The opening of a new organization, regardless of its organizational and legal form, is accompanied by the need to form an authorized capital - a resource necessary to start activities. There are authorized capital of JSC, LLC (contributions of founders), share capital of business partnerships (shares, contributions of participants), authorized capital of state unitary enterprises and municipal unitary enterprises (funds allocated free of charge to the organization), mutual fund (share contributions of cooperatives). To account for the authorized capital and settlements with the founders (shareholders), accounting accounts 75 and 80 are used, broken down by subaccounts.
Question: How to reflect in the accounting of an organization the acquisition of a share in the authorized capital of a limited liability company (LLC) from an individual (a tax resident of the Russian Federation) who is not an employee of the organization, if the acquisition price is greater than the nominal value of the share? The organization acquired from an individual a fully paid share in the authorized capital of the LLC for 380,000 rubles. The nominal value of this share is 200,000 rubles. Funds are transferred to the bank account of an individual. For notarization of the purchase and sale transaction of a share in the authorized capital of an LLC, the organization paid a state fee in non-cash form. The organization uses the accrual method of tax accounting. View answer
Essence and types of management company
Forming an authorized capital (AC) is the responsibility of commercial organizations (Clause 1, Article 66 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Article 12 of the Federal Law “On State and Municipal Unitary Enterprises” dated November 14, 2002 No. 161-FZ), including:
- public and non-public joint stock companies (PJSC and JSC; abbreviations are given in accordance with the recommendations of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, given in letter dated 09/04/2014 No. SA-4-14 / [email protected] );
- limited liability companies (LLC);
- state and municipal unitary enterprises (SUE and MUP);
- business partnerships (HT).
It is called differently in these organizations:
- in business companies (PJSC, JSC, LLC) - authorized capital;
- in unitary enterprises (SUE and MUP) - authorized capital;
- in HT - share capital.
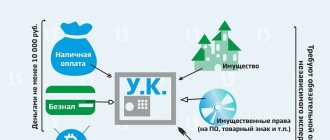
The management capital is the initial amount of funds contributed by the founders (legal entities or individuals, including foreign ones, or constituent entities of the Russian Federation), with which the organization’s activities begin. The decision on its value is made by the first (constituent) meeting of owners, and this value is fixed in the charter. The founders, by contributing their funds, receive the right to part of the legal entity’s property, expressed in shares (PJSC, JSC) or shares (LLC, HT). The owner of all property of unitary enterprises is the state, its subject or municipal entity, and the enterprise disposes of it with the right of operational management or economic management.
The minimum permissible size of the capital is legally limited:
- for PJSC - 100,000 rubles. (Article 26 of the Federal Law “On Joint-Stock Companies” dated December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ).
- JSC and LLC - 10,000 rubles. (Article 26 of Law No. 208-FZ and Clause 1 of Article 14 of the Federal Law “On Limited Liability Companies” dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ).
- SUE - 5,000 minimum wage (clause 3, article 12 of law No. 161-FZ).
- MUP - 1,000 minimum wage (clause 3, article 12 of law No. 161-FZ).
The minimum wage used to determine the size of the capital company in state unitary enterprises and municipal unitary enterprises must correspond to its legally established size on the date of state registration of the enterprise. The minimum wage is regularly indexed and in 2015 and 2021 it is 5,965 and 6,204 rubles, respectively. (Federal Law “On the minimum wage” dated June 19, 2000 No. 82-FZ).
The law does not provide for restrictions on the amount of share capital in HT.
Calculations for the formation of the authorized capital of a unitary enterprise
The founder of a unitary enterprise is a state or municipal body.
In a unitary enterprise, subaccount 75-1 is called “Calculations for allocated property.”
Reflect the formation of the authorized capital of a unitary enterprise by posting:
DEBIT 75-1 CREDIT 80
– the authorized capital of the unitary enterprise was formed.
The actual receipt of property or funds on the balance sheet of a unitary enterprise from its founder - a state or municipal body - should be reflected as follows:
DEBIT 08 (10, 50, 51, 58, ...) CREDIT 75-1
– property (cash) was received from the founder of the unitary enterprise.
Receipt of fixed assets in excess of the amount of the authorized capital is reflected with the following entries:
DEBIT 75-1 CREDIT 84
– reflects the cost of fixed assets to be received in excess of the amounts of the authorized capital;
DEBIT 08 CREDIT 75-1
– fixed assets received in excess of the amount of the authorized capital;
DEBIT 01 CREDIT 08
– received fixed assets are accepted for accounting.
The seizure of property by the owner within the authorized capital is reflected in the following entries:
DEBIT 80 CREDIT 75-1
– the authorized capital is reduced in accordance with the procedure established by law by the initial cost of fixed assets;
DEBIT 75-1 CREDIT 01
– fixed assets written off at residual value;
DEBIT 75-1 CREDIT 91-1
– the difference between the original and residual value of the fixed asset is written off.
Features of the management company
A management company is part of the total capital of a legal entity, which is associated with a fairly large number of requirements established at the legislative level:
- For state unitary enterprises and municipal unitary enterprises, the period for the actual formation of the management company is limited (no more than 3 months from the date of registration of the enterprise).
- Incomplete payment of management companies in PJSC, JSC and LLC prevents the payment of dividends and the issue of bonds. One of the options for limiting the total nominal value of all bonds issued by a business entity is the size of its charter capital.
- In the case of distribution of profits received by a PJSC, JSC or LLC among the owners, this is done in proportion to the shares of their participation in the management company. A different procedure may be established in HT.
- The formed and paid charter capital can then be increased or decreased in accordance with the established procedure. The reduction will only be possible after notification of all creditors.
- In economic societies and HT there is the possibility of leaving the participants. Including a refund of the cost of the deposit made.
- Owners of deposits in PJSC, JSC and LLC are responsible for losses from business activities only within the limits of the amounts of their deposits (even if these deposits are not fully paid by them) and are not liable for other obligations of business entities. The HT provides for additional liability of owners for the obligations of the partnership.
- Critical for the management company may be its comparison with the value of net assets (NA). If the value of the NA of a PJSC, JSC or LLC for 2 years in a row does not exceed the authorized capital, then the authorized capital must be reduced to the value of the AV. If at the same time the private equity becomes less than the minimum size of the capital company established by law, then the economic company must be liquidated. For state unitary enterprises and municipal unitary enterprises, this ratio is checked based on the results of each past year and the value of the authorized capital is immediately (if necessary) adjusted. If the NAV of a state unitary enterprise or municipal unitary enterprise turns out to be less than the minimum allowable capital and this situation is not corrected within 3 months after the end of the year, then the enterprise is subject to liquidation or reorganization.
For information on how to calculate the NAV value, read the article “The procedure for calculating net assets on the balance sheet - formula 2015”
Management account and reporting
Accounting for the authorized capital is kept on account 80 with analytics:
- by founders (participants);
- stages of formation (in PJSC, JSC and HT);
- types of shares (in PJSC and JSC).
The credit balance on account 80 must be equal to the amount of the capital reflected in the charter, regardless of the fact of its payment. The first entry for accounting of the authorized capital is made on the date of registration of the legal entity. Subsequent adjustments to the accounting of the authorized capital are made according to the date of registration of changes made to the charter in relation to the size of the charter capital.
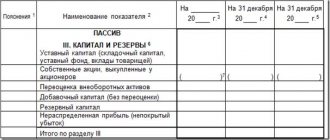
Account balance 80 is reflected in the “Capital and Reserves” section of the balance sheet on line 1310.
Accounting for additional capital
Additional capital is a source of increasing the value of an organization's property.
To account for additional capital, passive balance sheet account 83 “Additional capital” is used.
The formation and increase in additional capital is reflected in the credit of account 83 and can be carried out through:
- increase in the value of fixed assets as a result of revaluation;
- share premium from the issue of securities;
- directing part of the net profit to it;
- formation of exchange rate difference when making a contribution to the authorized capital of foreign currency.
Organizations have the right to revalue fixed assets no more than once a year (at the beginning of the reporting year). The amount of additional valuation of fixed assets as a result of revaluation is charged to additional capital:
D-t 01 K-t 83 - for the amount of increase in value;
D-t 83 K-t 02 - for the amount of increase in depreciation.
The amount of revaluation of an item of fixed assets, equal to the amount of its depreciation carried out in previous periods and attributed to other expenses, is included in other income of the reporting period.
Share premium is generated by organizations when they sell shares of an OJSC at a market price above par value:
D-t 75 K-t 83.
Foreign currency can be made as a contribution to the authorized capital. In accordance with PBU 3/2006 “Accounting for assets and liabilities, the value of which is expressed in foreign currency,” the exchange rate difference associated with the formation of the authorized capital is subject to credit to additional capital.
Added to the additional capital are appropriations received from the budget of any level, which are spent by the organization to finance long-term investments:
D-t 86 “Targeted financing” D-t 83 “Additional capital”.
Entries in the debit of account 83 can be made in the following cases of using additional capital:
- allocation of funds to increase the authorized capital: D-t 83 K-t 75; D-t 83 K-t 80;
- loss repayment: D-t 83 K-t 84;
- distribution of amounts between the founders of the organization: Dt 83 Kt 75.
When disposing of fixed assets, the amount of revaluation is transferred from additional capital to the organization’s retained earnings:
Dt 83 Kt 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss).”
Analytical accounting for account 83 is organized separately for each type of funds from which additional capital was formed.
Synthetic accounting of additional capital is maintained in journal order No. 12.
First contribution to the management company
The formation of a contribution to the capital of the newly created legal entity will be the first entry made in it. And it will reflect the accrual of the capital in correspondence with the debt of the founders for its payment: Dt 75 Kt 80.
Thus, in the accounting of the authorized capital its total value will appear, corresponding to the charter. And actual settlements with the founders on deposits will be carried out on account 75.
The contribution can be made either in money or any other property. The specific form of the contribution and its value are stipulated in the constituent agreement. On the date of actual deposit of money or property, the debt of the founders on the contribution to the capital company is repaid, which is recorded by entries: Dt 07 (08, 10, 11, 21, 41, 50, 51, 52, 58) Kt 75. The balance on the debit of account 75 will show the amount unpaid criminal code. In account 80 in the accounting of the authorized capital, its unpaid part is usually not reflected separately.
Receipts that are a contribution to the capital company are not taken into account in the recipient’s profit base (subclause 3, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Settlements with founders (account 75)
The founder of an LLC can be a legal entity, as well as an individual of the Russian Federation, foreign organizations and citizens. The steps to register an LLC and the nature of the documentation may vary depending on the composition of the founders.
In general, the number of LLC founders should not be more than 50 people. They can be citizens who have reached the age of majority and are legally capable; Persons with limited legal capacity also have the opportunity to engage in business, but only with the consent of the trustee. The founders of the LLC are not liable for its obligations, but bear the risk of losses that are associated with the activities of the Company and are within the value of the shares of the founders of the LLC that belong to them, according to the authorized capital of the LLC.
During the functioning of the organization, it may be necessary to replace the founder.
Rights and obligations of LLC founders
After registration, the founders have certain responsibilities and rights. As the current legislation of the Russian Federation states, LLC participants have the right to:
- take part in the processes of managing the affairs of the LLC
- have access to information about the activities of the LLC and the opportunity to familiarize itself with its documentation in the manner established by the charter of the Company
- participate in the profit distribution process
- exit from the LLC by alienating the share owned by the founder to the Company, if this is provided for by the charter of the LLC or request the acquisition of the share by the Company
- in the event of liquidation of the Company, receive part of the property that remains after settlement with creditors, or receive the value of this property
In addition to rights, LLC founders also have certain responsibilities. These include the obligation to pay for one’s own share in the authorized capital of the Company and a ban on disclosing confidential information relating to the activities of the LLC. LLC participants who have not fully paid their debts are also jointly and severally liable. It is within the value of that part of their shares that is unpaid.
The law of the Russian Federation may also prohibit or limit the possibility of participation of certain categories of citizens in LLCs - for example, military personnel and municipal employees do not have the right to engage in business, including being founders of commercial organizations.
The obligations and rights of the founders of LLC individuals also apply to legal entities, but there are some restrictions. According to the law, local government bodies and state bodies have the right to be the founders of an LLC, unless this is prohibited by law of the Russian Federation.
The liability borne by the founders (participants) of an LLC is minimal. It is for this reason that a limited liability company is the most common organizational and legal form of legal entities.
Accounting for settlements with founders (postings)
After the LLC registration procedure has been completed, in addition to conducting business activities, there is a need to maintain accounting records for the company.
Authorized capital is the amount of funds that the founders are willing to contribute at the very beginning of the company's development. In the future, these funds will be used for the activities of the enterprise.
These funds represent a liability of the enterprise, and will be a source of formation of assets.
To find out on which account the authorized capital is calculated, you need to select it from the Chart of Accounts. There is an account. 80 “Authorized capital”. Its purpose is to take this capital into account. Since the authorized capital is a liability, this means that the account is also 80 is also passive. An increase in a liability is reflected in a credit, and a decrease in a debit.
The Chart of Accounts also contains an account. 75 “Settlements with founders.” This account is needed to carry out all settlements with the founders, that is, payment of dividends, contributions to the authorized capital, etc.
Settlements with the founders of the transaction:
Debit 75 reflects the amount of the authorized capital (debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital).
Loan 75 reflects the founders’ contributions to the authorized capital.
So, let's make the wiring:
D75 K80 - reflects the debt of the founders of the LLC for contributions to the authorized capital.
When repaying a share in the authorized capital, the debt of the founders to the organization decreases. This decrease will be reflected in the credit account. 75. The second account involved in the posting is selected depending on the type of contribution.
Contributions of LLC founders to the authorized capital:
If the share is contributed by non-cash means, the second will be the account. 51 "Current account". In its debit we will reflect the contribution coming from the founder.
D51 K75 - deposit of funds (non-cash) to the current account.
When depositing cash, we enter the contribution amount into the debit of the account. 50 "Cashier".
D50 K75 - contribution to the authorized capital in cash.
The contribution can also be made by property. In this case, the following accounts will act as corresponding accounts: 10 “Materials”, 01 “Fixed assets”, 04 “Intangible assets”, 41 “Goods”, etc.
Postings for the repayment by the founder of the share in the authorized capital with property:
D10 K75 – entry to reflect the contribution in the form of materials;
D41 K75 - contribution in the form of goods, etc.
Receipt of dividends by the founder:
In addition to contributions, dividends are also taken into account in account 75. First, dividends are calculated and then paid out. These are two different operations and they are reflected in two transactions:
D84 K75 – entry for accrual of dividends to founders from retained earnings;
D75 K51 – entry for the payment of dividends to the founders from the current account.
Typical accounting entries for accounting settlements with founders:
During the operation of the enterprise, the founder can provide financial assistance, both free of charge and repayable.
Valuation of contribution by property
The easiest way to pay for a deposit is with money, including foreign currency (for foreign founders). This is due to the fact that the assessment of property contributions in accounting and tax accounting differs greatly.
In accounting, property entered into the charter capital is accepted at its value agreed upon in the founding agreement. This is indicated in the texts of the PBU:
- for OS - in clause 9 of PBU 6/01, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n;
- for intangible assets - in clause 11 of PBU 14/2007, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia on December 27, 2007 No. 153n;
- for MPZ - in clause 8 of PBU 5/01, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/09/2001 No. 44n;
- for financial investments - in clause 12 of PBU 19/02, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 10, 2002 No. 126n.
In this case, the value at which the property was listed in the accounting records of the transferring party does not matter. The transferring party will show the difference between the amount of the contribution to the capital company and the accounting value of the property (including the restored amount of VAT) in account 91.
In tax accounting, property received as a contribution to the capital company is reflected at its tax value (including the residual tax value for depreciable property), determined according to the accounting information of the party transferring this property (subclause 2, clause 1, article 277 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) . Also, additional expenses can be included in the price if they are specified in the memorandum of association as a contribution to the charter capital. In the absence of documentary evidence of this value, it is considered equal to 0. Property contributed to a contribution by an individual or a foreign organization must have a value no higher than the market value, which must be confirmed by an independent assessment (subclause 2, clause 1, article 277 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
These differences, as a rule, entail a difference in the accounting and tax value of the property included in the charter capital, and, as a consequence, the amount of depreciation on the depreciable property.
Increase in capital
The Criminal Code can be increased in the following cases:
- changes in the organizational and legal form of a legal entity or type of activity to those requiring a larger capital amount;
- the owners make a decision about this.
An increase becomes possible only with full payment of the initially formed capital stock and registration of changes in the amount of the capital stock in the charter. PJSC and JSC that have already placed all the shares declared in the charter capital, after registering the changes made to the charter, will have to register an additional issue or conversion of shares with the Federal Financial Markets Service, and then with the Federal Tax Service, within 3 months from the date of the decision to increase the charter capital.
An increase is possible in the following ways (with appropriate accounting entries):
- Admission of a new participant and increase in the authorized capital for his share (in LLC and HT): Dt 75 Kt 80.
- Making additional contributions by previous participants (in LLC, SUE, MUP, HT): Dt 75 Kt 80.
- Increasing the share due to retained earnings or additional capital (in LLC, SUE, MUP, HT): Dt 83, 84 Kt 80.
- Additional issue of shares of the same par value at the expense of additional contributions from shareholders or other persons (in PJSC and JSC): Dt 50 (51, 52, 70, 75) Kt 80.
- Increasing the par value of shares due to retained earnings or additional capital (in PJSC and JSC): Dt 83 (84) Kt 80. In this case, shares of one par value are replaced with shares of a different par value.
Personal income tax must be withheld from the amount of increase in the individual’s share at the expense of profit (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 21, 2013 No. 03-04-05/4-117). If the capital increases due to the revaluation of the capital or as a result of the reorganization of a legal entity, then such income from individuals will not be taxed (clause 19 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Participants (shareholders) - legal entities, when their contribution to the capital company increases, does not generate income subject to income tax (subclause 15, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated February 16, 2009 No. A65-11409/ 2006).
Change of authorized capital
In the course of the enterprise's activities, it is possible to change the amount of the authorized capital both up and down. Let's look at how the authorized capital decreases and increases. What entries to increase the authorized capital must be reflected in accounting.
The procedure for changing the authorized capital is due to several reasons. Increasing the capital of an enterprise makes it possible to increase its attractiveness to contractors and partners, and it is also possible to introduce additional capital into production, avoiding tax costs in the form of VAT and income tax.
An increase in the authorized capital can be carried out at the expense of documented property or monetary contributions of the organization’s participants or at the expense of various property of the organization or company. If participants contribute property, its price is necessarily determined by independent market appraisers.
The company, in a number of cases provided for by Federal Law, may carry out procedures for reducing the authorized capital. The decreasing parameter can be the nominal value of each participant’s share or the share owned by the company and its redemption.
A company in its activities cannot reduce capital if such a procedure could lead to an amount of authorized capital less than the minimum established in the Federal Law for an organization of a specific structure and type as of the date of registration of the company with the relevant tax authorities. Reducing the capital by reducing the nominal value of the share of participants must be carried out in such a way that the size of all shares of participants in this same company is preserved.
How to increase the authorized capital in a joint stock company?
The increase in the authorized capital of a joint-stock company is carried out according to the following scheme. First, at the board of shareholders, a decision is made to increase the capital; before entering and registering their data in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, they must first submit documents for the additional issue of securities to the Federal Service for Financial Markets or its territorial division.
The procedure for reducing or increasing the capital capital differs in an open and closed joint stock company from the procedure that would be legal in a limited liability company. But, despite the differences, in accordance with the terms of Federal Law No. 129 “On State Registration”, any change in capital, be it an increase or decrease, the organization is obliged to register at its location.
How to increase the authorized capital of an LLC?
Let's consider the procedure for changing the authorized capital using the example of an LLC.
Sources of increasing authorized capital:
In this case, the increase can be done in one of three ways:
- At the expense of the company's property,
- due to additional contributions,
- at the expense of contributions from third parties that are accepted into the company, unless this item is prohibited by the statutory documents.
Procedure for increasing the authorized capital of an LLC
The increase at the expense of property is carried out by an official decision, which is adopted at the general meeting, where 2/3 of the list of votes of the organization’s participants voted “for”. The second case - an increase in the capital can be done by referring to the financial statements for the previous reporting year.
A statement that the organization is registering changes in its authorized capital must be submitted to the branch of the body that carries out state registration of legal entities. This application must be submitted no later than one month from the date of the decision to increase the capital at the expense of the company’s property. From the moment of certification and registration, this change comes into force for all third parties.
If an increase in the capital capital occurs by making additional contributions, then for this procedure it is necessary to hold a meeting and vote of all members of the company. And if more than half of the participants are in favor, then the changes in capital are considered legal.
At the general meeting the value of the general additional contributions must be determined. In addition, participants must determine a common ratio for all of the value of additional contributions of each participant and the amount of increase in the nominal value of his share.
If the increase in capital occurs through the contribution of funds by third parties, then simultaneously with this decision it will be necessary to make a decision on the admission of these third parties to the company, on determining the changed size of the share and the nominal value for the newly joined persons. Such a decision must be made unanimously at the meeting.
In order to change the authorized capital of an LLC, you must have the following documents with you:
- OGRN certificate of registration of the taxpayer as a legal entity
- Certificate showing that the organization is registered with the tax authorities
- Extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities
- Banking on the right along the credit line
- Charter
- Copies of passports of all founders and general director of the LLC
- Application form P13001, signed by the General Director. The director's signature is certified by a notary
- Decision of the Company's participants on changes in capital
From the moment of registration with the territorial tax authorities, the changed authorized capital is considered valid.
Accounting entries:
The procedure for increasing the capital must be reflected in accounting using certain entries.
Increase in authorized capital accounting entries:
D75 K80 – posting reflecting an increase in the capital account due to additional founders' contributions.
D83 (83) K80 - posting reflecting an increase in the capital at the expense of the organization’s own funds.
Decrease in capital
A reduction in capital may be necessary:
- When changing the organizational and legal form of a legal entity to one in which a smaller amount of the authorized capital is permissible.
- The owners decide on this.
- The presence of unsold shares or shares purchased by a PJSC, JSC or LLC during the year. Accounting for such shares (shares) is kept in account 81. When they are redeemed by the company, the entry Dt 81 Kt 50, 51, 52, 75 arises.
- Situations when the value of the NAV for 2 years in a row (for PJSC, JSC or LLC) or at the end of the past year (for state unitary enterprises and municipal unitary enterprises) turns out to be less than the value of the authorized capital.
- The impossibility of paying the retiring LLC participant the real value of his share due to the insufficiency of the difference between the NA and the capital for this purpose.
It is impossible to reduce the Criminal Code if, as a result, it turns out to be less than its minimum possible value for the day:
- submission of documents for registration of changes in the amount of the capital in the charter, if the decision to reduce is the initiative of the owners;
- registration of a legal entity, if the need to reduce the capital capital is caused by legal requirements.
Mandatory preconditions for reducing the capital are informing the Federal Tax Service about this and publishing this information twice (within a month) to notify creditors who, in such a situation, have the right to demand early payment of the debt. PJSC and JSC must register with the Federal Financial Markets Service the conversion of shares or the redemption of part of their number.
An important point when voluntarily reducing the capital is to ensure that, as a result, the assets do not end up being less than the capital.
The reduction is carried out in the following ways (with the corresponding accounting entries):
- Departure of a participant and reduction of the capital for his share (in LLC and HT): Dt 81 Kt 75 (in an LLC, where the share is actually bought out) or Dt 80 Kt 75 (in HT, where the share capital is simply reduced).
- Reduction of existing shares with the return of part of their amount to participants (in LLC, SUE, MUP, HT): Dt 80 Kt 75.
- Reduction of existing shares with an increase in the amount of retained earnings (in LLC, SUE, MUP, HT): Dt 80 Kt 84.
- Reduction of the capital by the value of shares or shares not sold during the year after the company’s repurchase (in PJSC, JSC, LLC): Dt 80 Kt 81.
- Reducing the number of outstanding shares due to their repurchase (in PJSC and JSC): Dt 81 Kt 50 (51, 52, 75). And their subsequent liquidation: Dt 80 Kt 81.
- Reducing the par value of shares with the return of the difference to shareholders (in PJSC and JSC): Dt 80 Kt 75. In this case, as with an increase in par value, shares are replaced.
- Reducing the par value of shares with an increase in the amount of retained earnings (in PJSC and JSC): Dt 80 Kt 84. Shares are also replaced with similar documents with a different par value.
The amount of the difference in the amount of the contribution paid to participants and shareholders should not be greater than the amount by which the capital is reduced. Such a payment cannot be made when:
- The CC has not been paid;
- the legal entity has signs of bankruptcy;
- dividends already declared by the company have not been paid or have not been paid in full;
- shares or shares for which there is a requirement for their redemption have not been repurchased.
When deciding to reduce the capital on a voluntary basis, participants (shareholders) may simultaneously decide that the amount of the reduction will not be paid to them. Then the legal entity reducing the capital will have income, and in the entries for accrual of debt to participants (Dt 80 Kt 75), account 75 will be replaced by 91.
It is also possible for participants (shareholders) to refuse to receive the amounts due to them for reducing the authorized capital after they have been accrued. In this case, after posting Dt 80 Kt 75, posting Dt 75 Kt 91 will be made in relation to persons who refused to receive accrued payments. In part of these amounts, the legal entity reducing the capital capital will also receive income.
retained earnings
The profit (loss) that the accountant identified by reforming the balance sheet is reflected in account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss).”
Account 84 - active-passive, balance, balance. The organization must distribute the profit received during the reporting year in the next year. The decision on what to use these funds for is made by the founders of the organization at a general meeting. At the same time, they must comply with the conditions specified in the constituent documents and accounting policies, as well as legal requirements.
The amount of net profit (loss) is written off to account 84 with the final entries of December from account 99 “Profits and losses”:
D-t 99 K-t 84 - retained earnings are written off;
D-t 84 K-t 99 - uncovered loss is reflected.
In the balance sheet, account 84 is shown as a liability. The amount of uncovered loss in the balance sheet is shown in brackets and is subtracted when calculating the balance sheet currency.
At the beginning of the year following the reporting year, the owners (founders) of the organization (for example, a general meeting of shareholders or a meeting of participants in an LLC) make a decision on the distribution of net profit.
Net profit can be used for:
- payment of dividends to shareholders (participants) of the organization: D-t 84 K-t 75 (70);
- creation and replenishment of reserve capital: D-t 84 K-t 82;
- repayment of losses from previous years.
The meeting of shareholders (participants) of the organization may decide not to distribute the profit received at all (or leave part of it undistributed).
Example.
At the end of the year, the net profit of Granit CJSC amounted to 100,000 rubles. In analytical accounting for account 84, the accountant provided subaccounts:
84/1 “Profit subject to distribution”;
84/2 “Retained earnings”.
On December 31, when reforming the balance sheet, Granit’s accountant made the following entry:
D-t 99 K-t 84/1 - 100,000 rub. — net profit is reflected.
In February, at the general meeting of shareholders, it was decided to use net profit as follows:
5% should be used to replenish reserve capital;
40% will be used to pay dividends to shareholders.
Based on this decision, the accountant will reflect the use of profits:
D-t 84/1 K-t 82 - 5000 rub. (100,000×5%) - funds were allocated to replenish reserve capital;
D-t 84/1 K-t 75/2 — 40,000 rub. (100,000 x 40%) - funds were allocated to pay dividends;
D-t 84/1 K-t 84/2 — 55,000 rub. (100,000 - 5000 - 40,000) - reflects the amount of retained earnings.
Analytical accounting for account 84 can be carried out according to the areas of use of profit, for example, you can open a sub-account for account 84 “Retained earnings used”.
Example.
Let's use the data from the previous example. After the distribution of profits in February, the credit balance in subaccount 84/2 amounted to 55,000 rubles.
In March, at a meeting of shareholders, it was decided to use funds from retained earnings to develop production. Granit purchased equipment worth RUB 35,400. (including VAT RUB 5,400).
When putting the equipment into operation, the accountant made the following entries:
D-t 01 K-t 08 - 30,000 rub. — the equipment has been put into operation.
D-t 68 K-t 19 - 5400 rub. - VAT deduction has been made. D-t 84/2 K-t 84/3 — 30,000 rub. — reflects the use of net profit.
If losses are incurred at the end of the year, they can be covered by reserve capital, additional capital funds, targeted contributions from the founders, or by (means of) reducing the authorized capital.
Losses may arise as a result of:
- losses from financial and economic activities and non-operating operations;
- the occurrence of expenses at the expense of profit, the amount of which exceeded the amount of profit.
Sources for covering losses may include:
- reserve capital funds: D-t 82 K-t 84;
- free funds contributed by the founders: D-t 75 K-t 84;
- additional capital (with the exception of capital gains due to revaluation): D-t 83 K-t 84.
If the available sources are not enough to cover the uncovered loss of the reporting year, a decision is made to leave the uncovered loss on the balance sheet with the possibility of writing it off in future periods.
For organizations that received a loss from sales in the previous year, the part of the profit that is used to cover this loss is exempt from income tax. If the loss exceeds the tax base for income tax, it is carried forward to the following reporting periods.
Taxes in connection with the reduction of the capital
For a legal entity where a decrease in capital is taking place, 3 options are possible:
- According to the requirements of the law: Dt 80 Kt 84 or Dt 80 Kt 81. Then the amount of the reduction should not be considered his income (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 17, 2015 No. 03-03-06/1/53369).
- By a voluntary decision without payment to participants and shareholders of the difference in the amount of the contribution. In this case, the amount by which the Criminal Code is reduced is included in the taxable income of the legal entity (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 6, 2013 No. 03-03-10/31651): Dt 80 Kt 91. Moreover, for OSNO, regardless of the accounting method (accrual or cash), and under the simplified tax system this inclusion is made on the date when the changes made to the charter are registered (clause 1 of article 271, clause 2 of article 273, clause 1 of article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Firms operating on UTII will have to pay income tax on such income (clause 4 of Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). With the simultaneous application of OSNO and UTII, income arising from a decrease in the capital capital is not distributed between the regimes (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 15, 2005 No. 03-03-01-04/1/116), however, expenses related to it must be distributed ( clause 7 of article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Accordingly, the profit base can be reduced only by that part of the expenses that will be distributed to OSNO.
To learn how to organize separate accounting for OSNO and UTII, read the article “How to properly maintain separate accounting for OSNO and UTII?”
- On a voluntary basis, with payment to participants and shareholders of the difference in the amount of the contribution: Dt 80 Kt 75. At the same time, the legal entity carrying out the reduction of the capital will not receive income.
The amount that a participant (shareholder) - a legal entity receives in an amount not exceeding the amount of the contribution made by him to the management company, is not subject to profit taxation when:
- Reduction of the capital according to legal requirements (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 28, 2008 No. 03-03-06/1/209).
- Termination of participation in the management company (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 10, 2006 No. 03-03-04/1/428). In this case, there is no need to tax the income of foreign legal entities (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 28, 2013 No. 03-08-05/51682).
- Division of property of a legal entity ceasing to exist (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/09/2014 No. 03-03-06/1/27663).
The excess over the amount of the contribution to the capital company made in fact will be subject to tax accrued on profits. It can occur if:
- Termination of participation in an LLC or HT or their property is distributed and it turns out that the real value of the share is greater than the actual contribution made. The real value corresponds to the difference between the NAV and the capital determined for the year in which the termination of participation occurs. When the difference between the capital and the capital is insufficient to pay the share, the capital must be reduced (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 21, 2006 No. 03-03-04/1/378). If the amount of the actually made contribution exceeds its real value, a loss is formed that is not taken into account when determining the income tax base (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated October 10, 2007 No. 20-12/096643).
- Payment of the difference in the amount of the authorized capital when it is reduced on a voluntary basis (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 20, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/567). The costs associated with this income cannot be taken into account (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 05/07/2007 No. 03-04-06-01/144).
- Sale of deposit (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 14, 2006 No. 03-03-04/1/222). To reduce such income, you can take into account the cost of the deposit reflected in the accounting and the costs of sales (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 21, 2010 No. 03-03-06/2/5). In the case of a sale at a loss, it is accepted when determining the base for calculating income tax (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 11, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/742).
- Redistribution of deposit amounts in the management company (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 10, 2006 No. 03-03-04/1/428).
Income generated as a result of a decrease in the capital of participants (shareholders) - individuals, is subject to personal income tax (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated June 13, 2007 No. 28-11/055629).