Types of accounting policies of a motor transport enterprise
Each motor transport enterprise must have its own accounting policy. It is necessary to take into account that the trucking company:
- is obliged to maintain accounting - for this it is necessary to formulate an accounting policy for accounting purposes;
- has the right to choose a tax regime that is beneficial for itself, fixing the nuances of tax accounting in tax accounting policy.
The company has the right to combine these types of accounting policies in a single document (providing separate chapters for this) or draw up 2 documents - the law does not establish strict requirements in this matter.
Study the accounting features reflected in the accounting policies under various tax regimes using the materials posted on our website:
- “Rules for drawing up accounting policies for UTII”;
- “How to draw up an organization’s accounting policy (2021)?”.
You can create an accounting policy using an accounting program. Examples of UE for each tax system can be downloaded in the Typical situation from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
Accounting Policy Services
Accounting Policy Accounting Policy General Accounting Policy (production)
Accounting Policy (trade) Accounting Policy (construction)
.
.
.
Accounting Policy Services for Accounting Purposes
Accounting Policy Services for Tax Accounting Purposes
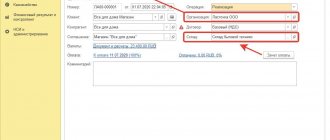
Limited Liability Company "ХХХХ"
ORDER No.
on approval of accounting policies for accounting purposes
___________ 12/31/20 __
I ORDER:
1. Approve the accounting policy for accounting purposes for the year 20__ in accordance with the Appendix
2. Entrust control over the execution of the order to the Chief Accountant I.I. Ivanov
General Director ____________________ P.P. Petrov
| Appendix to the order dated 12/31/20__ No. |
Accounting policies for accounting purposes
Accounting policies for accounting purposes are developed in accordance with
Federal Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”, Regulations on Maintaining
accounting and financial statements in the Russian Federation, PBU 1/2008 “Accounting
policies of organizations”, Chart of Accounts and Instructions for its
application, by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n “On forms
financial statements of organizations."
1. Accounting is maintained by the accounting department of XXXXX LLC under the leadership of the Chief Accountant.
Reason: Part 3 of Article 7 of Law No. 402-FZ.
Possible Options:
1) Accounting is maintained by a structural unit (accounting) that is directly subordinate to the Deputy Director for Economics and Finance.
2) Accounting is maintained by a third-party organization that provides specialized accounting services in accordance with the contract.
3) Accounting is carried out by the director of the organization.
2. Accounting is carried out automatically using a working Chart of Accounts in accordance with Appendix 1.
Reason: clause 8 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n.
3. For the following types of activities, accounting for assets and liabilities is carried out separately:
- provision of information services;
- leasing of office space;
- transactions with securities.
4. Separate divisions of the organization are not allocated to a separate balance sheet.
5. Unified forms approved by the State Statistics Committee of Russia are used as forms of primary accounting documents
When conducting business transactions for which standard forms of primary documents are not provided, independently developed forms are used.
The list of forms approved for use in the organization, as well as samples of non-standard documents are given in Appendix 2.
Reason: part 4 of article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ.
6. The right to sign primary accounting documents is granted to the officials listed in Appendix 3.
Reason: clause 7 of part 2 of article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ.
7. Accounting is carried out using accounting registers, the list and form of which are established in Appendix 4.
Reason: Article 10 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ.
8. The reporting period for the preparation of internal interim financial statements is a calendar month. The internal interim financial statements include a balance sheet and an income statement.
Reason: part 3 of article 14 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ and paragraph 49 of PBU 4/99.
9. The criterion for determining the level of materiality is set at 5 percent of the value of the accounting object or financial reporting item.
Reason: clause 3 of PBU 22/2010 and clause 11 of PBU 4/99.
10. An inventory of property and liabilities is carried out once a year before drawing up the annual balance sheet, as well as in other cases provided for by law, federal and industry standards governing accounting.
Reason: Part 3 of Article 11 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ.
eleven . There is no revaluation of fixed assets in 20___.
Reason: clause 15 of PBU 6/01.
12. An object is accepted for accounting as a fixed asset if it is intended for use in the statutory activities of the organization and for management needs. In this case, the following conditions are met:
- the object is intended for use for a long time (over 12 months);
- the organization does not intend the subsequent resale of this object;
- the cost of the object exceeds _______ rubles.
Reason: paragraphs 3 – 5 of PBU 6/01.
13. The useful lives of fixed assets are determined according to the Classification of fixed assets, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 1, 2002 No. 1.
Reason: clause 20 of PBU 6/01, paragraph 2 of clause 1 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated January 1, 2002 No. 1.
14. For fixed assets used for work under extended shift conditions, the useful life determined in accordance with the Classification of fixed assets is reduced by 2 times.
Reason: clause 20 of PBU 6/01.
15. Depreciation for all fixed assets is calculated using the straight-line method.
Reason: clause 18 of PBU 6/01.
16. Items with a useful life of more than 12 months and an initial cost of no more than ______ rubles. are written off as they are put into operation.
Reason: clause 5 of PBU 6/01.
17. Costs for current and major repairs of property are included in the organization’s expenses for the reporting period.
Reason: clause 27 of PBU 6/01.
18. The unit of accounting for inventories is the inventory number of inventories.
Reason: clause 3 of PBU 5/01.
19. Purchased inventories are reflected in accounting at discount prices without using an account
16 “Deviations in the cost of material assets.”
Transport and procurement costs are accounted for in a separate subaccount to account 10 “Materials”.
Reason: clause 5 of PBU 5/01, clauses 80, 83 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n, Chart of Accounts and Instructions for its application.
20. Upon disposal, all groups of inventories are valued at average cost.
Reason: clause 16 of PBU 5/01.
21. Expenses reflected in account 26 “General business expenses” during the month are completely written off at the end of the month to the debit of account 90 “Sales” without distribution by type of activity.
Reason: clause 9 of PBU 10/99.
22. Expenses that are included in the cost of services provided are recognized as:
- all material expenses, except general business expenses;
- labor costs for personnel involved in the provision of services:
- accrued amounts of contributions for compulsory pension (social, medical) insurance;
- the amount of accrued depreciation on fixed assets used in the process of providing services.
Reason: clause 9 of PBU 10/99.
23. Expenses attributable to the cost of all types of services provided form the financial result from the provision of services on the last day of the current month.
Reason: clauses 16 and 18 of PBU 10/99.
24. The unit of accounting for financial investments is ___________ (specify).
Reason: clause 5 of PBU 19/02.
25. Costs for the acquisition of financial investments that do not exceed the level of materiality established in paragraph 8 of this Accounting Policy are recognized as other expenses.
Reason: clause 11 of PBU 19/02.
26. The current market value of financial investments from which the market value can be determined is adjusted quarterly.
Reason: clause 20 of PBU 19/02.
27. Financial investments for which the current market value is not determined are subject to reflection in accounting and financial statements as of the reporting date at their original cost.
Reason: clause 21 of PBU 19/02.
28. All groups of financial investments for which the current market value is not determined are, upon write-off, valued at the original cost of each unit of financial investment.
Reason: clause 26 of PBU 19/02.
29. Checking for impairment of financial investments in order to create a reserve for impairment of financial investments is carried out annually.
Reason: clause 38 of PBU 19/02.
30. Deductions to the reserve for doubtful debts are made quarterly.
Reason: paragraph 70 of the Regulations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n,
paragraphs 6 and 7 of PBU 1/2008.
31. To calculate the reserve for vacation pay, the following procedure is used:
- the estimated liability in the form of a reserve for vacation pay is determined on the last day of each quarter;
- the amount of the reserve is calculated as the product of the number of vacation days unused by all employees of the organization at the end of the quarter (according to personnel records) by the average daily earnings for the organization for the last six months, taking into account accrued contributions for compulsory insurance.
Reason: clause 5 of PBU 8/2010, clause 7 of PBU 1/2008.
32. Exchange differences on foreign currency transactions are taken into account
on account 91 “Other income and expenses” as transactions are performed and at the end of each month.
Reason: clause 7 PBU 9/99, clause 7 PBU 3/2006, Chart of Accounts and Instructions for its application (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n).
33. Revenue from sales is reflected in accounting:
- in relation to information services - upon the provision of services on the date of signing the act on the provision of services;
- in relation to income from the rental of non-residential premises - monthly.
Reason: clause 12 of PBU 9/99.
34. Differences caused by differences in accounting and tax accounting are reflected in the accounting accounts as they appear, separately for each deviation based on primary accounting documents.
Reason: clause 3 of PBU 18/02.
35. The current income tax is determined on the basis of data generated in accounting in accordance with paragraphs 20 and 21 of PBU 18/02.
Reason: clause 22 of PBU 18/02.
36. The list of officials entitled to receive funds on account is given in Appendix 5. The deadline for submitting advance reports on amounts issued on account (except for amounts issued in connection with a business trip) is 30 calendar days. Upon returning from a business trip, the employee is required to submit an advance report on the amounts spent within three working days.
Reason: paragraph 26 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2008 No. 749.
37. The document flow schedule is approved by order of the manager. Compliance with the schedule is controlled by the chief accountant.
Reason: clause 8 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n.
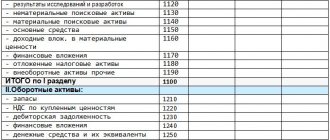
38. To prepare interim and annual financial statements, the forms of balance sheet and profit and loss statement are used in accordance with Appendix 1 of Order No. 66n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010.
Reason: paragraphs 1 and 2 of the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n.
39. Interim and annual financial statements are submitted within the time frame and composition provided for by law and federal standards governing accounting:
- to the tax office;
- to Rosstat (balance sheet and financial statements and appendices thereto);
- founders (according to the list).
Reason: Article 18 of Law No. 402-FZ.
Chief accountant __________________________ I.I. Ivanova
. . .
Accounting Policy Services for Tax Accounting Purposes
Accounting Policy Accounting Policy General Accounting Policy (production)
Accounting Policy (trade) Accounting Policy (construction)
.
.
We are forming an accounting policy for a transport company - what nuances should we take into account?
The accounting methods and methods established in the accounting policy (AP) of a transport company largely depend on the types of transport activities it carries out (transportation of goods, delivery of passengers, leasing of vehicles, repair and maintenance of automotive equipment, etc.).
If a trucking company simultaneously provides different types of services, the accounting policy must provide for separate accounting algorithms.
Learn about the nuances of accounting for motor transport activities from the article “Rules for accounting in a transport company (nuances).”
When developing a transport company’s management program, it is important to take into account the specifics of its work. In particular, reflect the following nuances:
- forms of specific primary information used (waybills, waybills, etc.);
- methodology for rationing fuel consumption (depending on the time of year, degree of wear of vehicles, etc.);
- the procedure for recording and writing off car tires;
- algorithms for accounting for other expenses characteristic of transport activities (motor insurance, recognition of expenses for medical examinations of drivers, etc.).
You can view a sample accounting policy of a motor transport company for accounting purposes on our website:
What types of accounting policies can a merchant create? You will learn about this from the materials on our website:
- “Accounting policies for management accounting purposes”;
- “Accounting policies in IFRS format - main provisions”.
What happens if I haven’t drawn up an accounting policy?
At first, you are in no danger. There are no fines for this. But when checking, the Federal Tax Service has the right to request your UE. A fine will be imposed for failure to provide it.
In addition, the tax office strictly checks your transactions for compliance with accounting policies. And if it is missing, then wait for additional charges.
To make your work easier and save time, consider the accounting web service Kontur.Accounting. It has already developed accounting policy options for different tax regimes and their combination. The program makes it easy and convenient to maintain accounting and tax records, pay taxes, salaries, and submit reports via the Internet. We give all newbies a free 14-day trial period.
Tax calculation
In 1C the calculation is carried out:
- quarterly—advance payments are set in the settings;
- at the end of the year - the settings do not set the payment of advances.
Tax calculation, including advance payments, is carried out through the Month Closing procedure - operation Calculation of transport tax.
During the reporting period
At the end of the year
Reconciliation with the Federal Tax Service for transport tax
From 2021, the tax return for transport tax has been canceled (Clause 9, Article 3 of Federal Law No. 63-FZ of April 15, 2019).
The tax authority sends a message to the organization about the calculated amount of transport tax for the tax period within 6 months. after the tax payment deadline, i.e. after March 1 of the year following the reporting year (clause 4 of Article 363 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The notification about the calculated tax is sent to the location of the vehicles within the following time limits:
- at the end of the year - within 10 days after the message is generated, but no later than 6 months from the date of expiration of the tax payment period for the period;
- when clarifying data for calculating tax - no later than 2 months from the date of receipt of documents (information) for calculating (recalculating) tax;
- when liquidating an organization - no later than 1 month from the date the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate receives information about the start of the liquidation procedure.
If an organization does not agree with the amount of tax calculated by the Federal Tax Service, it sends a Message to it within 10 days from the date of receipt
- explanations in free form with the Appendix: Application for the destruction of a vehicle (form, approved by Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated March 18, 2020 N BS-4-21/4722) - upon liquidation of a taxable object;
- Applications for transport tax benefits (form, approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated July 25, 2019 N ММВ-7-21/ [email protected] ) - if benefits are available;
- Messages about the availability of vehicles (form, approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated February 25, 2020 N ED-7-21 / [email protected] ) - in the presence of vehicles not taken into account by the Federal Tax Service when calculating the tax.
- supporting documents (optional).
Even if the 10-day period is violated, the tax authorities will consider the explanations and, if there are grounds, recalculate the tax (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated August 13, 2019 N AS-4-21 / [email protected] ).
If, despite the explanations and actually existing grounds for reducing the tax, the organization received from the tax authority a Request for payment of arrears of tax calculated according to the Federal Tax Service, it has the opportunity to resolve the issue by sending a complaint to a higher authority - the Federal Tax Service.
Display in accounting
The organization is required to register all vehicles that contribute to the generation of income. Tax is paid for each unit.
We talked in more detail about transport tax for organizations here.
If the owner transfers the vehicle for free use, he must notify the traffic police and tax authorities. Otherwise, the obligation to pay tax will remain with the previous owner. He also pays for transport transferred to another by proxy.
For each type of vehicle, the tax base and rate are calculated in accordance with Articles 359 and 361 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Transport is classified according to the following parameters :
- having an engine;
- air with a jet engine;
- water non-propelled;
- other water and air transport.
Subjects of the Russian Federation can reduce or increase tax rates. But their size should not exceed those established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation by more than ten times.
Each unit of transport must be accounted for individually . Long-term repairs or downtime of a vehicle does not exempt the taxpayer from paying the fee.
Check
Accounting for taxes in accounting is carried out on account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”. The chart of accounts provides a subaccount for accounting for transport fees. As stated in clause 5 of PBU 10/99, it is included in expenses. They usually relate to the main activity.
Posting upon accrual
The correspondence of invoices depends on the method of use of the vehicles. Transport can be used in the production and sale of products.
When tax is calculated, the accounting entry looks like this::
- D-t 20 “Main production” (23, 25, 26, 44, etc.) K-t 68 when using transport in the production and sale of products.
- Dt 91.2 “Other expenses” Dt 68 , if the operation of the vehicle does not occur in the main activity.
Paid:
- Dt 68 and Kt 51 “Current account”.
- D-t 68 and K-t 50 “Cash desk”.
Type of consumption
Which expense item the transport fee will relate to depends on the accounting policy chosen by the legal entity. Most often, tax is included in the main activity and reflected in the appropriate accounts (20,23,25,26,44, etc.).
If the company rents out vehicles, the fee should be reflected in account 91.2 “Other expenses”. Only on the condition that renting out vehicles is not the main way to generate income.
Taxpayers make quarterly advance payments, unless otherwise provided by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. The accounting certificate serves as the basis for classifying transport fees and payments as expenses.
What to approve in the accounting policy
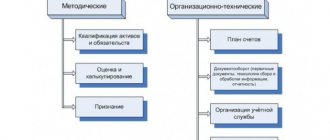
The accounting policy approves:
- a working chart of accounts containing synthetic and analytical accounts necessary for maintaining accounting records in accordance with the requirements of timeliness and completeness of accounting and reporting;
- forms of primary accounting documents, accounting registers, as well as documents for internal accounting reporting;
- the procedure for conducting an inventory of the organization’s assets and liabilities;
- methods for assessing assets and liabilities;
- document flow rules and accounting information processing technology;
- the procedure for monitoring business operations;
- other solutions necessary for organizing accounting.
This follows from paragraph 4 of PBU 1/2008.
Previously on the topic:
Fundamental differences between the two standards for asset accounting
Accounting
Our organization offers accounting services:
- accounting of transport tax and a number of other taxes, fees,
- filling out and submitting company documents,
- settlements with funds, Federal Tax Service.
The company provides comprehensive accounting services.
We provide such a service as tax optimization for an organization. Cost planning allows you to reduce the amount of taxes for their use in business activities. Call and get advice from professional accountants on all issues.
Our services include ]mandatory reporting audit[/anchor] and selection of an accountant.