Starting from 2021, losses incurred in 2007 and later can be carried forward to an unlimited number of subsequent tax periods, and profits for the reporting (tax) periods 2017-2020 can be reduced by the amount of losses from previous tax periods by no more than 50 percent. 1C experts spoke about how these changes are supported in the 1C: Accounting 8 program, edition 3.0 for BUKH.1C.
Federal Law No. 401-FZ dated November 30, 2016 amended Article 283 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which regulates the procedure for transferring losses to the future. Please note that the concept of “carrying forward losses” is used only for profit tax purposes, since in accounting the procedure for accounting for losses is different.
Regulatory regulation of loss write-off
| Tax Code of the Russian Federation part 2 | Procedure for calculating income tax |
| Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 N 34n | Approves PBU |
| Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 19, 2002 N 114n | Approves PBU 18/02 |
| Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 N 94n | Approves the chart of accounts and its application |
| Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 19, 2016 N ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] | Income tax return form |
Reduction of authorized capital
The decision to reduce the authorized capital is made at the general meeting of shareholders, which is its exclusive competence (subclause 7, clause 1, clause 2, article 48 of the Law on Joint Stock Companies).
The issue of reducing the authorized capital is within the competence of the general meeting of participants of the limited liability company (subclause 2, clause 2, article 33 of the LLC Law).
In a joint stock company, the reduction of the authorized capital is carried out by reducing the par value of the shares (without paying cash to shareholders or transferring issue-grade securities to them) (Clause 1, Article 29 of the Law on Joint Stock Companies). The total number of outstanding shares does not change.
In an LLC, the reduction of the authorized capital is carried out by reducing the nominal value of the shares of all participants in the company in the authorized capital of the company. At the same time, the size of the shares of all participants in the company does not change (Clause 1, Article 20 of the LLC Law).
The decision to reduce the authorized capital to the net asset value must be made no later than six months after the end of the relevant financial year. After making such a decision, the company must, within three working days, report this to the body that carries out state registration of legal entities - the tax inspectorate (Article 30 of the Law on Joint Stock Companies, paragraph 3 of Article 20 of the Law on LLCs).
In addition, the company is obliged to publish a notice of the decision twice (once a month) in the media, where data on state registration of legal entities is published (the dates of publication of these messages are indicated in the application for state registration of changes made to the constituent documents).
Then you need to submit a package of documents to the tax office. It includes, in particular:
- application for state registration of changes made to the constituent documents (form R13001, approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 25, 2012 No. ММВ-7-6/ [email protected] );
- decision of the meeting of owners (participants, shareholders) to reduce the authorized capital;
- changes made to the constituent documents, or constituent documents in a new edition in two copies;
- document confirming payment of the state duty (according to subparagraph 3, paragraph 1, article 333.33 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, its amount is 800 rubles).
The registration authority is obliged to carry out state registration of changes in the authorized capital of the company within five working days from the date of submission of documents.
The date of reduction of the authorized capital will be considered the day of making changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. In the accounting registers, the decrease in the authorized capital should be reflected by posting on this date:
DEBIT 80 “Authorized capital” CREDIT 84 “Retained earnings from previous years”
As a result, society acquires a more stable financial position.
Let us also dwell on the fact that when registering a decrease in the authorized capital, the company incurs certain expenses. This:
- payment of state duty;
- payment for publications in the media;
- notarization of documents if necessary, etc.
All these expenses in accounting are classified as other expenses and are accrued by postings:
DEBIT 91-2 “Other expenses” CREDIT 68 subaccount “State duty”
– a state fee has been charged for registering a decrease in the authorized capital;
DEBIT 91-2 “Other expenses” CREDIT 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”
– costs associated with registering a decrease in the authorized capital are reflected.
EXAMPLE.
REDUCTION OF AUTHORIZED CAPITAL TO THE VALUE OF NET ASSETS At the end of the reporting year, the uncovered loss of Passive LLC amounted to 200,000 rubles.
The value of net assets as of December 31 of the reporting year amounted to 70,000 rubles. The authorized capital of the company is 300,000 rubles. An extraordinary meeting of the company's participants decided to reduce the authorized capital by 230,000 rubles. (from 300,000 rubles to a net asset value of 70,000 rubles) by reducing the nominal value of the shares of all participants. Registration of changes in the charter was made on May 15 of the following year. On this date, the accountant made the following entry: DEBIT 80 “Authorized capital” CREDIT 84 “Retained earnings of previous years”
- 230,000 rubles. – the authorized capital was reduced. As a result, the resulting loss was completely covered, and an indicator of retained earnings in the amount of 30,000 rubles was formed in the accounting. (RUB 230,000 – RUB 200,000).
Basis for writing off losses from previous years
During the write-off of losses incurred in previous years, it is reflected in the corporate income tax, which is a direct tax, and its value is directly proportional to the final financial results. The rules for imposing this tax are defined in Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
A loss is the negative result between income received and expenses. In this case, the tax base for this reporting period is assumed to be zero. It is possible to reduce the tax base due to losses incurred in previous periods in the next period. In this case, the loss must be documented, that is, the grounds that led to such losses (contracts, checks, receipts, invoices, acts, etc.) are required. The declaration for previous periods is not the basis for confirming this loss, so it is important to keep the primary documentation. If there are no supporting documents, any audit will be considered an unlawful reduction in the tax base and additional income tax will be charged.
Important! If a taxpayer who uses special regimes receives losses after switching to OSNO, the taxpayer will not be able to take into account losses incurred during periods of being in the special regime on OSNO.
How to pay off losses
Only profits from certain activities of the organization can be used to pay off some losses. In particular, this applies to:
- losses from the activities of service industries and farms. They can be covered only from the profits received from the activities of these industries and farms (except for the situation when the number of employees of the organization is 25 percent or more of the working population of the corresponding locality (Article 275.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- losses on transactions with securities that are not traded on an organized market. They can only be covered by profits from transactions with such securities (clause 22, article 280, clause 3, article 304 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax Code of the Russian Federation on the transfer of losses
The Tax Code has granted taxpayers the right to reduce the tax base due to losses received in previous years by the amount (part thereof) of the loss incurred.
From 01/01/2017 to 31/12/2021, the limit on the amount of write-off has changed - the maximum of the tax base of the reporting period should be 50% (that is, the current taxable profit can be reduced by no more than 2 times).
This procedure is used to write off losses for the previous 10 years. Thus, in declarations for 2021, you can write off losses from 2007 and later, in 2021 - from 2008 and later, etc.
At the same time, it is possible to write off losses both at the end of the year and at the end of the reporting period, that is, the declaration assumes the calculation of advance payments based on the results of the reporting periods, taking into account past losses.
Losses incurred in different periods should be carried forward in the order in which they were received, that is, losses for 2009 can be carried forward only after they have been repaid for 2008 (in 2021).
Losses on transactions taxed at a rate of 20% reduce the income tax base at the corresponding rate.
conclusions
Any organization is created for the purpose of making a profit. But in market conditions, some make losses at the end of the year. Often such losses are covered by profits not distributed among participants or by reserve and additional funds. If losses exceed income, then the negative balance can be carried forward to later periods. You can reduce the tax base for income tax by the amount of losses that were received in previous tax periods. There is no time limit; losses can be carried forward until the resulting loss for all previous years is completely written off. Losses must be transferred in chronological order based on the fact of occurrence. It must be remembered that before reducing the tax base of the current year by the amount of losses from previous years, check the availability of documents that confirm the amount and period of occurrence of losses.
To non-operating expenses in accordance with clause 2 of Art. 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, losses of previous tax periods identified in the current reporting (tax) period are equated. A similar norm in terms of profit is provided for in paragraph 10 of Art. 250 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
R.I. Ryabova
The main question that arises when identifying losses from previous tax periods in the current tax period:
In which tax period should this loss be reflected (as well as income identified in the current tax period, but relating to previous tax periods)?
There is a contradiction between articles 250 and 265, 54 and 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
According to Art. 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation “if errors (distortions) are detected in the calculation of the tax base relating to previous tax (reporting) periods, in the current tax (reporting) period, the tax base and tax amount are recalculated for the period in which these errors (distortions) were committed” .
If it is impossible to determine the period of errors (distortions), the tax base and tax amount are recalculated for the tax (reporting) period in which the errors (distortions) were identified.”
Article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides the following:
“If a taxpayer discovers in the tax return submitted by him to the tax authority that information is not reflected or is incompletely reflected, as well as errors leading to an underestimation of the amount of tax payable, the taxpayer is obliged to make the necessary changes to the tax return and submit an updated tax return to the tax authority in accordance with the procedure established by this article.
If a taxpayer discovers inaccurate information in the tax return submitted to the tax authority, as well as errors that do not lead to an underestimation of the amount of tax payable, the taxpayer has the right to make the necessary changes to the tax return and submit an updated tax return to the tax authority in the manner established by this article "
At the same time, Articles 250 and 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allow losses (income) to be recognized in the period in which they are identified.
The Russian Ministry of Finance has repeatedly explained its position on this issue, namely: if the period of the error is known, then an updated return for any tax, including income tax, should be submitted (letter dated September 18, 2007 No. 03-03-06/1 /667).
The most common disputes considered in arbitration courts are disputes about the procedure for applying subparagraph. 3 paragraph 7 art. 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The date of recognition of expenses in the form of third-party services, commissions, rental (leasing) payments and other similar expenses in accordance with this subclause is:
– settlement date in accordance with the terms of concluded agreements
– or the date of presentation to the taxpayer of documents serving as the basis for making calculations,
– or the last date of the reporting (tax) period.
Of these options, the most controversial is “the date of presentation to the taxpayer of documents serving as the basis for making calculations.”
The Russian Ministry of Finance understands this date as the date of drawing up the document - an act or an invoice (letters from the Russian Ministry of Finance on this issue are given in the section “General principles for recognizing expenses”, see p. 75).
In this case, the date of drawing up the act is considered to be the latest date on this document - the date set by the customer.
If one of these documents is received by an organization after submitting a declaration for the previous tax period, but the date of preparation of the document refers to the previous year (before December 31 of the previous year), then, in the opinion of the Russian Ministry of Finance, an updated declaration for the previous year should be submitted.
This position is contained in the Instructions for filling out corporate income tax returns, approved by Order of the Ministry of Taxes of Russia dated December 29, 2001 No. BG-3-02/585. Application
No. 2 to Sheet 02 contains line 301 “Losses of previous tax periods identified in the current reporting (tax) period.”
Clause 7.3 of the Procedure for filling out a tax return for corporate income tax, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/07/2006 No. 24n, states that line 301 does not include expenses related to previous reporting (tax) periods, regardless of the period of receipt (discovery) of documents confirming these expenses drawn up in previous reporting (tax) periods.
Only one of the latest letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia (dated 09/06/2007 No. 03-03-06/1/647) contains an explanation that semi-fixed expenses (for example, utility bills) can be taken into account in the period in which the primary documents are received .
Arbitration practice on this issue develops differently.
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated May 23, 2007 No. F04-2976/2007(34246-A27-37)
The court considers that sub. 1 item 2 art. 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation should be applied taking into account the provisions of paragraph 1 of Art. 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, i.e. Losses from previous years can be attributed to non-operating expenses of the current reporting (tax) period, but only if it is impossible to determine the specific period of the error (distortion). Failure to include expenses due to failure to receive the relevant primary documents is not grounds for transferring expenses to another tax period as part of losses from previous years identified in the current tax period.
A similar position is contained in the decisions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated October 8, 2007 No. F09-8153/07-S3, the Moscow District dated August 2, 2007 No. KA-A40/3580-07, the Northwestern District dated June 25, 2007 No. A56-51992/2005, East Siberian District dated 03/06/2007 No. A33-19739/05-F02-6753/06-S1, North Caucasus District dated 05/29/2007 No. F08-2109/2007-875A.
No exceptions are made for taxes included in expenses that are additionally assessed during audits for previous periods.
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated May 14, 2007 No. A56-15769/2006
During the next tax audit, it was established that the company included in non-operating expenses as a loss from previous years the amount of tax on road users, additionally assessed for previous years based on the results of a tax audit conducted earlier.
The court agreed with the position of the tax authority. The company had to increase the expenses of those periods for which the specified tax was additionally assessed by the amount of the additional tax on road users. Accordingly, an updated income tax return should have been filed.
However, in some cases, courts recognize it as justified not to submit an updated declaration, but to include the identified expenses in non-operating expenses as a loss from previous years.
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the East Siberian District dated February 26, 2007 No. A33-4264/06-F02-592/07
The court found it unlawful to classify a change in the terms of the contract as an error (distortion) in calculating the tax base. Before changing the terms of the agreement, when calculating the tax base, the taxpayer used primary documents that corresponded to the intentions of the parties, did not contain errors or defects, and were drawn up in accordance with the requirements of current legislation. Consequently, the provisions of Art. 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation do not apply when taking into account the impact of the results of these changes on taxation. The change in the real amount of income (expense) resulting from the additional agreement is subject to reflection in tax accounting as an adjustment to the tax base of the current tax period.
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated September 26, 2007 No. Ф04-6623/2007(38518-А75-40)
The court recognized that losses from previous years identified in the reporting year include, for example, additional costs for orders for which payments were completed in previous years, refunds of amounts in settlements with customers for products paid for in previous years, and other similar amounts.
However, the conclusion that expenses incurred in previous years are clearly considered as losses of previous years was recognized by the court as based on an incorrect interpretation of tax legislation.
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated September 11, 2007 No. KA-A40/7748-07-P
The subject of the dispute between the tax authority and the taxpayer was the amount included in the expenses of the current period. This amount was formed from identified expenses of previous years as a result of late receipt of primary documents used to document business transactions.
The court found the following.
Since in the period to which the untimely received documents relate, the company had no basis for reflecting expenses, since they were not documented (clause 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), it lawfully did not reflect these business transactions in its accounting.
The total expenses in question fully correspond to the concept of losses from previous years, as set out in subparagraph. 1 item 2 art. 265 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated July 31, 2007 No. KA-A40/7550-07
The court found that the company is justified in accordance
with subp. 1 item 2 art. 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation included in non-operating expenses losses from previous years identified as a result of reconciliation of settlements with the counterparty.
To prove the existence of debt, a bilateral reconciliation act of settlements as of a certain date, a power of attorney for the person who signed the reconciliation act, an agreement on debt restructuring, payment requests and invoices are presented.
Similar is the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated February 15, 2007 No. A12-13348/06-C33 on the legality of reflecting expenses identified during the reconciliation of calculations as losses of previous years.
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated July 19, 2007 No. A55-15098/06
This Resolution talks about the relationship between Art. 54 and sub. 1 item 2 art. 265 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with sub. 1 item 2 art. 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, non-operating expenses are equivalent to losses received by a taxpayer in the reporting (tax) period, in particular in the form of losses from previous tax periods identified in the current reporting (tax) period. This rule is special and does not contain reference to Art. 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which defines only general issues of calculating the tax base and is not applicable in this case.
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated February 22, 2007 No. F04-613/2007(31564-A45-3)
Work performed in the previous year, but accepted by the customer (forms No. KS-2 and KS-3 are signed) in the current year, is recognized by the customer as expenses in the current year.
Please note the following Decree.
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated November 1, 2006 No. KA-A40/10694-06
The Resolution refers to the date of recognition of payments for water and electricity as expenses, which, in accordance with subparagraph. 5 p. 1 art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation relate to material costs.
Electricity, heat, water are continuous supplies. In this regard, the tax inspectorate considered that expenses should be recognized in the period in which the supply of these resources was made, regardless of the date of preparation of the primary documents.
The court did not agree with this position.
It was established that documents for the supply of water and electricity for the period September – December 2004 (acts of completion, invoices) were dated May 31, 2005.
Under such circumstances, the courts came to the conclusion that since the expenses for the purchase of electricity and water were actually incurred by the company in the expired tax period (2004), and the primary documents confirming the expenses incurred were dated to the next tax period (2005) , these expenses were legally taken into account by the applicant as part of the corresponding expenses of the next tax period, reducing taxable profit.
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated 07/09/2007 No. A56-22982/2006
The dispute concerns the period in which the costs of paying remuneration for the use of a trademark must be taken into account.
Under the terms of the license agreement, the company's expenses for paying remuneration for the right to use the trademark arise monthly upon receipt by the company of revenue from the provision of services using the trademark.
The date of non-operating and other expenses in accordance with subparagraph. 3 paragraph 7 art. 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (as amended in force during the audited period) is recognized, unless otherwise established by Articles 261, 262, 266 and 267 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the date of settlements in accordance with the terms of concluded agreements or the date of presentation to the taxpayer of documents serving as the basis for making settlements, or the last day of the reporting (tax) period - for expenses in the form of commission fees, expenses for payment to third-party organizations for work performed (services provided), rental (leasing) payments for rented (leased) property and in the form of other similar expenses.
The company took into account the costs of paying remuneration for the right to use a trademark as a periodic monthly payment based on the date of presentation of invoices for payment, i.e. in full accordance with the provisions of sub-clause. 3 paragraph 7 art. 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, the company rightfully attributed the disputed expenses in full to the reporting (tax) period in which it actually incurred these expenses in accordance with the terms of the license agreement: to the period after receiving revenue from the provision of services
using a trademark. Until this point, under the terms of the transaction, the taxpayer did not have the obligation to transfer the relevant payments.
Under such circumstances, it should be recognized that the court rightfully declared the contested non-normative acts of the tax authority invalid.
From the author. From the text of the Resolution it can be understood that remuneration for the use of a trademark was recognized not at the end of the current month, but in the next month based on the terms of the contract. If there were no special procedure in the agreement, then the remuneration could be taken into account at the end of the reporting month.
The author is an IPB consultant, a lecturer at the Moscow State University Accountant Training Center, and a 2nd rank tax service advisor.
An example of transferring losses from 2007 to 2010 to 2021
Based on the results of 2007-2010, Alpha and Omega LLC received the following losses: (click to expand)
| Years | Amount of loss, rub. |
| 2007 | 100000 |
| 2008 | 50000 |
| 2009 | 100000 |
| 2010 | 50000 |
These losses were not previously taken into account by the organization. In 2021, a profit from core activities was generated in the amount of RUB 200,000.
The 10-year limit on writing off losses does not apply from 2021 (but the earliest period is 01/01/2017), therefore, for 2021, in calculating the income tax, Alpha and Omega LLC can write off a loss for 2007 in the amount of 100,000 rubles ., which represents 50% of 2021 profits. The remaining losses for 2008-2010 can be written off in subsequent reporting periods (provided there is a profit). And first you need to write off the loss for 2008 (50,000 rubles), and subsequently - the losses for subsequent years.
The procedure for closing reporting periods and determining financial results
The reporting period is closed as follows:
- expenses are written off (for production and sales)
- comparison of data on debit and credit of accounts 90 and 91
- debiting to account 99:
- profit (positive difference) on credit 99
- loss (negative difference) to debit 99
Calculation of conditional income (or expense) for income tax
According to PBU 18/02, with the closing of the reporting period, the conditional income tax expense (income) is reflected in accounting using the following formula:
Conditional income tax expense (or income) = Accounting profit (or loss) for the reporting period (balance on subaccounts 90-9 and 91-9) * 20%
This amount is reflected in account 99 Profit and loss in the open subaccount Conditional expense (income) for income tax.
In accounting, the accrual of the amount of the conditional expense for the reporting period will be reflected by the posting:
D 99 subaccount Conditional income tax expense K 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax”
And the accrual of the amount of conditional income for the reporting period
Debit 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” Credit 99 subaccount “Conditional income for income tax”
At the end of the reporting period, the following entry is made in tax accounting to reflect the loss (repaid in the following reporting periods):
Debit 09 Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax”
How the financial result is reflected - postings
A loss in accounting (hereinafter referred to as BU) is determined at the end of the reporting period by comparing the costs incurred and the revenue received. The financial result (profit or loss) is obtained from the sum of the results for the usual types of activity for the enterprise and other inflows and outflows. To record financial results, the chart of accounts (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n) provides for account 99 “Profit and Loss”. During the financial year, the periods for which interim reporting is generated are closed, and the following entries are made:
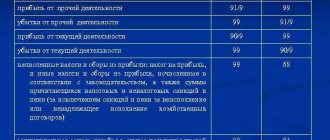
| Dt | CT | Description |
| 90.9 | 99 | Profit from ordinary activities is shown (if the turnover according to Kt 90.1 is greater than the sum of turnover according to Dt 90.2, 90.3, etc.) |
| 99 | 90.9 | The loss for ordinary activities is shown (if the turnover according to Kt 90.1 is less than the sum of the turnover according to Dt 90.2, 90.3, etc.) |
| 91.9 | 99 | The profit for other activities is shown (if the turnover according to Kt 91.1 is greater than the turnover according to Dt 91.2) |
| 99 | 91.9 | The loss for other activities is shown (if the turnover according to Kt 91.1 is less than the turnover according to Dt 91.2) |
Note that the reflection of the facts of financial and economic activities for all subaccounts of accounts 90 and 91 is carried out continuously throughout the year, on an accrual basis. And only when the balance sheet is reformed at the end of the year, they are reset by postings Dt 90.1 Kt 90.9, Dt 90.9 Kt 90.2 (90.3). For count 91, the reformation is performed in a similar way. Accordingly, the accountant does nothing with the loss incurred at the end of interim reporting periods - the financial results are simply accumulated in account 99. But at the end of the year, the accumulated balance in account 99 is included in retained earnings or uncovered losses by postings:
| Dt | CT | Description |
| 84 | 99 | The uncovered loss of the reporting year is shown |
| 99 | 84 | The profit of the reporting year is shown as part of retained earnings |
Accounting for writing off losses from previous years
According to the Instructions for the chart of accounts and PBU 18/02, losses are recognized at a time. Due to the fact that the loss for tax purposes is taken into account in subsequent reporting periods, deductible temporary differences are formed in accounting, which will lead to the formation of a deferred tax asset.
The amount of the deferred tax asset will be repaid when the loss is written off in tax accounting and will be repaid as the resulting loss is taken into account when assessing income tax.
In a situation where the organization has not taken into account the loss, the outstanding balance of the deferred tax asset will need to be reflected by posting:
D 99 K 09 – the outstanding deferred tax asset is written off
Confirmation of the loss in the form of documents must be kept for the period during which the profit decreases by the amount of the loss. After repayment of the entire amount of the loss, supporting documents must be kept for 4 years (Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Securities loss coverage
Income and expenses from transactions with marketable securities are taken into account in the general tax base (clause 21, article 280 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, losses from transactions with such securities must be taken into account in a general manner. At the same time, losses that were not taken into account when calculating income tax on transactions completed before January 1, 2015, also reduce the overall tax base. They can be carried forward annually for 10 years in the amount of no more than 20 percent of the original loss determined as of December 31, 2014.
This follows from the provisions of Part 3 of Article 5 of the Law of December 28, 2013 No. 420-FZ.
A different procedure applies when losses are incurred from transactions with non-negotiable securities. This loss can be taken into account when calculating profit from transactions with similar securities separately from the general tax base (clause 22 of article 280 and clause 3 of article 304 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Please note that losses that were not taken into account when calculating income tax on transactions with non-negotiable securities completed before January 1, 2015 can be carried forward to the future, but for no more than 10 years. At the same time, the tax base for non-traded securities can be reduced per year by no more than 20 percent of the original amount of such losses determined as of December 31, 2014. This follows from the provisions of Part 4 of Article 5 of the Law of December 28, 2013 No. 420-FZ.
Example of accounting for losses carried forward
For the first half of 2021, profit is reflected in the Alpha and Omega tax accounting. For 2021 as a whole, a loss of 50,000 rubles was formed.
Posting was done in December 2021:
D 09 K 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” – 10,000 rubles. (RUB 50,000 * 20%) – a deferred tax asset is reflected.
In the first quarter of 2021, a profit of 80,000 rubles was received. This profit must be reduced due to the loss of 2021 by 40,000 rubles.
The tax asset is reimbursed in the following way:
D 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” K 09 – 8000 rub. (RUB 40,000 * 20%) – part of the deferred tax asset is repaid.
The remaining amount of loss is 10,000 rubles. approximately in the next reporting periods the income tax base will be reduced and the remaining portion of the deferred tax asset in the amount of 2,000 rubles will be repaid. (10,000 rub. – 8,000 rub.).
The procedure for reflecting losses in the declaration
The transfer of losses must be indicated in the income tax return.
The declaration does not provide for the calculation of a limit of 50% of profit, but the report must indicate that the decrease in profit is only for the loss that is recorded in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (50%): (click to expand)
- lines 010-130 reflect the entire amount of losses from previous years, supported by documents
- lines 140 and 150 must match the following: line 150 is less than or equal to line 140 * 50%.
The amount of income tax reflected in accounting at the end of the reporting quarter or year must match the amount reflected in the tax return.
Acting State Advisor of the Russian Federation, 3rd class S. Razgulin
Errors when carrying forward losses
- When transferring losses that have arisen in the activities of an organization when operating under other tax regimes (special), the income tax base is not reduced, that is, if losses were incurred when applying the simplified tax system until the end of 2013, since 2014 the organization has been operating under the OSNO, then it is possible transfer losses incurred since 2014 (according to letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 25, 2009 No. 03-03-06/1/617). At the same time, losses during the transition from OSNO to the special regime are not transferred.
- With regard to losses generated during periods of application of the 0% profit tax rate, it should be noted that they cannot be carried forward to the future (medical, educational organizations and social service organizations, agricultural producers, participants in the Skolkovo project).
Answers to common questions
Question No. 1 : Based on the results of the reporting period, a loss was received. Can it be transferred to the future?
Answer : Not possible. The reason is that the income tax base for the year is determined on an accrual basis and the loss of the reporting period is an intermediate result that is not carried forward to the future, but only the final one.
Question No. 2 : Is it possible to write off losses from previous years by developing your own procedure at the enterprise and approving it by order?
Answer : The Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the following main points: losses must be generated no earlier than 01/01/2007, the chronological order of their write-off and the possibility of writing off only 50% of the profit received by the organization. Thus, its own procedure must comply with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.