Labor legislation guarantees full and timely payment of wages to employed citizens. In this case, the payment should not be lower than the minimum wage established by law. If the employer, for one reason or another, does not comply with this rule, the employee has the right to file a complaint against him and defend his rights in court. You will have to answer for the violation.
The article explains what exactly employees need to do if the employer deliberately lowers the minimum wage in its own interests and when a reduction in the amount of wages would be legal. In addition, the issue of liability of employers who violate the labor rights of citizens is revealed.
- Where can I complain about low pay?
Differences between salary and minimum wage
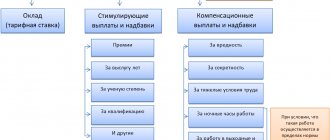
Salary is considered a broader concept than salary.
It includes the main part in the form of salary, which is fixed as the size of the tariff rate or the base salary. Compensatory additional payments provided for by law and the employer are added to the main part (Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Supplements include the following:
- monthly bonuses;
- one-time, annual rewards;
- additional payments for difficult and harmful working conditions;
- other compensation payments provided for in the contract.
You cannot directly compare the salary itself with the minimum wage; there is no relationship between these values. Whether the salary can be less than the minimum wage in a budgetary organization or in enterprises with private capital - the form of ownership in this matter is not of fundamental importance.
If the employee’s salary, which includes salary and additional allowances, is greater than or coincides with the minimum wage, then there is no violation on the part of the employer in this case. A violation is considered to be the case when the employee’s salary with all applicable allowances is below the minimum wage.
Compliance of wages with the approved minimum wage does not exempt the employer from paying personal income tax. Therefore, after paying the tax, the employee will receive an amount that will be less than the minimum wage, which is not considered a violation of the law.
For example, in 2021 the minimum wage = 12,130 rubles. After paying 13% personal income tax (12,130 – 11,280 x 13%) = 12,130 – 1466 = 9814 rubles, the amount of the salary that the employee will actually receive.
Example of savings
Employees who switch to part-time working conditions will receive a salary based on how much they worked (at least according to documents). This means that wages will decrease proportionally. For example, if a full-time salary is 11,163 rubles, then for a seven-hour day, this is 0.875 of the full rate, it will be 9,767.63 rubles. (RUB 11,163 × 0.875). Thus, employee salaries will remain almost at the level of the previous minimum wage - 9,489 rubles. And the employer will feel the savings (including savings on insurance premiums).
Legal standards
The Constitution of the Russian Federation reserves for every citizen the right to free labor activity, which must be paid no less than the fixed minimum wage (Part 3 of Article 37 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation).
Detailed regulation of labor relations between the parties to an employment contract follows the following standards:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation;
- regulatory legal acts of a narrow focus (for example, explanatory letters from the Ministry of Labor, the Federal Tax Service).
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation has established that the monthly wage of an employee who has worked the required working hours for a month must not be lower than the minimum wage adopted at the federal level (Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, when asked whether a salary can be lower than the minimum wage, the legislator provides for the possibility of paying less than the established limit in situations where the employee did not work the established working hours and (or) did not fulfill the established labor standard.
How does the increase in the minimum wage in 2021 relate to the cost of living?
Article 133 of the Labor Code determines that the minimum wage cannot be less than the subsistence level of the working population. From January 1, 2021, the minimum wage will be based on the median salary.
Median salary is a value that conditionally divides all workers into 2 categories; the first will have earnings higher than it, and the second will have lower earnings. The new minimum wage will be 42% of this value.
Here's what the Ministry of Labor approved for 2021:
| Living wage, rubles | Category |
| 12702 | Able-bodied citizens |
| 10022 | Pensioners |
| 11303 | Children |
Thus, the cost of living is updated every year, and with it the minimum wage also changes. Most often in the direction of weak growth to cover inflation.
Deputy Prime Minister T. Golikova announced that in 2021 the minimum wage will exceed the subsistence level for the first time.
When the regional minimum wage can be higher than the federal one
The same norm of the Labor Code provides for the right of constituent entities of the Russian Federation to approve a minimum wage higher than the federal value, but funding will already come from the budget of a specific region. If the employer has not completed the procedure for abandoning the regional minimum wage in favor of the federal one, he will have to pay at the regional rate.
For example, in Moscow the minimum amount is higher than the federal one and is about 20,000 rubles for 2021. The employer has the right to abandon the Moscow minimum wage and switch to the federal rate. Only when registering a refusal, it is necessary to meet the 30-day period from the date of official publication of the cost of living by the Moscow government.
The law establishes a classification of budgets that provide subsidies to the minimum wage:
- for budgetary enterprises and organizations - these are funds from a national source;
- budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (regional) and funds received from commercial activities;
- For private businesses, the source of financing the minimum wage is the entrepreneurs’ own funds.
Territorial coefficients and bonuses for those working in the Far North and areas equivalent to it are calculated in excess of wages and are not included in the minimum wage (Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation No. 38-P of December 7, 2017).
In 2021 the minimum wage is 12,130 rubles.
What should an employee do if the salary is low?
Next, let’s look at a company employee who is paid little (below the minimum wage) and find out where to apply and where it’s pointless. We will also give step-by-step instructions for action.
Where can I complain about low pay?
You can file a complaint about wages below normal to the following authorities:
- Trade union organization . It is authorized to evaluate the activities of employers and verify their compliance with labor standards.
- Prosecutor's office . Here they mainly consider complaints against government agencies. For this reason, it is better to complain here about state or municipal structures if the latter have committed violations in the labor sphere.
- State Labor Inspectorate . Authorized to conduct inspections in all cases of violation of labor standards by employers.
- Court . If there are supporting documents, then you can defend your legal rights through the court. Applications are accepted either by the district court or the magistrate.
Prosecution
To understand how to act in a specific situation of violation of labor rights, first of all, you need to familiarize yourself with the general procedure for bringing perpetrators to justice.
Step 1. Submitting a complaint to the State Tax Inspectorate
We have already discussed the process of filing a complaint in detail separately here, so below we will only briefly recall the main points.
This organization is primarily authorized to verify the facts stated in citizens' complaints and respond to them. The purpose of the inspection is to identify and eliminate violations of the labor rights of citizens. The culprits will definitely be brought to justice.
The organization carries out verification of all complaints, provided that they are not anonymous. It is possible to hide the identity of the complainant upon a separate written request from the complainant.
You can submit a complaint in person, send it by mail (including e-mail), using the State Services portal, through the official GIT portal or the onlineinspection.rf service.
Step 2. Inspection of the employer by Rostrud inspectors
Based on the submitted complaint or application, an unscheduled inspection of the potential violator will be initiated. During the inspection, other violations of labor laws may also be revealed. Liability for each violation will be separate.
The legal basis for inspections is the Labor Code and FS No. 294 of December 26, 2008. Such inspections are carried out suddenly, without warning the organization’s management.
Inspectors are authorized to check a fairly wide list of documentation: constituent, local, affecting a specific area of interaction between employees and administration, relating to accruals, payments, additional payments for work performed. The full list of powers is specified in Article 357 of the Labor Code.
Step 3. Issuing an order to eliminate the violation
When cases of violations of labor legislation are identified, the inspector prepares and submits to the organization an order to correct them.
The document describes the violations and how they can be corrected. It should be clear how exactly the inspector will check the results of correcting the situation.
After the expiration of the instruction, representatives of Rostrud will conduct an additional unscheduled inspection of compliance with the requirements.
An extension of the period allotted for correcting a violation is possible, but at a separate request from the employer and if there are good reasons. Such a petition to extend the deadline for fulfilling the order is submitted no later than 10 working days before the end of the period stated in the order for correcting detected violations of labor legislation (Administrative Regulation No. 354n dated October 30, 2012).
If signs of major violations (administrative and criminal) are detected, the materials are transferred to law enforcement agencies or the court (Article 357 of the Labor Code).
Step 4. Go to court
After going to court, an employee whose labor rights have been violated has the right to demand part of the unpaid wages and compensation.
The period for employees to file a lawsuit is limited to 1 year. It is counted from the moment when the salary should have been paid in full (Part 2 of Article 392 of the Labor Code).
It is recommended to contact the above-mentioned supervisory authority in advance. Documents collected by the inspectorate after an inspection of the organization will be useful.
When going to court, an employee has the right to claim payment from the employer:
- compensation for the entire period during which he received payment below the established minimum;
- additional monetary compensation for delayed payments;
- moral damage in financial equivalent.
Additionally, the employer will be held liable for evading mandatory tax payments.
There is no need to pay a state fee when filing a claim (clause 1 of part 1 of Article 333.36 of the Tax Code).
When is paying wages less than the minimum wage legal?
Let's look at a situation where a salary can be legally less than the minimum wage. This applies to cases where the employee did not reach the established production standard and (or) did not work the required amount of working time.
Who can be paid less than the minimum wage (Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- labor activity was not started from the beginning of the billing month or was completed before the end of the month;
- there was a deprivation of wages for the period of absenteeism;
- fact of downtime at work due to circumstances not related to the employer’s decision;
- employee leave at his own expense;
- part-time employment. Remuneration in this case is calculated in accordance with the days and hours worked;
- the employee made a defect, which is either not paid, or the calculation is based on a reduced price list;
- the employee did not pass the established production standard;
- the salary is less than the minimum wage, but there is a bonus;
- temporary incapacity for work (sick leave). Only days actually worked are paid; sick leave compensation comes from Social Insurance Fund funds.
If it is not an employment agreement, but a GPC agreement, then the employer is not obliged to comply with the minimum wage.
When the salary is not established or is small, the minimum wage is applied, for example, when calculating sick leave or maternity benefits.
Employer's responsibility for wages below the minimum
The law indicates that if the administration of a business entity has set its employee’s salary less than that provided for by the current labor legislation, then it will be held liable in accordance with Part. 6, 7 tbsp. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The same article punishes non-payment of wages on time.
In addition, the manager may become disqualified for a period of 1-3 years.
Also, partial non-payment of wages for 3 months, complete non-payment for 2 months or more, as well as payment of wages less than that established by law for 2 months and are more subject to punishment in accordance with Art. 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Part-time work: Labor Code
Set the following work schedule for accountant A. A. Ivanova:
- Five-day work week with two days off.
- Working hours: Monday – Friday: from 9:00 to 17:00, lunch break: from 13:00 to 14:00.
- Reducing the duration of daily work by one hour.
- The working week is thirty-five hours long.
The accounting department will calculate A. A. Ivanova’s salary in proportion to the time she worked.
4. Entrust control over the implementation of the order to the Deputy Director for Personnel V. Khorkina.
V. Chief Accountant Tsvetkova I.P. Head of HR Department Ershova A.
T. Deputy Director for HR Khorkina V.
B. All agreements or additions to them are made only in writing (Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Of course, all changes in the employment contract should not worsen the position of employees in comparison with the clauses of the collective agreement.
Part-time salary 2021 according to Russian law
There is only one limitation: during the month, the total time of part-time work should not exceed 1/2 of the monthly work rate at the main place of work.
For each employee, a personal registration card is also issued in the T-2 form, and if, in addition to the main job, the person also has a part-time job, then in this case 2 cards will be issued.
Based on the provisions of Art. 60.1 of the Labor Code there are 2 main types of part-time work - internal and external. Each of them has its own characteristics.
In what cases is it possible to extend an employment contract? Find out here. This is a job with the same employer, only in a different specialty if he has available positions. Any part-time job requires the execution of an additional employment contract, in which