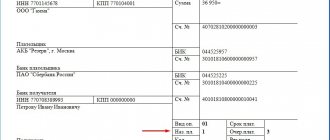
Expert of the magazine “Regulatory Acts for Accountants” A.F. Klyuev provides a commentary on the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 14, 2013 No. 03-04-06/42790.
A branch of a Russian organization pays taxes in the foreign country in which it is registered. For personal income tax purposes, are the payments he makes to employees income received from sources outside the Russian Federation:
- wage;
- compensation for travel expenses to your place of work and residence;
- payment of the cost of visas and health insurance;
- average earnings while on vacation and on a business trip;
- material aid;
- payment of travel expenses?
Income from sources outside the Russian Federation
In a published letter, the Russian Ministry of Finance noted that the branch of the organization, which is the source of payment to its employees of all of the above income, conducts commercial activities in a foreign country. Therefore, the above payments to employees relate to income from sources outside the Russian Federation.
In letter dated June 11, 2010 No. 03-04-06/6-118, the Russian Ministry of Finance considered a similar situation when a branch of a Russian organization located outside of Russia and registered as a legal entity of a foreign state pays its employees for accommodation, food and medical care. According to the Finance Ministry, such payments also apply to income received from sources outside the Russian Federation.
Types of permitted transactions on foreign accounts
Individuals and legal entities, as well as individual entrepreneurs using the services of foreign banks, have the right:
- make transfers between your accounts in banks of different countries;
- receive income from interest on open depository accounts;
- receive wages, as well as non-commercial payments: scholarships, alimony, pensions;
- receive payments for cases in foreign courts, as well as money from foreign insurance companies.
If accounts are opened in a country that is a member of the OECD or FATF, the following is additionally permitted:
- take loans or borrowings in monetary units of another state;
- rent out foreign real estate and receive monetary compensation for it;
- use income from securities.
Important! The sale of securities is not included in the list of possible transactions if it was carried out through an exchange not included in the list approved by law. You also cannot use foreign account accounts to deposit money from the sale of real estate, when receiving an inheritance, etc.
In case of non-compliance with these requirements, a fine of 75 to 100% of the amount of the transaction declared illegal is imposed.
Taxation of personal income tax
In addition, the Ministry of Finance of Russia in a published letter recalled that personal income tax payers are individuals who (clause 1 of Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- are tax residents of the Russian Federation;
- are not tax residents of the Russian Federation, but receive income from sources in Russia.
Reference
Tax residents are individuals who are actually in the Russian Federation for more than 183 calendar days over the next 12 consecutive months (clause 2 of Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This means that branch employees who are not tax residents of the Russian Federation are not recognized as personal income tax payers in relation to income received from sources outside the Russian Federation.
It turns out that those employees of the branch who are tax residents of the Russian Federation are recognized as payers of personal income tax in relation to income received from sources outside the Russian Federation.
Thus, income paid to employees of a branch of a Russian organization in a foreign country relates to income from sources outside the Russian Federation and:
- are not subject to personal income tax if employees are not tax residents of the Russian Federation;
- are subject to personal income tax if employees are tax residents of the Russian Federation.
As a rule, personal income tax is withheld from the income of tax residents of the Russian Federation at a rate of 13 percent.
Currency legislation requirements
The first obligations to the state arise immediately after opening an account in a foreign bank: all residents are required to report this to the Federal Tax Service within 30 days from the date of the transaction. A special form can be sent from your online account or by Russian Post.
In the future, owners of mutual account accounts abroad are required to regularly report on the flow of funds and ongoing operations. Documents must be submitted annually by April 30 (that is, the report for 2019 is submitted by April 30, 2020).
Individual entrepreneurs who use foreign accounts for business activities, as well as legal entities, report much more often: reports must be submitted at the end of each quarter (during the next calendar month).
After submitting the reports, the state makes a decision on applying the legislation on currency regulation to the resident. If regulatory authorities have suspicions about the legality of ongoing transactions, they may request documents confirming the legality of transactions, money transfers and payments. They are considered contracts, invoices, and if money was transferred to relatives - passports, birth or marriage certificates.
Fines for non-compliance with legal requirements
If a resident violates the deadlines for submitting reports or completely “forgets” about them, several types of sanctions should be expected:
- for failure to submit reports by an individual - up to 5,000, legal - up to 1,000,000 rubles;
- a report submitted in violation of the deadlines specified in the law entails a fine of 300 to 3,000 rubles, and in case of repeated violation - up to 20,000;
- for legal entities, the fine for late reports varies from 5 to 50 thousand for the initial violation and from 120 to 150 for subsequent ones;
- if a resident is also a taxpayer, then failure to submit reports is equivalent to concealment of income - under this article the amount of penalties reaches up to 500,000 rubles.
Responsibilities of tax residents of the Russian Federation
It should be borne in mind that those tax residents of the Russian Federation who receive income from sources outside of Russia calculate, declare and pay personal income tax independently at the end of the tax period (that is, the calendar year). The basis is subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 and paragraph 2 of Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Moreover, with regard to employee income received from sources outside the Russian Federation, the employing company is not recognized as a tax agent. That is, in relation to the indicated income, she does not need to fulfill the duties of calculating, withholding and transferring personal income tax to the budget of the Russian Federation.
EXAMPLE: Let’s say that during a calendar year, an employee’s status changes to non-resident and remains so until the end of the tax period. In this case, such an individual, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 207 of the Code, is not recognized as a personal income tax payer on income received from sources outside the Russian Federation. Accordingly, such an employee does not have any taxpayer obligations to declare income from sources outside the Russian Federation, including those received before acquiring non-resident status, and to pay personal income tax. Similar explanations are given in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 28, 2012 No. 03-04-06/6-183, dated June 11, 2010 No. 03-04-06/6-120.
Automatic exchange of financial account information (CRS)
In September 2021, papers were signed, as a result of which Russia joined the CRS standard, which provides for automatic information exchange between banks of different countries. To date, 110 countries from Europe, Asia, and the Pacific region (including all major players in the international financial market) are already participating in the exchange. Left behind were mainly island and African states, Moldova, Montenegro and Mongolia.
Bilateral agreements on the exchange of information with Russia have been concluded with 91 states: some of them have already entered into force, others will begin to work in 2021. This means that the tax authorities of our country are already receiving information about the accounts of Russian residents in banks of Andorra, China, Great Britain, Singapore, Switzerland and a number of other countries.
The exchange takes place once a year: that is, if tax residents did not submit reports on time (before June 1), then the Federal Tax Service will become aware of this in the fall.
Statute of limitations for violations of tax and currency laws
From April 2021, the statute of limitations for cases related to violations of currency legislation has been increased to 2 years, and the starting point is the fact of violation itself (that is, if the state has identified “flaws” committed before 2021, then no fines will be assessed for them) .
Tax crimes have a statute of limitations of three years, so transactions from 2021 are taken into account for penalties.
Working abroad is not a business trip
For the purposes of calculating personal income tax, income received from sources outside the Russian Federation includes, in particular, remuneration for the performance of labor or other duties, work performed, service provided, action performed in a foreign state (subclause 6, clause 3, article 208 of the Tax Code RF).
If employees of an organization perform all their labor duties stipulated by employment contracts outside the Russian Federation, then the actual place of work of the employees will be in a foreign country. And they cannot be considered to be on a business trip. Indeed, in accordance with Article 166 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a business trip is a trip by an employee by order of the employer for a certain period of time to carry out an official assignment outside the place of permanent work.
When employees are sent to work abroad, when they perform all their labor duties stipulated by the employment contract at their place of work in a foreign state, the salary they receive is remuneration for work in the territory of a foreign state. It does not apply to income from sources in the Russian Federation. This is reported in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 25, 2012 No. 03-04-06/6-289, dated June 11, 2010 No. 03-04-06/6-120.
General recommendations
Declaring your income is a question that every investor must decide, based on his moral and material principles. A Russian investor, entering the Russian securities market, understands that tax will be withheld from his positive performance results and agrees to this. The same principle should be present when investing in foreign markets - part of your income must be transferred to the budget. Although at first glance declaration is associated with certain difficulties, tax evasion still carries incomparably greater risks.
Our service: Preparation of tax returns on foreign investments
How does a non-resident pay taxes?
If a citizen of the Russian Federation does not qualify for resident status, he will file a declaration and pay taxes according to special rules. For property, transport and a number of other taxes, the rate will remain unchanged. However, the personal income tax rate of 13% will apply only to certain categories of non-residents expressly specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (for example, sailors of domestic ships will retain this right). For other non-residents (usually foreigners) the rate will be 30%.
Naturally, if a non-resident permanently resides and works abroad, i.e. is absent from Russia for more than 183 days, his employer will pay taxes according to the national legislation of the host country. There is no need to report to the Federal Tax Service for such income, and you will only have to pay income tax if you receive additional income in Russia.
Solutions that reduce potential tax threats
1
Try to make all movements of your funds through personal accounts transparent and simple. The advice is quite simple, but at the same time, not everyone understands its power. It will simply be impossible to accuse or suspect you of anything if you carry out all operations with the simplest and most detailed descriptions of their purpose.
2
Try to avoid cash transactions, or at least reduce their volumes. If you are a kinesthetic person, it will be difficult for you to resist the desire to withdraw all your cash on the day you receive it. But it is precisely this behavior that will cause the greatest suspicion. If you spend the same funds from your account through payments in stores and for online purchases, then this will be absolutely transparent and understandable for the Federal Tax Service, because There is no room for fiscal suspicion here.
3
Pay close attention to deadlines for filing your taxes and paying all taxes. It may also seem simple. But, it is better to remember that in March of each year you need to try to calculate all your income for the previous year, from which personal income tax was not charged at the source. This must be done in order to have time to submit a declaration for the previous year before the end of April. You also need to remember that all taxes for the previous year must be paid before July 15 of the current year. Accordingly, you should have this money at least by the beginning of July.
4
Start building up personal savings for yourself in a foreign bank. Why there? So that the tax service does not have the opportunity to block your foreign account without acceptance. This is necessary because tax services often make mistakes, and tax payments are calculated due to certain technical problems.
Previously, this happened mainly with legal entities, of which there are much fewer in our country. What errors there will be with the accounts of individuals, of which there are many times more, is anyone’s guess.
Therefore, in order not to be left completely without funds, open an account in a foreign bank.
Why is it profitable to open an account with a foreign bank in 2021?
We are talking specifically about foreign banks, and not about branches of foreign banks operating in Russia. The fundamental difference between the latter is that they all operate under the same laws as Russian banks. Accordingly, all your funds stored with them will be available for direct debit and blocking by the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
Foreign banks are outside the reach of the Russian financial system. Accordingly, your funds cannot be blocked there by the tax service.
They can only request information from a foreign bank about your accounts, but not block or withdraw your funds without your consent.
Moreover, a foreign bank is not obliged to report you to the Federal Tax Service of Russia about suspicious, in their opinion, transactions, which Russian banks are obliged to do.
In addition to all of the above, there are also the following reasons for opening an account in a foreign bank by Russian citizens:
- in foreign countries there is a more stable economic and political situation, which affects the stability of the bank in which your funds are located. It is impossible to deprive a foreign bank of its license for the political preferences of its founders or the fact that some power group liked it or, on the contrary, somehow interfered with their work, which could often be observed in recent years;
- you are protected from currency risks by storing funds in several currencies in one multi-currency account;
- you are more free when traveling abroad with a plastic card from a foreign bank and do not spend money on high conversion fees, as is the case with many Russian banks;
- you can offer your services to foreign employers, who will be much more comfortable paying you into a foreign bank account than into a Russian bank, many of which are under US and EU sanctions;
- you can start saving for your foreign education or your growing children;
- Having an account abroad, knowing a foreign language and working for a foreign company, you can choose any place on planet earth where it would be more comfortable for you to live, develop and raise your children.
Double taxation and how to avoid it
Owners of apartments abroad will not be affected by the issue of paying duties to the state until they want to sell the property. Very often, ignorance of the tax code leads to entrepreneurs losing a lot of money, wanting to make a profit from the transaction. Payment of duty on the sale of real estate is also mandatory and is calculated at a rate of 13 percent, depending on the place of residence of the owner. To dispose of an apartment in this way, you must be its owner for at least 5 years. It is possible to sell real estate earlier, provided that the owner acquires another property in a short period of time, at a cost specified in the terms of the program for obtaining citizenship of the country.
In Russia, in this case, 5 years of ownership of an apartment or other object allows you to sell it without paying taxes. If the property was inherited or was acquired outside of various programs, then it can be sold at any time by paying 13% of the profit to the Russian tax authorities. In addition, there are also other taxes when selling an apartment in different countries of the world.
A resident of the Russian Federation who owns an apartment in Bulgaria and wants to sell it without a huge loss of money on payment will need to familiarize themselves with the agreement in order to avoid double taxation. The document indicates all types of taxes for which it is valid, and all persons who can fall under it. Russia has signed this agreement with 82 countries. The agreement applies to situations where the property of an individual is located in a state where he is a non-resident.
It is also worth remembering about additional costs when selling an apartment in Bulgaria. One of these is the tax on increases in the market value of capital. If the price of the property has increased compared to the purchase price, the owner will have to pay 10 percent of this difference. Profit from the sale of an apartment that has been the owner’s permanent residence for more than three years is exempt from taxation.