The software can be acquired by an organization with exclusive or non-exclusive rights to it. To register, you must have a license agreement or an agreement on the alienation of software to the buyer, an act of transfer of rights. In some cases, the license agreement may be replaced by sublicensing contractual documentation.
IMPORTANT! An exclusive right presupposes sole ownership of an asset, acquired through independent development of software for one’s own needs or through purchase under an alienation agreement.
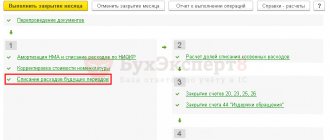
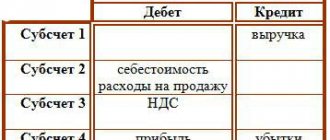
Documents for processing receipts and debits from 01 software product accounts
In this case, indicate in the certificate: the name of the primary document, the basis, number, date and name of the business transaction; if it is not possible to fill out the section “Note on acceptance for accounting” in the primary document - when transferring the authority to maintain accounting to centralized accounting (Guidelines approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2015 No. 52n). In this case, indicate in the certificate: the name of the primary document, the basis, number, date and name of the business transaction; operations to fulfill, withhold or pay off obligations, accrual of taxes, fees, insurance premiums and other obligatory payments (clauses 129, 131 of Instruction No. 174n, clauses 157, 159 of Instruction No. 183n); writing off unrecoverable accounts receivable and unclaimed accounts payable and accruing income from the rental of property (clause
98, 150 Instructions No. 174n, paragraph 101, 178 Instructions No. 183n)
The procedure for writing off inventory items from an off-balance sheet account
Inventory and inventory items are recorded on off-balance sheet accounts in the following cases:
- Acceptance of materials from other companies for processing - records of these operations are kept on the account. 003 “Materials accepted for processing.”
- Commission agents account for goods for resale on the account. 004 “Goods accepted for commission.”
- Acceptance for storage - this is what the account is intended for. 002 “Inventory and materials accepted for safekeeping” of the Chart of Accounts (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n).
Let's take a closer look at the procedure for writing off materials from these off-balance sheet accounts. Postings for capitalization and write-off from the account. 002 look like this: Debit Credit Contents of transaction 002 Acceptance of inventory items for secondary storage 002 Disposal of inventory items accepted for secondary storage Write-off of inventory items from the account.
002 is carried out on the basis of:
- form or similar document developed by the organization (taking into account the requirements of paragraph 2 of Article 9 of Law No. 402-FZ)
Features of the procedure
The company's values are the following:
- Raw materials.
- Finished goods.
- Unfinished products.
Write-off involves the official deregistration of objects. The procedure is carried out in the presence of these circumstances:
- Launch of raw materials into production.
- Defects.
- Loss of quality due to unforeseen circumstances (for example, flood, fire, hurricane).
- The service life has expired.
- Obsolescence of equipment.
- Depreciation of assets.
The detection of such circumstances is usually the responsibility of asset managers. Write-off is carried out when keeping valuables on the register is no longer profitable. Sometimes the presence of valuables can lead to losses for the company. Therefore, write-off is a procedure that can be profitable. In addition, it is needed to prevent abuse by employees working with valuables.
It is not possible to simply write off assets. This is a procedure that is strictly regulated by law. In particular, the manager needs to form a commission specifically responsible for write-offs. It is formed on the basis of the order of the manager. The commission usually includes specialists from different departments: the chief accountant, financially responsible employees.
How software accounting is carried out
:
- duration of use exceeds the threshold of 12 months.
- availability of documentation confirming the right to own and use the object;
- the prerequisites have been created for obtaining financial benefits from the operation of the asset;
The software is placed on the balance sheet at its original cost, which includes the costs incurred to purchase the licensed product. If the cost of the program does not exceed 100 thousand rubles, then, according to tax accounting rules, the asset may be considered non-depreciable. In accounting, the threshold for classifying objects as depreciable is at around 40 thousand rubles.
When a decision is made to charge depreciation on the purchased software, the service life is determined according to the technical documentation and is correlated with the standards of Art. 258 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This rule is fixed for tax accounting; in accounting, depreciation may not be charged if the service life of the intangible asset is unknown.
How much to take into account software (Kosheleva Yu.A.)
As a primary document, we can recommend issuing a certificate (f.
Software products acquired on the basis of a non-exclusive right cannot be depreciated.
0504833). In addition, according to clause 334 of Instruction No. 157n, a card for quantitative and total accounting of material assets is opened for each software product (f. 0504041). However, natural questions arise: for how long should it be taken into account there and how can it be written off. And about what she is silent. From the above provisions of Instruction No. 157n we can conclude that the starting point for accounting for the receipt and disposal of software on off-balance sheet account 01 is the license agreement.
Relations under such an agreement are regulated by civil law, in particular Art.
We recommend reading: Check passports for validity on the FMS website
1235 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. According to paragraph 2 of Art. 1235 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a license agreement is concluded in writing. If the contract specifies its validity period, the software products are written off at the end of this period. In the case where the license
Postings in commercial structures
Operations where a commercial institution acquires the exclusive right to use a new program must be recorded in accounting by a set of correspondence:
- By the date of acquisition, to reflect the amount of expenses incurred, a transaction is generated between D08.5 and K60.
- At the moment when the program is installed and you can start using it, a record is created for the cost of the software with D04 and K08.5.
- Every month, when depreciation amounts are calculated, account 20 (or 26, 44) is debited while account 05 is credited.
If the program was purchased at a cost not exceeding 40 thousand rubles, then the accountant draws up the following set of transactions:
- When purchasing software, expenses are taken into account through correspondence D08.5 - K60.
- When the program is put into operation, account 04 is debited and account 08.5 is credited.
- The full cost of the software in tax accounting is immediately transferred to the enterprise’s expenses by entry between D20 (or 23, 26, 25, 44) and K04.
- Depreciation will be calculated in accounting; correspondence D20 (or 23, 26, 25, 44) - K05 is intended for this.
If an institution purchased the software and received non-exclusive rights to it, then:
- when making a one-time payment at the time of purchasing the software, account 97 is debited, account 60 is recorded as a credit;
- the software license is accounted for as a debit turnover in off-balance sheet account 012;
- Every month, part of the costs incurred is transferred to the expenses of the upcoming periods by posting D20 (or 23, 26, 25, 44) - K97.
IMPORTANT NUANCE! It is legally prohibited to use illegal versions of software. The use of pirated programs in work is punishable by civil and criminal law in Art. 1252 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and Art. 146 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
When carrying out the procedure for updating a software product or performing specialized maintenance, the money spent on this is shown in debit 20 (25, 23, 44, 26) and credit 60 of the account.
How are exclusive rights to software developed in-house reflected in accounting?
In which off-balance sheet account should the software in use be accounted for?
This procedure follows from paragraphs 66 and 302 of the Instructions to the Unified Chart of Accounts No. 157n.
After putting the computer program into operation, the costs of its acquisition, accounted for as deferred expenses, are subject to write-off to the financial result of the current financial year. The procedure for writing off expenses that relate to several reporting periods is established by the institution independently. For example, an institution can write off a one-time one-time payment for the use of a computer program evenly over the period established by order of the head of the institution.
Fix the applied option for writing off deferred expenses in the accounting policy for accounting purposes.
Accounting for fixed assets on off-balance sheet accounts in 1C: BGU 8
I will structure the article as follows: I will draw your attention to how accounting was previously carried out on off-balance sheet accounts, and how it is now necessary to maintain it.
Expenditures on the program that will not be included in the intangible assets are carried out under subarticle KOSGU 226 “Other work, services.” Reflect them on accounts that are linked to this code: 302.26, 401.20.226.2 If the institution received a computer program for use, reflect it on off-balance sheet account 01.
In general, off-balance sheet accounts are necessary for full accounting of fixed assets, since these fixed assets do not play a role in the balance sheet of the institution, but they still require control.
There is also special reporting for government agencies on values in off-balance sheet accounts. As we all remember, accounting for off-balance sheet accounts is carried out according to a simplified scheme: the principle of double entry may not be used (in postings with off-balance sheet accounts there may be no corresponding account).
The lack of rigor in recording transactions with off-balance sheet accounts is explained by the fact that they do not participate in the formation of the balance, for which double correspondence must be observed. Let's summarize: - accounting on off-balance sheet accounts is important for control;
Tax nuances
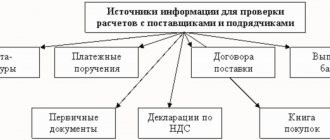
The organization must confirm the purchase of the software with a license agreement, invoice, and receipts for payment. If the software is “out of the box”, then the terms of its use are stated not in the agreement, but on the packaging. Then the contract for operating the program is considered to come into force from the moment it is installed on the computer. In this case, the acquisition costs can be written off as “profitable”.
When calculating income tax, funds spent on the purchase of software are taken into account as other expenses. However, as mentioned earlier, some experts believe that it is better to write off the costs of licensed programs throughout the entire service life. If it is not specified in the agreement or on the packaging, it is automatically determined to be 5 years. This means that you will write off 42 thousand over 5 years.
Sincerely, Natalia.
Accounting on off-balance sheet accounts in 1C.
Budget accounting
Recording on accounts, unlike balance sheet accounts, is simple; a corresponding account is not needed to generate postings.
The main business situations in which an institution, in accordance with current legislation, needs to make entries on off-balance sheet accounts.
Before the entry into force of the amendment to Instruction 157n dated March 31, 2018, accounting for both rented property and property received for free use was kept in account 01 “Property received for use.”
In the latest edition of Instruction 157n, the purpose of account 01 is interpreted differently:
“The account is intended to account for property received by an institution for use that is not leased”
.
These changes are associated with the introduction of account 111.40 “Rights to use non-financial assets”, which currently accounts for the rights to use non-financial assets in accordance with the terms of lease agreements.
Important to consider
Accounting for fixed assets on off-balance sheet accounts in 1C: BGU 8
I will structure the article as follows: I will draw your attention to how accounting was previously carried out on off-balance sheet accounts, and how it is now necessary to maintain it. In general, off-balance sheet accounts are necessary for full accounting of fixed assets, since these fixed assets do not play a role in the balance sheet of the institution, but they still require control. There is also special reporting for government agencies on values in off-balance sheet accounts.
As we all remember, accounting for off-balance sheet accounts is carried out according to a simplified scheme: the principle of double entry may not be used (in postings with off-balance sheet accounts there may be no corresponding account). The lack of rigor in recording transactions with off-balance sheet accounts is explained by the fact that they do not participate in the formation of the balance, for which double correspondence must be observed.
Let's summarize: - accounting on off-balance sheet accounts is important for control;
Is it necessary to account for this software in off-balance sheet account 01?
In accordance with paragraphs. 66 and 333
“Instructions for the use of the Unified Chart of Accounts.”
, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 1, 2010 N 157n (hereinafter referred to as Instruction N 157n), intangible assets received for use by an institution (licensee) are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 01 “Property received for use” at a cost determined based on the amount of remuneration established in the contract for the entire period of use.
66 Instructions No. 157n are also indicated by the judicial authorities (see, for example, the decision of the Twelfth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated October 23, 2014 No. 12AP-6735/14,
Recycling of computer equipment
Computer equipment contains various elements, including:
- substances hazardous to the environment, i.e., subject to the Law “On Waste” dated June 24, 1998 No. 89-FZ;
- precious metals - thanks to the precious “filling”, the decommissioned computer is subject to the Law “On Precious Metals” dated March 26, 1998 No. 41-FZ, as well as the instructions of the Ministry of Finance on the special accounting of precious metals.
Thus, computer equipment is one of the objects that cannot simply be thrown into a landfill when decommissioned. They must be handed over to a licensed specialist company for disposal. The disposal procedure should be indicated and approved in the set of documents for disposal.
NOTE! If, as a general rule, the process of decommissioning computers looks quite simple, then the need to attract a licensed company for disposal may entail the need for additional examination of the equipment by specialists of the recycling company.
Read about why waste control is required and how to fill out a waste inventory report here.
How to take into account the recycling of computer equipment in accounting? Detailed instructions for this procedure can be found in ConsultantPlus. Get a free trial access to the system and read expert explanations.
The procedure for recording a computer program and the procedure for writing off from an off-balance sheet account
However, it should be taken into account that maintaining a journal of transactions No. 99 for off-balance sheet accounts is not provided for by Instruction No. 157n.
Similar explanations are given in letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 2, 2013 N 02-06-10/40915, dated August 29, 2013 N 02-06-10/35603. The institution is required to account for intangible assets received for use by the institution (licensee) in off-balance sheet account 01 in accordance with the requirements of paragraph.
Therefore, develop the procedure for recording and storing documents on movements on off-balance sheet accounts, the procedure for creating a journal, and the procedure for filing documents with the journal yourself and approve it in the accounting policy of the institution.
Rationale From the recommendation of Sergei Razgulin, Actual State Advisor of the Russian Federation, 3rd class. How to formalize and reflect in accounting and taxation the acquisition of a computer program. An institution can not only create a computer program on its own, but also buy it.
By purchasing a computer program, an institution acquires:
- exclusive rights to it under an alienation agreement;
- rights to use it (non-exclusive right, license) under a license agreement.
This procedure is established by paragraph 1 of Article 1233, paragraph 1 of Article 1235 and Article 1236 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Application of KOSGU 352 and 353 in 2021
In Instruction 209n, many accounting transactions previously related to the item “Other services” received an independent code in the classifier of transactions of the public administration sector. In the article we talk about the procedure for applying KOSGU 352 and 353.
Let's consider the compliance of KOSGU codes 352 and 353 with types of expenses and examples of the use of KOSGU in accounting. Test School of the Chief Accountant of a State Institution Thank you for passing the test. We already know the result, you can find out too ↓ Find out the result In 2021, with the introduction of Instruction 65n, KOSGU 350 was added to reflect the increase in the cost of use rights.
In 2021, article KOSGU 350 was detailed and sub-articles were allocated to include expenses for the acquisition of user (non-exclusive) rights to the results of intellectual activity, which were previously accounted for. According to decoding in 2021, for budgetary institutions KOSGU 352 is applied if rights with an indefinite period of use are acquired.
The results of intellectual activity should be understood as:
- software;
- reference and information databases and updates to them.
The methodological recommendations of the Ministry of Finance to Instruction 209n (letter dated June 29, 2018 No. 02-05-10/45153) state that the classification of intangible assets depending on the period of use should be carried out on the basis of regulatory legal acts. Based on the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, deadlines can be established:
- agreement of the parties.
- provisions of law;
- other regulations;
When determining KOSGU, you should focus on the agreement concluded with the copyright holder.
Accounting for software on an off-balance sheet account
What documents, in addition to the contract and act, should the developer (if he is one, and not an intermediary) of software, domains and Internet versions submit to the accounting department? Answered by Olga Troshina, senior expert You must reflect on off-balance sheet account 01: the right to use a computer program, the right to access electronic versions. 2. If the license is unlimited, and the program is updated over time, then these changes do not need to be reflected on the 01 balance sheet.
if an institution has been transferred the rights to a computer program under a license agreement, it will be an intangible asset received for use. Such a computer program should be recorded at a cost determined based on the amount of remuneration under the contract. This is stated in the Instructions to the Unified Chart of Accounts No. 157n.
3. When purchasing a computer program (use right), the institution enters into a license agreement with. An acceptance certificate is attached to it.
Form of the act
Even if the faulty equipment can be repaired, the service company must provide a full estimate to fix the problem. This will allow you to determine the economic benefit of the repair. If repair is not practical, the equipment is subject to write-off. Thus, it is the expert’s opinion that allows you to determine whether faulty OS can be written off.
Instructions for filling out an act for write-off of fixed assets
The form has three sections. Each of them is designed to display specific information. An accounting employee is responsible for filling out the document. This can also be done by an employee who is responsible for the safety of fixed assets. In addition, a special commission is created that is directly involved in drawing up the act. Filling is carried out in four stages:
Purchasing the necessary software for a company’s operation is a reality of our day. Often, a company incurs significant costs for the purchase and maintenance of computer programs. Their value is written off depending on how the rights to use them were reflected in accounting. Let's consider how these operations are carried out in each situation.