The authorized capital of a joint-stock company reflects the valuation of shares. For accounting purposes, the share of each founder and the types of securities are of greatest importance. Based on these data, dividends are calculated and the rights of shareholders in managing the company are determined. Let's take a closer look at how the issue of shares is displayed in accounting (the entries that are used to account for corporate rights will not be ignored either).
Formation of the management company
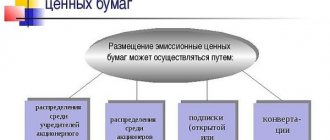
The activities of joint-stock companies are regulated by Federal Law No. 208 of the same name. This law describes the procedure for creating and reorganizing companies, the rights and obligations of founders. According to Art. 7, in closed joint-stock companies shares are distributed only among participants. According to Art. 9, the founders enter into an agreement on the creation of a company, which specifies the procedure for carrying out activities, the amount of capital, types of shares, and the procedure for their payment. The first section of the liabilities side of the balance sheet is formed at the expense of the nominal value of the securities. It is the same for all ordinary shares. After state registration of a joint-stock company, 50% of the securities must be repaid within 3 months, and the rest within a year.
Accounting for the issue of shares
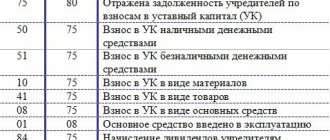
According to PBU, account 80 “Authorized capital” displays information on the composition and movement of capital. The balance corresponds to the volume of the company's own funds. The amount of debt of the founders is reflected by posting KT 80 DT 75-1. The receipt of money to pay for corporate rights is reflected in KT 75-1. Analytics is carried out for each participant.
In order for transactions on shares to fully reflect the rights of all founders, stages of capital formation and types of securities, it makes sense to open sub-accounts for account 80 that contain information about the movement of different types of capital:
- 80-1 “Announced” - used to reflect the nominal value of securities intended for sale.
- 80-2 “Subscription” - used for accounting for securities with subscription.
- 80-2-1 “Corporate rights of the first founder.”
- 80-2-n “Central Bank of the nth founder.”
- 80-3 “Paid” – the cost of redeemed securities.
Common mistakes in securities accounting
It's no secret that accounting is a delicate matter, and you can't make a mistake. Even the smallest mistake will have consequences. Below we list the most common mistakes that accountants make when accounting for securities. The first common mistake is related to the execution of bills. Incorrect design will result in incorrect wiring.
The next mistake is in accounting for the buyer’s own bill. It is reflected by 58 scores. But here it is very important to know whether the buyer issued his bill or transferred it to third parties. In the first case, the bill must be reflected in the debit of account 62 (settlements with buyers and customers). And in the second case, you need to reflect the bill as a debit and assign it to the short-term debt account.
The third mistake is again related to bills. A bill of exchange (and any other security) can be obtained free of charge from the supplier (contractor). And many companies mistakenly believe that they do not have to report to the tax authorities for this. But this is not so, even for gratuitous receipts a legal entity is obliged to report to the Federal Tax Service. And the last common mistake is that the costs of selling securities are indicated in the expense item. This cannot be done; the costs of selling securities will not help reduce tax payments.
Example
The three founders decided to found a joint stock company. Capital in the amount of 800 thousand rubles. divided into 800 shares. Nominal value of the Central Bank: 800,000: 800 = 1000 rubles. Shares are distributed among the founders in the following proportions: 40%, 35% and 25%. When placing, 50% of the securities were paid. The remaining amount should arrive in three months.
For NU purposes, income in the form of property received as a contribution to the capital of an organization is not taken into account when determining the basis for calculating the NPP (Article 1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Let's display the issue of shares in accounting. The postings are presented in the table below.
| Operations | DT | CT | Amount (thousand rubles) |
| Registration of JSC | |||
| The management company is reflected in accordance with the charter | 75-1 | 80-1 | 800 |
| Payment of 50% of shares from the share of each participant | |||
| first (800 x 40%) second (800 x 35%) third (800 x 25%) | 50 | 75-1 | 160 140 100 |
| The report on the issue of the Central Bank was approved | |||
| The value of the shares is reflected: first founder second founder third founder | 80-1 | 80-2-1 | 320 280 200 |
| The cost of securities paid is reflected: by the first participant second participant third party | 80-2-1 | 80-3-1 | 160 140 100 |
| Accounting records for the payment completion date | |||
| Funds were received on account of the remaining portion of the Central Bank: first founder (320 -160) second founder (280 – 140) third founder (200-100) | 50, 51 | 75-1 | 160 140 100 |
| The cost of paid securities is reflected (for each shareholder) | 80-2-1 | 80-3-1 | 160 140 100 |
The accounting entries reflecting the issue of uncertificated shares are no different from those presented above. Confirmation of a contribution to the company is a certificate or an extract from the register of owners of securities.
How to reflect in accounting the sale and other disposal of shares (shares) of other organizations
The owner has the right to independently dispose of his property, including assets such as shares and participation interests in other organizations. These financial investments, in particular, can:
- sell; — transfer as payment for goods (work, services); - give away for free; — invest in the authorized (share) capital of other organizations.
This follows from paragraphs 1–2 of Article 209 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Attention : when selling shares (shares) of an LLC or CJSC, offer to purchase them:
— other participants (shareholders); - the company itself, whose shares (shares) are being sold. This must be done if the company's charter provides for its pre-emptive right to buy out a share (shares), and other participants have not used their pre-emptive right to purchase.
If this procedure is violated, the participants (shareholders) or the company have the right, within three months from the moment the violation is discovered, to demand in court the transfer of the rights and obligations of the buyer to them.
This procedure is established in paragraph 3 of Article 7 of the Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ and paragraphs 4 and 18 of Article 21 of the Law of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ.
Attention: donations between commercial organizations in the amount of more than 3,000 rubles are not allowed. (except for commercial founding organizations, if such an obligation is provided for in their charter) (Article 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Accounting: implementation
In accounting, reflect the sale (other disposal) of shares or shares as a disposal of financial investments (clause 25 of PBU 19/02). That is, use account 58 “Financial investments” subaccount “Units and shares” (58-1). Make the following accounting entries:
Debit 76 Credit 91-1 – shares (shares) of another organization are sold (transferred) (if income arises from the disposal of shares (shares));
Debit 91-2 Credit 58-1, 76 – the cost of shares (shares) and expenses associated with the sale (transfer) of shares (shares) are written off.
This procedure follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 58, 91, 76), paragraph 7 of PBU 9/99 and paragraph 11 of PBU 10/99.
In accounting when disposing of shares (interests), include in the organization’s income:
— proceeds from sales (for example, those provided for in a purchase and sale agreement, barter). Do this at the moment of transfer of ownership of the financial investment to the counterparty;
— the amount of the reserve for the impairment of retired shares (stakes) not traded on the organized securities market (if one was created). Do this at the end of the accounting period in which the unlisted shares or interests are disposed of.
This procedure is established by paragraphs 34 and 40 of PBU 19/02, as well as paragraphs 7 and 16 of PBU 9/99.
Costs associated with the disposal of shares (shares) should be taken into account at the time of transfer of ownership of the financial investment to the counterparty. Include in expenses:
— cost of acquisition of retired shares (shares); — other expenses associated with disposal (for example, payment for the services of an intermediary, depository, bank, etc.).
This procedure is established by paragraphs 26, 30 and 36 of PBU 19/02, as well as paragraphs 11 and 17–19 of PBU 10/99.
In this case, determine the expenses in the form of the cost of acquiring retiring financial investments depending on what is retiring:
— a share that is traded (quoted) or not traded (not quoted) on the organized securities market; - share.
Determine the value of listed shares taking into account the latest revaluation carried out by the organization based on market value.
Determine the value of unquoted shares in one of the following ways:
- at the original cost of the retiring unit; — at the average initial cost; - at the original cost of the first financial investments acquired (FIFO method).
Determine the cost of disposal of the share based on the initial cost of its acquisition.
The chosen method of evaluating a particular financial investment should be reflected in the organization’s accounting policies for accounting purposes.
This procedure is established by paragraphs 26 and 30 of PBU 19/02 and paragraphs 7 and 8 of PBU 1/2008.
For more information on the rules for determining the cost of disposal of shares and unquoted shares, see the appendix to PBU 19/02 (clause 33 of PBU 19/02).
An example of how to reflect in accounting and taxation the sale of shares traded on the organized securities market. The organization applies a general taxation system
On July 22, Alfa CJSC sold 2,000 shares of its shares in Master Manufacturing Company OJSC at a price of 5,800 rubles. for each share (purchased in the previous year). The purchase and sale took place outside the organized securities market.
Change in capital amount
Article 28 of Federal Law No. 208 provides for an increase in the capital stock of a closed joint-stock company through additional issue of shares. The corresponding decision is made at a meeting of shareholders. The number of additional shares, their type, method of placement, price, form of payment are also determined at the meeting of shareholders. Securities can be paid for in cash or property rights. In the second case, an independent expert is hired to evaluate the transferred property. Resolution No. 19 of the FC Central Bank regulates the issue of additional shares. Accounting entries are entered on the basis of a report on the results of the issue: the value of shares, their number and categories.
In the example discussed below, materials will be used to pay for securities. To account for them, the accounting system provides account 10 of the same name. If the placement price is higher than the nominal value of the securities, then the difference between the amounts received is charged to additional capital. Also in the example, the following postings for shares will be used:
- KT 80 DT 75-1 – increase in capital through the issue of shares.
- KT 83 DT 75-1 – creation of additional capital.
The nominal value of the issue is taxed at a rate of 0.8% (Federal Law No. 2023-1). The amount to be paid is determined by the enterprise independently and transferred to the federal budget along with documents for registration of the issue. In accounting, the accrual of tax on transactions with securities is reflected in the entry DT 91-2 “Other expenses”, CT 68 “Tax calculations”. State registration of the issue of additional shares is carried out if the number of subscribers exceeds 500.
Annual share reporting
The requirements for financial reporting of joint stock companies are established by the accounting law. It is compiled annually and includes a balance sheet, a form on profits and losses, changes in capital, cash flows and their intended use, appendices, an explanatory note, and audit results.
To disclose information on the issue of shares, JSCs must prepare an annual report. The requirements for its content are in Regulation No. 454-P dated December 30, 2014. The document must contain the following information:
- JSC's place in the industry;
- Key activities;
- Report of the management board on the results of the development of the joint-stock company;
- Data on the volume of energy resources consumed per year (by quantity and amount);
- Development forecast;
- Interest payment report;
- Indication of the reasons for the risk;
- List of major transactions completed during the year and detailed information about them (conditions, responsible person, etc.);
- The composition of the supervisory board, changes in it, biography of members, transactions carried out by them;
- Other information (Article 70.3 of Regulation No. 454-P).
According to the Law on JSC No. 208-FZ of December 26, 1995, public companies must disclose data on the annual report and accounting final papers, a securities prospectus, and report on the holding of a meeting of shareholders. The volume and procedure for providing information is regulated by Regulation No. 454-P.
Example
The founders of the OJSC decided to increase the authorized capital by 0.5 million rubles by issuing 500 securities with a starting value of 1 thousand rubles. at a price of 1050 rubles. As a result of the issue, all shares were sold. Of these, 300 pieces were paid for in cash, and for the rest the JSC received materials worth 210 thousand rubles. We will display the issue of additional shares. Postings:
| Operation | DT | CT | Amount (thousand rubles) |
| Tax charged on transactions with the Central Bank (500 x 0.8%) | 90-2 | 68 | 4 |
| Money transferred to pay taxes | 68 | 51 | 4 |
| The money received from the founders in payment of the Central Bank was capitalized (300 x 1.05) | 50, 51 | 75-1 | 315 |
| Materials were capitalized to pay for shares | 10 | 75-1 | 210 |
| Increased capital | 75-1 | 80 | 500 |
| The amount of additional capital is reflected (300 x 1.05 + 210 – (500 x 1)) | 75-1 | 83 | 25 |
The contribution to the authorized capital can be paid using goods that have been previously assessed by an independent expert at market value. Let's look at how records are generated that reflect the accounting of finished products. Accounting entries:
DT 43 CT 20 – production of goods by the main (auxiliary, servicing) production.
Here's how an additional share issue is accounted for. The postings presented earlier can be used in case of payment of the contribution with other property, for example, OS.
Accounting for fixed assets and intangible assets
The procedure for accounting for fixed assets and intangible assets received from the founders (third parties) depends on whether they are recognized as depreciable property or not.
Fixed assets or intangible assets received from the founders (third parties), the value of which is greater than that specified in paragraph 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, must be depreciated (Clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the cost of fixed assets does not exceed the cost criterion established by clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, include it in material expenses as they are put into operation (subclause 3 of clause 1 of Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For more information about accounting for fixed assets contributed to the authorized capital of an organization, see How to formalize and reflect in accounting and taxation the receipt of fixed assets as a contribution to the authorized capital.
On accounting for intangible assets with a value less than the limit established by paragraph 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, see What property is considered depreciable in tax accounting.
Reduction of capital
The authorized capital can be reduced by changing the par value or repurchasing its own securities in order to reduce them. At the same time, the new amount of own funds should not be less than that provided by law. If the first method is used, then additional shares are issued, the transactions for which will be discussed further, of a lower value, which are converted into outstanding securities. Based on the issue report, changes are made to the charter. At the same time, the amount of the issue of the Central Bank, which is intended to reduce the capital, is not subject to taxation.
Example
By decision of the founders, the charter capital of the OJSC is reduced by 300 thousand rubles through the conversion of securities. The difference between the nominal and market values is paid to the founders upon issue. The transfer of money is carried out by an agent whose services cost 12 thousand rubles including VAT. We will display the issue of additional shares in the accounting system. Postings:
| Operation | DT | CT | Amount (thousand rubles) |
| Amount to be paid upon conversion of shares transferred to the agent | 76 | 51 | 300 |
| Disbursement to shareholders | 75-1 | 76 | 300 |
| Agent's remuneration (including VAT) | 91-2 | 76 | 12 |
| Payment for agent services has been transferred | 76 | 51 | 12 |
| Reflected decrease in capital | 80 | 75-1 | 300 |
Cancellation of the Central Bank
When an organization repurchases its own shares in bookkeeping, a difference may arise between the nominal price and the actual price paid. It is taken into account under article 80 (if the price is below the face value) or as part of own funds (if the price is above the face value), as well as under the article “Other monetary documents” (account 56). Most often, securities are purchased at a reduced value. Let's look at standard wiring:
- DT56 KT50(51) – the cost of the costs of repurchasing shares is taken into account.
- DT56 KT80 - excess of the nominal value over the redemption value.
- DT88 KT56 - excess of the redemption value over the nominal value.
If securities are purchased for the purpose of cancellation, then the following transactions are generated:
- DT80-3 KT80-1 – reduction in the cost of paid-in capital.
- DT80-1 KT56 - amount of canceled shares (entry is generated after amendments to the charter)
or:
- DT48 KT56 - reflects the par value of the securities sold.
- DT51(50) KT48 - cash was received as payment for the shares sold.
- DT48(80) KT80(48) – profit (loss) was received from transactions with the Central Bank.
What securities can be called valuable?
Securities are, first of all, shares and shares, bonds, bills, checks and mortgages. To make these terms more understandable, we can give them the following brief definitions:
- Shares secure the right of the owner of this security to claim part of the company's profits in the form of dividends.
- The bond allows the holder to claim its face value, as well as a specified interest.
- The share assigns to its owner the opportunity to receive part of the property assets of the enterprise.
- A bill of exchange is a document certifying that a certain person (citizen or organization) must pay a second person a specific amount of money within a limited time period.
- A check is a piece of paper that is directly associated with the bank. On a check, the owner specifies an amount and instructs the bank to pay that amount to a specific person or business.
Reorganization
Sometimes it may be necessary to change the par value of shares through splitting or consolidation. If the amount received clearly corresponds to the size of the capital account, no additional entries are generated in the accounting system. Changes are made only to the register of shareholders. If the size of the management company is not clearly divided by the number of new founders (for example, with a capital of 6 thousand rubles, the number of securities is reduced from 300 to 25), then changes are made to the charter documents and an additional issue of shares is formed. The wiring used is similar to that shown above.