Difference between new and used car
Depending on whether a car is purchased new or used, the act is drawn up by the accountant of the purchasing company or the seller of the car:
| New car | Used car |
| As usual, a dealer or showroom issues an invoice when selling a car, but does not deal with acceptance and transfer acts, so the responsibility falls on the buyer. | It makes sense to ask the seller to draw up the act. He will have to indicate in it information from the accounting system and data for calculating depreciation in the accounting system. This information includes:
You can accept UPD from the seller with the caveat that the data mentioned above will be indicated separately in the document. |
If you do not receive information about the useful life of a used car, all that remains is to accept it as equal to the useful life of a new vehicle, the values of which, of course, are not equal. This will significantly increase the company's costs and lead to incorrect calculations of depreciation and other indicators, and, as a result, to claims from tax inspectors.
The initial cost of the car consists of:
- the amount spent on the purchase of a car;
- expenses incurred during the purchase.
The legislative framework
The definition of the category “movable property” is in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in Art. 130. All property is divided into known real estate and movable objects.
The first type of objects includes land and everything that is located on it, property that cannot be moved without causing significant damage. This includes objects and unfinished construction structures.
This also applies to the category of real estate of inland navigation vessels that are registered in the name of the state.
All other objects of taxation, such as financial assets and capital (money), documents, cars and everything that can move or move without causing harm to others are considered movable property.
Costs related to purchasing a car
- State duty for traffic police services for car registration To avoid problems with the tax service, it is better to add the amount of the duty to the original cost of the car. The tax claims are related to the fact that money is written off over a long period of time, through depreciation expenses. In the case of a one-time attribution of expenses to other expenses, the company underestimates the income tax.
- Vehicle modernization. The tax inspectorate calls any addition to a car a modernization, since this will not change the characteristics and purpose of the car (and it doesn’t matter whether the car is new or used). There is an option for additional accounting. equipment costing more than 40 thousand rubles as an independent fixed asset. Or you can recognize an expense in the current period if the replenishment cost less than 40 thousand. However, designing a heater in this way can cause controversy because connecting it changes the characteristics of the car.
- Input VAT. VAT specified by the seller is also paid separately from the original cost. It is legal to take it into account as an expense under general conditions.
- Loan interest. In cases where the car was purchased with borrowed money, the overpayment on the loan is not included in the original cost. It is included in the lists of expenses as a percentage of any other debts, and the interest is necessarily normalized (the write-off occurs within the limits of the refinancing rate, multiplied by a coefficient of 1.8).
Car rent
The rented car is accounted for in off-balance sheet account 001 “Leased fixed assets” in the valuation specified in the lease agreement (Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). At the end of the contract, the property is written off from the tenant's off-balance sheet account.
The company's costs associated with the rental of a vehicle used for management needs are classified as expenses for ordinary activities and are recognized monthly in the amounts established by the agreement (clauses 5, 6, 6.1, 7, 16 of the Accounting Regulations “Costs of the organization” PBU 10/99, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 No. 33n).
Read also: “Payment for renting a car can be deducted from an employee’s salary”
Useful life of the vehicle
During the SPI, it is legal to write off the original cost of the car. For new cars, the terms are standardized according to the established Classification of Fixed Assets:
Important! Try to choose the minimum specified SPI, this will help you write off the cost of buying a car in the shortest possible time.
Difficulties arise with the SPI of used cars, it is calculated using the formula:
- SPI used = SPI of a similar new car - the period of operation by the previous owner.
A used SPI is included in the same depreciation group as the previous owner had it. It is better to charge depreciation, even if you have less than a year left to use the car. When a car was purchased from an individual who is not engaged in business, SPI is determined as based on new fixed assets that appeared.
What benefits are there?
Institutions that have at their disposal motor vehicles belonging to the third depreciation group can take advantage of benefits for paying property duties for organizations on movable assets.
Objects that are registered as a result of the liquidation of legal entities or their reorganization are deprived of preferential discounts.
Preferential programs for property duties are provided for organizations that are participants in the free economic zone, namely for purchased motor vehicles for the purpose of using them and conducting business for 10 years.
These benefits and amendments to legislation are aimed at avoiding tax evasion. After all, most legal entities, as a result of the reorganization of the institution, are trying to hide from debts to the state.
Due to changes in the law and amendments, not a large number of new taxpayers will be added.
After all, the majority of institutions will be exempt from paying duties as a result of using benefits (for the third depreciation group) or complete exemption from fees if motor vehicles belong to the first and other classification categories.
Calculation of depreciation on a purchased car
To correctly calculate depreciation, you need to have knowledge of two indicators:
- depreciation start date;
- SPI, during which the initial cost is written off.
| In accounting | In tax accounting |
| Depreciation begins on the first day of the month following the month the vehicle was registered as part of the operating system. To be clear, depreciation is calculated even for vehicles that are not used, if they are fit for use. | Depreciation is controlled from the first day of the month following the month when the car was actually used. Proof that this particular month was the month of start of use will be the date indicated in the act of putting the car into operation. |
Purchase and registration of a motor vehicle in 1C: Accounting ed. 3.0. – part 1
Published 08/13/2020 22:23 Author: Administrator We’ve released so many materials on vehicle registration lately – it’s impossible to count! They wrote about fines from the traffic police, they looked at compulsory motor vehicle insurance and motor insurance policies, and they didn’t forget to tell you about such expenses for a company car as parking and first aid kits. Of course, we cannot fail to mention our master classes “Accounting for fuels and lubricants and spare parts in 1C: Accounting”, “Leasing. Accounting for the lessee”. It would seem that we talked about everything! But no, “the main hero of the occasion,” as they say, was not considered, namely: the acquisition and registration of the vehicles themselves in 1C: Accounting ed. 3.0. We are in a hurry to get better soon.
So, let's start with the theoretical part. A car purchase and sale agreement is usually concluded in simple written form in triplicate: for the seller, the buyer and the traffic police. Such a transaction is not required to be notarized, as stated in Art. 158, 160, 161, 163 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition to the contract, a transfer and acceptance certificate must be drawn up. This document confirms the fact of transfer of the car from the seller to the buyer.
The next step for the new owner to register the car is to go to the traffic police department within 10 days after purchase. There you must fill out a special application to register the vehicle with the state in accordance with paragraphs. 1 clause 3 art. 8 Federal Law dated August 3, 2018 No. 283-FZ and pay the mandatory state duty, the amount of which is established by paragraphs. 36, 38 clause 1 art. 333.33 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Its reflection in the program depends on what goals you pursue when purchasing a car.
If a car is purchased for resale, then such property must be accepted as goods in account 41.
If the following conditions of clause 4 of PBU 6/01 are simultaneously met in relation to it, then the car is accepted for accounting as an item of fixed assets:
• the object will be used in production or management activities, or rented out for temporary use for a fee; • the period of use of the object exceeds 12 months; • no further sale of the property is expected; • the facility is capable of generating economic benefits in the future.
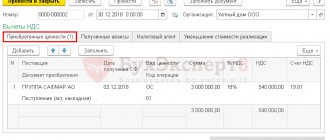
Let's consider a conditional example: on July 07, 2020, the organization Confetprom LLC purchases a 2021 KIA Sportage car worth RUB 2,300,500.00. (including VAT 20% - RUB 383,416.67) with an engine power of 180 hp. The car was put into operation on 07/09/2020 and registered with the Krasnodar traffic police on 07/13/2020. State fee for car registration in the amount of RUB 3,500.00. paid on July 13, 2020 and included in the organization’s expenses.
Step 1. Payment to the supplier.
We will pay the supplier for the car using the Bank-Client program. Next in the 1C program: Accounting ed. 3.0, let’s go to the “Bank and Cash Office” - “Bank Statements” section to reflect these transactions.
We will enter a document debiting from the current account, indicating in it all the basic data: recipient, amount, number and date of the agreement.
Click the “Pass” button. The program will generate the following transactions for us: Dt 60.02 Kt 51.
Step 2. Reflection of the fact of purchasing a car.
Next, we will register the car as a fixed asset. To do this, go to the “OS and Intangible Materials” section and create a new document “Equipment Receipt”.
We will arrange the item position on the “Equipment” tab according to the following figure. The item type must be “Equipment (fixed assets)”
By clicking the “Post” button, the program will generate transactions to offset the advance payment Dt 60.01 Kt 60.02, assign the car to account 08.04.1 and allocate VAT, according to the Instructions for using the chart of accounts, to account 19.01.
Next, we will accept the fixed asset for accounting. Let's go to the section “Fixed assets and intangible assets” - “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets”.
Let’s create a new document using the “Create” button.
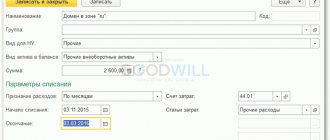
We enter the data we need: Financially responsible person, location of the car.
On the “Non-current asset” tab, be sure to indicate the method of receipt of fixed assets “Purchase for payment”.
On the “Fixed Assets” tab, add a new element using the “Create” button.
Be sure to indicate the OS accounting group “Vehicles”.
Next, fill out the “Accounting” tab, select the method of calculating depreciation, and the useful life of the OS.
In tax accounting, the useful life of fixed assets is established by the Classification of fixed assets included in depreciation groups (Government Decree No. 1 of January 1, 2002, clause 1 of Article 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In accounting, this period is set by the organization independently, taking into account the expected period of use of the car, physical wear and tear and other factors (clause 20 of PBU 6/01). In this case, the deadline in accounting can be set similar to the deadline in tax accounting.
To bring accounting and tax accounting as close as possible, we recommend choosing the same depreciation calculation method and useful life on the “Tax Accounting” tab.
You are responsible for filling out the “Depreciation Bonus” tab yourself. You can read about this in our article “Depreciation bonus when purchasing fixed assets in 1C: Accounting 8th ed. 3.0".
Let's look at the leashes generated by the program: Dt 01.01 Kt 08.04.1
Step 3. Reflection of state duty.
Now you need to reflect the payment and accounting of state duty.
The fee for registering a car with the traffic police is considered a state duty on the basis of paragraphs. 29 clause 1 art. 333.33 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
As a result of paying the state fee, you will receive state registration plates for the car, a vehicle passport (PTS) and a vehicle registration certificate.
The state duty paid for registering a car with the traffic police can be taken into account in two ways:
1) be included in the initial cost of the car as an asset (clause 8 of PBU 6/01), if it was paid before the object was registered as a fixed asset, i.e. before commissioning;
2) if the car has already been put into operation before registration with the traffic police, then the duty is taken into account either as part of expenses for ordinary activities, or as part of other expenses (clause 14 PBU 6/01, clause 11 PBU 10/99). This item depends on the intended use of the object.
In our example, the car was put into operation on 07/09/2020 before registration with the traffic police in Krasnodar. State fee for car registration in the amount of RUB 3,500.00. paid on July 13, 2020 and included in the organization’s expenses.
We will pay the state fee and generate a bank statement.
When entering the document “Write-off from the current account”, select the Transaction Type “Payment of Tax”. In the Tax field, we manually create the element we need by clicking the “Create” button.
Let’s enter the name of the state duty and the required BCC 18810807141011000110. Click the “Record and close” button.
The state fee for registering a car is a federal fee on the basis of clause 10 of Art. 13 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. We will indicate this when choosing the account 68.10.
By clicking the “Post and close” button, the program will generate transactions Dt 68.10 Kt 51.
There may be a situation where the state duty is paid in cash at the terminal in the traffic police department itself. Then you must make an advance report in the program.
Since the state duty is paid after the OS facility is put into operation, it is taken into account as expenses. This is done manually in the “Operations” section.
Let's enter the data we need. We create the cost item “State Duties” manually to correctly reflect costs on account 26.
We will indicate the type of expense as “Taxes and fees”.
Step 4. Calculation of depreciation.
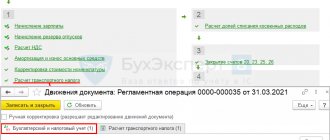
Let's check whether depreciation is automatically calculated on our car.
To do this, go to the “Operations” section and select the “Month Closing” procedure.
We will close the month for August 2021.
Let’s open the entries according to the regulatory procedure “Depreciation and depreciation of fixed assets.”
As you can see, the program perfectly calculated depreciation charges.
You can find out about the most common errors when calculating depreciation here.
We will consider the calculation of transport tax on a car and the reflection of this data in the transport tax return in our next article.
Authors of the article:
Irina Plotnikova
Oksana Kuznetsova
Did you like the article? Subscribe to the newsletter for new materials
Add a comment
Comments
0 Rostova Lyudmila Vasilyevna 08/21/2020 20:11 Good afternoon! Thank you for the information, it’s very relevant, but I also checked my past mistakes. The only thing is that I attributed the amount of state duty to account 91.02. And she did everything right.
Quote
0 Irina Plotnikova 08/20/2020 17:26 Quoting Olga:
Hello! How to offset VAT when buying a car? So it hangs on Dt19.01
Olga, good afternoon.
Check whether you have registered an invoice in the “Equipment Receipt” document. If yes, then by the regulatory operation “Creating purchase book entries” at the end of the month, VAT from account 19 will be transferred to account 68. Quote 0 Olga 08/19/2020 22:28 Hello! How to offset VAT when buying a car? So it hangs on Dt19.01
Quote
Update list of comments
JComments
Rationing of fuels and lubricants
Previously, the Ministry of Finance proposed rationing fuel and lubricants for correct tax accounting, but at the moment the financial department has recognized this as a right of organizations, not an obligation, due to the absence of such requirements in the tax code. Based on the foregoing, an enterprise registered for tax purposes under a simplified form of taxation can take into account the amounts spent on fuel and lubricants in full or within the limits of the norms.
If it was decided to use the standards, then you need to know that they may not coincide with the standards of the Ministry of Transport. The data reflected in the technical documentation of the machine manufacturer is suitable. Or there is an opportunity to identify your own indicators based on measurements and calculations carried out at the enterprise. Local tax authorities may still require compliance, so you will need to be able to defend your position.
The purchased fuel is credited to account 10 “Materials” subaccount “Fuel”. The write-off is carried out on the basis of data from waybills and receipts for the purchase of fuel and lubricants in full upon the fact. Cost accounts: 20, 26, 44, 91... It is also recommended to have a separate sub-account for the purchase of fuels and lubricants in excess of the standards.
Mandatory civil liability insurance
The organization is obliged to insure its civil liability no later than 5 days from the date of ownership. Insurance rates for compulsory insurance are established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 8, 2005 No. 739. These amounts will not be included in the initial cost of the car. In the accounting of an organization, the costs of obtaining a compulsory civil liability insurance policy are taken into account as part of expenses for ordinary activities. The policy is usually issued for a period of one year; in the future it is subject to renewal. Costs incurred by the organization in the reporting period, but related to the following reporting periods, “are subject to write-off in the manner established by the organization (uniformly, in proportion to the volume of production, etc.) during the period to which they relate.” Thus, the cost of insurance is taken into account as part of the expenses of future expenses, and then written off monthly as expenses of the reporting period during the policy period in the manner prescribed in the accounting policies of the organization for accounting purposes.