Who should undergo occupational safety training?
Every employee (including the head of the organization), as well as the individual entrepreneur who hired employees, must undergo training.
This follows from Article 225 of the Labor Code and paragraph 1.5 of the Procedure for occupational safety training (approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Ministry of Education dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29; hereinafter referred to as the Procedure). Complete training and receive a certificate of occupational safety specialist Submit an application
ATTENTION
Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that the employer must provide training for employees in safe methods and techniques of work. He also has other responsibilities: training in first aid for victims at work, conducting occupational safety training, on-the-job training, testing knowledge in the field of labor protection.
Who does the employer entrust to organize the listed events? Depends on how many people work at the enterprise:
- more than 50 people - an occupational health and safety specialist (with such a number of personnel, this position must be on staff);
- 50 people or less - to any employee assigned the corresponding functions, or to a third-party contractor.
Prepare labor safety documents in a special service Try for free
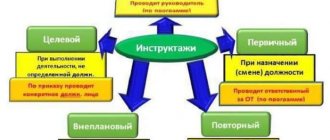
The difference between training and instruction
It can be difficult to understand the difference: how training differs from instruction. Their performers have different levels. Thus, OT training can only be carried out by a person who has completed special courses with confirmation of the level of knowledge and skills by a special commission. Whereas the instruction is carried out by the person in charge. This is due to the essence of the information transmitted and received.
Must have undergone both instruction and successfully completed training.
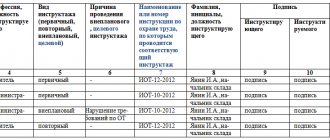
During the briefing, the personnel are informed of the basic requirements aimed at carrying out activities that are not hazardous to health and life, using equipment, and observing fire safety. Until the instruction has been completed, the employee is not allowed to enter his place of work. In addition, the training has the following features:
- relative short duration. The duration of the briefing rarely exceeds 2-3 hours;
- demonstration of safe operation of equipment and tools at a specific workplace;
- no time is provided to prepare answers to questions. Employees are interviewed immediately after completing the training;
- for instruction, the frequency is set at least once every 6 months.
Training is longer. Its main feature and difference from briefing lies in the fact that an employee can perform his duties without going through it. And again, training is usually carried out only once. Next comes only the assessment of knowledge and skills, which usually happens successfully.
Important : re-training is required only if there is a break of more than a year, failure of the test and a change in the work environment.
How to organize training on labor protection for employees
Occupational safety training for managers and specialists
Workers belonging to this category must undergo instructions and, separately, training in occupational safety.
Clause 2.3.2 of the Procedure lists positions for which, in general, it is necessary to undergo a training course at training centers. The list includes, in particular:
- heads of organizations;
- deputy managers supervising occupational safety issues;
- deputy chief engineers for safety;
- employers - individuals and other persons engaged in business;
- supervisors, specialists, engineering and technical workers who organize, manage and carry out work at workplaces and in production departments, as well as control and technical supervision of work;
- occupational safety specialists and employees entrusted with labor protection functions;
- members of the commission (committee) on labor protection or the commission for testing knowledge of occupational safety requirements;
- OSH representatives in trade unions.
IMPORTANT
Not every organization can provide training. The training center must be accredited in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated April 1, 2010 No. 205n. This was indicated by the Ministry of Labor in letter dated 02.13.18 No. 15-2/OOG-289. It is also necessary that there are teachers on staff, and that the curriculum includes disciplines on occupational safety and health (clause 2.3.6 of the Procedure).
Complete training at Kontur.School and receive a diploma in occupational safety and health
It is not necessary to train all managers and specialists of the organization in a third-party center. It is enough to send at least three workers there, and then form a commission from them to test their knowledge of labor protection requirements. If there is such a commission, the remaining employees can be trained by the employer (clause 2.3.2 of the Procedure).
Plus, managers and specialists must have knowledge of fire safety standards (clause 32 of the Fire Safety Standards, approved by order of the Ministry of Emergency Situations dated December 12, 2007 No. 645).
Occupational safety training for blue-collar workers
Employees of blue-collar professions must undergo occupational safety training and be trained in fire safety standards.
In addition, they need to gain knowledge:
- about safe methods and techniques for performing work (for those whose working conditions are harmful and (or) dangerous, they also need on-the-job training and passing exams);
- on providing first aid to victims.
This is stated in paragraphs 2.2.1-2.2.4 of the Procedure.
Screening test for blue-collar workers
Employees' knowledge of health and safety rules can be tested in various ways: from an exam (written or oral) to special computer testing using specialized programs.
Specialized health and safety tests are of particular importance for members of the workforce in blue-collar professions.
IMPORTANT! Blue-collar professions, unlike managerial ones (coordinating the work of other people), are associated with the performance of specific production operations by employees.
For example, in construction, representatives of such professions include masons, concrete workers, plasterers, painters, crane operators, and in metalworking, turners, mechanics and welders.
The defining feature when classifying a profession as a worker is the presence of many hazardous production factors, from which knowledge of occupational health and safety requirements will help protect you. For each working profession, screening tests must be developed taking into account their labor functions, requirements for the mechanisms used, working conditions and many other nuances.
An important feature of such tests is the need for their timely adjustment when legislation in the field of occupational safety and health changes, as well as in the presence of innovations in the company’s production process (if these innovations require employees to have special knowledge and skills in matters of occupational safety and health).
To test workers' occupational safety knowledge, you will need a protocol. You can download a sample of such a document, drawn up in accordance with all the rules, in ConsultantPlus, having received trial access to the system.
How often do occupational safety training take place?
The timing and frequency depend on the type of training and the specifics of the enterprise (see table).
Table
Time frame for completing occupational safety training
| Training program | When to take it for the first time | How often to repeat |
| For managers and specialists | ||
| OT training | Until June 16, 2020 - within 1 month upon starting a job. Starting from 06/16/20 - within 3 months from the date of entry to work (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 06/11/20 No. 849; see “Validity periods have been extended for the results of SOUT”). | At least once every 3 years. |
| Fire technical minimum | Within 1 month after hiring. | If the organization is not associated with fire and explosion hazardous production, then once every 3 years; if connected, then once a year. |
| For representatives of working professions | ||
| Training in safe methods and techniques for performing work | Within 1 month after hiring or transfer to another job (starting from 06/16/20 - within 3 months from the date of admission or transfer; Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 06/11/20 No. 849; see “For the results of the SOUT, the validity period has been extended "); within 1 month after resuming work in the profession, if the break lasted more than 1 year; when preparing an employee for a working profession; when retraining and mastering another working profession. If working conditions are harmful and (or) dangerous, internship and exams are required. | The frequency is set by the employer based on safety standards for specific types of work. |
| Providing first aid to victims | Until June 16, 2020 - no later than 1 month after hiring. Starting from 06/16/20 - within 3 months from the date of admission or transfer; Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated June 11, 2020 No. 849; see “Validity periods have been extended for the results of the SOUT.” | At least once a year. |
| Fire technical minimum | Within 1 month after hiring. | If the organization is not associated with fire and explosion hazardous production, then once every 3 years; if connected, then once a year. |
Retrain and improve your skills in the field of labor protection
ATTENTION. Special rules have been introduced for the case when the validity period of the learning results expires in the period from April to September 2021. In this situation, the validity is automatically extended until October 1, 2021 (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated June 11, 2020 No. 849; see “Validity periods have been extended for SOUT results”).
Frequency of training for different categories of employees
The frequency of this depends on the working conditions. Thus, if work activity is accompanied by an increased risk in relation to the health and performance of employees, then, according to current regulatory documents, the validity period of the obtained assessment for existing knowledge and skills is reduced. For example, when working at heights, in a metallurgical plant and a mine.
Important! The frequency varies regardless of the employee’s status - manager, specialist or simple worker. If their working conditions are normal, then they are given three years. Otherwise, there is only one.
Testing knowledge of labor protection requirements
The knowledge of managers and specialists must be checked at least once every 3 years (clause 3.2 of the Procedure).
ATTENTION. If 3 years have expired between April and September 2021, the validity period of the results of the previous inspection is extended until October 1, 2021 (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated June 11, 2020 No. 849; see “Validity periods have been extended for SOUT results”).
The frequency of inspection for blue-collar professions is established by the employer in accordance with regulatory legal acts (LLA) for specific types of work (clause 2.2.3 of the Procedure).
In a number of cases, an extraordinary inspection is required:
- when introducing new or changing existing regulations on labor protection;
- when commissioning new equipment and changing technological processes;
- when assigned or transferred to a new job that requires additional knowledge in occupational safety;
- at the request of labor inspectorate officials or other bodies;
- after accidents and incidents;
- in case of repeated violations by employees of regulations in the field of labor protection;
- during a break in work in a particular position, if the break lasted more than 1 year.
To conduct an inspection (both scheduled and extraordinary), it is necessary for the manager to appoint a commission, which consists of a chairman, deputy, secretary and other participants.
REFERENCE
The commission for testing knowledge of labor protection requirements includes: the head of the organization and heads of structural divisions, specialists from occupational safety services, chief specialists (technologists, mechanics, power engineers). You can also include a representative of trade unions. Moreover, there were at least three people on the commission. This requirement is contained in clause 3.4 of the Procedure.
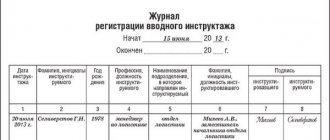
Based on the results of the inspection, the commission signs a protocol. An employee who has confirmed his knowledge in the field of occupational safety receives a certificate (protocol forms and certificates approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Ministry of Education dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29).
Compose HR documents using ready-made templates for free
Training centers can also test OT knowledge. But not for everyone, but only for employees who underwent training there (clause 3.9 of the Rules).
Test results
- The results of testing the knowledge of labor protection requirements of the organization's employees are documented in a protocol.
- An employee who has successfully passed the test of knowledge of labor protection requirements is issued a certificate signed by the chairman of the commission, certified by the seal of the organization that conducted the training on labor protection and testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements.
- An employee who has not passed the knowledge test of labor protection requirements during training is required to undergo a second knowledge test no later than one month.
What to do if an employee has not passed the labor safety knowledge test
According to the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an organization or individual entrepreneur is obliged to remove from work a person who “failed” an occupational safety exam. But you can't fire him. Instead, the employee is given a second chance - within a month after the first attempt. This is stated in paragraph 3.8 of the Procedure.
What to do if the re-exam is not passed? There is no clear answer. It is clear that dismissal is still impossible, since such a reason is not included in the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It turns out that the test should be carried out until the employee passes it.
About types of certification
There are three types of occupational safety certification for workers.
| View | Description |
| Primary | Conducted within the first month from the date of appointment of the employee to the position. This kind of certification is organized through preliminary training of employees, and it all starts with training followed by testing of knowledge. Knowledge is checked by a commission headed by the chairman, and those participating in the examination must have in their hands an OT certificate for the right to be members and chairman of the AC. |
| Periodic | It is carried out at a given frequency; as a rule, it is planned after three years. That is, it turns out that if the certification deadline is 03/02/2014, then the next deadline is 03/02/2017 and no later. If the certificate indicates the deadline for certification, and for some reason the employee did not pass the scheduled knowledge test in a timely manner, then this is accordingly considered a violation and may be punished by supervisory authorities. |
| Unscheduled | It is not planned, but it makes sense to talk about it in more detail. |
All types of certification are regulated by regulatory documents.