- How are accounts receivable different from accounts payable?
- Types of accounts receivable
- How does debt arise?
- Accounts receivable management
- More about inventory
- Accounts receivable turnover
- Collection of accounts receivable
- Write-off of accounts receivable
- Sale of debt
- Short review
The essence of accounts receivable can be described in just a few words - they owe you. This can include almost any debt. For companies, this is unpaid goods, a loan to an employee, overpayment of taxes or other mandatory payments, rent for an office or other work premises.
Types of accounts receivable
There are several types of accounts receivable. We are talking about normal and expired.
- In the first case, we are talking about debt for certain goods, which in fact already belong to the buyer, but the payment period has not yet arrived.
- Overdue accounts receivable are debts for goods for which payment has not been received within the time period specified by both parties. In turn, this type of debt may be doubtful or hopeless. In the latter case, the problem is resolved with the participation of collection agencies.
Regardless of the maturity date of receivables, they relate exclusively to the current assets of the company. Accordingly, this amount is managed at enterprises within clearly established limits. This function is often assigned to a financial manager, general or commercial director. In addition, responsibilities may be divided between the legal department and managers.
Criminal liability
Debts of an enterprise entail administrative sanctions such as fines and penalties. Such sanctions are specified in the contract. In addition, if a company has a large debt, it may be subject to the following fines:
- 200,000 rubles
- an amount equal to the company's income for 18 months
According to the law, in some cases, an official guilty of creating debts at an enterprise is assigned community service.
If during the trial a decision is made in favor of the creditor, then the debtor has to pay:
- the entire amount of debt
- penalties and fines stipulated by the contract
- fines imposed by the court
- legal costs incurred by the plaintiff during litigation
If the debtor does not comply with the court order to pay the debt, a decision is made to seize the property of the enterprise, which is carried out by bailiffs.
This violation means significant financial or property losses for the company, as well as the loss of its good name, which in the future turns out to be an obstacle to successful business.
According to the law, a debt is considered large if the amount exceeds one and a half million rubles. Malicious evasion of payment is considered to be the planned refusal of the debtor to make payments, despite the objective possibility of making them.
Debt overdue is considered malicious based on the following criteria:
- hiding company accounts
- alienation and concealment of company property
- hiding the fact that the company has additional sources of income
- presence of fictitious contracts and transactions
Based on these facts, the court comes to the conclusion that the company’s management deliberately does not pay the debt to the creditor. In this case, a criminal case is initiated after a court order to repay the debt is issued and enforcement proceedings begin.
If the fact of malicious evasion of debt payment is proven, the debtor risks not only financial and property losses, but also bears criminal liability.
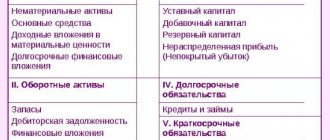
Long-term and short-term accounts receivable
The division of receivables into long-term and short-term is determined by the timing of debt repayment by accountable persons, borrowers, customers, and buyers.
Long-term accounts receivable are those in which debts are repaid after a period of 12 months after the conclusion of the contract. This is a non-current asset of the enterprise. This debt is assessed and displayed on the balance sheet at its current value, taking into account accrued interest.
There are several types of long-term receivables:
- for property transferred under financial lease, for example, equipment, buildings, housing;
- received long-term bills, which are a tool for long-term attraction of financial resources to finance the acquisition of specific assets, the implementation of long-term projects related to the implementation of real investments, etc.
That is, this is a large loan of funds from an organization that is subject to long-term repayment.
Short-term receivables are debts that are characterized by a short time to repay the debt - up to a year after the reporting date. It includes the debt of buyers and customers for goods and services - it is possible to secure them with bills of exchange.
This type includes settlements with the budget, repayment of debts on advances paid, accrual of income for the provision of funds for use, internal settlements, etc.
Short-term receivables are treated as payment subject to adjustment of the allowance for doubtful debts or overdue and bad debts. It dominates the total amount of debt because deferment of payment on debt for a period of more than a year is very rare.
Ways to reduce doubtful and hopeless receivables
Every entrepreneur faces a dilemma: to hold up funds in receivables or miss out on profits by refusing potential clients. Therefore, it is important to determine in advance the maximum amount of receivables, taking into account the cost of borrowed funds that will need to be taken before the debtors are settled. In addition, do not miss the point that not all counterparties can be financially disciplined. And also include the possibility of force majeure and other unforeseen delays when crediting funds.
To minimize the risks of doubtful and bad debts, you can use the following tools:
| Name | Description |
| Advance payments | If all contracts provide for 100% prepayment, then most of the receivables will not be generated. The downside is that not all clients are ready to work according to this scheme, and this will directly affect profits and lost benefits. This option is only suitable for monopolists or areas where there is very little competition. |
| Securing the deal | The security may be a pledge, surety or bank guarantee. In case of violation of contractual obligations, the guarantor assumes obligations to fulfill settlements. Or the supplier's collateral becomes at the disposal of the enterprise. |
| Letter of Credit | With this settlement option, the bank takes part in the transaction and issues the letter of credit. The money does not go directly to the seller, but to a special bank account. After this, the bank informs the supplier about the crediting of funds, and he ships the goods or provides the service. When the supplier provides documents on the fulfillment of obligations to the bank, he receives a settlement. The letter of credit form of payment protects the interests of both the seller and the buyer, but you will need to pay a third party for the service - the bank. |
To reduce risks, before concluding a contract, you should conduct an examination of the counterparty:
- check the condition of fixed assets and the level of solvency of the partner;
- find out information about the company and its authority in the field;
- check inclusion in the state register;
- on the FSSP website, monitor for the presence of initiated cases and enforcement proceedings against the company;
- find out all available information about the manager and financially responsible persons.
In addition, it is important to pay attention to those representatives of the counterparty who sign the agreement. Check their powers and rights to take such actions so that the transaction is legal.
An increase in accounts receivable - what does this mean, consequences
The dynamic growth of accounts receivable leads the company to certain financial difficulties. The desire to increase profits by any means possible without taking into account the possible consequences can lead to disastrous results.
For the banking system, an increase in accounts receivable means “pulling out” working capital from circulation and providing it to the borrower in order to receive additional income by returning the loan taken by the client with interest for using the loan. Non-repayment of a loan is a loss of the bank’s own money, and if the number of hopeless defaulters grows and the corresponding work to repay debts is not carried out, then the bank faces losses leading to inevitable bankruptcy.
Also for a trading company, a long-term debt to defer payments for services provided or products supplied can lead to unpleasant consequences in terms of the financial state of affairs and lead to a court settlement.
The solvency of an organization directly depends on the successful management of current assets, and preventing the growth of accounts receivable will prevent a shortage of working capital. If there is inadequate control over payment and settlement discipline and loans are provided without sufficient consideration of the borrower’s solvency, analysis of his reliability in repaying the loan, or market monitoring, then in this case the organization obviously dooms itself to a decrease in the liquidity of its own assets and a decrease in funds in its accounts.
The main goal of the company's management is to keep debt within an acceptable level, which depends on the size of the enterprise, on production volumes, on its territorial affiliation and on many other factors.
What to do with problem receivables
When the debt has already been classified as a doubtful receivable, all is not lost for the company that is owed. First of all, you should start the process of systematic work to collect the debt. Legal methods consist of the following steps:
- The first step is for the debtor to declare his company bankrupt. This development of events is not suitable for all businessmen. A complaint filed by a debtor to the tax service stimulates regulatory authorities to increase their attention to the debtor company. In some cases, this leads to faster settlement of doubtful accounts receivables.
- Sell the receivable to a collection agency. The amount that will be paid upon redemption rarely exceeds 30-50% of the total debt. But if the company is desperate to get its money back, then this approach will help reduce the losses incurred.
- File a lawsuit. In this case, the term of the debt should not exceed 3 years from the date of occurrence. The case is considered from 2 to 6 months.
- At the next stage, work takes place with bailiffs who help return the receivable.
- Contacting the debtor's bank. When a court decision is made, the bank is obliged to fulfill it. If there is money left in the debtor’s accounts, it will be used to pay off obligations.
- If nothing helps and the receivable remains, then all that remains is to write it off at the expense of your own created reserve.
Another way to minimize the risk of non-collection of receivables is to insure them. The insurance contract specifies the conditions of the insured event, the rules for assessing the solvency of the supplier and other points that will help regulate the actions of the parties.
about the author
Klavdiya Treskova - higher education with qualification “Economist”, with specializations “Economics and Management” and “Computer Technologies” at PSU. She worked in a bank in positions from operator to acting. Head of the Department for servicing private and corporate clients. Every year she successfully passed certifications, education and training in banking services. Total work experience in the bank is more than 15 years. [email protected]
Is this article useful? Not really
Help us find out how much this article helped you. If something is missing or the information is not accurate, please report it below in the comments or write to us by email