Capital is the main tool for a business owner, without which the entrepreneurial activity itself cannot even begin. Own capital consists of heterogeneous parts intended for specific purposes. One of the important and mandatory components of the capital of a legal entity is reserve capital. Unlike other shares of capital, there are some contradictory nuances in its formation, use and accounting.
Below we will consider the legal basis for its formation and application, main functions, connection with retained earnings, as well as the intricacies of accounting entries.
What is included in reserve capital ?
Reserve capital on the balance sheet is...
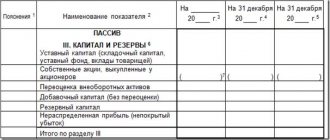
The amount of reserve capital is displayed in line 1360 of the balance sheet, which indicates that reserve capital is a component of the organization’s total capital, reflected in the final line 1300.
The fact that reserve capital is included in the company’s equity capital is also indicated in clause 66 of the Regulations on accounting and accounting, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n (hereinafter referred to as PVBU).
ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to reflect reserve capital on the balance sheet and what nuances need to be taken into account when filling out this line. To do everything right, get trial access to the system and go to the Tax Guide. It's free.
You can learn about what a company’s equity capital is from our article “Equity on the balance sheet is...”.
Community bonds when forming the authorized capital and redemption rules
Bonds belong to the group of securities, according to the text of Article 143 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
An addition needs to be made here. Bonds are paid out of the reserve capital only when there are no other sources of payment. Other expenses usually include the amount representing the difference between the redemption cost and the nominal price, in a larger direction.
This situation can arise only if other miscellaneous expenses stop being generated. This requires the complete absence of any actions related to the conduct of business of entrepreneurs.
Recommendations for wiring will look like this:
- The amounts used to redeem bonds and transactions on them are displayed in Debit 82 and Credit 66 or 67. But not everyone recognizes this option as correct. The placement of bonds is associated with the formation of a credit balance in the loan and credit accounts. Due to the processing described above, the debt may increase.
- Reverse wiring also becomes impossible. For example, Debit 66 (67) and Credit 82. Repayment of debt due to borrowed funds cannot be the reason why reserve capital is increased.
Reserve capital - an asset or a liability?
The company's capital and reserves are considered its liabilities, so it is logical that reserve capital, as a component of equity capital, is, of course, a liability.
In addition, in accounting, information about the state and movement of reserve capital is summarized in account 82, which is also passive.
Reserve capital is intended to accumulate part of net retained earnings, which will subsequently be spent primarily on covering losses.
You will receive more information about liabilities and assets when studying the article “Balance Sheet (Assets and Liabilities, Sections, Types).”
Characteristics of account 82
Accounting for reserve capital (hereinafter referred to as RK) is maintained using account 82, designed to collect all information about the state and movement of this type of capital.
To account for the formation of reserve capital, account 82 corresponds with account 84. In special cases, account 82 corresponds with account 75, for example, when forming the Republic of Kazakhstan in non-profit organizations and agricultural enterprises. In order to reflect operations on the use of accumulated reserve capital, the account corresponds with accounts 66 (67).
By studying the features of account 82, you can create the following characteristics of it. This is the account:
- passive, since with its help the sources of the enterprise’s property are taken into account; RK is one of the components of the capital of a joint-stock company and, like all sources of assets, is reflected in the liability side of the balance sheet;
- balance sheet, because its indicators are reflected in the balance sheet;
- stock, since it is intended to account for the sources of formation of funds belonging to the joint-stock company - the capital of the company;
- the main one, because it is intended to control the state and movement of sources of formation of the company’s property (in this case).
You can read about the sources of capital formation in our article “Main sources of equity capital formation.”
Reserve capital for JSC and LLC - what are the differences?
Unlike LLCs, joint stock companies are required to accumulate reserve capital. For an LLC, the creation of a reserve fund is the right of the company in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 30 of the law of 02/08/1998 No. 228-FZ, and not an obligation. At the same time, the size and targeted nature of such a fund for an LLC are not regulated by law, but are prescribed in the charter.
The amount of reserve capital in joint-stock companies cannot be less than 5% of the authorized capital, while the founders can establish a larger size of this fund (clause 1, article 35 of the law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ). The same legislative act specifies the intended use of the fund and the procedure for its formation.
How is reserve capital formed?
- In accordance with current legislation, the main source of reserve capital formation is deductions from net profit.
In joint stock companies, reserve capital is formed through deductions from net profit, and the amount of annual replenishment of reserve capital should not be less than 5% of net undistributed profit for the reporting period (paragraph 2, clause 1, article 35 of Law No. 208-FZ). Deductions from net profit in favor of the reserve fund are made until the limit established in the charter is reached.
Example:
The charter of Kolos-info JSC provides for the creation of a reserve fund in the amount of 6% of the authorized capital. The authorized capital at the time of the meeting of the board of directors (02.20.20XX) amounted to 90,000,000 rubles, reserve capital was formed at the level of 5,200,000 rubles. The net profit of Kolos-info JSC for the year 2020 amounted to 6,000,000 rubles.
In accordance with the charter, Kolos-info JSC must create reserve capital in the amount of 5,400,000 rubles (90,000,000 × 6%). To complete the formation of reserve capital, it remains to contribute another 200,000 rubles (5,400,000 – 5,200,000). At the meeting held on February 20, 20XX, it was decided to allocate 200,000 rubles from the net profit of 20XX to replenish the reserve fund.
EXPLANATIONS from ConsultantPlus: Is it possible to indicate in the charter of an LLC that profits are not distributed among the participants, but are sent to the reserve fund or for the statutory purposes of the company? How to reflect this? For answers to these and other questions, see the K+ legal reference system. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
If the company happened to turn to a source of reserve capital to cover losses incurred at the end of the reporting period, then in the next period it will have to again make deductions from net profit until the statutory value is reached.
- In addition to the above method of replenishing reserve capital from a part of retained earnings, there is also the possibility in special cases of forming reserve capital from the property contributions of the founders.
Contributions made by shareholders that are transferred to the company in the form of property, according to clause 2 of PBU 9/99, are not recognized as income of the company. And in sub. 3.4 clause 1 art. 251 of the Tax Code states that income recognized for tax purposes does not include contributions of shareholders with property made in order to increase net assets and funds. This means that they can also be used to form reserve capital.
Based on the above, we can conclude that shareholders, in order to increase net assets, can make contributions with property (moral and property rights) also through the formation of reserve capital.
You will get more information about net assets by studying our articles:
- “How is the accounting value of net assets calculated?”;
- “What are the consequences of negative net assets?”
For example, many non-profit organizations create reserve funds at the expense of share contributions from participants (subclause 16, clause 3, article 1, subclause 1, clause 4, article 6 of the law of July 18, 2009 No. 190-FZ, clause 7, art. 34 of the Law of December 8, 1995 No. 193-FZ). And the chart of accounts for agricultural enterprises, approved by order of the Ministry of Agriculture dated June 13, 2001 No. 654, directly provides for the possibility of forming a reserve fund from contributions from participants.
Example 1:
In order to increase the size of net assets, the shareholders of the agricultural company decided to make a contribution to the reserve capital (hereinafter - RK) in the form of materials in the amount of 100,000 rubles.
In this regard, 2 entries will be made in accounting:
- Dt 10 Kt 75 in the amount of 100,000 rubles - upon receipt of materials from shareholders for the purposes stated above;
- Dt 75 Kt 82 in the amount of 100,000 rubles - formation of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Example 2:
At the board of shareholders, they decided to increase net assets by making a contribution of 2,000,000 rubles to the RK JSC. Shareholders made contributions in the total amount of 2,000,000 rubles.
In this regard, 2 entries will be made in accounting:
- Dt 51 Kt 75.3 in the amount of 2,000,000 rubles - receipt of funds from shareholders to replenish the Republic of Kazakhstan;
- Dt 75.3 Kt 82 in the amount of 2,000,000 rubles - formation of the Republic of Kazakhstan from contributions made by shareholders.
Read about the nuances of accounting for reserve capital in ConsultantPlus. Study the material by getting trial access to the K+ system for free.
conclusions
Thus, reserve capital represents a certain part of the company's property or a certain share of its profits.
Reserve capital serves as a safety net – a financial “cushion” – in case the organization has problems fulfilling external obligations (for example, there are not enough funds to pay the bills of counterparties). Thus, it guarantees the uninterrupted functioning of the enterprise and ensures the company’s responsibility to creditors. And the priority source of formation is considered to be the retained earnings of a legal entity.
In accounting, reserve capital is defined as the amount of funds that accumulates to finance specific company expenses or cover its losses. The basis of such capital is considered to be a reserve fund. It is created either on a mandatory basis (if this is clearly prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation), or on a voluntary basis (if this is provided for in the constituent documentation of the company).
How does the reserve capital increase/decrease?
In a situation where the board of directors has decided to increase the authorized capital, which is within its competence in accordance with Art. 65 of Law No. 208-FZ, and as a result of this it turned out that the size of the reserve fund has become less than the mandatory 5% of the capital, there is a need to increase the reserve capital.
The decision to increase the authorized capital by increasing the par value of shares is made by the general meeting of shareholders (Clause 2 of Article 28 of Law No. 208-FZ).
Example:
At the meeting of shareholders, it was decided to increase the authorized capital from 200,000,000 rubles to 300,000,000 rubles. At the same time, at the time of making this decision, the JSC already had reserve capital in the amount of 10,000,000 rubles. Accordingly, after increasing the size of the charter capital to 300,000,000 rubles, the JSC will have to increase its reserve capital by 5,000,000 rubles (300,000,000 rubles × 5% – 10,000,000 rubles).
If a decision was made to reduce the size of the capital, then there is a basis for reducing the capital. This change can be legally carried out only after state registration of changes in the charter relating to the reduction in the size of the charter capital. The decrease in the RK in accounting is documented by posting Dt 82 Kt 84.
Results
For joint stock companies, reserve capital for a specific intended use is a mandatory component of equity capital. Its size is strictly defined at the legislative level and cannot be less than 5% of the authorized capital. The composition of the Criminal Code of the joint-stock company is established by the norms of Art. 99 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and Art. 25 of Law No. 208-FZ.
When changing the company's charter capital, it is also necessary to review the amount of reserve capital.
If an increase in the capital has been made, and the size of the formed capital has become less than the limit, then it should begin to be filled from net profit or, in cases established by law, from property contributions from shareholders aimed at increasing net assets (or share contributions). You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.