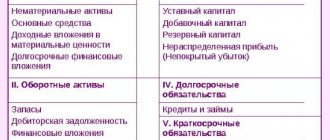
Accounts receivable is an amount that shows how much an organization owes to other companies, individuals, and other business entities. In this article we will tell you what the concept of accounts receivable includes, what account it is reflected on, and how information about it must be shown in the financial statements.
Accounts receivable include amounts that are due to the company for transfer from various creditors. It can arise as a result of various facts of economic life, for example:
- Products have been shipped to the buyer, but payment for them has not been received;
- an advance payment is made to the supplier for a future delivery;
- paid wages to company employees in advance;
- taxes and fees paid to the budget in excess.
In order to reflect that the company has acquired receivables, the accounting account is determined depending on the type of obligations, according to the Plan approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n dated October 31, 2000.
What is accounts receivable and how to avoid writing it off?
Accounts receivable (RA) are the debts of counterparties (legal entities and individuals, including company employees) for delivered products (goods, services).
The occurrence of DZ is due to a number of reasons, including:
- sales of products with deferred payment;
- purchase of raw materials and other property on an advance payment basis with a delay in delivery;
- insolvency of counterparties or their dishonesty;
- other similar reasons.
Receivables are funds diverted from circulation, and it is important for a company to properly structure work with such debts so that diverted funds are returned to circulation in a timely manner, and hopeless funds and those with expired statutes of limitations are written off on time.
In order not to lose finances, not to “delay” payment relationships with debtors and not to divert resources to processing the write-off of debt, it is necessary to properly organize comprehensive work with receivables, including:
- debt planning (dividing debts into critical and working);
- organization of work with defaulters (formation of regulations for working with contractors on debt claims, setting deadlines for sending reminders to debtors about debt repayment, appointment of responsible persons for representing the interests of the company in collecting debt claims in court, etc.).
Writing off receivables in tax accounting has its own peculiarities. ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to correctly reflect write-offs in tax accounting. Full trial access to the K+ system can be obtained for free.
Financial specialists and accounting employees perform their functions in this set of activities, including:
- monitoring the timing of payment of debt in accordance with concluded agreements in order to form a reliable amount of the reserve for doubtful debts;
- regular inventory of debts;
- timely identification of debts with expired statute of limitations and bad debts.
If, as a result of working with the receivable, it was not possible to collect or reclaim some of the debts, they must be written off from the accounting accounts in a timely manner. What kind of transactions accompany the write-off of accounts receivable will be discussed in the next section.
On our forum you can clarify the correct solution to any problem that you encounter during accounting. For example, here they will help you understand how to write off the advance payment received from the buyer after the statute of limitations has expired.
Find out more about the types and accounting nuances of financial statements (including from the standpoint of IFRS) from the materials on our website:
- “Accounts receivable are...”;
- “Accounting for accounts receivable according to IFRS.”
Discounts
The contract with the buyer may provide for discounts if certain conditions are met. The discount can be expressed:
- In price reduction
- In kind (receiving free goods or additional goods)
If a discount is provided at the time of shipment or before the transfer of goods, then the company must reflect the sale according to the documents, taking into account the price reduction.
If the discount is provided after shipment, then it is necessary to prepare an adjustment invoice.
Write-off of overdue accounts receivable – postings
Writing off debt is a process that is necessary and important for any company. It allows:
- generate information about real debts to be repaid or required to be collected;
- reflect it reliably in reporting.
To write off accounts receivable, entries can be of two categories:
Basic:
- Dt 63 Kt 62 (76, 60, 58. 3) - written off DZ due to the reserve for doubtful debts;
- Dt 91-2 Kt 62(76, 60, 58. 3) - DZ not covered by the reserve was written off.
Additional:
Dt 007 - reflection of the written-off DZ on the balance sheet (within 5 years).
Find out what happens with VAT when you write off a property loan from the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. Trial access to the system can be obtained for free.
To reflect the write-off of property in accounting, it is not enough to use the indicated transactions - you must first carry out a number of organizational and design procedures:
- create an inventory commission and, within the time limits established by the order, carry out an inventory of the property, documenting its results in a separate document (for example, in an act form No. INV-17 or another document independently developed by the company and approved in its accounting policy);
- take measures to restore documents confirming the presence, type and size of the remote control if, as a result of the inventory, their absence or insufficiency is revealed (clause 1, article 9 of the law dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ);
- issue an order to write off the receivables (clause 77 of the Regulations on accounting and reporting, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n).
The material “Inventory of receivables and payables” will help you learn more about the inventory procedure.
Only after all preliminary procedures is it possible to write off the debt from the accounting accounts. In this case, special attention must be paid to the corresponding accounts - write-off of receivables according to accounting standards can occur due to the reserve formed not only for regular receivables reflected in accounts 60, 62 and 76 (sellers, buyers, customers and other debtors), but also in correspondence with account 58.3, which reflects issued loans. For tax accounting purposes, this approach is unacceptable - more on that in the next section.
Non-monetary payment of obligations
The contract may stipulate that the buyer will repay his debt with non-monetary means.
When repaying a debt with a bill of exchange, you need to open a separate sub-account for it in account 62. And when repaying the debt, the following entries are made:
- Debit 62 Credit 62 – a bill of exchange was received to repay the debt
The organization shipped goods worth RUB 223,742 to the buyer. (VAT 34130) their cost is 112,120 rubles. The buyer issued a promissory note to repay the debt. He paid it off after 2 months.
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 62 | 90.1 | Revenue from the sale of goods is reflected | 223 742 | Packing list |
| 90.3 | 68 | VAT on sales reflected | 34 130 | Invoice ref. |
| 90.2 | 41 | Products written off | 112 120 | Packing list |
| 62.3 | 62.1 | Bill received | 223 742 | Accounting information |
| 62.3 | The bill has been repaid | 223 742 | Bank statement |
How to write off bad receivables in tax accounting
It is possible to write off debt in tax accounting in the following order:
- at the expense of the reserve for doubtful debts formed under clause 5 of Art. 266 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- reflect the DZ as part of non-operating expenses (subclause 2, clause 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It should be clarified that not all overdue and unsecured receivables allowed in accounting fall into the tax reserve. For the purposes of tax accounting, only DZ is reserved that is directly related to the sale of goods (works, services).
When writing off receivables, quite a lot of controversial situations arise. You will find a selection of law enforcement practices on many of them in K+. Get free trial access, go to the Encyclopedia of Dispute Situations and find out, for example, whether it is possible to take into account the liability in expenses if you have not taken measures to collect it; or if the debtor is declared inactive and excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities by tax authorities, etc.
In addition, you need to remember the following important nuances:
- writing off debt will directly increase non-operating expenses if the company decides not to create a tax “doubtful” reserve - unlike accounting in tax accounting, this reserve does not need to be created;
- Companies that use the cash method of calculating income tax are forced to write off their income tax immediately as part of non-operating expenses - the formation of a reserve for them is not provided for by law.
Use (restoration) of the previously created reserve for doubtful debts
All any changes that occur with existing debts are reflected in the amount of the previously created reserve. This means that in the case when a debt for which a reserve had already been created earlier, for justifiable reasons, passes into the category of bad debts based on the inventory carried out and subsequently generated orders, the debts are written off as they are recognized as non-operating expenses.
At the same time, it is necessary to recall that these debts do not disappear anywhere after being written off as losses; accounting keeps them in a specially created off-balance sheet account.
At its core, this operation is an adjustment to the estimated value, just as the repayment of the debt itself affects the amount of the created reserve. The only difference is in the accounting entries that the accountant creates for each specific operation based on its functional meaning.
Results
Writing off accounts receivable is a multi-stage procedure, including organizational (creating a commission and conducting an inventory), registration (documentation of orders and inventory acts) and accounting (making accounting entries) steps.
It is possible to write off receivables through the reserve for doubtful debts or directly as part of expenses (other - in accounting, non-operating - in tax accounting).
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Is past due debt an asset or an expense?
A receivable with an expired statute of limitations (overdue and hopeless for collection) cannot be included in current assets for the following reasons:
- it does not meet the criteria for an asset;
- the likelihood of repaying the overdue debt is minimal or zero (the company is unlikely to receive cash or other economic benefits);
- According to accounting and tax accounting standards, it is subject to write-off.
Thus, receivables with an expired statute of limitations are not reflected in the balance sheet and must be written off as expenses (or through a reserve).
Writing off earlier or later than the limitation period means that:
- information about the amount of debt of debtors in accounting will be distorted;
- claims and sanctions from regulatory authorities are possible.
In this case, it is important to correctly calculate the statute of limitations, taking into account the following rules:
- the debt is written off if 3 years have passed since the payment date established by the contract (Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), and no funds or other assets have been received from the buyer;
- the statute of limitations was not interrupted.
Both the debtor and the creditor can interrupt the limitation period if:
- the creditor went to court to collect the debt;
- the debtor acknowledged the debt: signed a reconciliation act, sent a written promise to repay it, admitted the claim, etc. (Article 203 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
After these steps, the calculation of the limitation period starts from scratch.
It should be noted that repayment of part of the debt does not interrupt the statute of limitations for the remaining outstanding amount (clause 20 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated September 29, 2015 No. 43).
The statute of limitations has another limitation date - it cannot last more than 10 years from the date of violation of the right (even if it was interrupted for some reason).
When the suspension and restoration of the limitation period occurs, see the material “Limitation period for accounts receivable” .
Find out more about overdue accounts receivable in a situation where the statute of limitations has not yet expired.
Effective methods of collection
Unfortunately, the relationship of trust between the parties to a transaction, where the service is provided and the money must be paid later, is not always justified. There are times when you need to return your funds almost with a fight. That is why we will consider several effective measures for debt repayment:
- Negotiable. In this case, you can communicate with the counterparty. The seriousness of intentions will be evidenced by penalties, interest, penalties and other penalties for each overdue day. As a rule, the risk of a significant increase in debt forces counterparties to rush to make payments.
- Pre-trial negotiations. The purpose of this method is to find a constructive solution to resolve the situation. For example, if the financial condition of the debtor is not in the best shape, installment/deferred payment measures or changes in the terms of their payments may be proposed. But making concessions to the debtor is usually beneficial only if he is a regular client and can be trusted.
- Trial. This is the most popular and effective method of returning money. Its disadvantage is the time that needs to be spent to achieve the desired result. In addition, paying legal fees is often not cheap. But if the decision is in favor of the plaintiff, the debt is almost guaranteed to be collected.
- Criminal procedure. A good example when you can use this method is if the supplier refuses to ship an item for which you have already paid. You can contact the criminal authorities even if bankruptcy proceedings begin. This behavior is clearly suspicious and indicates fraud.
In any case, if it is possible to collect the debt, you need to do it. It doesn't matter whether it's a large amount or not.
How to write off arrears from counterparties and overpayments of taxes?
When debts are displayed in account 91.2, accounts receivable are also written off at the same time to off-balance sheet account Dt 007. The legislation provides for a procedure by which the procedure is carried out separately for each debtor.
After write-off, the debt remains on the off-balance sheet account of the legal entity for no more than 60 months. During this period of time, the organization may find additional (reserve) funds to repay it. Only after the specified period has passed, the debt is completely written off. The entry in the off-balance sheet account changes from 007 to Kt 007.
In cases where the balance sheet contains data on overpayments of taxes or other forms of government payments, the company is required to conduct a reconciliation with the Federal Tax Service. The organization must apply for a refund of overpaid funds within 3 years.