The regulation on bonuses for employees is a local regulatory document that is being developed to determine the procedure and conditions for assigning a bonus: monetary reward for certain results or for an event for a certain period.
In order to regulate the bonus system at enterprises, a document is adopted such as the regulation on bonuses and material incentives for employees (the name is not strictly enshrined in legislation and can be transformed). It does not apply to the list of mandatory local regulations under Art. 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but at large enterprises, in order to establish the validity and correctness of bonuses, labor inspectors recommend developing such a document.
Why do you need a Bonus Regulation?
Each enterprise has the right to independently develop a bonus system for its employees. The only condition for this is that it fully complies with the framework of the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
Generally speaking, the Regulations establish which employees, for what services and under what circumstances can receive financial incentives from the company’s management.
Thus, by developing the Regulations on bonuses, the enterprise administration usually achieves several goals at once:
- increased labor productivity and employee efficiency,
- the quality of products improves,
- labor discipline is strengthened,
- general prospects are expanding.
In some cases, in the future, the Regulations may become a legally significant document that has evidentiary force in court - for example, when resolving labor disputes and disagreements regarding the payment of wages and other material incentives to an employee. That is why its preparation should be treated with the utmost care, taking into account all the subtleties and nuances of the enterprise.
Order for a bonus
The manager's order is drawn up according to unified forms approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 5, 2004 No. 1: Form T-11 or Form T-11A (for bonuses to a group of employees).
The Instructions for Application and Completion of Forms state that Form T-11 and Form T-11A:
- used to formalize and record incentives for success in work;
- are compiled on the basis of a proposal from the head of the structural unit of the organization in which the employee works;
- signed by the manager or authorized person;
- are announced to the employee against signature.
Based on the order, an entry is made in the employee’s personal card (Form T-2 or Form T-2GS (MS)) and his work book.
When registering all types of incentives, except for monetary rewards (bonuses), it is allowed to exclude from Form T-11 the requisite “in the amount of ______ rubles. _____ cop.”
When filling out Form T-11, the full name, structural unit, and type of incentive (gratitude, valuable gift, bonus, etc.) are indicated. If we are talking about material assistance and valuable gifts as elements of bonuses, then, according to clause 28 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, personal income tax is not calculated if material assistance does not reach 4,000 rubles. per year, and if it has been reached, then personal income tax is accrued only on the excess and is separately exempted, also in the amount of 4,000 rubles, increasing from the beginning of the year, a gift.
Arbitration practice shows that a gift is not money, but a thing. However, sometimes the tax authorities regard money as a gift. Therefore, you need to be prepared for an ambiguous approach from the tax authorities to such situations.
Who draws up the Regulations
The responsibility for developing this document on bonuses for employees usually falls within the competence of the company's lawyer, personnel officer, and less often - the secretary or the manager himself. In any case, this must be a person who has the necessary theoretical knowledge in the field of labor and civil legislation and the skills to write such documents. And regardless of who is directly involved in this work, the final version of the regulation must be submitted for approval to the director of the organization.
How the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates bonuses
According to Article 129 “Basic concepts and definitions” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2001 No. 197-FZ (as amended on August 2, 2019), workers’ wages are defined as:
- the basic salary paid for performing work under an employment contract (Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- compensation allowances for work in difficult climatic conditions or associated with danger and harm to health;
- incentive payments paid in the form of monetary incentives for success in work.
Bonuses according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are mentioned in section No. 4 “Payment and standardization of labor”, in article 191 “Incentives for work”, as a reward for the high-quality performance of one’s work and achievements in performing work tasks.
Is it necessary to familiarize employees with the Regulations?
Theoretically (and often practically) the Regulation applies to every employee of the enterprise, so all employees must be familiar with it. As a rule, the document is studied directly during employment or, if the document was developed during the period of active work of the organization, at any stage of its activities.
Typically, companies have special journals in which employees sign that they are familiar with the company’s internal regulations, including the Regulations on Bonuses.
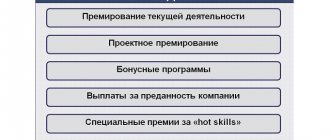
Types of awards
There are two types of awards:
1. Bonuses that are provided for by the remuneration system based on specific indicators and bonus conditions developed in the company.
Such bonuses are part of the material motivation of employees; they are stimulating in nature. They are paid periodically (monthly, annual, quarterly, etc.) and are usually set in a certain amount.
2. One-time bonuses that are not included in the remuneration system.
Paid to an employee for certain achievements, many years of conscientious work, completion of an urgent and important task, or for significant events (for example, anniversaries and professional holidays).
Payment of a one-time bonus is carried out at the unilateral discretion of the employer. The basis is the Order of the head.
Convenient and error-free maintenance of personnel records in a web service
To learn more
Rules and example of drawing up Regulations on bonuses
There is no standard, unified, one-size-fits-all form of this document, so organizations can develop the Regulations in free form. The main condition is that it contains:
- name of company,
- creation date
- and the signature of the manager.
It is recommended to note a number of information that it is desirable to include in the document, these are:
- conditions for awarding the award,
- its size
- and payment terms.
It is also advisable to note that bonuses are solely the initiative of the employer - this, if anything happens, will help avoid unreasonable demands from subordinates.
Is it possible to deprive a bonus?
For employers, there are no restrictions on depreciation and bonuses for employees in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The company management has the right to deprive an employee of bonuses or reduce the amount in the following cases:
- dishonest performance of work duties;
- causing damage;
- systematic absenteeism, tardiness and absence from work;
- disciplinary sanctions;
- complaints against the employee from clients.
The main provisions of bonus reduction must be reflected in the regulatory documents of the organization. If an employee does not agree with the employer’s opinion, he has the opportunity to file a complaint in court to challenge the decision.
Rules for document execution
The document can be drawn up on a simple blank A4 sheet or the organization’s letterhead - this does not matter, just like whether it is written by hand or printed on a computer. The only rule is that it must have the signature of the head of the company or another person responsible for the approval of such employee documents. It is not necessary to certify the document with a seal, since from 2021 legal entities, as previously and individual entrepreneurs, have the right not to use seals and stamps to endorse their documentation.
The regulation is usually drawn up in a single copy , registered in the company's accounting policies, and then contained together with other internal regulations in a certain order. After losing its relevance, it is transferred for storage to the archive of the enterprise, where it remains exactly as much as is established by law. After the expiration of this period, the Regulation can be disposed of.
How are bonuses taken into account when calculating average earnings?
The calculation of average earnings is determined by Art. 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Government Decree No. 922 of December 24, 2007. This issue, in particular, is detailed in paragraph 15 of the Decree.
The resolution does not define sick pay, but vacation pay and business trips, since the average salary is calculated during business trips. Therefore, paragraph 15 applies to these two cases.
Paragraph 15 says that when determining average earnings, the following are taken into account:
- monthly bonuses actually accrued in the billing period, but not more than one payment for each indicator for each month of the billing period
If several bonuses were awarded for one indicator in the billing period, then one bonus is included. Let’s say that sales managers are awarded three bonuses depending on sales: 1% of sales volume, 0.5% of sales as an incentive for particularly successful managers, and 5% of sales from the bonus fund. Accordingly, in this case, only one bonus will be included in the calculation, since all listed bonuses are paid on the same basis.
If you have one bonus awarded for sales, and the second for going to work on weekends, then you need to include both bonuses, because these payments are based on different indicators.
- bonuses for a period of work exceeding one month (for example, quarterly), but not more than the billing period (one year)
Such premiums are included if they were accrued for a period of more than a month, but not longer than the billing period. One is included for each indicator (for example, if a bonus was paid based on the results of work for the quarter and there was also a bonus for individual employees for completing urgent tasks).
- premiums for a period greater than the estimated one
Such premiums are included in the calculation in the amount of the monthly part for each indicator for each month of the billing period.
For example, this could be a bonus at the end of a large project that lasted several years. In this case, the annual calculation will be included in the amount of 1/3.
- year-end bonus
As a rule, such a bonus is awarded in February. In this regard, the question often arises: what to do if an employee quits at the end of January? Should he be given a bonus in this case? The answer to the question is contained in the company's internal documents. If they state that the bonus is paid at the end of the year, then an employee who has worked for 12 months and quits at the end of the year must receive it.
If internal documents state that an employee who quit before the bonus was accrued is not entitled to it, then the employee has no right to claim the payment. The legislation does not provide guidance on this issue.
According to Resolution No. 922, remuneration based on the results of work for the year, accrued for the calendar year preceding the event, is taken into account regardless of the time of its accrual.
Do I need to pay an annual bonus to an employee who quit in October?
The Appeal Ruling of the Supreme Court of the Republic of Karelia dated September 25, 2018 No. 33-3344/2018 considers the situation when the employer, having issued an order for an annual bonus, which was paid taking into account the time worked, did not include in the lists an employee who quit two months before the end of the year.
The court considered that such actions were discriminatory (the employee was placed in an unequal position with others) and collected a bonus from the company.
Subscribe to our Telegram channel to stay informed about the most important changes for business.
How to make changes?
All documents sometimes need additions, corrections and amendments, and the promotion regulations are no exception . Any changes can be made to the document at any time. If the company has a trade union, then any change must be agreed with it.
- All changes and additions must be recorded in the regulations in the same order in which they were originally developed.
- In case of significant changes, it is possible to draw up completely new regulations.
- When making changes and additions to the old regulations, it is necessary to draw up a corresponding order (if it was issued when the original regulations were formed).
To summarize, it can be noted that the incentive regulations are a necessary document for the company , which is an excellent tool for stimulating and motivating employees.
Regulations on remuneration, bonuses and additional payments for employees
GENERAL PROVISIONS
- This Regulation has been developed in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Remuneration is understood as a system of relations related to ensuring that the employer establishes and makes payments to employees for their work in accordance with laws, other regulations, these Regulations and employment contracts.
- The Company has established a tariff system of remuneration, which includes a tariff rate (salary). Tariff rate (salary) is a fixed amount of remuneration for an employee for performing job duties of a certain complexity (qualification) per unit of time.
- The monthly tariff rate (salary) is determined by the Company’s staffing table.
- The monthly tariff rate (salary) does not include additional payments, allowances and grants, other compensation and social payments.
- The monthly tariff rate (salary) changes if changes are made to the Company's staffing table.
- Managers and specialists whose salaries are set are paid according to the staffing schedule approved by the head of the enterprise and the amount of time worked.
- Tariff rates (salaries) are set based on a 40-hour working week; for part-time workers - based on a 16-hour working week and a 3.2-hour working day.
Remuneration of the Organization's Employees includes:
- wages, consisting of salary (official salary), as well as additional payments and allowances for special working conditions (hard work, work with harmful and (or) dangerous and other special working conditions), as well as for working conditions deviating from normal (if performing work of various qualifications, combining professions, working outside normal working hours, at night, on weekends and non-working holidays, etc.);
- incentive and incentive payments for the proper performance of job duties, made in accordance with these Regulations and the Regulations on Bonuses. Payment of wages in the Company is made in cash in rubles.
- Deductions from an employee's salary are made only in cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws.
- The total amount of all deductions for each payment of wages cannot exceed 20%, and in cases provided for by federal laws - 50% of wages due to the employee (Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- In certain cases (collection of alimony for minor children, compensation for harm caused by the employer to the health of an employee, compensation for harm to persons who suffered damage in connection with the death of the breadwinner, and compensation for damage caused by a crime), established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, the amount of deductions from wages cannot exceed 70%. Deductions from payments that are not subject to foreclosure in accordance with federal law are not allowed (Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Upon termination of the employment contract, payment of all amounts due to the employee from the employer is made on the day the employee is dismissed. If the employee did not work on the day of dismissal, then the corresponding amounts are paid no later than the next day after the dismissed employee submits a request for payment. In the event of a dispute about the amount of amounts due to the employee upon dismissal, the employer undertakes to pay the amount not disputed by him within the period indicated above (Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Wages not received by the day of the employee’s death are issued to members of his family or to a person who was dependent on the deceased on the day of his death. Payment of wages is made no later than a week from the date of submission of the relevant documents to the employer.
- Downtime caused by the employer, if the employee warned the employer in writing about the start of downtime, is paid in the amount of at least two-thirds of the employee’s average salary.
- Downtime due to reasons beyond the control of the employer and employee, if the employee has warned the employer in writing about the start of downtime, is paid in the amount of at least two-thirds of the tariff rate (salary).
Downtime caused by the employee is not paid.
WAGE SYSTEM
In these Regulations, the remuneration system refers to the method of calculating the amount of remuneration payable to Employees for the performance of their labor duties.
Direct piecework wages
For employees of production departments (workshops for production, metal loading), a direct piece-rate wage system has been established, since the results of their work can be quantitatively measured and they are expressed in kind.
Specific prices are set for the production of each unit of production. Their size is determined by order of the general director for six months. Salaries are calculated in the following order: the quantity of a particular type of product produced by an employee is multiplied by the prices (set for one unit of production). Then the total amounts for each type of product are summed up. The result obtained is the salary, unless the reduction factor for defects provided for in paragraph 2.2.2 is applied to this amount. of this Regulation.
If there is a defect in the products produced by an employee in an amount exceeding 2% of the total volume of products produced by this employee, a reduction factor of 0.8 is applied to the amount of salary accrued based on the quantity of products produced. For every additional 2% of defects, the reduction factor decreases by 0.2.
Chord system of remuneration
For teams and groups working on specific projects and tasks, a lump sum wage system is established. Employees' salaries are calculated based on the collective results of the entire team (group). 40% of the income received by the brigade goes to the salaries of its workers.
The received amount is distributed among the employees by the foreman (group leader). He can distribute the amount to everyone equally, equally, or differentially, depending on the contribution of a particular employee to the common cause and his compliance with labor discipline.
Absenteeism without reason gives the foreman (group leader) the right to reduce the salary of the offending employee by 15%, and for showing up to work drunk - by 10%. The salary of the foreman or group leader himself exceeds the average salary of his subordinates by 25%. The difference in salaries of employees who are members of the same brigade (group) cannot be more than 20%.
Time-bonus wage system
For the rest of the company's employees, a time-based bonus payment system is established.
The salary of this category of employees consists of two parts:
- fixed part - salary;
- variable part - a bonus accrued based on the timing and quality of work performed and the achievement of certain results.
All employees of the company may also be paid an additional one-time bonus for significant achievements in their work.
SALARY (POSITION SALARY)
The procedure for establishing an employee's salary
In these Regulations, salary (official salary) means a fixed amount of remuneration for the Employee for fulfilling labor standards or labor duties of a certain complexity per month.
The amount of the employee’s salary (official salary) is established in the employment contract.
The amount of salary (official salary) (excluding additional payments, allowances, bonuses and other incentive payments) of an employee who has worked the full working time cannot be lower than the minimum wage established by federal law. Change in employee salary
An employee’s salary increases when he is transferred to another position that involves greater responsibility, workload and, accordingly, higher pay (included in a grade for which higher pay is provided).
The salary can also be increased if the employee consistently shows good results for one and a half to two years, does not violate labor discipline, fulfills and exceeds the plan, demonstrates loyalty to the company and interest in increasing labor efficiency.
The decision on promotion is made by the employee’s manager, makes a proposal for him and transfers it to the personnel service. She reviews the submission and, in agreement with the company’s management, makes a decision based on the financial capabilities of the organization. An employee’s salary may be reduced if, for health reasons or at his own request, he is transferred to a position with less responsibility and workload, as well as with less pay.
The organization has the right to reduce the salary of an employee if the certification shows that he demonstrates low work results, does not fulfill the plan, does not cope with job responsibilities, does not have the necessary knowledge in full and the necessary competencies, and does not correspond to the position held.
The decision to reduce the salary can be made in this case only based on the results of personnel certification and only by a special labor commission, which includes representatives of the personnel service, the head of the company or deputy, the employee’s immediate superior, specialists from legal and financial services. The fact that the labor commission has adopted The decision to reduce the official salary based on the results of certification is notified to the employee at least two months in advance.
ADDITIONAL PAYMENTS
Types and amounts of surcharges
The following additional payments are established for the Organization's employees:
- for overtime work;
- for working on weekends and holidays;
- for working on the night shift;
- for performing the duties of a temporarily absent Employee;
- for combining professions (positions).
Additional payments for overtime work
In these Regulations, overtime means work performed by the Employee at the initiative of the Employer outside the established working hours, daily work (shift), and in the case of cumulative accounting of working hours - in excess of the normal number of working hours for the accounting period.
For overtime work, Employees are provided with additional payments: for the first two hours of overtime work - in the amount of 150 percent of the hourly rate;
for subsequent hours of overtime work - in the amount of 200 percent of the hourly rate.
These additional payments are not made to Employees who have irregular working hours.
Additional payments for working on weekends and holidays
For work on weekends and holidays, employees paid on a time basis are provided with additional payments:
- in the amount of 100 percent of the hourly rate - if work on a weekend or holiday was carried out within the monthly working hours;
- in the amount of 200 percent of the hourly rate - if work on a weekend or holiday was carried out in excess of the monthly working time standard.
Additional payments for night work
In these Regulations, night work means work from 10 pm to 6 am.
For work on the night shift, employees paid on a time basis are provided with additional payments in the amount of 40 percent of the hourly rate. Additional payments for performing the duties of a temporarily absent Employee
For performing the duties of a temporarily absent Employee, an additional payment is established in the amount of 50 percent of the salary (official salary) for the main job.
The specified additional payment is paid during the entire period of performance of duties of the temporarily absent Employee.
Additional payments for combining professions (positions)
For combining professions (positions), an additional payment is established in the amount of 50 percent of the salary (official salary) for the main job.
The specified additional payment is paid during the entire period of combining professions (positions).
Procedure for calculation and payment of additional payments
- Accrual and payment of additional payments listed in paragraphs 4.2-4.6 of these Regulations are made monthly in accordance with working time sheets.
- The hourly rate is calculated by dividing the amount of wages accrued in the billing period by the number of working days in this period according to the calendar of a five-day working week and by 8 hours (the length of the working day).
- The total amount of additional payments established for the Employee is not limited to the maximum amount.
- At the request of the employee, he may be given another day of rest, and then the work will be paid at a single rate.
SUPPLEMENTS
Types of allowances
The following types of salary supplements are established for the Organization's employees:
- for long work experience in the Organization;
- for the intensity and intensity of work;
- for using a foreign language in work;
- for class.
- Long-term work bonus
For long work experience, the Employee is given an increase to his salary (official salary) in the amount of 10 percent of his salary (official salary).
In these Regulations, long-term work experience is considered to be work in the Organization lasting more than 10 years.
Allowance for intensity, intensity of work
For the intensity and intensity of work, the Employee is given a bonus of up to 20 percent of his salary (official salary).
The specific amounts of allowances are established by order (instruction) of the head of the Organization.
Bonus for using a foreign language at work
For using a foreign language at work, the Employee is given a bonus in the amount of 15 percent of the salary (official salary).
The specified allowance is established for Employees whose job responsibilities include contacts with foreign partners or work with foreign literature.
Drivers' allowance
Drivers of the Organization are given a premium for class in the amount of up to 10 percent of the official salary.
The specific amount of the bonus is established by order (instruction) of the head of the Organization.
BONUS
Types of bonuses
Current and one-time (one-time) bonuses are established for employees of the Organization holding full-time positions.
- Current bonus Current bonuses are paid based on performance results for a month or other reporting period in accordance with the Regulations on bonuses.
- The size of the current bonus is set by the manager by simply calculating quantitative performance indicators. Qualitative indicators are assessed exclusively by the employee’s immediate supervisor
- The size of one-time (one-time) bonuses is not limited to the maximum amount and depends on the financial performance of the company.
- The amount of one-time (one-time) bonuses is established by order (instruction) of the head of the Organization.
Bonuses are not awarded to Employees who have disciplinary sanctions for:
- absenteeism (absence from the workplace without a valid reason for more than 4 hours in a row during the working day);
- showing up at work in a state of alcoholic, toxic or other drug intoxication;
- being late for the start of the working day without warning the immediate supervisor;
- failure to comply with the instructions of the manager;
- failure to perform or improper performance of the duties assigned to the Employee. The Employer has the right to early remove a disciplinary sanction from the Employee on its own initiative, at the request of the Employee or at the request of his immediate supervisor.
The specified order is formalized by order of the head of the Organization.
Bonuses for organization leaders
Bonuses for the General Director, Executive Director, Advisor to the General Director, Business Development Consultant.
- The size of the bonus is determined based on the results of the company’s financial and economic activities and depends on three company indicators - quantitative, qualitative and financial.
- The size of the bonus and the frequency of its payment are approved by order of the General Director.
- The bonus is paid only to those managers who are working in the company at the time of payment.
MATERIAL AID
- In these Regulations, material assistance means assistance (in monetary or material form) provided to the Organization’s Employees in connection with the occurrence of emergency circumstances.
- The following circumstances are considered extraordinary:
- death of husband, wife, son, daughter, father, mother, brother, sister;
- causing significant damage to the Employee’s home due to fire, flood and other emergency situations;
- injury or other harm to the Employee’s health.
The employer may recognize other circumstances as extraordinary.
- Financial assistance is paid from the net profit of the Organization on the basis of an order (instruction) of the head of the Organization upon the personal application of the Employee.
- Financial assistance is provided upon presentation by the Employee of documents confirming the occurrence of emergency circumstances.
ACCRUAL AND PAYMENT OF WAGES
- Wages are accrued to Employees in the amount and manner provided for by these Regulations.
- The basis for calculating wages is: staffing table, employment contract, time sheet and orders approved by the head of the Organization.
- Time sheets are filled out and signed by the heads of structural units. The HR manager approves the time sheet.
- For employees who work part-time, wages are calculated for the time actually worked.
- The determination of wages for the main and combined positions (types of work), as well as for positions held part-time, is carried out separately for each of the positions (types of work).
- Wages are paid to Employees at the Organization's cash desk or transferred to the bank account specified by the Employee under the conditions stipulated by the employment contract.
- Before payment of wages, each Employee is issued a payslip indicating the components of wages due to him for the relevant period, indicating the amount and grounds for deductions made, as well as the total amount of money to be paid.
- Payment of wages for the current month is made twice a month: on the 20th of the billing month (for the first half of the month - an advance payment of 50% of the salary) and on the 5th of the month following the billing month (final payment for the month).
- If the payment day coincides with a weekend or non-working holiday, wages are paid on the eve of this day.
- If the Employee fails to fulfill his official duties due to the fault of the Employer, payment is made for the actual time worked or work performed, but not lower than the Employee’s average salary.
In case of failure to fulfill official duties for reasons beyond the control of the parties to the employment contract, the Employee retains at least two-thirds of the salary (official salary).
In case of failure to fulfill official duties due to the fault of the Employee, payment of salary (official salary) is made in accordance with the amount of work performed.
Downtime caused by the Employer, if the Employee warned the Employer in writing about the start of downtime, is paid in the amount of at least two-thirds of the Employee’s average salary.
Downtime due to reasons beyond the control of the parties to the employment contract, if the Employee has warned the Employer in writing about the start of downtime, is paid in the amount of at least two-thirds of the salary (official salary).
Downtime caused by the Employee is not paid.
- Deductions from the Employee's salary are made only in cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws, as well as at the request of the Employee.
- Amounts of wages, compensation, and other payments not received within the prescribed period are subject to deposit.
- Certificates regarding the amount of wages, accruals and deductions from them are issued only to the Employee personally.
- Payment for vacation to Employees is made no later than three days before its start.
- Upon termination of the employment contract, the final payment of wages due to the Employee is made on the last day of work. If the Employee did not work on the day of dismissal, then the corresponding amounts are paid no later than the next day after the Employee submits a request for payment.
In the event of a dispute about the amount of amounts due to the Employee upon dismissal, within the period specified above, the Employee is paid the amount not disputed by the Employer.
In the event of the death of an Employee, wages not received by him are issued to members of his family or a person who was dependent on the deceased no later than a week from the date the Organization submits documents certifying the death of the Employee.
WAGE INDEXATION
- The Employee's salary is indexed in connection with rising consumer prices for goods and services.
- Salary, taking into account indexation, is paid to the Employee starting from the first month of each quarter.
- At the end of the year, the labor commission makes a decision on salary indexation. It takes into account the company’s financial indicators, the inflation index, as well as the growth of consumer prices in the country, determined on the basis of Rosstat data.
- The commission determines how much wages are increased and sets the indexation amount as a percentage. It cannot be less than the official inflation index, but it can exceed it.
EMPLOYER'S RESPONSIBILITY
- For delays in payment of wages, the Employer is liable in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
- In case of delay in payment of wages for a period of more than 15 days, the Employee has the right, by notifying the Employer in writing, to suspend work for the entire period until the delayed amount is paid. The specified suspension of work is considered forced absenteeism, while the Employee retains his position and salary (official salary).
FINAL PROVISIONS
- This Regulation comes into force from the moment of its approval and is valid indefinitely.
- This Regulation applies to labor relations that arose before it came into force.
Prize registration rules
To correctly register bonuses for employees, you can fill out unified forms T-11 (if one employee receives the money) or T-11a (if the money is intended for a group of employees, for example, an entire department). You can download them in the legal systems “Consultant” or “Garant”. However, organizations have the right to develop and use their own form of the document.
The payment of bonuses should be based on the internal regulations on bonuses - a special document that reveals the procedure for calculating all types of additional payments in a given organization.
Drawing up such a document is not as difficult as it might seem at first glance. Below is a sample provision on bonuses for LLC employees. Let's take a closer look at what this act includes and how it is approved.
Is it necessary to have a bonus clause?
Russian labor law standards do not oblige employers to award bonuses, much less draw up regulations about them. Bonuses are a right, not an obligation of the company. If the head of the organization does not plan to stimulate productivity with monetary payments, of course, he does not need the position. Also, if the employer plans to pay them several times a year, theoretically, it is also possible to do without a special document and include the necessary items in the salary regulations.
But in the case when the payment of bonuses will be regular, it is necessary to develop a special document that can be referred to when placing orders and calculating the amount of payments. The approved provision will become a source of information for employees about prospects in the field of material remuneration.
Position structure
The award regulations must include the following sections:
- General information, introduction. Name of the enterprise, purpose of writing the document, source of payment (wage fund), documentary basis for the incentive.
- Conditions of bonuses and rules for calculating bonuses. The best option is to list all positions on the staffing table, indicating the conditions when different types of bonuses are paid. It is better to enter this data into a table.
- Remuneration procedure. The entire procedure for transferring employee benefits is described.
- Conditions of non-payment. The circumstances are indicated (in separate paragraphs) in which the employer has the right to suspend the payment of bonuses. For example, failure to fulfill the plan, violation of an employment contract or discipline, claims from partners.
- Final provisions. All additional information that the head of the organization considers important is indicated here. For example, the validity period of the document (until cancellation or replacement with a new one), the procedure for familiarization (when concluding an employment contract against signature), and so on.
Procedure for calculating payments
The rules for calculating additional payments are fixed in a special provision. Simplified, it is implemented in the following steps:
- A decision is made to accrue additional monetary incentives to the employee in the reporting period.
- The clerk/secretary prepares the order.
- The manager signs it.
- The clerk/secretary prepares supporting documents for the accounting department (for example, copies of the production plan or concluded contracts).
- The accounting department calculates the payment based on the order.
Document approval
The bonus regulation comes into force after the signature of the head of the company. To approve the document, you need to prepare a special order, also signed by the manager, to which the regulation itself will be an appendix. In the text of the order, it is permissible to use the following wording: “to approve the Regulations on bonus payments to employees of LLC “...”. It is possible (but not required) to indicate the person responsible for communicating information to employees of the organization.
The employer must familiarize all employees with this document. The most convenient way to do this is to attach a special familiarization sheet to it, where you record the dates, names and signatures of the employees who read the document.
The procedure for material incentives for employees
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain a definition of the concept of bonuses, nor does it oblige employers to award bonuses to employees. At the same time, the Labor Code contains rules by which bonuses can be awarded, and also determines the procedure for fixing the procedure for bonuses.
So, according to the provisions of Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, wages are not a single payment. It is divided into various components such as:
- Payments for employees performing their duties. The amount of such payments depends on various criteria, namely: the qualifications of employees, the complexity of the work performed, its quantitative and qualitative indicators, and working conditions.
- Compensation payments. These are various types of additional payments that are subject to accrual to employees subject to certain conditions. For example, such additional payments are awarded in northern climate zones, for special working conditions in hazardous industries, etc.
- Incentive payments. They include bonuses, allowances, and additional payments.
Due to the requirements of Art. 191 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, bonuses are a method of rewarding an employee who properly performs job duties, i.e. in fact, he works well and is not subject to penalties. The employer himself determines the amount of incentive payments, the terms and procedure for calculation. The bonus regulations may reflect the conditions for payment of bonuses, the procedure for their implementation, size, grounds for refusal to accrue, etc. Below we will talk about how to compose a document. A sample provision on bonuses for employees can be found at the end of the article.
What is the document used for?
There are two groups of regulations:
- mandatory (labor rules regulated by Article 189 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation; vacation regime; regulations - instructions on labor protection, etc.);
- optional (these include regulations on employee incentives, because the Labor Code does not contain any requirements for the need to develop this document).
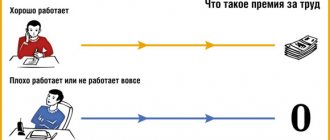
Bonuses may or may not be assigned based on the results of work performed. This is an effective stimulation of work activity and activity of employees . For high achievements (fulfilling and exceeding the plan, developing innovations, etc.), employees receive a bonus, but for minor successes no bonus is awarded.
With the help of the developed and implemented algorithm for calculating bonuses, the employer can seriously save wage fund reserves. If the amount of earnings is divided into two parts, basic and bonus, then it becomes possible not to spend money on issuing bonuses. In this case, these funds can be saved, leaving them in the company’s circulation legally, or distributed among specific employees based on their achievements.
Whatever the employers’ motives, it is always very profitable for them to manage the bonus fund themselves.
This benefit will be clearly expressed when any actions (assignment or deprivation of a bonus) are carried out in accordance with the current legislation (LC, TC, Civil Code of the Russian Federation). This is why it is necessary to develop a regulatory internal act that will fully reflect all the requirements and goals. The employee incentive regulations allow :
- from the point of view of documentation: there is no need to separately specify all the points related to bonuses in employment agreements concluded with employees;
- avoid unnecessary questions and claims from representatives of tax authorities (in connection with the inclusion of bonuses in labor costs when calculating income tax);
- avoid controversial issues regarding the calculation of temporary disability benefits (with the social insurance authority).
Each company has provided and developed its own individual bonus system, based on production, technological and organizational features of the work.