- November 27, 2018
- Accounting
- Anna Kuklina
Working capital is one of the main criteria that determines the financial stability and efficiency of a company. The term, introduced into use by Adam Smith, does not lose its relevance to this day. Since what does the working capital formula look like, why do you need to determine its optimal value for the company and the industry as a whole? We will tell you everything in detail below.
Net working capital on balance sheet
This capital represents part of the current assets, financed from its own or equivalent borrowed resources. It is not without reason that financiers call this capital a safety net, since its presence often saves an enterprise when the need arises to urgently repay short-term obligations and continue work, even in a reduced volume.
It is impossible to see the actual value of this indicator in the balance sheet, since the amount of net working capital is calculated, and several balance sheet values serve as the basis for it.
When calculating the amount of net capital, it is necessary to remember that short-term liabilities (CL) (for example, bank loans) are not taken into account in their composition, since part of the net capital is most often used to repay them. This difference will be the size of net assets that determine the level of financial solvency of the company, and the formula will be as follows:
Net working capital = Current assets (OA) – Short-term liabilities (KP)
Normal coefficient value
First of all, it is worth noting that the previously mentioned ratio has not been used by foreign companies in financial analysis for quite a long time. For Russian enterprises, the working capital ratio was introduced at the legislative level in order to determine which companies are on the verge of bankruptcy and are undesirable for receiving credit sponsorship. To date, one of these orders has been canceled and has completely lost its force. However, despite this, companies still use it to this day.
According to the documents that prescribed the calculation procedure, the normal value of the coefficient should not be lower than 0.1. According to the experts who drew up this order, this value indicates that the company is not bankrupt and is solvent at the time of reporting. If the company's SOC ratio is below the established standard, then the company's balance sheet is considered unsatisfactory.
It is also worth mentioning that this criterion is quite strict for Russian companies, since almost no one manages to achieve the standard value. In this situation, it would be much more reasonable, as in foreign countries, to cancel the calculation of this coefficient.
Net working capital analysis
The calculated value of the indicator is assessed in absolute and relative values, calculating its total value, structure, profitability and turnover.
A positive value, i.e., the excess of working capital over liabilities, indicates the solvency of the company, since its own funds are enough to carry out the work process without attracting borrowed capital. However, the amount of net working capital should not be too high. A value that has not decreased over several reporting periods indicates:
- about inefficient use of funds: the company does not invest them in the development of production and does not invest in profitable enterprises;
- on the long-term use of long-term borrowed resources in financing working capital.
Negative net working capital indicates a lack of equity, which could lead to bankruptcy in the future, and the need to attract external financing.
Standards
The value of the NER depends on many factors, which makes it difficult to draw the only correct conclusion about which figure will be optimal when calculating. Those that influence the value of PSC include the industry that the company has chosen for its operation, and the scale of production itself (private enterprise, joint-stock company, TNC, etc.). The volume of production and sales of products have an important influence. It is also necessary to know what turnover the OPFs have and what the market conditions are at the time of calculating the indicator.
To determine a sufficient value of the NER parameter, it is necessary to resort to the fact that from one’s own funds one finances what is most difficult to transform into a money supply in the short term. In other words, these are raw materials reserves and “work in progress”. By adhering to this rule, you can easily determine the value of the NER, which will be sufficient to cover expenses or finance projects.
Standard value of the NER indicator
The sufficient size of the NSC of an enterprise, recognized as a standard value, differs depending on the industry of activity and the individual characteristics of the enterprise. General unified standards for PSCs have not been developed. Even within the same enterprise, the indicator varies from period to period. Rationing working capital is a prerequisite for running a business.
The minimum (sufficient) value of NSC is defined as the amount of funds required to finance low-liquidity inventories. Objects with low liquidity include mainly inventories stored in raw materials and supplies, as well as work in progress. When identifying criteria for grouping by degree of liquidity, additional economic indicators are used, for example, turnover.
When calculating the standard value of NER, the formula changes:
NOW min = Inventories of materials and raw materials + Work in progress
Features of determining the value of PSC standards:
- When calculating the standard value, the basis is the rule: equity capital should finance the least liquid reserves from among the working capital. When using borrowed funds, investment is aimed at securing reserves with the greatest liquidity.
- As a company develops, the constituent elements of inventories change from a liquidity point of view. Current assets often move from one level of liquidity to another due to the passage of stages of the technological process.
- The data obtained when calculating the indicator is used only in the current calculation period. When business conditions change, the size of the indicator changes and shows an irrelevant size.
To obtain standard indicators, it is necessary to group current assets by degree of liquidity. Each enterprise is based on individual conditions. The grouping is based on the turnover period. Several liquidity groups are used - high, medium, low. For example, for an asset with high liquidity, a company may set a conversion period of a month, for medium liquidity - a quarter, and so on.
Based on the analysis of the structure, a sufficient NER value is determined for each element and working capital as a whole. In order to obtain up-to-date information, the standard and categories of inventory liquidity must be regularly reviewed. Calculation of the indicator is also required when changing the structure of assets, introducing a new nomenclature, or additional types of activities.
Using balance sheet data for analytical activities
Based on the information presented in the second section of the reporting document, specialists have the opportunity to calculate various ratios used to assess the financial condition of the company. These include, in particular:
- Working capital mobility coefficient – balance sheet formula:
Coefficient = (Page 1240 + Page 1250) / Page 1200
- Own working capital – balance sheet formula:
Own working capital = Page 1200 – Page 1500
- Average value of current assets on the balance sheet. This indicator is determined by comparing the working capital values at the end of two reporting periods. Accordingly, for the calculation you will need:
Average asset turnover = (Line 1200Year1 + Line 1200Year2) / 2.
Thus, the use of information presented in the balance sheet allows the company to evaluate the effectiveness of its activities. At the same time, working capital - the formula on the balance sheet - is a set of lines that disclose information about all current assets available to the company.
The need to reflect information about the company’s working capital in the balance sheet is enshrined in the norms of the current Russian legislation.
Similar articles
- Classification of working capital of an enterprise
- Own working capital
- The increase in current assets indicates
- Corporate working capital management
- Other current assets include
First method of determination: formula
To determine the SOC, it is enough to subtract the amount of long-term funds and property not involved in turnover from the total amount of the company’s internal sources of financing. The total calculation looks like this:
SOK = SK – (VNA – DO), where
- SK is the amount of equity capital, taken in line 1300 of the balance sheet
- VNA is non-current assets (line 1100)
- TO are long-term liabilities (line 1400)
Calculation rules
Important! Long-term loans and credits are taken into account only to the extent that they are used to finance VNA. This also includes debt under leasing agreements. That is, only the value of such VNAs that are financed from internal sources is taken.
The company's internal resources (IC) are recorded as a total amount in Section 3 of the balance sheet. In addition to the authorized capital, they include reserve and additional capital, and retained earnings. VNA includes fixed assets, long-term financial assets. investments, intangible assets and other components of Section 1. Subsidiaries are included in Section 4 of the balance sheet.
Practical example. Financial position of the company and the level of NSC
The management of the enterprise, the indicators of which are reflected below, declares the reliable financial position of the company, since the structure of existing liabilities contains a large share of equity capital.
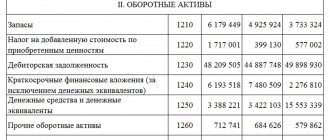
| Position, million rubles | Reporting period | |||
| 1 Apr. 2015 | 1 Jul. 2015 | 1 Oct. 2015 | 1 Jan 2016 | |
| General non-current assets | 46, 852 | 46, 325 | 46, 380 | 46, 401 |
| Current assets | 6, 450 | 6, 421 | 5, 816 | 6, 321 |
| Volume of authorized capital | 35, 950 | 35, 950 | 35, 950 | 35, 950 |
| Volume of additional capital | 32, 820 | 32, 820 | 32, 820 | 32, 820 |
| Volume of accumulated capital | -27, 692 | -27, 500 | -28, 739 | -28, 711 |
| Total net worth | 41, 077 | 41, 269 | 40, 031 | 40, 059 |
| Total long-term liabilities | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total current liabilities | 12, 851 | 12, 418 | 14, 008 | 14, 441 |
| CHOC | -5, 774 | -5, 055 | -6, 349 | -6, 341 |
Even a cursory glance at the presented table is enough to understand that there can be no talk of any financial stability: the company’s NER has entered a deep minus and continues to decline. The lack of financing in the form of own funds and, as a consequence, low financial stability is further confirmed by the negative value of accumulated capital. The company will not have enough own funds in the near future to maintain production activities, despite the fact that their share in total financial sources is almost three-quarters.
How to properly manage the CSC?
Working capital needs to be effectively regulated. The best measures in this direction could be:
- assessment of the level and structure of current assets;
- establishing and monitoring compliance with the proportions between long-term and short-term loans, current assets and liabilities;
- optimization of investment in each of the current assets and the structure of balance sheet liabilities;
- formation of an optimal ratio of accounts payable and receivable;
- maintaining company liquidity and monitoring cash flows.
Any company must determine for itself the optimal size of PSC and use it to adjust the amount of current assets and liabilities. This is the only way it can maintain its profitability and solvency at the required level.
A good example
Let's look at an example of calculation using specific numbers. To do this, we provide conditional data for reporting that does not exist as of December 31, 2016 (thousand rubles):
- 97 415 – VNA
- 103 480 – OA
- 61,500 – UK
- 65 103 – BEFORE
- 74 292 – KFO
Calculation examples
We check that the amount of assets and liabilities in the company’s balance sheet is equal:
97 415 + 103 480 = 61 500 +65 103 + 74 292 = 200 895
Let's calculate the value of SOC as of the reporting date in two versions.
Option 1. Let's assume that long-term loans and credits are aimed at financing the company's BNA, which corresponds to the norm. In this case:
- first method 61,500 – (97,415 – 65,103)
- second method 103,480 – 74,292 = 29,188
It can be seen that according to both formulas the result was the same: 29,188 thousand rubles. If this does not happen, there was an error in the calculations.
The result is a positive number. This means that according to this indicator the company will be considered financially stable. Current assets in the amount of 29,188 thousand rubles. financed from the company's internal sources. VNA in the amount of 65,103 thousand rubles. are formed with the help of attracted external long-term sources, the rest (32,312 thousand rubles) - from their own money.
Option 2. Due to long-term obligations, the enterprise forms an OA, which initially does not correspond to the norm. The calculations are as follows:
- the first way 61,500 – 97,415
- the second way 103,480 – 74,292 – 65,103
As you can see, the indicator is negative and amounts to -35,915 thousand rubles. The company is in a difficult financial situation. The company's own funds are not enough to form an OA; the company is not able to pay off its current debts using only funds in circulation.
The two calculation options considered show that the same balance sheet data can be interpreted differently and lead to opposite results. It is important to correctly evaluate and classify long-term loans and borrowings. Without knowing the purposes and directions of their use, it is impossible to correctly determine the SOC. In reality, the entire volume of long-term borrowings of an enterprise does not have one purpose of use. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully analyze all available loans.
In general, to maintain a normal level of the indicator under consideration, and therefore ensure the financial stability of the company, the following should be done:
- strive to obtain and increase profits
- optimize non-current assets of the enterprise
- monitor the size and quality of accounts receivable
- do not allow the use of long-term liabilities to form current assets
- maintain an optimal balance structure
These measures will help the normal functioning of the enterprise. Using the indicator, you can assess whether a company is able to pay off its short-term debts with liquid funds.
Top
Write your question in the form below