Generally obligatory elements of taxation
The development and improvement of the taxation system has provoked the emergence of many types of taxes and fees, which have their own distinctive features and purpose.
However, despite the multiplicity of types, each tax consists of mandatory, additional and optional elements that serve as the main tools for the implementation of tax policy.
Generally obligatory or general elements of tax include the tax base and tax rate, the object of taxation, the algorithm for calculating the tax burden, etc.
Article 53 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is devoted to the disclosure of the legal essence of the concepts “tax base” and “tax rate”.
Concept and main aspects of the tax base
According to the requirements of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax base is both the cost and physical characteristics of the object subject to tax.
In other words, this concept means any object that is subject to taxation.
The conditions, principles and procedure for establishing the tax base are regulated by relevant regulations, in particular the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
For example, the tax base for VAT is the total cost of products sold, for personal income tax - income received by an individual, for inheritance tax - the value of inherited property, for gift tax - the value of a gift.
So, the tax base (NB) is:
- one of the main elements of the tax, on the basis of which its amount is calculated;
- a specific object from which tax is collected in the manner prescribed by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- a certain amount on the basis of which the amount of tax is calculated in accordance with the established rate;
- income of a person on which taxes and fees must be paid.
Determination of the tax base is required to quantify the object of taxation.
A specific tax base is applied to each specific tax. For example, for VAT, NB is calculated in accordance with the specifics of the sale of products or purchased goods.
Fictitious CSCs are established on a relatively low financial base as a mechanism to cover a certain group of risks.
They are typically registered in locations where tax rates and insurance laws are most favorable, and are often operated from another location using modern communications technology. [p.165] TAX TARIFFS - a systematic list of rates, expressed in fixed amounts or as a percentage, at which various goods, services provided, etc. are taxed. The most typical tax tariffs are customs tariffs (see). [p.87] Tax tariffs are a systematic list of rates expressed in fixed amounts or [p.114]
Tax tariffs - see Tax tariffs. [p.181]
TAX TARIFF - a rate determined in monetary terms or as a percentage at which various goods, services provided, etc. are taxed; the most common tax tariff is the customs tariff. [p.650]
Despite this, many governments are taking a number of measures that, consciously or unwittingly, lead to some restrictions on the volume of foreign trade. First of all, this is the establishment of increased customs tariffs (taxes on goods imported into the country). Such tariffs are established either for purely fiscal purposes (to directly increase tax revenues to the state budget), or to protect domestic producers from foreign competition (for “protectionist” purposes). Another instrument of the government’s protectionist policy may be the establishment of quotas (restrictions) on the import of certain goods, again, with the aim of reducing foreign competition in the domestic market of certain goods. Final economic [p.17]
In 1993-1994 Wholesale prices of fuel and energy resources, rather than fuel and energy enterprises, rose at a faster rate. This was due to an increase in transport tax and the tax component. In 1993, the tariff for transporting goods by rail increased 19 times, causing the price for consumers to increase. The transport component became equal to 15% of the price of oil, and for petroleum products - 20% of the prices of the corresponding industry products. [p.135]
The policy of including Russia in international economic cooperation should not be used for the unilateral pumping of domestic raw materials, but for a radical structural restructuring of the Russian economy, since one of the most pressing problems of our industry is the need to renew fixed capital. In conditions of almost complete deterioration of production assets, not only are the trends of turning the Russian economy into an appendage of industrial countries intensifying, but the risk of environmental disaster is also increasing. Hence, state regulation of industry should contribute as much as possible to all forms of capital renewal (tax incentives for investments, liberalization of tariffs on the import of equipment). This will allow enterprises to concentrate certain financial resources for technological modernization and reconstruction of production. [p.250]
The tax system is a set of different types of taxes, in the construction and methods of calculation of which certain principles are implemented. It consists of direct and indirect taxes; direct taxes are established directly on the income or property of the taxpayer, the latter are included in the form of a surcharge in the price of the product (service tariff) and are paid by the consumer. Indirect taxes include excise taxes (fiscal monopolies, customs duties. [p.498]
Payment of customs duties and tariffs is made at the time of import or export of the leased item - in the amount of the paid part of the customs value of the property, which is confirmed by bank documents; in the future, customs duties and tariffs are paid simultaneously with leasing payments or within 20 days from the date of receipt of leasing payments. This procedure for paying customs duties and tariffs is not considered a deferment of customs payments or an investment tax credit. [p.182]
The crisis situation of recent years has exacerbated existing contradictions. There have been attempts to actually close down regions, introduce administrative regulation of prices for basic necessities, establish their own rules for the sale of goods, create their own gold and foreign exchange reserves, establish control over the tariffs of natural monopolies, carry out their own tax policy, etc. [p.321]
If the State Duma rejects federal laws on amendments and additions to tax legislation, to legislative acts on the tariffs of insurance contributions to state extra-budgetary funds before consideration in the first reading of the draft federal law on the federal budget, calculations for all indicators of the federal budget are carried out on the basis of current legislation. [p.382]
Thus, the customs tariff is a complex and multi-valued phenomenon that has not only an economic, but also a political dimension. However, from the standpoint of financial science, customs duty is one of the types of indirect tax that is imposed on foreign trade turnover of goods due to the fact of the movement of goods across the customs border. Customs duty has all the main tax attributes [p.154]
Customs duty is a tool for regulating foreign economic activity. Together with the domestic tax system, import and export tariffs regulate such indicators as prices, profits and profitability of enterprises. Customs duty is paid by enterprises when moving any goods across the customs border of the Russian Federation; it is collected by customs authorities before or at the time of acceptance of the customs declaration. [p.128]
Q Transport organizations set regulated tariffs independently, taking into account the system of tax regulation of enterprise income. They can be introduced for a period of price stabilization. [p.425]
Name of goods (description of work performed, services provided) Unit of measurement Quantity Price (tariff) per unit of measurement Most of goods (work, services), total without tax Including excise tax Tax rate, % Amount of tax on goods (work, services), total including sales tax amount Country of origin Freight customs declaration number [p.448]
To calculate VAT, tax rates of 0, 10 and 20% are applied. In addition, when selling goods, (work, services) at prices and tariffs that include VAT, as well as in cases provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, organizations have the right to use the calculation method for determining the tax rate. [p.101]
According to Art. 188 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when paying for gas transportation services through gas distribution networks, the cost of these services and the amount of tariffs were not included in the tax base. The FEC resolution approved tariffs for gas transportation services through gas distribution pipelines, and not through gas distribution networks. In this case, tariff rates for the use of gas distribution pipelines and tariff rates for gas transportation services are applied. Therefore, Law No. 57-FZ provides for a new version of this provision. [p.110]
The tax base is defined as the cost of goods (work, services) sold, calculated on the basis of applicable prices (tariffs) taking into account VAT and excise taxes (for excisable goods) without including sales tax [p.130]
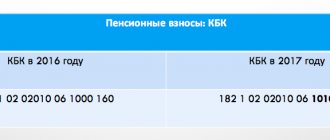
It should be noted that in accordance with Art. 10 of the Federal Law of December 15, 2001 No. 167-FZ On compulsory pension insurance in the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 167-FZ), the object of taxation of insurance premiums and the base for calculating insurance premiums are the object of taxation and the tax base for the unified social tax, established by the chapter 24 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. According to paragraph 3 of Art. 22 of Law No. 167-FZ, the tariffs provided for in paragraph 2 of this article are applied by policyholders - persons making payments to individuals, if the requirements established by paragraph 2 of Art. 241 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If the average tax base per individual is less than 2,500 rubles, then until the end of the tax period, insurance premiums are calculated and paid at the maximum rates determined by Art. 22 of Law No. 167-FZ, regardless of the actual size of the tax base for each individual. [p.186]
In Parus LLC, the 1st employee belongs to the group of men born in 1953 - 1966, respectively, the insurance premium rates for the tax base are up to 100,000 rubles. are 12% for the insurance part of the pension, 2% for the funded part of the pension, and for the Tax base from 100,000 to 300,000 rubles. — 12,000 rub. + 6.8% on amounts exceeding RUB 100,000. — for the insurance part of the pension, 2000 rubles. + 1.1% from an amount exceeding 100,000 rubles - for the funded part of the pension [p.190]
To be included in a taxpayer's income, these goods, works or services must be valued. In this case, the inevitable question is at what prices such an assessment should be carried out. Tax legislation gives an unambiguous answer to this question; the cost of these goods, works and services is calculated based on their market prices or tariffs in force on the day such income was received, and with state regulation of prices or tariffs - based on these government regulated retail prices or tariffs. [p.254]
Tax regulation of foreign trade activities. The instruments of tax regulation of foreign economic activity are the rates of customs duties and taxes levied during export-import transactions, benefits (preferences) on customs tariffs and taxes, penalties. [p.489]
Tax proceedings include the regulation of foreign trade activities by changing tax regimes, but this is usually carried out in cases of extreme necessity. Changes in tariff regimes may be valid without legislative registration. This is the area of state pricing policy. Taxation comes into contact with it to the extent that issues of budget formation are resolved. In this case, the principle of legality of taxes is not violated. Duties, fees, and tariffs by their nature are not taxes, although when implementing budget policy they are classified as such. But they are also legalized by the Customs Code. [p.124]
The provisions of the RF Law on Investment Tax Credit contain a special mechanism for indexing investment funds specified in the agreement with the tax administration. The return of a tax credit, issued as compensation for debt on tax payments, after two years occurs with profound changes in market conditions, the ratio of currencies, external and internal prices (tariffs), and lending rates. These objective factors make the tax credit burdensome for the unbalanced state budget. [p.165]
Arbitration courts, referring to the Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of October 12, 1998 No. 24-P In the case of verifying the constitutionality of clause 3 of Art. 11 of the Law of the Russian Federation of December 27, 1991 On the fundamentals of the tax system in the Russian Federation, at paragraph 2 of Art. 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, satisfy the claims of taxpayers. As in previous years, in 1999, the reason for satisfying a number of taxpayer claims was the ambiguous position of tax authorities and courts on the issue of including in the costs of privately practicing notaries the amounts of tariffs for performing notarial acts in relation to persons with state duty benefits, membership fees to the notary chamber , amounts of payments for insurance of notarial activities. [p.406]
Mutually influencing factors are external factors determined by the financial and credit policy of the state, including taxes and tax rates, interest rates on loans, to a certain extent prices, tariffs and fees, as well as internal factors, including cost, labor productivity, capital productivity, capital-labor ratio , turnover of working capital. [p.23]
Define the following key concepts: customs duty protectionism free trade customs tariff functions of customs duties classification of customs duties single-column and multi-column customs tariff specifics of the customs tariff as an indirect tax customs policy of the Russian Federation goals of the customs tariff in the Russian Federation customs duty benefits methods for determining customs value in the Russian Federation tax fees when moving goods across the customs border. [p.162]
The amount of tax determined in accordance with the tax base and the established rate is presented by the taxpayer when selling goods, works or services at free selling prices or tariffs to the buyer in addition to the price or tariff. A similar procedure is also applied when the taxpayer sells goods, works or services at state-regulated wholesale prices or tariffs that do not include VAT. [p.191]
On January 1, 1997, the new Law of the Russian Federation of February 1, 1997 No. 26-FZ On the tariffs of insurance contributions to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund, Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund, Employment Fund for 1997 came into force. Entrepreneurs reacted extremely negatively to the provisions of the new Law, whose insurance contribution to the pension fund increased from 5 to 28%. For farms, the insurance premium was set at 20.6%. However, we should not forget that entrepreneurs pay income tax on the amount reduced by the amount of the insurance contribution to the Pension Fund. According to the instructions of the Pension Fund administration (letter dated March 20, 1997 No. EB-09-11/2147-IN), insurance premiums are not charged for the amounts of contracts of sale, exchange, rental of vehicles (including maintenance), rental of premises, donation, loan , as well as loan agreements. The conditions for paying insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation for public organizations of disabled people have changed. Public organizations of disabled people and pensioners, as well as enterprises, institutions and organizations whose authorized capital consists entirely of contributions from public organizations of disabled people and the number of disabled people employed is at least 50% of the total number of employees, including enterprises, are exempt from paying insurance premiums. institutions and organizations that have these benefits and are subject to transformation before July 1, 1999 in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. If the number of working disabled people is less than 50% of the total number of employees, exemption from payment of insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation applies to payments accrued in favor of disabled people and pensioners, regardless of the sources of financing. Thus, the collection of insurance premiums is closer to the requirements that tax legislation imposes on public organizations of disabled people. [p.333]
The procedure for determining the tax base
The basic principles of calculating the tax base (TB), according to which it is determined, are:
- the determination of the tax base is carried out in accordance with tax regulations, in particular the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- calculation (determination) of the tax base by tax payers who are legal entities is carried out at the end of the next tax period. The implementation of the procedure is carried out on the basis of information from accounting registers or other documents confirming data on taxable objects;
- If errors and inaccuracies are identified in the calculation of the tax base made in the previous tax period, the tax base and tax amount are recalculated only for the time period in which the violation occurred. If it is impossible to determine the period of commission of the distortion, the recalculation procedure is carried out for the period when the violations were identified;
- Individual entrepreneurs, private notaries, lawyers-founders of law offices determine the National Bank at the end of the next tax period and in accordance with the accounting data of income and expenses, under the conditions and in the manner established by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation;
- tax agents are also required to adhere to the principles and procedure for calculating the tax base established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and other special acts of lawmaking.
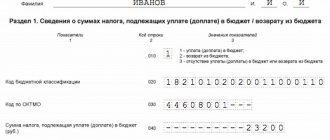
Payment procedure
According to Art. 287 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, income tax is paid by tax agents to the federal budget through the local Federal Tax Service. It is important to comply with the deadlines for payment of the fee, otherwise the tax authorities will charge penalties and, in the future, fines.
Step-by-step instructions for paying the fee:
- Calculate the tax amount.
- Fill out the appropriate declaration.
- Pay the fee: online on the official website of the Federal Tax Service or through the Sberbank cash desk. A payment order can be received at a bank branch or generated in your personal account on the official tax office resource.
The completed form must be submitted on the day the fee is paid - before the 28th day of the month following the reporting period.
Concept, legal characteristics and methods of expressing the tax rate
The concept of a tax rate (TS), as well as the procedure for its calculation, is inextricably linked with the tax base, since, in essence, the TS is the amount of the tax payment on a specifically established object subject to tax.
The tax rate can be expressed in the following forms:
- as a percentage of the size of the tax base. Such examples could be property tax, profit tax, VAT, personal income tax, land tax, etc.;
- in the form of a fixed monetary amount, when each tax unit corresponds to a certain payment amount. For example, most excise taxes, transport fees;
- in a combination of solid and percentage components, so to speak, in a combined form. For example, inheritance tax, gift tax, some types of excise taxes, as well as Unified Social Tax (UST).
The form of expression of the tax rate depends on the method and order of measurement of taxable objects.
Types and Types of Tax Rates
The standard classification of tax rates is carried out on certain grounds. Thus, according to the degree of burden for the taxpayer, the following types of tax payments are distinguished:
1. Basic NS. This concept does not provide for the classification of the taxpayer into any specific group, which gives him the opportunity to enjoy tax benefits and other preferences;
2. An increased tax rate is established in relation to taxpayers whose activities can be characterized as such, which gives the state the right to levy an increased tax from the payer;
3. Reduced NS. The use of this type of tax rate allows the taxpayer to enjoy tax benefits and preferences, up to the use of zero tax.
According to the method of establishment, tax rates can be:
1. Absolute.
The absolute tax rate is a fixed value determined for each specific object of taxation separately;
2. Relative.
The size of the relative tax directly depends on the size of the taxable object and is calculated in proportion to it.
According to the jurisdiction of approval, tax rates are divided into the following:
- federal;
- regional;
- local.
Combined tax rate that applies to income now!
From January 1, 2021, a combined tax rate applies to income with a payment date set in 2021. This tax rate is a symbiosis of a fixed (expressed in a fixed amount) tax rate and an interest (expressed as a percentage) tax rate. This tax rate is applicable to income that exceeds 5 million rubles.
You can take a closer look at the main types of tax rates by reading Art. 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation at the link: More >>>
That's all, thanks for your attention!
Main types of taxes, procedure for determining their amounts
1. Main types of federal taxes:
- Personal income tax. According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax rate for personal income tax is calculated as a percentage of the object of taxation and is 13% (for Russian citizens). As for persons who do not have the status of a citizen of the Russian Federation, a thirty percent tax rate for personal income tax is established for them. Payment of personal income tax is provided for all types of income that an individual receives (salary, sale of real estate, performance of work, provision of services);
- VAT. The tax rate for VAT, in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as personal income tax, is calculated as a percentage; in the territory of the Russian Federation it is equal to 18%. An exception is made for organizations operating under the simplified tax system, for which the tax liability in relation to VAT is set to zero;
- tax levy on enterprise profits. Income tax is calculated as a percentage and is applied primarily to representatives of large businesses.
- tax on proceeds under the simplified taxation system. As a rule, the simplified tax system is used by beginning entrepreneurs (representatives of small and medium-sized businesses), whose annual turnover does not exceed 60 million rubles. For such persons, zero VAT tax is provided.
2. Main types of local taxes:
- land tax. According to the law, the tax rate for land tax is regulated by municipal regulations and ranges from 0.3 to 1.5%. The amount of the established tax depends on the category of taxable land. Land categories are established by land legislation;
- tax on real estate of individuals. It is established by representatives of the municipal government, calculated as a percentage of the value of the property, as a rule, it is no more than 0.3%.
3.Main types of regional taxes:
- property tax for enterprises. This is a regional tax, which must be paid by organizations whose balance sheets include property, both movable and immovable;
- transport tax. This type of tax is regional; the tax rate for it is calculated based on data such as the year of manufacture of the vehicle, its capacity, engine power, etc.
Author of the article
In what cases are the above tax rates applicable?
Tax rate of 13%
A tax rate of 13% is applied to individuals (citizen taxpayers) on income received from the sale of property (securities are not included here), on income received from the sale of a share or several shares in property, income in the form of the value of property that was received through a gift, based on income received in the form of insurance payments and pension payments.
Tax rate of 15% (as indicated above)
Tax rate of 35%
A tax rate of 35% applies to income received as a result of winnings and prizes from participation in competitions, games and other events, if such income exceeds 4,000 rubles. Together with that:
- the amount of savings on interest when taxpayers receive borrowed (credit) funds;
- income in the form of fees for the use of funds of members of a consumer credit cooperative, as well as interest for the use of funds raised in the form of loans by an agricultural credit consumer cooperative.
Tax rate of 30%
A tax rate of 30% applies to all income received by non-tax residents of the Russian Federation (a tax resident is an individual actually located in Russia). Also, a tax rate of 30% applies to income received from securities that were issued by Russian organizations.
Tax rate of 9%
A tax rate of 9% is applied to income expressed as interest on mortgage-backed bonds, provided that they were issued before January 1, 2007, as well as to income of the founders of trust management of mortgage coverage, which was received on the basis of the acquisition of mortgage certificates participations that were issued before January 1, 2007.