A bonus paid to employees based on their work for the year is an excellent motivating factor. Many entrepreneurs who have implemented the “13 salaries” scheme have noted a decrease in staff turnover and an increase in employee performance.
Let's look at how the system of remuneration for employees, which includes this pleasant element for them, functions, clarify the nuances of calculation and taxation of wages, and also help draw up the appropriate order.
Question: Is a bonus payable to an employee based on the results of the year (quarter), the payment order for which was issued after the termination of the employment contract with the employee? View answer
Regular bonuses
Regular bonuses are incentive payments upon achievement of predetermined results. They are permanent and are included in the wage system. If the bonus conditions are met, the employee receives a pre-agreed remuneration. If the conditions are not met, the premium is not paid.
Regular bonuses, in turn, are divided into:
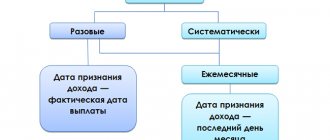
- Monthly.
They are paid every month along with the salary and are included in the average salary of the employee.
- Quarterly.
Paid based on the employee's performance for the quarter. Typically, such bonuses are issued for the 1st, 2nd and 3rd quarters.
- Annual.
The calculation period for calculating this bonus is from January 1 to December 31. It is paid once a year, subject to the fulfillment of a production task.
Data on regular bonuses are not entered into the employee’s work book or personal card.
CALCULATION OF BONUSES AT THE RESULTS OF THE YEAR AT THE ACCOUNT OF BUDGET FUNDS
The institution makes incentive payments from the wage fund, formed both from budgetary funds and from income-generating activities. Savings on the wage fund can also be used to stimulate employees.
Budgetary financing for the remuneration of full-time employees of the institution is carried out on the basis of planned indicators reflected in the budget estimate. To plan the wage fund according to the budget, tariff lists are drawn up for January 1 of the planned year, the planned amounts of budget allocations for the payment of vacation pay and payment for work on holidays are calculated.
When planning the wage fund, additional funds are provided for bonuses at the end of the year. The amount is set as a percentage of the planned wage fund.
One-time bonuses
These payments are one-time in nature and are not included in the wage system. In most cases, a one-time bonus is paid not when certain indicators are achieved, but based on the results of an overall assessment of the employee’s work.
Bonuses that are not part of the remuneration system are not taken into account when calculating the employee’s average earnings. They also cannot be the subject of a labor dispute, since their payment is at the discretion of the employer. But this type of incentive must be entered into the employee’s work book and personal card (clause 4 of article 66 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 24 of the Rules for maintaining and storing work books, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225).
A one-time bonus is given to an employee on the basis of an incentive order signed by the director of the organization. You can familiarize yourself with the procedure for drawing up and a sample of this document in the article “One-time bonus: sample order”.
An incentive order is drawn up on the basis of a submission (petition or memo) to reward an employee. In this document, the employee’s immediate supervisor evaluates his work and argues for the need to assign him a bonus. The head of the organization, on the basis of this document, issues an order for incentives.
You can find out more about how to write a memo for employee bonuses in this article.
One-time bonuses can be divided into two types:
- Production.
Expert opinion
Gusev Pavel Petrovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in defense in court.
The basis for paying such a bonus may be the achievement of certain work results, conscientious and high-quality performance of one’s duties, or the completion of an important or urgent task.
- Non-productive.
Their payment is not tied to work results, but to specific events: public holidays, anniversaries, the employee’s retirement or the birth of a child.
Possibility to challenge the decision to forfeit the bonus
If an employee believes that management has deprived the bonus unreasonably, then he has every right to contact the labor inspectorate. After submitting an application, the organization will schedule an inspection by inspectors regarding compliance with legal standards. First, the paperwork on the basis of which the decision to deprive was made is reviewed. After review, the inspector will write comments on the results.
It is important to know! It is worth remembering that in addition to the application, the inspectorate will need to provide copies of documentation that sets out the conditions for payments. These may include, for example, the following copies: an employment contract, an order for the accrual of bonuses, a regulation on remuneration, an official record of a violation, an order to reduce or cancel incentives. Within three working days, the organization must provide these copies to the employee after a written application.
Conditions for payment of bonuses
The indicators at which an employee is paid a bonus are:
- High quality.
They are determined not by the number of actions performed, but by their result (quality). These indicators include: a high level of customer service, the absence of comments and errors in work, the introduction of new innovative ideas into production.
Qualitative bonus indicators are suitable for assessing the work of employees not involved in the production process.
- Quantitative.
Such indicators have a clear numerical expression. These include: concluding a certain number of transactions, fulfilling a plan for the production of goods, selling a large number of goods. Quantitative assessment of labor is more suitable for workers involved in the production process.
Bonus conditions are prescribed in the Regulations on Bonuses, an employment contract or other local regulatory act (LNA). You can learn how to draw up a Regulation on bonuses for employees from this article.
If the bonus is not included in the remuneration system (one-time bonus), the conditions for its payment do not need to be specified separately. More information about the reasons for rewarding employees can be found here.
Reduction in bonuses
The procedure according to which the bonus is paid must be determined by the internal documents of the enterprise.
However, it must be taken into account that it must be determined in detail in what cases to apply and how exactly to implement:
- deprivation of bonuses;
- deprivation of the right to receive a bonus;
- reduction of the bonus payment due to the employee.
In the first case, we are talking about the fact that this is a punishment in case of failure to fulfill the plan or any other offenses. For this purpose, it was decided that the employee was not entitled to receive this amount.
The second concept - deprivation of the right to a bonus - may have reasons not related to the employee. This could be, for example, the difficult economic situation of the enterprise.
In the third case, only a partial reduction in payment is made. This is usually used as a disciplinary measure.
Let's sum it up
- Bonuses are divided into two types: regular, paid on an ongoing basis, and one-time, transferred at a time.
- Data in the employee’s work book and personal card is entered only about one-time bonuses.
- The conditions for permanent bonuses must be specified in the LNA; for one-time bonuses, this need not be done.
The types of bonuses to employees are determined by the employer or by the provisions of local acts, collective agreements, and agreements. In the article we will analyze the issues of bonuses for employees, highlight the main types of bonuses, and talk about the procedure for securing incentive payments.
What is 13th salary
During the Soviet Union, this type of bonus was given to all hard workers at the end of the year. The enterprises were all state-owned, bonuses were set “from above” and were mandatory for everyone. The 13th salary was paid at the end of the year, which is why it got its name. Although it is called that only among the people. There is no such concept in the accounting departments of organizations and cannot exist. There is no thirteenth month of the year, which means there should be no salary for the fictitious period. That is, the 13th salary is nothing more than a bonus at the end of the year.
What types of bonuses are there for employees - the main classifications of types of bonuses and their differences
The current legislation does not establish types of bonuses. In Art. 191 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that bonuses are incentive payments for conscientious performance of duties. In practice, organizations pay various types of bonuses, which can be classified:
By the number of employees awarded:
- Individual awards. Paid to a specific employee.
- Collective awards. Paid to a group of employees. They can work in the same department or division. As a rule, bonuses are paid when joint results are achieved in work activities, for example, the fulfillment of certain indicators.
In order to determine the amount of payments:
- In a fixed amount of money.
- As a percentage of salary.
- In shares of salary.
- As a percentage or fraction of the total salary (for example, from salary + bonus for length of service, etc.).
According to the frequency of accrual.
- One-time.
- Systematic. They can be paid once a month, once a quarter, semi-annually or annually.
Based on the basis for calculation.
- For good work.
- For fulfilling the plan.
- For any other employee achievements.
According to the method of consolidation in the organization:
- Enshrined in employment contracts.
- Collective agreements.
- Local acts.
- Agreements.
- Not fixed in internal documents, paid at the initiative of the manager (these bonuses are not provided for in the remuneration system).
Next, let's talk about the main types of employee bonuses that are most often found in organizations.
Features of bonus payment terms
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes restrictions on payment terms:
- salaries (and, accordingly, advances on them) and vacation pay (Article 136);
- calculation upon dismissal (Article 140).
There is no mention of bonuses in connection with payment terms in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, the bonus, which is part of the salary, may be paid at a frequency that differs from the frequency of salary payment. In this regard, the Ministry of Labor of Russia, in information dated September 21, 2016, posted on its website, recommends indicating in the local regulatory act on bonuses not only the month of accrual of the bonus, but also the month or specific date of its payment. If only the month of payment is indicated, this will mean that bonuses must be paid no later than the 15th day of the specified month.
If the regulatory document does not indicate the month of payment of the bonus, but there is an indication of the timing of its accrual, then the bonus must be paid before the 15th day of the month following the month the bonus was calculated (letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated August 23, 2016 No. 14-1/B-800).
Responsible persons
The main person responsible for bonuses to employees is the head of the enterprise. He has the right to independently determine not only the amount of bonuses, but also the criteria according to which remuneration is calculated (Article 144 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
But, despite this, there are cases when not only the manager, but also a representative of the workforce participates in the development of bonus regulations.
In the process of work, the responsible person for submitting reports for bonuses is the head of the structural department. It is he who analyzes the work, in the form of monitoring his subordinates, and has the right to apply for a monetary reward in connection with a job well done.
All other work on accrual and registration is performed by the personnel department and accounting department of the enterprise.
Personal income tax and insurance premiums
Regardless of the taxation system that the organization uses, for the amount of the bonus based on the results of work for the year, accrue:
- contributions for compulsory pension (social, medical) insurance (Part 1, Article 7, Article 9 of the Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ);
- contributions for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases (clause 1 of article 5, clause 1 of article 20.1 of the Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ).
This rule applies regardless of whether the bonus is provided for in the employment contract or not.
The amount of the annual bonus is included in the tax base for personal income tax (subclause 6, clause 1, article 208 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Situation: in what month should the amounts of annual bonuses be included in the personal income tax base - in the month of accrual or in the month of payment?
The amount of the premium will be included in the personal income tax tax base of the month in which it was paid.
For the purpose of calculating personal income tax, bonuses accrued for a period of work of more than a month (including annual ones) cannot be classified as labor costs. This conclusion can be made on the basis of paragraph 2 of Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It states that the date of receipt of income in the form of wages is the last day of the month for which the income is accrued. And these bonuses are accrued for a period exceeding one month. Consequently, in this case, the date of receipt of income is the day of payment (transfer to the employee’s account) of the bonus (subclause 1, clause 1, article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Make an entry for tax withholding at the time of payment of the premium.
The Ministry of Finance of Russia adheres to a similar position regarding determining the date of receipt of income in the form of bonuses (letters dated March 27, 2015 No. 03-04-07/17028, dated November 12, 2007 No. 03-04-06-01/383).
Situation: is it necessary to charge insurance premiums on the annual bonus paid to an employee who has already resigned? The employee has completed the bonus period (year).
Yes need.
The fact is that insurance premiums are levied on payments accrued to an employee within the framework of an employment relationship. An annual bonus accrued to a person for the period that he worked in the organization is considered a payment within the framework of an employment relationship, since during the bonus period such a relationship still existed. Therefore, even though the employee quit, the annual bonus paid to him after dismissal is subject to insurance premiums in the generally established manner .
This conclusion follows from Part 1 of Article 7 of the Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ, paragraph 1 of Article 20.1 of the Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ and is confirmed by the letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia of September 2, 2013 No. 17-3 /1450.
The procedure for calculating other taxes depends on the tax system that the organization uses.
Rules and payment procedure
After submitting a report to the head of the structural unit, the head considers this request. The decision to award an employee a bonus is made by the manager after an analysis of the work performed.
Then the manager’s order is processed in the accounting department, where the bonus calculation itself is carried out (you can find out more about why an order to reward an employee is needed, and also see a sample document here).
Rewarding an employee of an enterprise with a monetary payment and a sample order for bonuses for an employee.
If the bonus amount is determined as a percentage, then the accountant multiplies the salary by the corresponding percentage specified in the bonus order. And then, according to paragraph 6 of Art. 164 of the Tax Code, already deducts income tax from the amount received, which is 13%.
In the case where the bonus is a fixed amount, then 13% is immediately calculated from it, that is, income tax (we talked about the peculiarities of taxation of funds allocated for bonuses to employees here). The remaining amount will be paid to the employee.
- Example: An employee worked for a full month, and his monthly salary is 10,000 rubles. The employee receives a bonus of 30% of his salary.
The bonus is 30% of the salary.
From the amount received you will need to subtract contributions to the funds. These calculations are carried out in the same way as when calculating regular wages.
In the case where the bonus is a fixed amount, it is summed up with accrued wages for the time actually worked, and 13% is calculated from the resulting amount. Example: The monthly salary of an employee who has worked for a whole month is 20,000 rubles. He receives a bonus of 5,000 rubles.
- 25,000×13%= 3250 – income tax;
From the amount received, it will be necessary to make an accrual to the funds, which is carried out as for regular wages.
Read more about how to register and record the payment of one-time bonuses here.
Calculation examples
Let's look at the procedure for calculating quarterly bonuses using specific examples.
Example No. 1. How to calculate a quarterly bonus from an employee’s salary
An employee of Vesna LLC was awarded a bonus for the 3rd quarter of 2021 in the amount of 150% of the official salary. According to the staffing table, the salary is 50,000 rubles.
Calculation of quarterly bonus payment: RUB 50,000. × 150% = 75,000 rubles.
Let’s assume that the employee’s bonus is set at 3/4 of the official salary.
Calculation: 50,000 rub. × 3/4 = 37,500 rubles.
Example No. 2. Example of calculating bonuses for actual time worked for the 3rd quarter of 2021
Vesna LLC has a five-day work week. In the 3rd quarter of 2021, the norm is 57 working days. The specialist was sick from September 16 to September 25, 2021, of which 8 working days. The amount of the bonus is determined in the amount of the official salary, taking into account the actual time worked. The salary was 85,500 rubles.
Calculation: 85,500 rubles / 57 days (work norm) × 49 days (57 days - 8 days is actually time worked) = 73,500 rubles.
Example No. 3. Percentage of revenue - an example of calculating a quarterly bonus for trade workers
TORG LLC has established that bonuses for the quarter are calculated as 10% of the revenue received by the company based on the results of the work of the sales agent. The company employs three sales representatives, their revenue for the 3rd quarter of 2021 was:
- Ivanov I.I. — 1,000,000 rubles;
- Petrov P.P. — 800,000 rubles;
- Sidorov S.S. — 900,000 rubles.
We calculate quarterly bonuses:
- Ivanov I.I. — 1,000,000 rub. × 10% = 100,000 rubles.
- Petrov P.P. — 800,000 rub. × 10% = 80,000 rubles.
- Sidorov S.S. — 900,000 rub. × 10% = 90,000 rubles.
How the bonus is calculated: general step-by-step instructions
Awards can vary not only in size, but also in nature. The most common of them are:
- incentive bonuses;
- incentive bonuses.
Incentive payments
Incentive bonuses are most often paid to employees for good work during the year, length of service, or dedicated to holidays and special occasions (you can find out what a sample order for a bonus for a professional holiday looks like here, and in this article we told you what the procedure is accrual of incentives for the anniversary). Incentive bonuses have a slightly simplified calculation method.
Let's look at the step-by-step instructions, using the example of bonuses for a special date:
- The head of the company issues an order for bonuses to his employees.
- The HR department or accounting department processes the manager’s order.
- Rewarded employees familiarize themselves with the manager’s order and put their signatures.
order to issue an incentive bonus
- The document is sent to the accounting department for accrual and calculation of bonuses to the employee.
- Payment of bonuses.
- Entry in the work book.
- The head of a structural unit writes a memorandum indicating the fact that a certain employee has exceeded the plan.
- The head reviews the note and issues an order.
- The order is signed by the manager, the employee being awarded and stamped.
Incentive bonuses most often have a fixed amount of monetary remuneration and are paid to employees regardless of their position.
Incentive rewards
Incentive bonuses are most often awarded for excellent work done, production above the norm, or delivery of work within a certain time frame. Let's look at step-by-step instructions for calculating an incentive bonus, using the example of bonuses for exceeding the plan:
order to issue an incentive bonus
How to calculate 13th salary
In this section, we will look at how to find out what amount the 13th salary will represent. How it is calculated, we look at the organization’s position. It can be calculated separately for each employee, but most often the calculation is carried out for the structural unit as a whole. Each department is allocated a certain bonus amount, which is divided among employees depending on their length of service at the enterprise and salary. There are several options for the calculation formula. Each of them is applied depending on how the director decided to reward employees. He can set the bonus as a percentage of annual earnings, depending on length of service, or choose a fixed payment.
The first case will be calculated using the formula: Ohm*12 months*10%, where Ohm is the monthly salary. When paying the seniority department, you will have to carry out a more complicated operation. First, you need to sum up the length of service of all employees in the department, then find the total earnings, calculate the ratio as a percentage of the salary of each employee and the total amount of money earned. Based on this figure, we calculate the share of each employee. Then we calculate the share depending on the length of service. The last step is to find the arithmetic mean between the share of salary and length of service. The final number is the bonus.
Documentation of the procedure
Expert opinion
Gusev Pavel Petrovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in defense in court.
Documentation of bonuses begins with a memorandum or template documents, which are called submissions for bonuses. The main information reflected in this note is:
- personal data of the head of the organization;
- document's name;
- personal data of the employee applying for bonuses;
- information about the employee’s work performed and his merits is recorded;
- a request for a bonus is made;
- the amount of incentive is indicated only if this information is not determined by the boss himself;
- personal data of the head of the structural unit who submits the report;
- signature;
- date of.
Today, the remuneration system increasingly includes bonuses for employees, thereby stimulating their work to increase the profitability of the enterprise. But for this, an important factor remains the correct execution of it. After all, only then does the manager have a chance to achieve economic growth of his enterprise.
An example of a document in the photo below:
Employee bonus:
A salary increase is a great way to encourage an employee, instill in him a sense of responsibility and a desire to develop. But do not forget about the moral side of work. After all, only a balance of moral and material rewards can give a positive result.
From the article you will learn:
1. How to document the accrual of bonuses to employees in order to avoid problems during tax and labor inspections.
2. What premiums can be taken into account in tax expenses under OSNO and simplified tax system.
3. What legislative and regulatory acts regulate the procedure for calculating bonuses and including them in expenses for taxation.
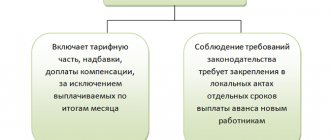
Employees' wages, as a rule, consist of several parts: wages (for hours actually worked, for the amount of work actually completed, etc.), compensation payments and incentive payments. Incentive payments include bonuses to employees.
Splitting the salary into a fixed part and a bonus part is in the interests of both the employer and the employee. The employer has the opportunity to stimulate employees to achieve higher indicators and results, and at the same time not overpay them if such indicators are not achieved.
And for employees, the bonus part of their wages is a real opportunity to receive greater rewards for their work. That is why almost all organizations and individual entrepreneurs-employers provide for the payment of bonuses to employees, and bonuses often make up the largest part of wages.
Given this fact, the calculation and payment of bonuses is the object of increased attention during inspections by the tax inspectorate and the state labor inspectorate. How to bring the calculation of bonuses into compliance with labor and tax laws and avoid problems during audits - read on.
What the tax inspectorate is interested in regarding bonuses to employees is whether wage costs (including the payment of bonuses) are legally classified as expenses that reduce the taxable base for corporate income tax or the single tax paid in connection with the application of the simplified taxation system.
What the state labor inspectorate is interested in is whether the rights of workers have been violated when calculating and paying them wages (including bonuses).
All bonuses to employees are subject to insurance contributions to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund, and Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund (Clause 1, Article 7 of Federal Law No. 212-FZ of July 24, 2009), therefore, when checking the Social Insurance Fund and Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, inspectors are usually interested in the total amount of accrued bonuses without detailed analysis.
Documentation of awards
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, establishing bonuses for employees is the right of the employer, and not his responsibility. This means that the employer has the right to approve a remuneration system that provides for a bonus component (salary-bonus, piece-rate-bonus system, etc.) and document this fact.
Please note that if the employer’s internal documents establish a remuneration system that includes bonuses, then in this case the calculation and payment of bonuses to employees, according to internal agreements, is the responsibility of the employer. Failure to fulfill this obligation may result in justified complaints from employees and serious claims from the labor inspectorate.
In this regard, it is important to correctly document the procedure and conditions for bonus payments to employees.
What documents need to reflect the conditions and procedure for bonuses to employees:
1. Employment contract with the employee. Conditions of remuneration, including incentive payments, which include bonuses, are mandatory for inclusion in the employment contract (Art.
57 Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, it must clearly follow from the employment contract under what conditions and in what amount the bonus will be paid to the employee.
There are two options for stipulating bonus conditions in an employment contract: fully specify the conditions and procedure for bonuses, or make a reference to local regulations that contain this information. It is advisable to use the second option, to provide a reference to local regulations in the employment contract, because when making changes to the conditions for rewarding employees, you will only need to make appropriate changes to these documents, and not to each employment contract.
2. Regulations on remuneration, regulations on bonuses. In these local regulations, the employer establishes all the essential conditions for bonuses to employees:
- the ability to accrue bonuses to employees (remuneration systems);
- types of bonuses and their frequency (for results based on the results of work for a month, quarter, year, etc., one-time bonuses for holidays, etc.)
- a list of employees who are entitled to certain types of bonuses (all employees of the organization, individual structural units, individual positions);
- specific indicators and methodology for calculating bonuses (for example, a certain percentage of salary for fulfilling a sales plan; a fixed amount and specific holiday dates, etc.);
- conditions under which the premium is not awarded. Thus, if an employee is given a bonus for conscientious performance of job duties in a fixed amount, then the employee can be deprived of this bonus only if there are sufficient grounds (failure to perform or improper performance of duties provided for in the job description; violation of internal labor regulations, safety regulations; violation resulting in disciplinary action and etc.);
- and other conditions established by the employer. The main thing is that all the conditions for bonuses for employees in the aggregate do not contradict each other and make it possible to unambiguously determine which of the employees, when and in what amount the employer is obliged to accrue and pay a bonus.
3. Collective agreement. If, at the initiative of the employer and employees, a collective agreement is concluded between them, then it must also indicate information on the procedure for paying bonuses to employees.
! Please note: in addition to the fact that the employee signs the employment contract, the employer must, upon signature, familiarize him with the regulations on remuneration, regulations on bonuses, and the collective agreement (if any).
Inclusion of bonuses in tax expenses under OSNO and simplified tax system
Labor costs for taxation purposes under the simplified tax system are accepted in the manner prescribed for calculating corporate income tax (clause 6 p.
1, paragraph 2, art.
346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, when including labor costs (including the payment of bonuses) in expenses that reduce the taxable base for income tax and the simplified tax system, one should be guided by Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
“The taxpayer’s expenses for wages include any accruals to employees in cash and (or) in kind, incentive accruals and allowances, compensation accruals related to working hours or working conditions, bonuses and one-time incentive accruals, expenses associated with the maintenance of these employees, provided for by the norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation, labor contracts and (or) collective agreements” (paragraph 1 of Art.
255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). According to clause
2 tbsp. 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, accepted labor costs for tax purposes include “accruals of an incentive nature, including bonuses for production results, bonuses to tariff rates and salaries for professional skills, high achievements in work and other similar indicators.”
Expert opinion
Gusev Pavel Petrovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in defense in court.
In addition, as a general rule, expenses in tax accounting are recognized as justified and documented expenses incurred by the taxpayer (Article 262 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, having combined all the requirements of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, we come to the following conclusion. Expenses for bonuses to employees reduce the tax base for income tax and the single tax paid in connection with the application of the simplified tax system, while simultaneously meeting the following conditions:
1. Payment of bonuses must be provided for in the employment contract with the employee and (or) in the collective agreement.
We discussed above the procedure for reflecting bonus conditions in an employment contract: either stipulating them in the employment contract itself, or referring to the employer’s local regulations. Not all employers conclude a collective agreement with employees, however, if one does exist, it should also provide for the possibility of paying bonuses and the procedure for bonuses.
! Please note: one order from the manager to pay bonuses is not enough to include bonuses in expenses. Bonuses for employees must be provided for in the employment contract with the employee and (or) in the collective agreement.
Otherwise, tax authorities have every reason to remove “premium” expenses and charge additional income tax or tax under the simplified tax system. This position of the tax authorities is confirmed by numerous court decisions in their favor.
2. There is a need for a direct relationship between the awarded bonus and the employee’s “production results”, that is, the bonus must be economically justified and related to the receipt of income by the organization or individual entrepreneur.
! Please note: bonuses are often awarded to employees with approximately the following wording: “For the timely and conscientious performance of their duties.” If you want to include bonuses in tax expenses, it is better not to use this wording, because the timely and conscientious performance of one’s work duties is the responsibility of the employee, and not the object of additional incentives.
In this case, the tax authorities will most likely remove such expenses. Therefore, if it is impossible to provide specific labor indicators for calculating a bonus, then it is better to indicate “For work results based on the results of the month (quarter, year, etc.).”
In this case, it is possible to defend the right to include such premiums in tax expenses.
Another point: the source of payment of bonuses. If profit is indicated as the source of payment of the premium, or as the basis for calculation, but a loss is actually received, then such premiums cannot be taken into account as expenses for taxation.
3. The accrual of bonuses must be properly completed.
The basis for awarding bonuses to employees is the bonus order. To draw up an order on bonuses, you can use the unified forms: Order (instruction) on encouraging an employee (Unified Form No. T-11) and Order (instruction) on encouraging employees (Unified Form No. T-11a), which are approved by the Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated 05.01. 2004 No. 1 “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for recording labor and its payment.”
However, from January 1, 2013, it is not necessary to use unified forms (clause 4 of Art.
9 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”). Therefore, an order for bonuses can be drawn up in any form that is approved by the organization.
The main thing you need to pay attention to when filling out an order for bonuses:
- the incentive motive must correspond to the type of bonus specified in the employment contract, local regulations, collective agreement (with reference to these documents);
- it should be clear from the order which employees the bonus is awarded (specific employees indicating their full name);
- the amount of the bonus for each employee must be indicated (the amount of the bonus must correspond to the calculated data);
- It is necessary to indicate the period for calculating the bonus.
4. It is better to issue bonuses to the head of an organization (who is not its sole founder) not by order of the head himself, but by the decision of the founder (general meeting of founders).
This is due to the fact that the employer in relation to the head of the organization is its founders. Accordingly, it is within their competence to establish the conditions for payment of bonuses and its amount to the manager.
Reflection of bonuses in accounting
In accounting, the accrual of bonuses is reflected in the same way as all wages in account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” in correspondence with cost accounts (20, 26, 25, 44). Since bonuses to employees are subject to personal income tax, bonuses are paid minus the withheld personal income tax.
If you find the article useful and interesting, share it with your colleagues on social networks!
If you have any comments or questions, write to us and we’ll discuss them!
Legislative and regulatory acts:
1. Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Expert opinion
Gusev Pavel Petrovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in defense in court.
3. Federal Law No. 212-FZ of July 24, 2009 “On insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund”
You can find out how to familiarize yourself with the official texts of documents in the Useful sites section.
Every employee loves to receive bonuses and material rewards for the results of their work. But not all employees understand what methods the employer uses when issuing a bonus to a particular employee.
That is why disagreements and misunderstandings often arise between employees, why one receives more and the other less.
What kind of bonus systems there are, which one is more convenient and best to use in a particular company, will be discussed in today’s article.
Reason for appointment
The basis for a bonus is an event or a set of certain factors, upon the occurrence or fulfillment of which the employee is entitled to an incentive bonus in the form of a bonus. The list of grounds for bonuses is determined solely by the employer. The decision will have to be enshrined in local regulations for the organization, otherwise problems with the State Labor Inspectorate and disputes with employees cannot be avoided.
Set the grounds for assigning bonuses:
- in the employment contract with the employee;
- in a collective agreement;
- in the wage situation;
- in a separate provision on bonuses;
- in the provision on employee incentives;
- at other disposal of management.
Please note that in addition to monetary incentives, other forms of incentives for conscientious work are provided for workers. For example, an employer has the right to express gratitude or award a distinguished employee with a valuable gift, a certificate of honor, or assign him an honorary title. For special labor services to society and the state, employees are nominated for state awards.
Is it necessary to pay an employee a bonus for a year or a quarter if the payment order is issued after his dismissal?
The answer is in the consultation of experts ConsultantPlus.
Recommendations for state employees
There is no special procedure for calculating the quarterly bonus in a budget organization. Issues in the area of remuneration for public sector employees are resolved by management independently, but taking into account the recommendations and standards communicated by the founders, higher ministries and departments.
The following grounds are possible for annual, monthly or quarterly bonuses for civil servants and other public sector employees:
- for conscientious performance of labor duties;
- for achieving certain labor indicators;
- in connection with anniversaries;
- in connection with professional holidays, etc.
Please note that for each reason you will have to describe in detail the events and indicators for bonuses. For example, for payments on an anniversary or holiday, specific holidays and dates of events should be indicated. Otherwise, workers will demand money for every holiday on the calendar.
With regard to bonuses for achieving labor indicators or conscientious work, it is possible to develop a point system of criteria and factors. For each task completed or goal achieved, a point is awarded. At the end of the quarter, the total amount of accumulated points and their value are determined, depending on the wage fund.
Recommendations for commercial organizations
For commercial structures, bonus rates are somewhat different. Here the employer has the right to establish a direct link with the quantitative or qualitative indicators of the business:
- for quality indicators, for example, employees of the sales department, it is allowed to establish a quarterly incentive for fulfilling the sales plan by 100% or more;
- for quality indicators, for example, employees of the accounting department and human resources department are often paid monthly bonuses for timely submission of reports, compliance with cash and contractual discipline, and successful completion of inspections.
It is important to describe the terms and principles of accrual in as much detail and clearly as possible. The more detailed the procedure for how the quarterly bonus is calculated, the fewer problems with calculations.
Bonus system and its features
What is a bonus system?
The bonus system at an enterprise is an excellent incentive to motivate employees to increase not only their productivity, but also to improve their professional knowledge and skills.
However, financial incentives do not always play a positive role on employees.
There are also situations when a poorly thought-out planning system leads to improper stimulation of employees and damage to the company as a whole and to a specialist in particular.
For example, when rewarding employees of a medical treatment institution for the number of patients they received and prescribed treatment for, you can achieve not an increase in the quality of services and attentive attitude towards patients, but the following problems:
- Workers will be interested in a large flow of patients, and accordingly the treatment they prescribe will not always be competent;
- In addition, many doctors will make “false” entries in patients’ records about visiting a doctor if they want to improve their performance and receive larger financial rewards;
- Also, specialists will try to see as many patients as possible; accordingly, less time will be spent examining patients, interviewing them and additional examinations, which will reduce the usefulness of their work for the patient;
- In addition, there are often schemes when one specialist “gives” work to another, telling the patient about the need for additional consultation with a particular specialist. There have been cases when a patient was sent around by doctors several times before treatment was prescribed.
That is why it is important to adequately approach the choice of a system of bonuses and incentives for employees as professionals.
This will not only motivate employees to develop and improve, but will also bring benefits to the company.
Income tax: general procedure
If the bonus is paid out of expenses for the normal activities of the organization, then include it in income tax expenses if the following conditions are met:
- the bonus is provided for in the employment contract (paragraph 1 of article 255 and paragraph 21 of article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the bonus was paid for labor performance (clause 2 of article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the annual bonus is paid from net profit, then it does not reduce the tax base for income tax.
Situation: is it possible to include a bonus paid to a resigned employee as part of income tax expenses? The employee resigned before the annual bonus was accrued. The bonus was awarded for labor performance.
Yes, it is possible if the payment of an annual bonus is provided for in the employment contract with the employee (paragraph 5, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This position is shared by the tax service and the Ministry of Finance of Russia (see, for example, letters from the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated May 5, 2005 No. 20-12/32623 and the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 25, 2005 No. 03-03-04/1 /294).
simplified tax system
Organizations that pay a single tax on income do not reduce the tax base by the amount of annual premiums (clause 1 of Article 346.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Organizations that pay a single tax on the difference between income and expenses include annual bonuses stipulated by the labor (collective) agreement as expenses. This can be done if bonuses are paid for labor performance. This conclusion follows from subparagraph 6 of paragraph 1, paragraph 2 of Article 346.16 and Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Situation: when is an annual bonus considered stipulated by the employment contract?
An annual bonus is considered stipulated by the employment contract if one of two conditions is met:
- the employment contract specifies the amount and conditions for calculating bonuses (paragraph 5, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- the employment contract contains a link to the organization’s local document regulating the procedure for calculating and paying bonuses (for example, the Regulations on Bonuses).
A link to a local document can be formatted as follows: “The employee is paid bonuses provided for in the Regulations on Bonuses (approved by Order No. ___ dated ______).”
This position is adhered to by the Russian Ministry of Finance in letter dated February 5, 2008 No. 03-03-06/1/81. It is confirmed by arbitration practice (see, for example, decisions of the FAS of the West Siberian District dated April 17, 2006 No. F04-10064/2005 (20874-A27-37), Far Eastern District dated January 25, 2006 No. F03-A51/05 -2/4903).
Include the amount of bonuses based on the results of work for the year into expenses at the time of their payment (clause 2 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An example of taxation of bonuses based on the results of work for the year. The organization applies a simplification, pays a single tax on the difference between income and expenses
Alpha LLC uses simplification. An organization pays a single tax on the difference between income and expenses.
The regulations on bonuses for Alpha and employment contracts with employees provide for the payment of an annual production bonus in the amount of 13,000 rubles. to all employees of the organization who have completed their full working period. The bonus is accrued along with the salary in January of the year following the reporting year. The bonus is paid within the deadlines established for the payment of salaries for January.
In January, storekeeper P.A. Bespalov was awarded an annual bonus. It was paid on February 5th.
The bonus amount will be included in the personal income tax base in February. Bespalov has no rights to deductions for personal income tax.
Personal income tax on the premium amount is equal to: 13,000 rubles. × 13% = 1690 rub.
The organization calculates contributions to compulsory pension (social, medical) insurance according to the basic tariff. Contributions for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases - at a rate of 0.2 percent.
The amount of contributions accrued from the premium for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases was: 13,000 rubles. × 0.2% = 26 rub.
The amount of contributions for compulsory pension (social, medical) insurance is 3900 rubles, including:
- contributions for compulsory pension insurance – 2860 rubles. (RUB 13,000 × 22%);
- contributions for compulsory social insurance - 377 rubles. (RUB 13,000 × 2.9%);
- contributions for compulsory health insurance credited to the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund - 663 rubles. (RUB 13,000 × 5.1%).
On February 5, the accountant transferred personal income tax, contributions for compulsory pension (social, medical) insurance and contributions for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases to the budget.
In February, the accountant took into account as expenses:
- bonus amount – 13,000 rubles;
- the amount of insurance premiums is 3926 rubles. (26 rubles + 3900 rubles).