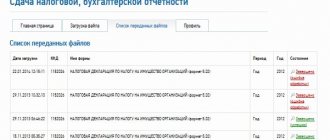
Tax reporting via the Internet
For taxes
As a general rule, for organizations and entrepreneurs the method of filing tax reports depends on the number of employees.
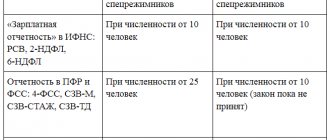
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs whose average headcount for the previous year exceeded 100 people must report to the Federal Tax Service strictly in electronic form via telecommunication channels (that is, via the Internet). This also applies to newly created (including reorganized) companies with more than 100 employees. Finally, electronic reporting is required for taxpayers classified as the largest. All other organizations and individual entrepreneurs have a choice: they can report both online and on paper. This follows from paragraph 3 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Submit all tax returns online for free
However, there is one exception to this rule - value added tax. All VAT payers and tax agents, regardless of the number of employees, are required to report electronically. The same rule is provided for those who are not VAT payers or are exempt from paying this tax, but issue invoices to buyers. This is stated in paragraph 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
By contributions
The method of submitting reports to funds on contributions to compulsory pension and compulsory health insurance, as well as insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity, also depends on the number of personnel. Thus, calculations for insurance premiums (DAM) must be sent via the Internet if the average number of employees of the employer for the previous period exceeds 10 people. This also applies to newly created (including reorganized) companies with more than 10 employees.
Fill out, check and submit insurance premium calculations online
All other contribution payers can submit the DAM both online and on paper. This follows from paragraph 10 of Article 431 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The heads of peasant (farm) households stand apart. They do not have the obligation to submit the DAM in electronic form, no matter the number of participants in such an enterprise (clause 3 of Article 432 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Let us add that starting with reporting for 2021, the DAM includes information on the average number of employees (see “Calculation of insurance premiums for 2021 must be submitted using a new form”).
Annual financial statements
Starting with reporting for 2021, there is only one acceptable way to submit the annual balance sheet - electronically, via telecommunication channels through an electronic document management operator (see “Accounting statements will be accepted only via the Internet”).
Prepare, check and submit financial statements to the Federal Tax Service via the Internet Submit for free
Interim financial statements 2021
From May 7, 2021, the preparation of interim reporting officially ceased to be mandatory for all organizations on the basis of Order of the Ministry of Finance dated April 11, 2018 No. 74n. The order canceled clause 29 of the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting, which required the preparation of interim reporting by everyone who is not exempt from it by law. Similarly, the decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation canceled paragraph 48 of PBU 4/99. Currently, it is necessary to prepare and submit interim reporting only in cases where this obligation is provided for:
- legislation;
- regulatory legal acts;
- contracts;
- constituent documents or decisions of owners.
For example, quarterly reporting is required for insurance organizations and securities issuers. If your organization does not fall under these conditions, it is obligatory to prepare only annual reports, but it is possible and useful to prepare interim reports on your own initiative.
Submission of interim reporting to tax authorities and statistical authorities is not required. But interim reporting may be needed when concluding agreements with counterparties, obtaining a bank loan or the requirements of the founder. In addition, interim reporting helps to monitor the situation, forecast financial results and verify the reliability of accounting data.
Electronic reporting to the Pension Fund of Russia
Form SZV-STAZH
No later than March 1, all policyholders must submit to the Pension Fund information about the length of service of the insured persons (Clause 2, Article 11 of Federal Law No. 27-FZ dated 01.04.96; hereinafter Law No. 27-FZ). You must report in the form SZV-STAZH, ODV-1 and other forms approved by Resolution of the Pension Fund Board of December 6, 2018 No. 507p.
The method of presenting information about length of service depends on the number of insured persons included in the report. If the number is 25 or more people, information must be submitted electronically. If the report reflects 24 people or less, you can present the information “on paper”. This rule is enshrined in paragraph 2 of Article 8 of Law No. 27-FZ.
Fill out and submit SZV-STAZH (SZV-ISKH, SZV-KORR) and EDV-1 via the Internet Submit for free
Form SZV-M
No later than the 15th day of each month, policyholders must submit to the Pension Fund information about the insured persons in the SZV-M form (this information includes full name, SNILS and TIN). This obligation is provided for in paragraph 2.2 of Article 11 of the Federal Law of 01.04.96 No. 27-FZ.
The method of submitting information on the SZV-M form depends on the number of insured persons included in the report. If the number is 25 or more people, information must be submitted electronically. If the report reflects 24 people or less, you can present the information “on paper”. This rule is enshrined in paragraph 2 of Article 8 of the Federal Law of 01.04.96 No. 27-FZ.
Fill out, check and submit the SZV-M for free via the Internet
Form SZV-TD
In connection with the advent of electronic work books, the SZV-TD form was introduced.
In 2021, it must be taken if the employee joined the staff, transferred to another permanent job, submitted an application to choose the form of the work record book (paper or electronic) or quit. In each of these cases, the deadline for submitting the report is no later than the 15th day of the month following the one in which the corresponding event occurred. If information is submitted for the first time, you must simultaneously provide information about your employment with the same policyholder as of January 1, 2021.
If the employee got a job in 2021 or earlier, and in 2021 did not quit, was not transferred, and did not apply to choose the form of the work book, he must proceed as follows. Submit SZV-TD for it as of January 1, 2021 no later than February 15, 2021 (see “General reporting on the SZV-TD form: who must submit information before February 15 and how to fill out the report”).
In 2021 and beyond, when hiring or dismissing an employee, you will need to submit the SZV-TD no later than the working day following the day the relevant order or other personnel document is issued. When transferring to another permanent job and when submitting an application to choose the work book form, SZV-TD must be submitted no later than the 15th day of the month following the one in which this event occurred. If there is no employment, transfer, dismissal or application regarding the work record, then there is no need to submit a report.
Policyholders who employed 25 or more insured persons in the previous month must submit the SZV-TD via the Internet. To do this, you can use the free program of the Pension Fund, or you can use any other service.
Fill out and submit the SZV-TD via the Internet Submit for free
Registers of insured persons
Employers who pay additional insurance contributions for a funded pension for their employees must create registers of insured persons in the DSV-3 form. Registers are submitted to the Pension Fund no later than the 20th day of the month following the quarter in which additional contributions were transferred.
The method of presenting information in the DSV-3 form depends on the number of personnel for the previous reporting period. If the number of employees is 25 insured persons or more, the report is submitted in electronic form, in other cases the report can be submitted on paper (Part 7, Article 9 of Federal Law No. 56-FZ of April 30, 2008).
Fill out and submit DSV-3 online for free
Composition of accounting records for a period of less than a year
Unlike annual reporting, interim reporting includes fewer forms. It is mandatory to prepare an interim balance sheet and a financial performance report. It also includes explanations if without them it is impossible to form a complete picture of the financial position of the organization and the financial results of its activities. If required by federal or industry accounting standards, founders or owners supplement interim reporting with a cash flow statement, explanatory notes and other forms.
The balance sheet contains information about the financial condition of the organization as of the current date. Assets provide information about property and liabilities to the organization. Liabilities reflect own and borrowed funds, allowing you to form an idea of the sources of property formation and the financial stability of the company.
The financial results report gives an idea of the organization's profits and losses for the period, allows you to assess the structure and dynamics of profits and identify problem areas and prospects.
Interim reporting forms are not approved by law; an organization can develop them itself, based on annual reporting forms. The reporting forms and its composition must be reflected in the accounting policies.
Reporting to the Social Insurance Fund in electronic form
4-FSS
Insurers must report quarterly on contributions to compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases in Form 4-FSS. The method of presentation depends on the average number of insured persons. Thus, calculations in form 4-FSS must be sent via the Internet if the average number of employees for the previous period exceeds 25 people. This also applies to newly created (including reorganized) companies with more than 25 employees. All other contribution payers can submit 4-FSS both online and on paper.
Please note: the method of submitting Form 4-FSS affects the deadlines. Reports in paper form should be submitted no later than the 20th day of the calendar month following the reporting period. You can report electronically no later than the 25th (Clause 1, Article 24 of Federal Law No. 125-FZ of July 24, 1998).
Fill out and submit 4‑FSS online using the current form
Registers of information for payment of sick leave
Since January 2021, in all regions, employees receive sick leave benefits not from employers, but directly from the Social Insurance Fund. Employers are required to submit to the social insurance fund registers of information necessary for the appointment and payment of benefits (see “Starting 2021, benefits will be paid directly from the Social Insurance Fund in all regions of Russia”).
The method of presenting the register depends on the average number of individuals who received payments from a given employer. If the average number of employees for the previous billing period exceeds 25 people, registers must be submitted via the Internet. This also applies to newly created (including reorganized) companies with more than 25 employees. All other employers can submit registers both online and on paper (clause 4 of the regulation approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2020 No. 2375).
Note that when submitting registers, those policyholders who use web services to prepare and check reports (for example, the system for sending reports “Kontur.Extern”) feel most comfortable. There, all current formats are installed automatically, without user intervention. The test program is also updated automatically. If the data entered by the policyholder does not correspond to the control ratios, the system will certainly warn him about this and tell him how to correct the errors.
Create and submit registers through “Kontur.Extern”
Preparing for interim reporting
The preparation of interim reporting includes several stages. First of all, you should prepare for its preparation. At the preparation stage, summarize all available data from primary and other documents, study the rules for drawing up forms and prepare the necessary data.
Interim reporting is prepared according to the same rules as annual reporting. It must be compiled in Russian, reflect numerical data in thousands of rubles or millions, negative indicators must be indicated in parentheses. Completed reports must be signed by the manager.
When compiling, the following data is required: full name of the documents, name of the organization, meters used, positions of persons responsible for accounting and reporting, and their personal signatures.
Complete accounting transactions at the end of the reporting period, check all entries in the accounting accounts and correct any errors found. Close accounts for cost accounting and formation of product costs on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year. Also, the preparation stage includes tax calculation.
Fines for violators
If a taxpayer who is required to report to the Federal Tax Service in electronic form submits a report “on paper”, he will have to pay a fine of 200 rubles. (Article 119.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For policyholders who violate the procedure for submitting information to the Pension Fund in the form of electronic documents, a sanction of 1,000 rubles is provided. (Article 17 of Law No. 27-FZ).
An insured who does not comply with the procedure for submitting Form 4-FSS in electronic form will be fined 200 rubles. (clause 2 of article 26.30 of Law No. 125-FZ).
Note that in practice, submitting paper reports instead of electronic ones often leads to other, more unpleasant consequences for business. Violators simply risk ruining relations with representatives of regulatory authorities. Officials take violators seriously and treat their reports, as well as their activities, more skeptically than the reports of bona fide payers. In addition, controllers are beginning to more often use various formal grounds for refusing to accept reports. And this, in turn, is fraught with fines for violating reporting deadlines.
Who might be interested in the balance sheet?
Persons interested in the procedure for preparing and submitting financial statements have the right to familiarize themselves with the balance sheet of the enterprise. These individuals include:
- owners of the enterprise;
- representatives of state statistical bodies;
- banks providing credit to organizations;
- investors;
- sponsoring organizations;
- partners, contractors with whom close cooperation has been established;
- representatives of the administration of the city, district, country;
- tax inspectors;
- financial and economic employees of the organization.
Who conducts audits for organizations subject to mandatory accounting audits
According to Art. 5 of Federal Law No. 307-FZ of December 30, 2008, mandatory audit of the accounting records of organizations whose securities are admitted to organized trading, other credit and insurance organizations, non-state pension funds, organizations in the authorized (share) capitals of which the share of state property is at least 25 %, state corporations, state-owned companies, public law companies is carried out only by audit organizations.
An agreement to conduct such an audit is concluded based on the results of an open competition at least once every 5 years in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation on the contract system in the field of procurement, goods, works, services to meet state and municipal needs.
Mandatory audit must be carried out by organizations subject to it annually.
What is the financial reporting of an enterprise, its role and significance
Accounting statements are classified, taking into account the requirements of the legislative framework governing accounting, data on the financial and economic condition of a business entity, the results of its economic activities as of a specific date, as well as information on its financial flows for a specific (reporting) period.
This information helps users and owners of financial accounting statements make informed and informed economic decisions regarding a business entity.
Financial statements (FOR) are not only an integral part of the annual reporting of an enterprise, but also a set of documents that allow its beneficiaries, as well as creditors and other persons, to make a conclusion about the effectiveness of the legal entity, its solvency, the state of settlements with counterparties, etc. .
The discrepancy between the control values in the financial statements of a business entity and the information on the basis of which taxes are calculated may become a reason for closer attention of the state supervisory authority to such an enterprise. Therefore, there is no need to approach the preparation of financial statements formally.
What financial reports are included in the financial statements, who is required to provide them and in what format
The structure of financial statements is regulated by the provisions of the Law “On Accounting” No. 402-FZ (Part 1, Article 14). It is primarily determined by the group of business entities to which the owner of the reporting belongs. So, for example, the preparation of financial statements is not mandatory for:
- individuals registered as individual entrepreneurs (IP);
- separate structural units of non-resident enterprises, if, in accordance with the current laws of Russia, they account for taxable income in accordance with the legislative norms of their countries.
Accounting statements according to the simplified type are prepared:
- small business firms;
- legal entities participating in the Skolkovo Research Center program, which, within the framework of it, carry out research and other related types of economic activities;
- non-profit organizations - persons whose activities are not aimed at obtaining benefits in the form of profit.
Accounting financial statements according to generally accepted rules are prepared by other organizations, namely:
- enterprises that, according to the law, must conduct an audit of their own activities;
- consumer cooperatives carrying out credit operations;
- microfinance companies (MFOs);
- public sector enterprises, political parties and their divisions;
- associations of lawyers, notaries;
- non-profit enterprises with the status of a foreign agent, which, in accordance with Federal Law No. 7-FZ of January 12, 1996, are included in the register of the same name (Clause 10, Article 13.1).
According to the general procedure, the following mandatory documents are included in the annual financial statements:
F No. 1:
The “balance sheet” is the fundamental document of the financial statements of any business entity. Allows you to analyze the economic activities of the company, draw conclusions about the entity’s belonging to a particular industry, determine the capital structure, degree of capitalization, etc.;
F No. 2:
“report of financial results” is the second most important document in the accounting report, which allows one to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of all types of activities of the enterprise, income received and expenses incurred in the reporting period, and the economic effect.
Forms No. 1 and No. 2
- These are the main forms of TSF. The current regulations governing accounting at enterprises also establish additional reporting (applications). It contains details and a breakdown of the indicators of the lines of the main forms. This includes:
F No. 3:
“Report on changes in capital” - this document reflects data on the movement of all types of capital of a business entity and changes in its structure;
F No. 6:
“Report on the intended use of funds” - current legislation obliges only non-profit organizations to generate this reporting form;
F No. 4:
“Cash flow report” is a document that allows you to obtain information about where funds come from to the company’s accounts and how they are spent. Summarizes data on all types of activities of the enterprise - operational, financial and investment.
The package of applications is closed by explanatory notes to the main forms of the FBO, which include information that helps to assess the financial and economic condition of the enterprise and analyze the results of its work for the past period.
These explanations primarily contain elements of a financial analysis of the entity’s activities - current indicators are compared with similar ones for the previous reporting period. Quarterly (interim, intra-annual) financial statements consist of:
- balance sheet;
- statement of financial results, if the provision of additional reporting is not regulated by law, registration documents, contracts or decisions of the owners of the company.
The simplified annual financial statements include:
- balance;
- report on the company's financial results;
- a report on the intended use of funds (this, as in cases with the preparation of this document by companies that keep records on a general basis, is mandatory exclusively for non-profit organizations);
- explanations to the above-mentioned financial statements of the company, which contain information that helps to assess its financial and economic condition and analyze its work.
Requirements and principles of filling
Without exception, all forms of financial statements must reflect comprehensive and truthful data about the financial condition of the company and the results of all types of activities performed. When drawing up an annual financial report, it is necessary to follow the norms of PBU 4/99, which establishes the main requirements for filling out reports, including the following principles:
- objectivity: the TSF must reflect the actual picture of affairs at the enterprise;
- accrual accounting: all transactions of the company must be taken into account - both those related to money and those that have a possible monetary value;
- compliance: costs that will be incurred in the future are capitalized and converted into expenses as benefits flow;
- costs for which the enterprise has already received a financial result, and their payment will be made in the future, should be considered as liabilities;
- conservatism: implies minimizing the risks of accepting overly optimistic data in the organization’s financial statements;
- reasonableness: excessive detailing of accounting should not be allowed.
Upon completion of filling out the financial statements, the accountant, on the recommendation of the Federal Tax Service, must check the control data ratios.
What reports are classified as the main forms of the TSF?
The forms of annual financial statements were adopted by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 66Н dated July 2, 2010. Currently, it is in force as amended on April 19, 2019 N 61н (additions No. 1-2 - for companies that form the FBO on a general basis, addition No. 5 - for those entities that prepare simplified reporting).
Updated financial reporting forms are used for the first time for reporting for 2019. To eliminate possible misunderstandings, when compiling the annual FSF for 2021, it is recommended to use a new list of financial statements, which can be downloaded on the website formy-i-blanki.ru. Next, let's look at the TSF forms in more detail.
F No. 1
— “balance sheet” (OKUD 0710001). This is the fundamental document of the reporting base, summarizing the results of ongoing economic activities. The report includes two sets of indicators – assets and liabilities. Together, they form the stakeholder’s understanding of what resources the company has and whether they are sufficient to cover its costs.
F No. 2
— “report of financial results” (it is also called “profit and loss statement”) (OKUD 0710002). This document reflects the sources and items of formation of income and expenses of the main activities of the subject.
Accounting reports forms 1 and 2 are the foundation of financial accounting reporting. Based on their information, accompanying and explanatory reports are compiled that allow a correct assessment of the enterprise’s performance.
F No. 3
— “report on changes in capital” (OKUD 0710004). It reflects the events that led to changes in the capital structure and their total expression.
F No. 4
— “cash flow report” (OKUD 0710005). This shows the inflow of funds into the company's accounts by source.
F No. 5
— explanations for FF1-2. In this document, the articles of the specified forms of financial statements are deciphered in more detail. It is drawn up in free form, but the sample recommended for filling out is in Addendum No. 3 to Order No. 66n.
F No. 6
– “report on the intended use of funds” (OKUD 0710003). By law, only non-profit organizations (NPOs) are required to fill it out - enterprises whose activities are not aimed at making a profit.
How often should financial statements be prepared?
According to the criterion of frequency of formation, financial statements are:
- annual;
- intermediate (intra-annual).
Intra-annual financial statements are combined financial indicators for a specific period of time (month, quarter, half year or 9 months). Annual financial statements are reports on the business and economic activities of an enterprise for the past year.
A business entity is always required to prepare annual reports (Law No. 402-FZ, Article 13, Clause 2). The need to prepare an intra-annual report, as well as the timing of its submission, are regulated by law, contracts, registration documents or relevant decisions of the owners of the business entity.
What information is reflected in the financial statements of enterprises
The content of the FBO must comply with the standards regulated by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 43n dated 07/06/1999 (as amended on 01/29/2018), which approved the fundamental accounting provision 4/99.
A balance sheet is one of the main forms of financial reporting that allows you to assess the financial condition of a company as of a certain date. The assets and liabilities reflected in it according to their circulation/repayment period must be divided into short-term (<12 months) and long-term (>12 months).
Balance sheet assets include current and non-current assets. Current assets with a circulation period of up to 12 months are, in turn, divided into groups according to liquidity (for example, the most liquid are cash, liquid are goods and receivables, etc.). It also reflects goods, inventories, debts of counterparties to the enterprise and other current assets. The non-current group includes intangible assets, fixed assets of the enterprise, financial investments for a period of >12 months. etc.
The liability includes data on the amount of own funds, as well as short-term and long-term obligations of the business entity - borrowed funds in the context of sources of formation (bank loans, debt of the entity to counterparties, reserves for future expenses, etc.).
The income statement expresses monetary indicators of sales volumes and the cost of products/goods, gross profit and indirect costs, interest payable and receivable, as well as other income and expenses. It also provides the result of the business entity’s activities before the payment of mandatory budget payments (taxes), the amount of such payments and the amount of the net economic effect (profit or loss).
In what form are financial statements submitted and within what time frame? How to punish for failure to report
Starting from 2021, the organization’s financial statements are submitted exclusively to the Federal Tax Service.
IMPORTANT! You no longer need to submit your balance sheet to Rosstat!
In 2021, financial statements, as before, are sent to the Federal Tax Service within three months from the end of the reporting year - that is, no later than 03/31/2020.
From January 1, 2021 all business entities must provide an annual accounting report in electronic form. This provision does not apply to SMEs. It is recommended to fill out and submit the amended financial reporting form when filling out the data for 2019.
If the economic activities of an enterprise are subject to audit by an auditor, its report must be submitted along with the FBO no later than 10 working days following the date of the report. The date of submission of the electronic report is the date of the receipt confirming receipt of the package of documents by the tax authorities.
For violators of the deadline for submitting an annual accounting report to the tax office, a fine of 200 rubles is established. However, the draft amendments to the Code of Administrative Offenses provide for the establishment of new fine rules. So, for example, for a company that conducts a mandatory audit, failure to provide the FBO by March 31 is fraught with a fine of 300 thousand rubles. – 500 thousand rubles. — for the company, 80 thousand rubles. – 100 thousand rubles. - for an official.
What changes came into force in 2020
Innovations for 2021, which affect the issues of filling out and submitting reports of organizations, are as follows:
- The company's annual financial statements are now provided only by electronic means. This norm does not yet apply to representatives of small businesses - they will begin submitting their reports electronically in a year, but for now submission in paper form or via TCS is allowed;
- Previously, the filing procedure was established by Rosstat, now by the Federal Tax Service;
- Previously, 1 copy of the reporting had to be submitted to statistics. Now the organization’s financial reporting forms and the audit company’s report are submitted only to NI;
- until 2021, the audit conclusion could be provided on paper, now only by electronic means, and exclusively to the Federal Tax Service;
- Previously, financial statements were considered signed only if they had the “living” signature of the manager. It is now possible to sign it using an electronic digital signature.
Compliance with the rules and regulations for preparing the balance sheet
There are different types of balance sheets applicable to different situations. To draw up a regular balance sheet for the internal needs of an enterprise, there are the following recommendations and rules:
- Data accounting is carried out taking into account the state of indicators on a specific date (balance) or by turnover periods (revolving);
- the information must display accounting or inventory data;
- quantitative indicators are displayed taking into account markups, depreciation, and reserve items;
- the balance sheet can be drawn up in both full and abbreviated form;
- the balance sheet can be reflected in the form of a correspondence between the sum of assets and the sum of liabilities and capital or in the form of a correspondence between capital and the difference between assets and liabilities;
- the balance sheet can be drawn up both for one enterprise and for several adjacent to it - branches, divisions (consolidated, consolidated balance sheets);
- the balance can also be interim, preliminary, final or forecast;
- Depending on the composition of the financial statements and the order of preparation, the balance sheet can be unifying, liquidating, opening, or dividing.