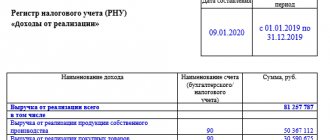
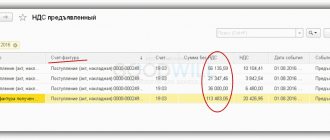
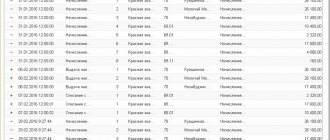
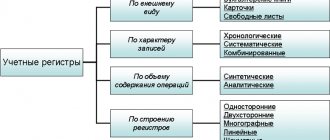
According to the norms of current legislation, companies and individual entrepreneurs that hire specialists in labor and civil law contracts perform the functions of fiscal agents: they calculate, withhold and transfer to the state budget income tax on payments to employees. Carrying out the above operations involves the formation of appropriate entries in the accounting program of a commercial structure. Let us say right away that a special personal income tax account is not provided for by the current chart of accounts. To reflect it separately, a subaccount is opened to account 68.
What transactions are used to reflect personal income tax?
When an accountant calculates income taxes, he does not make any entries. Entries in the accounting program are necessary only when withholding and transferring personal income tax to the state treasury. Depending on the situation, do the following lines:
| Wiring | What does it reflect? |
| Dt 70 – Kt 68.01 | Withholding income tax from the salary of a hired specialist, from the amount of his vacation pay |
| Dt 70.01 – Kt 68.01 | Withholding personal income tax from dividends paid to the company's shareholders. For ease of calculations and analytics, we recommend that the accountant open a separate sub-account for the account. 70 to reflect settlements with the founders. |
| Dt 73 – Kt 68.01 | Withholding of income tax on other types of payments transferred to the employee by the employing company. For example, the cost of gifts exceeding 4,000 rubles, financial assistance in excess of limits, etc. |
| Dt 76 – Kt 68.01 | Accrual of personal income tax on payments in favor of individuals who are not employees of the company. For example, citizens providing services to a company under a civil contract. |
| Dt 75 – Kt 68.01 | Withholding income tax on dividends paid to non-employee shareholders |
| Kt 67 – Dt 68.01 | Withholding personal income tax on interest paid on a long-term loan previously received from an individual |
| Kt 66 – Dt 68.01 | Calculation of income tax on interest paid to an individual for the use of short-term borrowing |
| Dt 68.01 – Kt 51 | Transfer of the calculated tax amount to the state budget from the company's current account |
As you can see, the main personal income tax accounting account is 68.01.
The general logic of reflecting personal income tax on accounting accounts is that when accruing it, it is shown on the credit account. 68.01 in correspondence with an account intended to reflect the corresponding type of income of individuals. When the total tax calculated by the accountant is transferred to the state treasury, the account is credited. 51.
Personal income tax: accounting
According to Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, income tax is calculated at the end of the month. But its deduction must be made only upon actual payment of income. Therefore, the accountant must keep records of calculated and withheld personal income tax in a special journal. It reflects the following:
- personal income tax calculated;
- Personal income tax withheld.
In this case, it is necessary to reflect the amounts of income tax, which is calculated at all tax rates applicable to the employee’s income.
Tax agents must also maintain personal income tax registers. They reflect the employee’s income for each code, their amounts, and the amount of calculated and withheld income tax. This takes into account income that is taxed at different rates. For example, a highly qualified employee (foreign citizen) receives a salary that is taxed at a rate of 13% (according to the legislation of the Russian Federation). Other payments that do not relate to wages will be taxed at a rate of 30%. All this must be reflected in the register.
Registers are maintained for each employee separately. The data specified in them is used for the correct preparation of the annual report in form 2-NDFL and 6-NDFL.
When determining the tax base for calculating personal income tax, it is necessary to take into account deductions that are issued by the employee. The tax base is reduced by their amount. For example, an employee receives a child deduction in the amount of 1,400.00 rubles. His salary is 27,000.00 rubles. To calculate income tax, you need to make the following calculations:
- 27000.00 - 1400.00 = 25600.00 (rubles)
- 25600.00 * 13% = 3328.00 (rubles).
Initially, we reduced the tax base for calculating personal income tax by the amount of the deduction provided. Then we calculated the amount of income tax that needs to be withheld from the employee’s salary and transferred to the budget.
Reflection of personal income tax in accounting: examples
To understand the principles of income tax reflection, let's look at practical situations.
EXAMPLE 1
Economist Ivanov is a shareholder. At the end of the year, he is due the amount of dividends - 50 thousand rubles. What accounting entries need to be made? Here are the ones:
- Dt 84 – Kt 75 in the amount of 50 thousand rubles. – accrual of dividends;
- Dt 75 – Kt 68.01 in the amount of 4.5 thousand rubles. (13% of 50 thousand) – income tax withholding;
- Dt 75 – Kt 51 – in the amount of 55.5 thousand (50 – 4.5) – transfer of dividends to Ivanov on a bank card;
- Kt 68.01 – Dt 51 – payment of tax to the state treasury.
Also see “Payment of personal income tax on dividends”.
EXAMPLE 2
Sales manager Petrov received a salary of 40 thousand rubles for the month he worked. He is not eligible for standard tax deductions. What amount is due to him and how to reflect it in accounting? Let's calculate the amount of personal income tax on income at a rate of 13%:
- 40,000 × 0.13 = 5200 – amount of tax to be withheld;
- 40,000 – 5200 = 34,800 – the amount of wages to be paid.
The accountant will make an entry for payroll Dt 44 - Kt 70 in the amount of 40 thousand rubles. Then it will withhold personal income tax (Dt 70 - Kt 68.01) in the amount of 5200. To reflect the transfer of tax to the budget, the entry Kt 51 - Dt 68.01 will be used.
Also see “Positions when withholding personal income tax from wages.”
Read also
19.05.2018
Features of calculation and payment of personal income tax
The personal income tax tax period is a calendar year, for which an individual is required to submit a declaration to the tax authority at the place of registration.
The tax is transferred by the employer no later than the day following the payment of income to the employee. At the end of the reporting year, employers submit a report to the tax authority at the place of registration in the form of $2$-NDFL for each employee by April 1 of the following year.
Too lazy to read?
Ask a question to the experts and get an answer within 15 minutes!
Ask a Question
Since 2016, for employers - agents of personal income tax payers, a period has been established - a quarter. A new form of calculation of $6$-personal income tax has also been introduced. This form reflects information about employee income, accrued and withheld personal income tax amounts for the reporting period. This calculation must be submitted no later than the last day of the month following the previous quarter.
Note 1
When determining the tax base of a taxpayer, all income that he received, both in cash and in kind, or the right to dispose of which he acquired, is taken into account, as well as income in the form of material benefits.
For taxation at the basic rate – $13\%$ there is a list of types of income (Fig. 1):
Figure 1. Types of income subject to personal income tax
Too lazy to read?
Ask a question to the experts and get an answer within 15 minutes!
Ask a Question
The personal income tax rate in Russia is $13\%$ of income. But for certain types of income the rate is different.
Accounting policy for personal income tax registers: detailed setup
Also, before you start calculating wages, you must correctly set up your accounting policy for personal income tax or insurance contributions. To do this, go to the “Main” section (step 1) and click on “Accounting Policy” (step 2). As a result, the system will open the settings.
In the new window, you should indicate your organization (step 3) and click on the link “Set up taxes and reports” (step 4). Next, the settings window will open again.
Open the “Personal Income Tax” (step 5) and o (step 6) tabs. From now on, personal income tax will be displayed and taken into account in tax registers on an accrual basis for the year.
Then click on the “Insurance premiums” tab (step 7), decide on the insurance premium rate (step and mark the Social Insurance Fund rate for accidents (step 9).
and mark the Social Insurance Fund rate for accidents (step 9).
The accounting policy has been set up, and you can begin displaying personal income tax in registers.
Primary settings for personal income tax accounting
Decide which payroll accounting options you need
The 1C 8.3 system provides a special program that allows you to keep track of wages. It is called “1C Salary and HR Management (ZUP)”. It allows you to record complex salary payment schemes and automatically determine sick leave and other benefits. Thus, the ZUP provides everything for successful accounting of salaries and employees in medium and large organizations. For a smaller number of frames (less than 60), you can use the 1C 8.3 Accounting program. Before you start calculating wages, you should indicate in the settings which program will be used to calculate wages. To do this, you need to go to “Administration” (step 1) and click on “Accounting Settings” (step 2).
In a new window, open the “Salary Settings” link (step 3), then the settings will open.
In the settings you need about (step 4) if you plan to use 1C 8.3 Accounting. If you use the 1C 8.3 ZUP system for payroll accounting, you should do (step 5).
Complete payroll and personal income tax calculations in 1C 8.3
To calculate wages, open “Salaries and Personnel” (step 1) and click on “All accruals” (step 2). The system will open a window for creating a new accrual.
Then in the window, click “Create” (step 3) and go to “Payroll” (step 4). The following window will open.
Click on “Fill” (step 5). The document will be filled out with all accruals for employees. Personal income tax (step 6) and insurance premiums (step 7) will be displayed in separate fields.
To save these accruals, click on “Record” (step 8), and then “Post” (step 9). To view all accounting entries and entries in personal income tax registers, click on “DtKt” (step 10). The accounting and tax records section will appear.
The “Tax Calculations” tab (step 11) shows entries in the personal income tax registers.
We'll configure 1C to suit your needs right now!
- Any settings, reports in 1C, 1C exchanges
- A specialist will arrive the next day
- We accept your applications 24/7
- Receive a gift when purchasing any 1C programs and services in the amount of 33,000 rubles or more!
To get a consultation
Accounting for accruals: make settings
When you select the “In this program” checkbox, you should continue with the settings. To do this, you need to click on “Payroll calculation” in the salary settings (step 1) and configure the following parameters:
- Keep records of sick leave, vacations and executive documents (step 2). Check this box if these deductions are planned;
- Salary calculation for separate divisions (step 3). Provides for those who have separate units;
- Automatically recalculate the “Payroll” document (step 4). If you want the taxes to be recalculated in the “Payroll” document immediately after changes are made;
The process of setting up payroll accounting methods
It is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the additional salary settings and, if necessary, make changes to individual items. This refers to the order in which salaries are displayed on accounting accounts.
Each organization, due to its specifics, can charge wages to different accounting accounts. For example, trading companies use account code 44 “Sales expenses”. And in production organizations, wages will be reflected in the following accounts:
- 20 “Main production”;
- 23 “Auxiliary production”;
- 25 “General production expenses”;
- 26 “General business expenses”;
It is important to note that even one enterprise can use several accounting methods for different departments, groups of employees or nomenclature groups.
To set up accounting methods, you need to click on “Reflection in accounting” in the salary settings (step 1). Then go to “Salary accounting methods” (step 2). As a result, a directory of accounting methods will be opened.
The directory has several ways to record salaries. If necessary, you can add new items. To do this, click on the “Create” window (step 3). Next, a window will open for adding a new method.
In this window you need to specify:
- Name of the new method (step 4);
- Accounting account (step 5);
- Nomenclature group (step 6);
- Cost item (step 7);
- To take into account consumption under the simplified tax system or not (step 8);
- Cost item for UTII (step 9);
You can save the new method by clicking on “Save and close” (step 10). As a result, a new method will be created and can be immediately used when calculating salaries.
Features of account accounting 68
This accounting account is classified as an active-passive account, that is, the balance of account 68 is not only debit, but also credit. It all depends on whose benefit the debt is: in favor of the company or the state.
Transactions should be reflected by type of tax liability. To organize this detailing in the working PS, special subaccounts are provided for account 68:
Please note that the company is not required to enter all of the above subaccounts. It is enough to include in the accounting policy only those that are used in the business activities of the company. Most Russian organizations use only two sub-accounts: accounting account 68-01 - to reflect personal income tax transactions for each employee, and accounting account 68-02 - for settlements with the VAT budget.
The final balance of account 68 in terms of tax obligations varies. Consequently, an expanded balance is formed for the existing subaccounts. For example, a debt on one tax is reflected in credit 68 of account, and an overpayment on another is recorded as a debit. In this case, when including accounting indicators 68 in the annual balance sheet and other financial statements, make sure that debit balances are included in the balance sheet assets, and credit balances are included in liabilities.
Personal income tax accrual - on which accounting account?
To record any transactions, it is necessary to use a chart of accounts in your work. In specialized programs, tax calculation is largely automated. However, sometimes transactions have to be reflected manually, since it is impossible to fully provide for all options for business transactions.
The chart of accounts (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n, as amended on November 8, 2010) uses account 68 to calculate taxes. It reflects all taxes paid by the company. To divide accounting by type of tax, separate subaccounts are introduced. Which subaccount to assign to personal income tax is decided and approved in its accounting policy by the company itself. Most often, account 68.1 (68.01) is used for personal income tax.