“Our organization uses the simplified tax system. In 2021, we plan to open an additional branch - a branch or just an additional office (not decided yet). In this case, will we lose the right to use the simplified tax system? Does it matter where the new division of the organization will be located: in the same subject of the Russian Federation with the head office or in different subjects? Will I need to register with the tax authority again? What tax reports will need to be submitted and where?” These are the questions our reader asked us. The answers are in the material provided.
HOW TO RETAIN THE RIGHT TO APPLY SYSTEM WHEN OPENING A DIVISION OF AN ORGANIZATION?
The use of a special tax regime - the simplified tax system - has a number of undeniable advantages that attract taxpayers, but there are also restrictions established by Chapter. 26.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. One of them is a ban on the use of the simplified tax system by organizations that have branches (clause 1, clause 3, article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
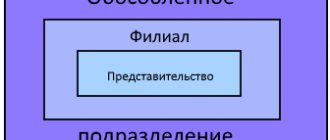
The Tax Code does not contain the concepts of “branch”, “representative office”, “additional office” (or similar). Article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation defines one general concept - “a separate division of an organization.”
The main features of a separate division of an organization are:
- territorial isolation from the organization;
- equipment of stationary workplaces at the location of this unit;
- independence from reflecting the fact of creating a separate division in the constituent or other documents of the organization;
- independence from the amount of authority vested in this unit.
Let's talk separately about the workplaces of a separate unit. To be recognized as a separate division of an organization, workplaces must be stationary. Based on Art. 209 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a workplace is a place where an employee must be or where he needs to arrive in connection with his work and which is directly or indirectly under the control of the employer. For these purposes, a workplace is considered stationary if it is created for a period of more than one month.
The equipment of the workplace means the creation of all the conditions necessary for the performance of work duties, as well as the very performance of these duties.
Let us note that the legislation does not specify the exact territorial location of the division and the location of the head office of this division (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 29, 2015 No. 03-11-06/62392). In this case, the territorial isolation of the unit from the organization is determined by an address different from the address of the specified organization (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 18, 2015 No. 03-02-07/1/47702). Accordingly, for the purposes of applying the simplified tax system, it does not matter where the separate division of the organization is located: in the same subject of the Russian Federation with the parent organization or in different ones.
Thus, an organization that opens a separate division has the right to continue to use the simplified tax system only if this separate division is not a branch. Tax legislation does not contain a separate concept of “branch”, and therefore, on the basis of clause 1 of Art. 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the designated concept is applied in the meaning in which it is used in the norms of civil law.
The concept of “branch” is given in Art. 55 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Main features of a branch:
- this is a separate division of a legal entity located outside its location;
- the branch carries out all the functions of a legal entity or part thereof, including the functions of a representative office;
- it is not a legal entity;
- the branch is endowed with the property of the legal entity that created it;
- he acts on the basis of provisions approved by the legal entity;
- the head of the branch is appointed by a legal entity and acts on the basis of his power of attorney;
- The branch is listed in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
It follows from these rules that if the creation of a separate division of an organization is not properly formalized as a branch of a legal entity, including if the branch is not indicated in the constituent documents of the organization and in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, then this organization has the right to continue to apply the simplified tax system subject to compliance with the norms established by Chapter . 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 29, 2015 No. 03-11-06/62392, dated October 14, 2015 No. 03-11-06/2/58685).
Similarities and differences between different structural units
Clause 2 of Article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains a clear explanation of the concept of “separate division”. It can be considered any division that is geographically remote from the company and in which jobs have been created and operate. Divisions of a company are recognized as separate even in cases where they are not mentioned in the constituent or other organizational documents of the legal entity.
The provisions of tax legislation nowhere mention such concepts as “representative office” or “branch”. Therefore, in terms of taxation, they should be used and understood in the meaning given to them by Article 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. It states that the representative office of the company is a separate division (SU), geographically located in another region, created for the purpose of representing the interests of the company and for protection.
Article 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation obliges companies to indicate in their constituent documents information about existing branches and representative offices. At the same time, various branches and representative offices, along with other structural divisions, do not have the status of a separate legal entity. They conduct their activities in terms of civil and other relations, as well as with regard to taxation, on behalf of the parent company.
From the above it is clear that the concept of “separate division” is broader than the concepts of “branch” and “representative office”. It includes absolutely all possible structural divisions of the company, regardless of their form, type of activity and powers.
DO I NEED TO REGISTER WITH THE TAX AUTHORITY WHEN CREATING A SEPARATE DIVISION?
If an organization using the simplified tax system has decided to create a separate division (in any form, except for a branch), then it is obliged to register for taxation at the location of this separate division (clause 1 of article 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Let us immediately make a reservation that the organization that opened a representative office has the right to continue to use the simplified tax system. A representative office is a separate division of a legal entity located outside its location, which represents the interests of the legal entity and protects them. The remaining criteria for a representative office coincide with the criteria for a branch. Accordingly, the registration authority has information about the opening of a representative office, since it must be indicated in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Therefore, registration with the tax authorities of a Russian organization at the location of the representative office is carried out on the basis of information contained in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. A legal entity, within three working days from the moment of creation of a representative office, is obliged to inform the registration authority at its location about this (Clause 5, Article 5 of the Federal Law of 08.08.2001 No. 129-FZ “On State Registration of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs”) . There is no need to register a representative office of the organization separately for tax purposes.
Since the vast majority of organizations open separate divisions that are not a representative office (hereinafter referred to as a separate division), we will consider their features of tax registration.
Firstly, since data on the creation of the named separate division is not submitted to the registration authority and is not entered either into the constituent documents or into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, the organization is obliged to register for tax purposes at the location of this separate division.
Secondly, registration with the tax authorities of a Russian organization at the location of its separate divisions is carried out by tax authorities on the basis of messages submitted (sent) by this organization in accordance with clause 2 of Art. 23 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The organization submits a notification on the creation of a separate division in the form S-09-3-1 “Notification on the creation on the territory of the Russian Federation of separate divisions (except for branches and representative offices) of a Russian organization and on changes to previously reported information about such separate divisions”, approved by the Order Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 06/09/2011 No. ММВ-7-6/ [email protected]
Note:
As a general rule, a notification about the creation of a separate division is submitted to the tax authority at the location of the separate division.
Only if several separate divisions of an organization are located in one municipality, the federal cities of Moscow, St. Petersburg and Sevastopol in territories under the jurisdiction of different tax authorities, the organization can be registered by the tax authority at the location of one of its separate divisions . The organization determines this independently. The organization indicates information about the choice of tax authority in a notification, the form of which is approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 11, 2011 No. YAK-7-6 / [email protected] and which is submitted to the tax authority at its location.
According to paragraph 9 of Art. 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if a taxpayer has difficulty determining the place of registration with the tax authority, a decision based on the data submitted by him (including documents, information about the activities of the organization through a separate division) is made by the tax authority.
Thirdly, specific deadlines have been established for reporting to the tax authority:
- on the creation of a separate division - within one month from the date of creation of a separate division of the Russian organization. The specified period is calculated from the beginning of the organization’s activities through the corresponding separate division (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 19, 2016 No. 03-02-07/1/9377);
- on changes in information about a separate division - within three days from the date of change in the relevant information;
- on termination of the activities of a separate division - within three days from the date of termination of said activities.
The process of tax registration of a separate division is completed by the fact that the tax authority carries out registration within five days from the date of receipt of the message from this organization and, at the same time, issues (or sends electronically) a notice of registration with the tax authority, which indicates the checkpoint of a separate unit.
Thus, if an organization using the simplified tax system has decided to create a separate division, then it is obliged to register for taxation at the location of this division. To do this, you need to submit a message in form C-09‑3‑1 within one month from the date of creation of a separate unit.
Since today there is no single position under which article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation to hold accountable for violating the deadline for registering a separate division - under Art. 126 (fine 200 rubles) or according to paragraph 2 of Art. 116 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (fine in the amount of 10% of income received during work without tax registration, but not less than 40,000 rubles) - we recommend compliance with the law (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 09/03/2012 No. 03‑02‑07/ 1‑211, dated 04/17/2013 No. 03‑02‑07/1/12946).
What powers do OP employees have?
In accordance with the provisions of the current legislation on LLCs and JSCs, only its director, the general manager, can represent the interests of the company and perform any actions on its behalf without a power of attorney. director, president, etc.
Other officials and employees, including those in whose hands the management of the structural unit is located, may act on behalf of the legal entity. person, as well as to represent or protect his interests, only with a valid power of attorney. The document is issued by the sole head of the company, for example, a director, must be certified by his signature and contain an imprint of the company's seal.
As for a separate division, one of the criteria on the basis of which it can be considered a representative office or branch is the extent of the powers vested in its employees. For example, the presence of a manager who has the right to perform any actions on behalf of the company (conclude contracts, sign primary documents, etc.) and has the appropriate power of attorney may well indicate that the structural unit is a branch (representative office).
It is not recommended to issue such title documents to other employees of the structural unit. The power of attorney for an ordinary employee should clearly and specifically state the list of rights with which this document gives him. The presence of a power of attorney by an employee, on the basis of which he receives the right to sign any documents, accept money from counterparties, or perform other actions in the interests of the company, does not at all indicate the creation of a branch or representative office.
When issuing a power of attorney to a person whose responsibilities include managing a structural unit, it is also advisable to indicate the range of his rights and responsibilities. And also clarify in the document that the right to perform all kinds of household chores. operations, resolution of management issues and protection of the rights of the organization remains with its sole leader.
DECLARATION OF TAX PAYABLE UNDER SUMMARY.
We are considering a case where an organization using the simplified tax system has created a separate division. In this situation, she continues to use the “simplified approach” while fulfilling all the restrictions established by Chapter. 26.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Note that the simplified tax system is applied by the entire organization as a whole, including a separate division. Chapter 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain requirements for separate accounting of goods sold, work performed or services provided in the parent organization and separate divisions.
Thus, an organization using the simplified taxation system keeps tax records of its activity indicators necessary to calculate the tax base and the amount of tax paid under the simplified taxation system for the organization as a whole, taking into account all income received and expenses incurred, regardless of where exactly these incomes were received and expenses were incurred: in the parent organization or a separate division.
In accordance with paragraph 6 of Art. 346.21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, payment of tax and advance payments for tax under the simplified tax system is made at the location of the organization. When calculating the “simplified” tax, it does not matter in which city (region) of the Russian Federation the separate division was created.
Based on the results of the tax period, taxpayers submit a tax return to the tax authority at the location of the organization (Article 346.23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Accordingly, at the location of the separate division, tax under the simplified tax system is not paid and a tax return is not submitted (letters from the Federal Tax Service for Moscow dated 08/31/2010 No. 16‑15/ [email protected] , dated 06/22/2011 No. 16‑15/ [email protected ] ).
Current account of the company at the location of its OP
A company can open a bank account in any bank located near the actual location of its division, regardless of whether it has the status of a representative office or a branch. The Bank, in turn, cannot prevent this in any way, since in accordance with Art. 846 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, an organization has the right to enter into an agreement on opening and servicing an account in any bank branch on the terms proposed by it. In this case, the bank is obliged to meet her.
Refusal is permitted only in the following cases:
- the bank does not have the opportunity to conclude a banking service agreement or fulfill its provisions in full;
- based on the decision of the Tax Service, any movements in the company’s accounts must be suspended;
- the client organization refuses to provide all the necessary identification documents that the bank has the right to request in pursuance of the Anti-Money Laundering Law.
In Russia, banks open current accounts for various legal entities. persons in accordance with certain rules prescribed in the BR Instruction No. 28I dated September 14, 2006. But this document does not contain any restrictions regarding the number of accounts opened by one organization or the location of the bank in which these accounts are opened.
In order to conclude an agreement with the bank on opening and servicing a bank account, the company must provide the following package of documents:
- OGRULE;
- Constituent documents (Charter, decision on the appointment of a manager, etc.);
- Licenses confirming the organization’s right to engage in a particular activity (if required);
- A card containing sample signatures of the manager, chief accountant, other authorized persons, as well as a sample of the company’s seal;
- Documents indicating that the indicated company representatives actually have full right to dispose of the company’s financial assets, which are stored in a bank account;
- Documents confirming the rights of the sole director of the company;
- TIN.
From all that has been said, it follows that the company can freely open current accounts in any bank branches, including those located at the location of the OP. By drawing up a card containing sample signatures of persons authorized to carry out financial transactions on the company’s account, the legal entity. the person independently decides whether to grant such a right to the manager and chief accountant of the branch (division).
REPORTING ON NDFL.
If an organization using the simplified tax system opens a separate division, then it, being a tax agent for personal income tax, must be ready to pay tax and submit reports for personal income tax (f. 2-NDFL and 6-NDFL) both at its location and at the location the location of each of its own separate divisions (clause 7 of article 226, clause 2 of article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the location of the separate division, personal income tax is paid and personal income tax reporting is submitted in relation to the employees of these separate divisions, as well as in relation to individuals who received income under civil contracts concluded by the separate division.
Note that if an organization has several separate divisions, then the payment of personal income tax and the submission of personal income tax reporting must be made both at the location of the parent organization and at the location of each division. In Letter No. 03‑04‑06/77778 dated December 23, 2016, representatives of the Ministry of Finance recalled that Ch. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain rules granting tax agents with separate divisions the right to independently choose a separate division through which tax transfers and, accordingly, personal income tax reporting would be submitted.
Representatives of the Federal Tax Service adhere to a similar opinion: the obligation of tax agents to submit calculations in Form 6-NDFL to the tax authority at the place of their registration corresponds with the obligation of tax agents to pay the total amount of tax calculated and withheld by the tax agent from the taxpayer in respect of whom he is recognized as the source of payment of income, to the budget at the place of registration of the tax agent with the tax authority (letters dated 10/05/2016 No. BS-4-11/ [email protected] , dated 11/09/2016 No. BS-4-11/ [email protected] , dated 11/25/2016 No. BS -4-11/22430).
Conclusions. What to do?
So, if a company still needs to use separate divisions in its activities:
- Taking advantage of the fact that from January 1, 2021, the Tax Code has established a restriction on the use of the simplified tax system by companies with branches, we recommend that you carefully distinguish between the concepts of a branch and a representative office, and use in your activities exactly this type of separate division as a representative office. The main danger here is that the tax authority does not detect signs of a branch in the activities of the representative office (clause 1, clause 3, article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- You can, of course, continue to work on the simplified tax system, using a branch in your activities and fully complying with the criterion of entrepreneurial activity “at your own peril and risk”, wait whether your company will be checked or not noticed. But in our opinion, such risks are not justified.
- Instead of a branch, you can open another legal entity (which would duplicate the economic activities of an existing one). But there is a new tax risk here! Recognition of firms as interdependent (a sign of fictitious division of business in order to obtain unjustified tax benefits).
- A legal and absolutely non-risky way is to obviously, before opening a branch, switch to the general taxation system. This, of course, does not sound so attractive and profitable, but having a good understanding of tax legislation, you can choose benefits for a specific type of activity and profitably use the general taxation system, for example, with reduced tax rates (10% instead of 18%).
CALCULATION OF INSURANCE PREMIUMS.
The procedure for paying insurance premiums, as well as submitting reports - calculating insurance premiums - does not depend on the applied tax regime, but is associated with the presence or absence of separate divisions of the organization (Article 431 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The legislator directly stated that the payment of insurance premiums and the submission of calculations for insurance premiums are carried out by the following organizations:
- at their location;
- at the location of the separate units.
But in this case we are not talking about all separate divisions of the organization, but only about those that accrue payments and other remuneration in favor of individuals (with the exception of separate divisions located outside the Russian Federation). The decision to vest a separate division established on the territory of the Russian Federation with the authority to accrue payments and rewards in favor of individuals is made by the payer of insurance premiums independently (letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 28, 2016 No. AS-4-11/25226, dated February 3, 2017 No. BS -4-11/ [email protected] ).
Accordingly, if a separate division of an organization does not independently calculate salaries and other payments to its employees, this is done centrally, then insurance premiums are paid and reporting on them is submitted only at the location of the parent organization.
If, according to the regulations on a separate division, payments to employees of this division are accrued by a separate division, then it independently pays insurance premiums and submits a calculation of insurance premiums at its location. The parent organization separately performs these responsibilities.
Judicial practice on this issue
Unfortunately, there is little judicial practice on this issue, and a number of cases that we found relate to the period 2010-2013, the so-called end of the “tax thaw” period.
When considering in court the issue of whether an organization has branches and representative offices, the courts will evaluate all the signs. The absence of at least one of them can be regarded as evidence that the structural unit is not a branch (representative office). Or it could be the other way around.
And vice versa, if we analyze judicial practice, we can see that despite the fact that the organization created separate divisions outside the location of the legal entity (they did not fall under the concept of a representative office or branch), since they did not represent the interests of the taxpayer; did not have an independent balance sheet or current account; were not indicated as a branch or representative office in the constituent documents. But they only carried out the sale of goods at retail.
Let's look at specific examples from judicial practice.
It is worth noting here that the above theses were selected from court decisions of 2010-2015. More relevant and as of 2016-2017. there are no solutions.
(Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated May 23, 2013 in case No. a27-16427/2012; Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Ural District dated December 29, 2014 No. F09-8604/14 in case No. A71-1573/2014;). The most revealing in judicial practice, where the court sided with the taxpayer, is the Determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated August 10, 2009 No. VAS-7488/09 on the refusal to transfer the case to the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation.
First case:
Companies did not lose the right to use the simplified tax system, despite the creation of separate divisions, since the courts came to the conclusion that these divisions did not contain signs of branches and representative offices (judicial practice in favor of taxpayers).
It is worth noting here that the following theses were selected from court decisions for 2010-2015, when it was possible to “fly away” from the simplified tax system by using not only a branch, but also a representative office in your activities. More current solutions, and as of 2016-2017. (when the presence of separate divisions in the form of representative offices does not exclude the use of the simplified tax system) no.
(See: Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated May 23, 2013 in case No. a27-16427/2012; Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Ural District dated December 29, 2014 No. F09-8604/14 in case No. A71-1573/2014; ). The most revealing in judicial practice, where the court sided with the taxpayer, is the Determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated August 10, 2009 No. VAS-7488/09 on the refusal to transfer the case to the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation.
Abstracts from court decisions:
The main position of the tax authorities and the reason for additional charges : According to the tax authority, outside the location of the company (in other regions), organizations create separate divisions that perform the functions of the parent organization and are branches, and therefore taxpayers are recognized as having lost the right to apply the simplified taxation system and are required to submit tax returns under the general taxation system.
Position of the arbitrators who supported the taxpayer and did not recognize him as having lost his right to the simplified tax system.
- The case materials do not contain evidence of the submission of relevant tax reports, the availability of data on the opening of current accounts for branches, the reflection of the activities of divisions in tax returns, the submission of information to the bodies of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation about branch employees, about the appointment of a branch director by the taxpayer and submission of a power of attorney confirming his authority.
- The tax authority’s conclusions about the presence of branches in the company were made by the tax authority only on the basis of a study of an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities containing information about the presence of branches (the formal approach of the tax authority without checking actual business activities was noted).
- The created separate divisions are structural divisions of a legal entity that do not fall under the concept of “branch” or “representative office”, since they do not represent the interests of the taxpayer and protect them; engaged only in the retail sale of goods; do not have an independent balance sheet and current account, and their property and funds are taken into account in the general balance sheet of the legal entity; separate divisions are not indicated as branches and representative offices in the constituent documents of the taxpayer.
- Lack of evidence confirming the actual existence and functioning of the Company's separate divisions outside the location of the legal entity; in fact, plans to create representative offices were not implemented; during the period of activity of the structural divisions (less than a year), the Company did not fulfill any requirements of Article 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in terms of organizing the activities of the representative office, and also did not begin to register separate divisions.
- The inspectorate did not provide sufficient and reliable evidence of the actual activities of the representative offices outside the location of the legal entity; The tax authority did not provide in the case materials information about their location at these addresses, evidence of the creation and functioning of equipped stationary workplaces in representative offices for a period of at least a month, etc.
Second case:
The company was denied application of the simplified tax system.
Abstracts from court decisions: (see Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Ural District dated March 16, 2016 No. F09-1692/16 in case No. A07-18712/2015).
Here the company went to court with a statement to declare illegal the tax inspectorate’s decision to refuse to satisfy the company’s application to switch to the simplified tax system.
The position of the arbitrators who supported the inspectorate’s decision to refuse the company’s application of the simplified taxation system.
- The case materials contain evidence of the creation and functioning of a branch of the company that meets the criteria listed in Art. 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Charter of the Company; registration of the branch; reflection of information about the branch in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities; availability of the Regulations on the branch approved by the general meeting of participants; availability of primary documents confirming the financial and economic activities of the company’s branch).
- Availability of signatures of the acting director of the branch on primary documents.
- An application to apply the simplified tax system was submitted before the decision to close a branch of the company.
Conclusions on judicial practice: So, it should be noted that, being on a simplified taxation system, using a separate division in your activities (even if it is a representative office that has not been prohibited since January 2021), you need to be careful. Indeed, in the best case, you will simply have to appeal the decision of the tax authority to refuse to satisfy the application for the transition to the simplified tax system, and in the worst case, if the company is already working on the simplified tax system and the tax authority proves the fact of creating a separate division in the form of a branch, there is a risk of huge additional charges (VAT , income tax), because the entire income of the company will be recognized as income received under the general taxation system.
LAND TAX DECLARATION.
Since “simplified people” are payers of land tax on a general basis, we note that, according to clause 3 of Art. 397 and paragraph 1 of Art. 398 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax and advance payments for land tax are paid by taxpayer organizations to the budget at the location of land plots recognized as the object of taxation (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 17, 2016 No. 03‑05‑06‑02/60364).
At the end of the tax period, taxpayers-organizations submit a land tax declaration to the tax authority also at the location of the land plot.
Thus, the presence of a separate division does not affect the procedure for paying land tax and submitting a declaration on it.
How to stay on track when opening a branch
Tax accounting under the simplified tax system is maintained in the Book of Income and Expenses Accounting (KUDiR). For organizations that have separate divisions, special accounting methods, as well as maintaining separate KUDiR for each division, are not provided for by law.
The parent organization maintains a single accounting book, and also submits a single tax report once a year - a declaration according to the simplified tax system. Indicators for separate divisions are included together with indicators for the head office and are not reflected separately.
The simplified tax and advance payments for it are paid to the Federal Tax Service at the location of the parent organization.
A separate division must be registered with the tax office at its location. Please note that this must be done if it is located in the territory under the jurisdiction of a tax office other than the one with which the organization itself is registered. Registration proceeds as follows: submit a message about the opening of a separate unit to your inspectorate where you are registered.
Its form No. S-09-3-1 was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 06/09/2011 No. ММВ-7-6/ [email protected] . The submission deadline is within one month from the date of creation of the unit. There is no need to attach any additional documents to the message. And you also do not need to contact the inspectorate at the location of the unit to register it.
The message can be brought to the tax office yourself, sent by registered mail or sent via TKS, certified by the digital signature of the head of the organization or another person authorized by a power of attorney.
Please note that a delay in submitting a notification about registering a unit will cost the company 10,000 rubles. fine (clause 1 of article 116 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, it is important to determine at what point a separate division can be considered created. Unfortunately, this issue is not clearly regulated in the Tax Code.
Thus, the month should be counted from the date of creation of this workplace or, for example, from the day the first employee was hired in a separate division. And in order to avoid disputes with tax authorities, it is worth meeting the one-month deadline and submitting a report to the inspectorate.
In addition, the branches of the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund in which the organization is registered must be informed about the opening of a new unit. The message is submitted in any form no later than a month from the date of creation of the unit (subparagraph 2, paragraph 3, article 28 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ). If you do not do this, you may be fined 200 rubles. (Article 48 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ).
The “simplified” tax and advance payments for it are paid to the Federal Tax Service at the location of the parent organization.
USN | 13:22 May 26, 2017
USN | 14:35 September 28, 2017
9:06 September 14, 2011
USN | 12:36 November 18, 2010
USN | 11:01 May 17, 2011
USN | 14:00 September 2, 2011
USN | 10:05 March 12, 2014
USN | 16:23 November 11, 2014, Unified Agricultural Sciences | 16:23 November 11, 2014
USN | 12:04 February 4, 2015, Unified Agricultural Sciences | 12:04 4 February 2015
recommended by letter dated May 20, 2015 No. GD-4-3/ for those applying preferential rates of the simplified tax system
What is what?
Loophole from the Ministry of Finance
All this is additional arguments in favor of the fact that the company has opened a separate division, and not a branch.
And don’t forget about the presumption of tax innocence (clause 6 of Article 108 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The controllers claim that you have opened a branch or representative office. Let them prove it.
Material provided by the magazine
Attention
Tax return 2-NDFL is also submitted here (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated December 16, 2011 No. 03-04-06/3-348). Payment of insurance premiums is carried out at the location of the separate branch, provided that it has a separate balance sheet and current account (Article 15 of the Law). Land tax is paid at the location of the plot (Article 397 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Submission of reports The following deadlines are established for submitting a tax return: Organizations Report by March 31 Individual entrepreneurs Submit a declaration by April 30 If the right to use the simplified tax system is lost, the taxpayer is required to report by the 25th day of the month that follows the previous tax period (Article 346.23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). What is the difference between a branch and a separate division? From the definitions given in the Civil and Tax Codes, as well as in Article 5 of the Federal Law of 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ, it follows that there are two forms of OP - branch and representative office. Thus, a branch is one of the forms of OP.
He also ruled that blocking the account and requiring tax officials to pay taxes under the general taxation system is illegal. The dispute flared up because, according to the Federal Tax Service, the company created separate divisions that performed the functions of the parent organization and, accordingly, were branches.
However, the court came to the conclusion that the taxpayer’s charter does not contain information about branches, and from the evidence presented it does not follow that the created separate divisions have the characteristics of branches defined in Article 55 of the Civil Code. Consequently, the tax authorities did not provide sufficient evidence confirming the creation and existence of branches by the company.
When and how to apply the special regime If the law does not oblige the fact of the creation (and functioning) of an EP to be reflected in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, then you can safely conduct activities under the simplified tax system with a separate division. True, there is an exception: from January 1, 2021, “simplified” people are allowed to create their own representative offices and this does not in any way affect the right to work for the simplified tax system.
Please note that the law does not oblige a separate division under the simplified tax system to maintain separate tax records. All manipulations are carried out by the head office in a regular book of income and expenses. There is no need to create any separate document in this situation. Also see “STS from 2021: how the limits on income and fixed assets will increase.”
PROPERTY TAX DECLARATION.
Since “simplified” organizations, as a general rule, are not payers of corporate property tax, we will consider only one case when they pay property tax - when they are the owners (or have the right of economic management) of real estate, in respect of which the tax base is determined as cadastral value and which is included in the corresponding list (Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Based on Art. 384, 385 and 385.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, payment of the property tax of organizations is carried out at the location of the organization, at the location of a separate division of the organization that has a separate balance sheet, as well as at the location of other real estate objects located outside the location of the organization or its separate division (Letter from the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 03‑05‑06‑02/60364).
Taking into account the features established by clause 13 of Art. 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an organization that uses the simplified tax system and has a separate division regarding real estate objects, the tax base for which is determined as the cadastral value, pays tax (advance tax payments) to the budget at the location of each of the specified real estate objects.
Calculations for advance tax payments and tax returns are submitted in a similar manner (Article 386 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
TRANSPORT TAX DECLARATION.
If an organization that uses the simplified tax system and has a separate division has a vehicle registered as an object of taxation, then it is a payer of transport tax.
Payment of transport tax and advance payments of tax is made by taxpayers to the budget at the location of the vehicles; The tax return is also submitted to the tax authority at the location of the vehicles (Articles 363, 363.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The location of the vehicle is determined in Art. 83 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
A vehicle can be registered with the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate either at the location of the parent organization (at the place of state registration) or at the location of a separate unit (clause 24.3 of Appendix 1 to Order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia dated November 24, 2008 No. 1001 “On the procedure for registering vehicles ").
Consequently, if, for example, a car is registered with the traffic police at the location of a separate unit, then the tax must be paid to the budget at the location (registration) of this separate unit and a transport tax declaration must be submitted there.
What exactly is the problem and what risks does it pose?
More than 20 years ago, the Simplified Taxation System (STS) was introduced to stimulate small businesses.
In order to exclude the use of the simplified tax system by large and medium-sized companies, many restrictions were introduced into the Tax Code. Taxpayers often try to circumvent them using dubious schemes, which leads to additional assessments. One of the restrictions is that organizations that have branches do not have the right to apply the simplified taxation system (clause 1, clause 3, article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Additional difficulties: if you are currently in a “simplified” state and you have so-called “separate divisions” (or what accountants consider to be separate divisions), then there is a risk... The risk that these divisions are recognized as branches, and as a result, You lose the right to apply the simplified taxation system.
In other words, they may recalculate all your taxes for the last three years, asking you to first pay VAT on all turnover for the last three years.
But let's not get ahead of ourselves. Let's consider all the nuances of this restriction.