Hello, Vasily Zhdanov, in this article we will look at an example of calculating the total capital of an enterprise. As practice shows, concepts such as “your own or your own capital”, “your own or your own funds”, as well as “net assets” are used as synonyms. In fact, they are truly interchangeable since their definitions are largely consistent. The words “own” and “your” are essentially identical. And economists quite rightly use the term “capital” when describing assets. Although its exact definition is capital - a combination of debt and equity capital.
An example of borrowed capital can be virtually any short-term and long-term obligations of an organization to individuals and other legal entities. Most often, credits and loans act in this capacity. Meanwhile, the enterprise’s capital (its own, its own) is considered from different positions.
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
In general, it is customary to say that your capital is part of the book. balance sheet, which reflects the residual claim of the founders to the legal entity they formed. During each reporting period it may change: decrease or increase. Its value depends on two main factors:
- Additional investments (for example, receiving valuables for free).
- The results of your own activities (for example, the net profit for a specific reporting period).
In fact, the following rule applies. The value of net assets changes (decreases or increases) over a specific period, and accordingly, the enterprise’s capital also changes. One change follows from another.
What is an organization's equity
This is a financial indicator that characterizes the amount of funds belonging to the participants of the organization.
The definition of equity capital (SC) is given in paragraph 66 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n). It says that the IC includes:
- capitals: authorized (share), additional, reserve;
- retained earnings;
- other reserves.
REFERENCE
Essentially, equity capital (also called equity) is the company's assets minus its liabilities. Another indicator is determined in a similar way - the value of the organization’s net assets (clause 4 of the Procedure for determining the value of net assets, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated August 28, 2014 No. 84n). Therefore, the concepts of “equity” and “net assets” are often equated.
Assess your organization's financial condition and get tips on how to improve it
Suggestions for optimizing accounting
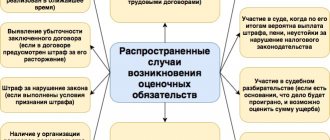
The proposed structure for constructing accounts for accounting for a company’s debt funds in order to increase its creditworthiness is as follows:
- first-order accounts, which combine all possible data on the state of the company's borrowed funds (both long-term and short-term);
- second-order accounts, which are capable of reflecting accounting information on generalized types of debt obligations, such as: loans and borrowings;
- third-order accounts are capable of detailing information on a more specific type of obligation, for example, a commercial loan, a loan agreement, etc.;
- fourth-order accounts, which are capable of recording information on various types of payments, for example, debt, interest, fines, etc.
Such a grouping of accounts for a company will allow a more in-depth study of analytical accounting for all types of debt obligations of the company. It can also improve control in this area, increase the efficiency of debt management of the company, and strengthen creditworthiness. It is recommended to improve the control system by introducing internal reports in the company, as well as the dynamics and structure of borrowed funds. Such reports can be prepared every month and submitted to management by the 25th. They will allow management to monitor timely negative trends in the structure of borrowed funds and capital of the company, eliminate them in a timely manner, thereby increasing the efficiency of debt management and the company’s creditworthiness indicators.
Methods for calculating equity capital
In practice, two methods are usually used.
The first one is very simple. Its essence is to take the figure indicated in a certain line of the balance sheet as the value of the capital account.
The second method is a little more complicated. It is based on the equality of the concepts of “equity” and “net assets”. For calculations, you must use the procedure for calculating net assets approved by the Ministry of Finance. Take the resulting value as the SC. Note that for the second method (as for the first), the data sources are balance sheet indicators.
Data on revaluation of fixed assets and intangible assets
Long-term assets are subject to revaluation. The operation is carried out to bring the residual accounting value of assets to their market price. Features of revaluation and sources of information in accounting:
- These revaluations are reflected as a separate line in the balance sheet. When carrying out a markdown, the amount is written off against the profit at the disposal of the company.
- Revaluation recognized as a source of equity in the balance sheet after the first revaluation must be carried out regularly, every year.
- The operation is not performed more than once a year.
- Subsequently, revaluation is carried out at the replacement cost of assets.
- The need for an annual revision of the value is reflected in the accounting policy of the enterprise.
The procedure is carried out during the reporting period, no more than once a year. Data on the additional valuation are reflected in the balance sheet at the beginning of the next reporting period.
Which line of the balance sheet contains the equity indicator
To apply the first method, you need to know where the company's own funds are reflected on the balance sheet. In the liability, in line 1300 “TOTAL capital”. The number in this line is the sum of the indicators of six lines.
- 1310 “Authorized capital (share capital, authorized capital, contributions of partners).”
- 1320 “Own shares purchased from shareholders.”
- 1340 “Revaluation of non-current assets”.
- 1350 “Additional capital (without revaluation).”
- 1360 “Reserve capital”.
- 1370 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss).”
Fill out and print the balance sheet using the current form in the web service Fill out for free
Results
It is advisable to analyze the company's own working capital in dynamics.
At the same time, it is necessary to study not only working capital, but also their structure. When making management decisions, it should be understood that the growth of own working capital leads to financial stability, but at the same time it is possible to reduce capitalization, divert part of the assets from circulation and reduce the turnover of working capital, reducing the efficiency of their use. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Net Worth Formula
To apply the second method, you need to use a formula that determines the value of net assets. This formula is enshrined in Order No. 84n of the Ministry of Finance dated August 28, 2014.
SC = ASSETS (minus receivables of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital) - LIABILITIES (minus deferred income associated with receiving government assistance)
Table
Decoding the indicators involved in the formula
| Index | Decoding |
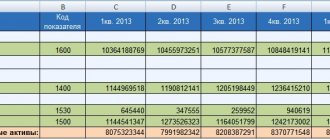
| ASSETS | Numbers from balance line 1600 “BALANCE (asset)” |
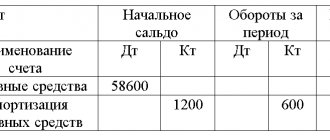
| Accounts receivable from founders for contributions to the authorized capital | Debit balance on account 75 “Settlements with founders” subaccount “Settlements on deposits in the management company” |
| OBLIGATIONS | The sum of the indicators in two lines of the balance sheet: 1400 “TOTAL long-term liabilities” and 1500 “TOTAL short-term liabilities” |
| Deferred income related to receiving government assistance | Credit balance of account 98 “Deferred income” sub-account “Gratuitary receipts from the budget” |
Classification
The main features for identifying types of debt capital are reflected in the table below.
- long-term (more than 1 year);
- short-term (less than 1 year)
- replenishment of working capital;
- investing in fixed assets;
- replenishment of funds;
- covering cash expenses
- external (banks, leasing);
- internal (lender)
- monetary;
- commodity
- bank loans;
- loans from other companies;
- leasing;
- franchising;
- factoring
- with collateral;
- without collateral
Optimal average equity capital
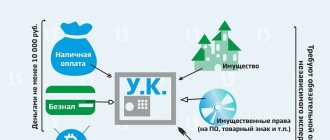
This indicator must be equal to or exceed the amount of the authorized capital (AC) of the company. If this condition is met, the business can be called successful.
IMPORTANT
By law, it is prohibited to allow the equity capital of an LLC to be less than the authorized capital. When faced with such a situation, society must take one of two paths. Either increase net assets to the level of the authorized capital, or reduce the authorized capital to the amount of net assets. If, as a result, the capital company turns out to be less than the minimum established by law (10,000 rubles), the LLC will have to be liquidated (clause 4 of article 4 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Get a sample accounting policy and do accounting in a web service for small LLCs and individual entrepreneurs Get it for free
Sometimes financiers use the following approach to determine the optimal average amount of equity capital. Add up the value of assets with minimal liquidity (these usually include inventories, non-current assets and work in progress). Own capital must be equal to or greater than the value found.
Improving management efficiency
To increase the efficiency of debt management, it is possible to introduce a document flow schedule and introduce the position of an accountant for debt obligations. The duties of such an accountant may include:
- control of the correct processing of primary documents on the company’s debts;
- checking the correctness of interest calculations;
- checking the correctness of recording of transactions accounting for the company's debts.
The introduction of these procedures helps reduce the percentage of errors and inaccuracies in accounting.
The next ratio used to evaluate the efficiency of capital use is return on invested capital (ROI).
Its characteristic feature is that when calculating profitability, working capital generated from short-term borrowed funds is excluded from the total amount of capital. That is, only Equity capital + Long-term borrowed funds are used in the calculation. This indicator characterizes the efficiency of using only equity and long-term borrowed capital. When calculating return on equity, net profit is taken into account without expenses for servicing borrowed capital. If only equity capital is used as the investment base, the resulting indicator will be called return on equity (ROE). When calculating it, profit is used without taxes, interest on debt service, and dividends on preferred shares. [p.251] Naturally, both options led to the same answer. Thus, the total amount of capital by the end of the five-year period will consist of income from depositing money in the bank (210.77 thousand rubles), return of the share from participation in the project for the last year (50 thousand rubles) and a one-time remuneration (80 thousand roubles.). The total amount will therefore be 340.77 thousand rubles. The proposal is not economically feasible. [p.278] Share of average cash balance in total capital (assets) Ch 0.017505 0.031445 0.013944 179.68 [p.403]
Share of current assets in total capital 0.60 0.653 +0.053 [p.315]
Total capital 1500 1250 1125 [p.324]
Intangible assets include patents, licenses, trademarks and trademarks, rights to use natural and other resources, computer software products, new technologies and technical solutions that bring benefits in the process of economic activity. Investments in intangible assets pay off over a certain period due to the additional profit received by the enterprise as a result of their use, and due to depreciation charges. With the development of market relations, the size and share of intangible assets in the total capital of the enterprise increase. Economic interest in increasing the profitability of an enterprise through the use of the enterprise’s exclusive right to the results of intellectual activity is also increasing. Hence, analysis of the efficiency of using intangible assets is important. The technique is most fully described by A.D. Sheremet [59]. [p.347]
Total capital 1000 1000 1000 [p.628]
The total amount of capital is the value of the funds (assets) of the enterprise. It is equal to liabilities plus equity, otherwise called the net balance sheet currency. (Line balance 399-217-390). [p.152]
Total capital Equity capital + Long-term liabilities [p.162]
Total amount of capital Own working capital [p.162]
Total capital [p.163]
The logic for constructing the main algorithms is quite simple and is based on the following idea. Free funds are invested in some type of business (in the simplest case - in a bank). The initial data for calculating income from such an investment is the amount of the initial deposit (Q the period for which the deposit is made (and) profitability (rate of return), for example, the interest rate at which dividends are calculated on the invested capital (r). Thus, after a year, profit on the invested capital is equal to C-g, and the total amount of capital is (C + C-g). If the rate of profit remains unchanged, then after n years the total amount will be C (7+ r)" i.e. time generates money. [c .352]
According to the balance sheet asset, capital is divided into fixed capital (sections I and II) and working capital (section III). The criteria for this division are the time of operation, the nature of use and sources of formation. Fixed capital is funds invested for long-term purposes in real estate, shares, mineral reserves, joint ventures, etc. related, immobile, funds taken out of circulation for a long time, the initial value of which is reduced, is included in the total amount of capital at their residual value . [p.9]
The balance sheet asset provides information about the total amount of capital of the enterprise and its placement (fixed, current), and the liability - about the total amount of capital and its composition by sources (own, borrowed). [p.21]
Total capital is the sum of equity capital (authorized capital, special purpose funds, retained earnings, special purpose financing and proceeds), share capital and debt capital. This ratio characterizes the share of debt in total capital. The higher this share, the greater the enterprise's dependence on external sources of financing. [p.74]
A partnership is similar to a sole proprietorship in all respects except that in a partnership there is more than one owner. In a general partnership, all partners have unlimited liability. They are jointly liable for the obligations of the partnership. Since one of the partners may bind the partnership to certain obligations, you should choose your partners carefully. In most cases, there is a formal agreement or partnership agreement that defines the powers of each partner, the distribution of profits, the total amount of capital invested by the partners, the procedure for attracting new partners and the procedure for re-registering the partnership in the event of [p.19]
Losses attributable to the minority interest and in excess of its share of the subsidiary's total equity in the consolidated statements are written off to the majority interest account. Losses proportionate to the minority interest in the capital of the consolidated group are reflected separately as [p.241]
At the first stage of the analysis, the dynamics of the total volume of formation of investment resources, the rate of growth of assets and the volume of sold products of the enterprise, the dynamics of the share of own and borrowed funds in the total amount of capital attracted for investment purposes are studied. [p.383]
Operating leverage ratio. The growth of the enterprise's profit is ensured by the joint manifestation of the effect of operational and financial leverage. Therefore, enterprises with a growing volume of product sales, but having a low operating leverage ratio due to the industry characteristics of their production, can increase the financial leverage ratio to a much greater extent (all other things being equal), i.e. use a large proportion of debt in total capital. [p.435]
Nominal capital is the total amount of capital for which the company has the right to issue shares [p.69]
The risk rate for each market in which a trader invests his funds should not exceed 5% of his total capital. In other words, the trader is ready to lose no more than 5% of the total amount of his funds if the transaction turns out to be unprofitable. The risk rate is the most important consideration that a trader must make when deciding how many positions he can open at once and where to set the level of protective suspension. For a single transaction, the risk rate should not exceed $5,000 if the total capital amount is $100,000. [p.429]
Losses attributable to the minority interest and in excess of its share of the total equity of the subsidiary are written off to the majority interest in the consolidated statements. Losses proportionate to the minority interest in the capital of the consolidated group are recognized separately as attributable to minority interests. The excess of the share of losses over the share of minority equity is not reflected in the financial statements. Subsequent profits shown by the subsidiary are recognized and reported as a majority interest until they offset the full amount of losses not previously reported as attributable to minority interests. [p.331]
Total capital, 47995 47982 -13 [p.68]
Financial autonomy coefficient (ratio of equity capital to total capital) > >0.5 [p.266]
The weighted average price of capital of an enterprise is determined by multiplying the share of equity capital by its price (page 1 page 3) plus the share of borrowed funds multiplied by its price (page 2 page 4), the resulting amount is divided by the total amount of capital, i.e. . by 100. [p.53]
AUTONOMY RATIO - the financial ratio determines the share of equity capital in the total amount of capital (to the balance sheet currency). [p.152]
TOTAL AMOUNT OF CAPITAL [p.200]
TOTAL AMOUNT OF CAPITAL - the total value of funds (assets) of the enterprise, equal to liabilities in the amount of equity capital. Otherwise called balance-net currency. [p.200]
In economic literature, share capital is understood as the authorized (share) capital of a joint-stock company. In our opinion, this is only true for newly created joint stock companies. Joint-stock companies that are already conducting business activities, along with the authorized capital, have in their own capital additional capital, retained earnings or various funds created from the profits remaining at the disposal of the company minus dividends. Moreover, the company may suffer a loss, as a result of which its capital and reserves will have a negative value, i.e., in fact, the authorized capital will be consumed. Therefore, it is proposed that share capital be understood as the total amount of capital and reserves minus targeted financing [p.382]
Total capital, million rubles. [p.172]
Thus, in modern theory there are two approaches to the concept of working capital. The majority of economists believe that this concept characterizes the total amount of capital advanced into all types of current assets of an enterprise, that is, it proceeds from the fact that the amount of working capital is equal to the amount of its current assets at any point in time. Another part of economists believes that this concept characterizes the amount of current assets of an enterprise, reduced by the amount of its financial liabilities in the form of total accounts payable (since, in their opinion, part of the current assets formed from accounts payable reduces the need for working capital of the enterprise) . [p.20]
In this regard, the cost of a company’s monetary capital is a weighted average value depending on two factors of calculation for each source of capital, i.e. the profitability that the owner of the funds requires for the right to use the share of each type of funds in the total amount of capital. [p.51]
Capitalization of the company (V) V = Rak x KA Rak - market price of ordinary shares KA - number of ordinary shares PE - net profit SS - equity capital Pv - profit before interest and taxes A - company assets Pr - profit from sales RP - sold products S - costs of production and sales k - cost of individual elements of capital d, - share of individual elements of capital in the total amount of capital. [p.27]
K4 - reinvested profit to all assets Ks - share of own working capital in the total capital. The critical value of the indicator is 2.675 Z 2.675 - the financial condition of the enterprise is stable. [p.125]
According to the calculation, the weighted average cost of capital used by the enterprise is 19.2%. Taking into account their share in the total capital, the cost of equity is 16.5%, borrowed capital is 2.7%. [p.170]
Total capital, million rubles. 1000 1000 1000 [p.187]
The total amount of income received from international bonds is known from a study conducted by the international banking group Orion and covering data on the movement of bond loans issued during 1963-1977. The total amount of capital in dollars invested during this period in Eurobonds was 45.2 billion. Of this, 21.3 billion was returned before 1982 through payments on the principal debt. Thus, the redemption amounted to 45% of the issue amount. However, during this period, $23.5 billion was paid in the form of interest.
Estimated values
The ZK indicator is used in the analysis and assessment of the efficiency of conducting economic activities of an enterprise. For example, having determined the ratio of equity to borrowed funds, we obtain the debt coverage ratio: how much the company is able to pay with its own funds. By calculating the inverse ratio of loans to equity assets, we find out the solvency ratio and financial stability of the company.
Return on borrowed capital (formula on the balance sheet) reflects the profitability of the circulation of borrowed finance in activities. The indicator is calculated in relation to one ruble of borrowed funds.
The coefficient of concentration of borrowed capital (balance sheet formula) determines the ratio of borrowed finance to the volume of total capital of an economic entity. In fact, this is the degree of debt load, encumbrance of the enterprise.
The indicators of financial statements for one calendar year are analyzed.