Transport tax rates in Moscow in the table
The rules for collecting tax fees for transport in the capital region are established by Law No. 29 of the Moscow Government. According to this regulatory document, the following rates are established, charged in rubles for each hp. engine:
| Bet size | Object of taxation |
| 7 | Motor vehicles with power up to 20 hp. |
| 12 | Passenger cars with engines up to 100 hp. |
| 15 | Motor vehicles with power from 20 to 35 hp. |
| 15 | Buses with engines up to 110 hp |
| 15 | Trucks up to 100 hp |
| 25 | Passenger cars with engines from 100 to 125 hp. |
| 25 | Other vehicles on wheels or tracks |
| 25 | Snowmobiles and motor sleighs with engines up to 50 hp. |
| 26 | Buses with power over 110 hp |
| 26 | Trucks with a power of 100-150 hp |
| 35 | Passenger cars with power from 125 to 150 hp. |
| 38 | Trucks with a power of 150-200 hp |
| 45 | Passenger cars with a power of 150-175 hp. |
| 50 | Passenger cars with a power of 175-200 hp. |
| 50 | Motor vehicles with a power of more than 35 hp. |
| 50 | Snowmobiles and motor sleighs with a power of more than 50 hp. |
| 55 | Buses with power over 200 hp |
| 55 | Trucks with power from 200 to 250 hp. |
| 65 | Passenger cars with power from 200 to 225 hp. |
| 70 | Trucks with power over 250 hp |
| 75 | Passenger cars with a power of 225-250 hp. |
| 150 | Passenger cars with power over 250 hp. |
When calculating car tax, in addition to the rate, you also need to take into account increasing factors. They apply to premium cars, the average price of which exceeds 3 million rubles. The list of such models is published annually on the website of the Ministry of Economic Development.
The value of the coefficient depends on the cost of the car and the year of its manufacture, ranging from 1.1 to 3 of the base rate.
Increasing tax rates for expensive cars
Since 2015, tax authorities began to apply increased transport tax coefficients for expensive cars worth more than three million rubles in the following amount:
1.1 - in relation to passenger cars with an average cost of 3 million to 5 million rubles inclusive, from the year of manufacture of which 2 to 3 years have passed;
1.3 - in relation to passenger cars with an average cost of 3 million to 5 million rubles inclusive, from the year of manufacture of which 1 to 2 years have passed;
1.5 - in relation to passenger cars with an average cost of 3 million to 5 million rubles inclusive, no more than 1 year has passed since the year of manufacture;
2 - in relation to passenger cars with an average cost of 5 million to 10 million rubles inclusive, no more than 5 years have passed since the year of manufacture;
3 - in relation to passenger cars with an average cost of 10 million to 15 million rubles inclusive, from the year of manufacture of which no more than 10 years have passed;
3 - for passenger cars with an average cost of 15 million rubles, the year of which no more than 20 years have passed.
A list of cars indicating the vehicle brand and cost is posted on the official website of the Ministry of Industry and Trade at the link.
The list of cars of more than three million includes cars of the following brands:
- Audi TT RS (2.5 TFSI), S6, RS 4, Q7, S7, A8,
- BMW X6, 550i, X5 xDrive30d, Z4 sDrive35is, M3
- Cadillac Escalade, CTS-V, Escalade Hibrid
- Hyundai Equus 5.0 V8 GDI
- Infiniti FX50, QX70, QX80
- Jaguar XJ, Jaguar F-Type, XFR
- Jeep Grand Cherokee SRT8
- Land Rover Discovery 4, Range Rover Sport 3.0 V6, Range Rover Sport TDV6 3.0
- Lexus LX 570, LS 460
- Mercedes-Benz ML 350, Mercedes-Benz SLK 55 AMG, Mercedes-Benz C 63 AMG, Mercedes-Benz GL 350
- Porsche Carrera 4S, Porsche Panamera GTS, Porsche Cayenne Turbo, Porsche 911 GT3, Porsche Cayenne Turbo S and others.
The price group over 15 million rubles includes cars from the brands Aston Martin, Bentley, Bugatti, Ferrari, Lamborghini, Rolls-Royce.
Federal benefits for payment of transport tax
Federal benefits include those prescribed in Article 358 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Part 2). It identifies types of transport (not only automobile) that are not subject to taxation, these include:
- rowing boats;
- specially equipped passenger cars intended for use by disabled people (engine power should not exceed 100 hp);
- sea or river vessels engaged in fishing;
- cargo and passenger ships intended for transporting citizens by sea or river, owned by a specialized organization carrying out transportation;
- specialized agricultural equipment: tractors, self-propelled combines, livestock and milk tankers, vehicles for transporting poultry and fertilizers. Moreover, all types of this transport must be registered with the organization carrying out agricultural activities. When using transport for other purposes, tax will need to be paid;
- transport owned by executive authorities, used in operational work that involves military or equivalent activities;
- stolen and wanted vehicles, in the presence of a document confirming the loss, issued by the authorized body;
- helicopters and airplanes belonging to medical organizations and sanitary services;
- court, according to the register.
Regional benefits for payment of transport tax
As noted above, each region has its own list of benefits when paying transport tax. To find out what benefits apply in your region, you need to contact your local tax office. There you will be provided with a full list of benefits. If you find out that you fall into one or more categories, then you need to apply in person for a benefit. In the application, you must indicate a link to the article of regional legislation, according to which you are entitled to a benefit, also indicate what vehicle you own (make, registration number, etc.), attach copies of documents confirming that you are the legal owner of this vehicle , copies of a document confirming your identity and rights.
Citizens entitled to the benefit, if there are several objects of taxation, are exempt from paying tax on one vehicle of their choice.
Transport tax benefits for pensioners
Pensioners are the most common group of citizens who have a chance to receive a transport tax benefit. Most often, a number of restrictions are introduced regarding the vehicle itself.
For example, in St. Petersburg, a pensioner will not pay transport tax at all if his car is of domestic production (Russian Federation, USSR until 1991). Also, boats, motor boats or other types of water transport (except for jet skis, yachts and sailing ships) whose engine power does not exceed 150 hp are not subject to taxation. inclusive.
Old-age pensioners in the Novosibirsk region are also entitled to benefits established by regional authorities. Thus, motorcycles and scooters whose engine capacity does not exceed 40 hp are completely exempt from the tax. A 20% discount on the tax rate in force this year applies to all types of passenger cars whose engine power does not exceed 150 hp. The 5% discount also applies to self-propelled vehicles and installations (machines or mechanisms) on crawler tracks. For more information about benefits for pensioners, read the article “Benefits for pensioners for paying transport tax”
Transport tax rate in Moscow Region in 2021
The transport tax in the Moscow region differs slightly in rates from those established in the capital. Their value is established by law of the Moscow Region Government No. 129.
- Passenger cars are subject to a rate, depending on the power - 10-150 rubles. with every horsepower.
- Motorized transport – from 9 to 50 rubles for each unit of power.
- Buses - from 27 to 100 rubles per horsepower.
- Trucks - from 20 to 85 rubles.
- Other vehicles are subject to a rate of 25 rubles.
In the Moscow Region, premium cars are also subject to a “luxury coefficient”, depending on the price of a particular model. Organizations are required to calculate the amount of transport tax they pay independently. Private citizens pay it in accordance with the notification sent from the Federal Tax Service.
Changes that will come into force in 2015
As you know, currently the amount of transport tax directly depends on the power of the car. But in 2015, significant changes - it is assumed that other key parameters will be taken as the basis for the calculation: the age of the car, the volume and environmental characteristics of its engine. The initial cost of the vehicle will also be taken into account - owners of cars more expensive than 5 million rubles. and you will have to pay a significant tax.
Thanks to innovations, it will become unprofitable for motorists to drive old cars that cause significant harm to the environment - the longer the car lasts, the more exhaust gases it emits into the atmosphere.
For example, the transport tax for happy owners of electric vehicles will be reduced to zero.
The initiators of the changes seek to support the Russian automaker and advocate for timely renewal of the vehicle fleet of both trucks and cars.
The new calculations will come into force in 2015, but they will reach car owners in the form of familiar receipts only in 2016.
Transport tax in 2021: changes in Moscow Region and Moscow
In 2021, there were no changes in the size and structure of tax rates for transport in the capital and region. The only innovations introduced this year are a new form for filling out the declaration . Another innovation that affects exclusively legal entities is their receipt of notifications about the amount of the fee from the Federal Tax Service.
Previously, companies owning vehicles independently calculated the amount of contributions due to the local budget. Starting from the coming year, the Federal Tax Service will do this for them, sending a receipt with the amount due for payment.
Results
The statute of limitations for transport tax for payers - individuals is actually three years. Tax officials cannot present taxes for payment for earlier periods. If you fail to fulfill your obligation to pay taxes on time, the inspectorate may begin collection. The collection procedure and terms are strictly defined by the Tax Code.
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Features of transport tax for pensioners in Moscow
Transport tax is a regional tax, so the main nuances of its collection are established by local authorities. By decree of the Moscow government, certain categories of Muscovites. However, these do not include people of retirement age. Pensioners living in the capital and Moscow region will have to pay the tax fee in full, like other vehicle owners.
An exception is the situation when the pensioner is a disabled person of groups I or II , a parent of many children, a WWII veteran, a hero of the Russian Federation or the USSR, a full holder of the Order of Glory. In these situations, the transport tax for pensioners in Moscow will be reduced or completely abolished .
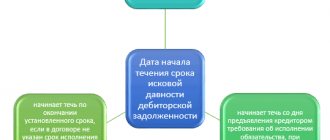
What is the statute of limitations and when does it expire?
Do not confuse the statute of limitations for holding people accountable for tax offenses, which we discussed above, and the statute of limitations. The statute of limitations is the period during which the Federal Tax Service has the right to go to court to collect tax debts from the debtor.
To physical persons paid taxes on time and did not accumulate debts, the tax service authority:
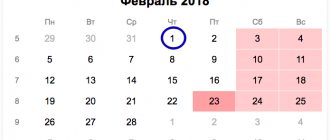
- Sends a tax notice no later than 30 days before the end of the payment period ( Part 2 of Article 52 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ) indicating the tax amount.
- Sends to the taxpayer tax claim, which indicates the amount to be paid and penalties if payment was not made on time.
If the taxpayer does not pay the debt after receiving the demand, the tax office has the right to sue him, and it is obliged to do this within a certain time frame. The limitation period for transport tax depends on the date of receipt of the demand for payment of the debt and its total amount. Upon completion of this period, the tax office loses the right to demand payment of the debt. The general limitation period is three years. Unless otherwise established by law, the limitation period begins from the day when the person learned or should have learned about the violation of his right and who is the proper defendant in the claim for the protection of this right ( Articles 196, 200 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation ).
Let's look at each stage in more detail.
Transport tax for large families in Moscow
According to the current standards in the capital, large families include families with three or more minor children. Their biological relationship does not play a role here: each child or some of them can be adopted.
Such families, according to a decree of the Moscow government, are completely exempt from paying the transport fee. The benefit is canceled when one of the youngest children reaches the age of 16 .
The following benefits are not covered:
- Guardians with more than three young children.
- Parents whose children were removed from the family and placed in orphanages for upbringing.
- Persons deprived of parental rights.
How to fill out a payment order
Payment of transport tax is made through the bank using a payment order.
You can fill out the document:
- in handwritten form on bank letterhead;
- with the help of an employee of a banking institution, having paid a certain amount for registration according to the organization’s tariffs;
- through the banking program;
- using the Client-Bank system.
In each case, you will need to fill out:
- details of the payment recipient, which can be clarified at the bank or on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for a specific region. The details include: TIN, KPP, KBK, BIC, current account, full name of the recipient;
- payment amount, which is calculated independently using the above method.
All data is entered into the payment order. Payment can be made in cash or from the account of the payer organization.
Filling out the form is greatly simplified if you use special programs or Client Bank. Filling out the document in this way allows you to avoid errors and typos.
Sample payment order:
So, the document is filled out in the following order:
| 3 | order number (set by the bank accepting the payment) |
| 4 | date of document preparation |
| 5 | type of payment being made (filled in by a bank employee) |
| 6 | amount to be paid (rubles must be filled in in words, and kopecks in numbers) |
| 7 | amount to be paid, indicated in numbers |
| 8 | name of the legal entity paying the tax |
| 9 | account number of the person making the payment |
| 10 | bank paying for the document |
| 11 | Payer's BIC |
| 12 | counts the payer in the bank |
| 13 | name of the beneficiary bank |
| 14 | Recipient's BIC |
| 15 | account of the person receiving the payment |
| 16 | recipient's name |
| 17 | recipient's bank account number |
| 18 | order code (when paying transport tax, indicate 01) |
| 19, 20 | not filled in |
| 21 | order of payment made |
| 22, 23 | not filled in |
| 24 | purpose of payment (payment of transport tax for a certain period) |
| 43, 44 | seal and signature of the payer's representative |
| 45 | filled in by a bank employee |
| 60 | Payer's TIN |
| 61 | TIN of the recipient organization |
| 62, 71 | filled out by a bank employee |
| 101 | payer status (for a legal entity it is set to 01) |
| 102 | Payer checkpoint |
| 103 | Checkpoint of the person who is the recipient of the money |
| 104 | KBK |
| 105 | OKATO |
| 106 | type of payment (when paying transport tax, TP is entered, that is, payment of the current period) |
| 107 | tax payment period |
| 108 | document on the basis of which the payment is made (when paying taxes, it is established as TP - payment request) |
| 109 | document date from field 108 |
| 110 | type of payment made (in this situation TS – payment of tax) |