indicator, allows you to assess the bank’s place in the market and the direction of its development - growth or decline, but no more. And therefore, it is impossible to place bets on this indicator as an objective one, because it does not allow us to identify the causes of this condition. I focus on this because in my practical banking activities I met a manager who attached extreme importance to this indicator. His working day began with him coming out to us, his employees, sitting in a small office space, and, loudly slapping the table, extremely proudly announced the next figure in the balance sheet currency. It was not possible to convey to him the insignificance of this indicator, so I would now like to remind future and current bank clients that information about the volume of balance sheet currency can often be misleading. For example, a bank entering the market may have extremely active growth in its balance sheet currency, but at the same time, its loan portfolio quality may be low, and the resources attracted may be short-term and expensive, which may result in losses.
Returning to the analysis, it must be said that the most revealing is the assessment of the dynamics of the balance sheet currency in relative terms, i.e. as a percentage compared to the previous period. This indicator is called the growth rate, which shows by how many percent the volume of the balance sheet currency increased (decreased) in a given period compared to the previous one.
The growth rate is calculated using the formula:
, Where
TpVb is the growth rate of the bank’s balance sheet currency; Vb1 - volume of balance sheet currency in the previous period; Vb2 - volume of balance sheet currency in the current period;
Let us apply this formula to calculate the growth rate of the balance sheet currency of Bank A in 2006 compared to 2005.
= 45,14%
So, the calculation showed that the volume of balance sheet currency in 2006 was. increased by 45.14%. But this indicator in the singular does not allow us to estimate the growth of bank volumes, so it is necessary to compare this indicator with the growth rate indicator for other periods. The purpose of this comparison is to determine how consistently this growth has occurred. It should be noted that the stability of growth rates is a very important characteristic of the bank’s activities, since it allows us to assess the quality of management. A positive trend will be a constant stable increase, not characterized by recessions.
Let us calculate the growth rate of the balance sheet currency of Bank A during the periods under study and enter them into the table:
| Jar | 2006/2005 | 2007/2006 | 2008/2007 |
| Growth rate of balance sheet currency, % | 45,14 | 38,65 | 20,86 |
Analysis of the data obtained showed that the growth rate of the balance sheet currency of Bank A tends to decrease, and if in the period 2005-2006. it was 45.14%, then for the period 2007-2008. - only 20.86%. At the same time, it is necessary to pay attention to the fact that if in absolute terms the balance sheet currency of Bank A is growing, then in relative terms the bank’s problems are clearly visible - it is losing its business activity in the market, because There is no stability in growth rates. The forecast in this case will be as follows: if the bank’s management does not take appropriate measures, the bank’s leading position will be lost and its place will be taken by a more active bank.
Comparing the growth rate of the balance sheet currency of Bank A with similar indicators of Banks B and C will allow us to determine the bank that can replace the first.
Let's analyze the growth rate of the balance sheet currency of the compared banks:
| Growth rate of balance sheet currency, % | 2006/2005 | 2007/2006 | 2008/2007 |
| Jar | 45,14 | 38,65 | 20,86 |
| Bank B | 38,28 | 44,19 | 50,29 |
| Bank B | 34,31 | 28,59 | 22,16 |
The analysis showed that the most actively growing bank among the banks of the group is Bank B, the growth rate of its balance sheet currency is in a positive direction and is the maximum. It can be assumed that this bank, all other things being equal, will become the leader of the group.
In the following lessons we will talk in detail about the composition and structure of assets and liabilities, which will allow us to identify the reasons for changes in the currency of the bank’s balance sheet.
To be continued.
[1[1]for example, by following the link you can get the value of the balance sheet currency of the bank OJSC Avtovazbank, where in line 10 you can see the value of total assets, which will be the balance sheet currency of the bank. It should be noted that to obtain the value of liabilities, you need to add the data from line 18 (Chapter II Liabilities) “Total liabilities” to the data from line 27 (Chapter III “Sources of own funds”) “Total sources of own funds”, i.e. perform the formula above “assets = liabilities: (liabilities + capital)”
Approaches to creating a balance
In accounting practice, there are several approaches to preparing a balance sheet:
- Gross balance is a balance sheet compiled by the usual addition of debit and normal addition of credit balances on the accounts of the enterprise;
- The net balance sheet is a balance sheet compiled by summing separately active and separately passive items, adjusted to their real (residual) value.
The difference in balancing approaches is due to the presence of regulating accounts in accounting, among which one is recognized as the main account, and the second as a counter account (specifying the value of the main account).
Contrary accounts include: depreciation of non-current assets (02 and 05), deviation in the cost of material assets (16), trade margin (42), reserves for depreciation of financial investments (59), reserves for doubtful debts (63), own shares and shares (81), uncovered losses (84).
Officially, in the Russian Federation, since 1992, reporting is based on the net balance principle. The gross document is drawn up by the accountant independently for internal control purposes.