Is it possible to return overpayment of tax?
The content of the article
If a subject sees an overpayment of mandatory payments, then first it is necessary to figure out how it arose.
This may be the case if:
- An error was made when paying tax.
- If advance payments at the end of the year turned out to be more than in the annual declaration (for example, an overpayment of income tax or an overpayment according to the simplified tax system is reflected at the end of the year in the declaration under the simplified tax system).
- Use of tax benefits when tax is simultaneously paid by a legal entity and withdrawn by decision of the Federal Tax Service, etc.
Overpayment of taxes can be refunded only when the tax authorities agree with this fact. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the Federal Tax Service must inform the payer about this within 10 days from the moment the excess payment is discovered so that he can make an appropriate decision. But in practice this happens very rarely.
However, the taxpayer himself has the right, if an overpayment is detected, to submit an application for a refund of the amount of overpaid tax. Before this, it is advisable for him to reconcile the calculations with the Federal Tax Service. You don’t have to do this, then the inspectors of the Federal Tax Service, if questions arise, will ask you to provide a number of documents that confirm the fact of the overpayment.
Important! The taxpayer must also remember that a refund of overpaid tax is possible only if three years have not passed since the overpayment.
If the overpayment occurred due to the fault of the tax authorities, then this tax amount can be returned within one month from the moment the taxpayer learned about it, or from the date the court decision entered into force.
However, in the latter case, the Federal Tax Service can take advantage of three months to verify the fact of the overpayment and make a decision on the refund.
Accountant's responsibility
An accountant may be held financially liable under the law if it was not possible to repay the overpayment at the expense of the employee. The basis for holding the accountant accountable can be an act recording (Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 247):
- the amount of material damage;
- the reason for the loss.
The amount of loss can be repaid by an accountant in two ways:
- if there is a liability agreement with him, repayment occurs in full;
- if there is no contract of liability, repayment occurs in the amount of average monthly labor payments (Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Articles 244, 248).
If the accountant does not agree to repay the amount of the error voluntarily or the month period discussed above has expired, the issue of collection is decided exclusively by the court.
On a note! The full financial responsibility of an accountant can be fixed in an employment contract with him.
In which case is it not possible to return the money?
There are also situations when the Federal Tax Service refuses to refund the overpaid tax. Quite often this is due to the fact that taxpayers miss the statutory limitation periods of three years - if the overpayment of taxes arose due to the fault of the enterprise, one month - when the inspectorate itself is to blame.
Here, proof of the time of discovery of the fact of overpayment of tax is of great importance. If the taxpayer has the opportunity to submit them, and they do not exceed the established deadlines, then through court proceedings it is possible to obtain the return of overpaid tax.
Refund or credit - which is better?
In addition to a tax refund, the taxpayer has the right to ask the Federal Tax Service to offset the amount of any overpayment of tax against the enterprise's existing obligations to the budget.
However, there is a limitation when crediting excess tax. It can only be done for taxes within one budget (federal, regional or local).
In most cases, the decision on a refund or offset is made only by the taxpayer (in the absence of tax debts). Therefore, what is better is a credit or a refund, each business entity decides independently, assessing the current situation in specific conditions, as well as the amount of overpaid tax.
In addition, it matters in what status the tax overpayment occurred. After all, if an excess payment was made by a tax agent, then he cannot take these amounts into account for obligations where he acts as a taxpayer. Only returns are possible here.
How to identify overpaid taxes
As noted above, overpayment of tax can arise for a variety of reasons and can be identified either by the tax authorities or by the taxpayer himself.
Let's take a closer look at how to identify an overpayment by a taxpayer.
Many taxes require advance payments either monthly or quarterly. Therefore, overpayment of such taxes can be identified after the annual report has been compiled.
At the same time, many declarations require indications in the tax report of the amounts of advance payments and the amount of tax for the year, and therefore the report indicates the amount of the overpayment, if any.
The same situation arises if the report is clarified, as a result of which, due to a benefit or for some other reason (incorrect indication of the tax base), the amount of the taxpayer’s obligation to the budget is reduced.
Often, when transferring taxes, errors can be made in payment orders, so it is possible to identify overpayments of taxes if the money went to the wrong place by periodically checking with the budget for mutual settlements.
You can find out about the resulting surplus from the tax office or on your own:
- The inspector can call or send a letter. When calling, it is important to write down where they called from, for what tax and in what amount the overpayment was made. Sometimes the tax office may require additional documents to check whether it is really an overpayment. In this case, there is no point in refusing. Alas, tax authorities rarely report identified overpayments themselves.
- Through your personal account on the tax website. If an organization or individual entrepreneur has a qualified digital signature, you can open a personal taxpayer account for free. Through it, it is very convenient to track your relationship with the tax office - it will contain information not only about underpayments, but also overpaid amounts.
How to get back overpayment of overpaid taxes
If an organization or individual entrepreneur has discovered that the amount of taxes has been overpaid, then there are two possible scenarios: return the funds to your current account, or offset the excess to another tax (KBK).
Procedure for refund
If an organization decides that the overpaid tax must be returned back to the current account rather than offset, a special application for a tax refund is drawn up for this purpose.
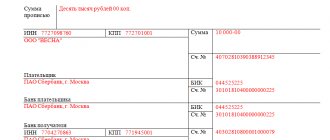
A special KND form 1150058 has been developed for it. It was updated in 2021, and is currently more reminiscent of a declaration. The application must indicate the name of the company, the amount of overpayment, the BCC for the tax, and the details of the taxpayer’s current account.
The completed document is submitted to the Federal Tax Service in several ways:
- In paper form personally by the taxpayer or his representative by proxy;
- By post with notification of receipt;
- In electronic form via the Internet, but an electronic digital signature will be required.
The process of refunding excess tax can be divided into several stages:
- Determine that an overpayment has occurred. This can be done, for example, by requesting a tax reconciliation report from the Federal Tax Service. The document will show for what tax and in what amount the excess transfer of funds occurred.
- Submit a return application. In it you need to indicate information about the company, the amount to be returned and the details of the bank account to which this should be done;
- Submit the application to the tax office in person or through a representative, by mail or via the Internet;
- After 10 days, receive the result of the application review. If the authority unlawfully refuses a return, prepare documents to transfer the case to court;
- Within a month from the date of filing the application, the Federal Tax Service must return the funds to the current account;
- If the time has expired, but enrollment has not been made, write a complaint to a higher inspection and prepare documents to transfer the case to court.
How to offset overpaid tax
If the taxpayer decides not to make a refund of overpaid tax, he can offset it:
- For further payment of the same tax;
- To pay off a debt for another unpaid tax.
When performing an offset, you must follow the rule - a payment can only be offset within the budget of the same level. That is, an overpayment for a federal tax will be credited only to another federal one, for a regional tax - to another regional one, etc.
The Federal Tax Service has the right, if an overpayment is detected, to independently offset the underpayment of another tax. In this case, the company's consent is not required.
To make an offset, you must submit an application for tax offset using a special form KND 1150057.
To what account should the refund from the tax office be credited?
What entries should be made to reflect income from compensation of expenses (recovery of expenses)
If the military registration and enlistment office reimburses expenses, then reflect the money under article KOSGU 130 “Income from the provision of paid services (work)” (Section V of Instructions No. 65n).
Make settlements with the military registration and enlistment office in the accounting of a budgetary institution using the following entries: 1.
Income was accrued in the form of compensation for expenses for the earnings of an employee who participated in military training: Debit 2.209.30.560 Credit 2.401.10.130 2.
The amount of compensation was received in the institution's account: Debit 2.201.11.510 Credit 2.209.30.660 Increase in off-balance sheet account 17 (analytics code 130) In the accounting of budgetary institutions, reflect the penalty from a supplier who violated the terms of the contract as income from paid activities. The source of financing of the obligation does not matter. Make the following entries in accounting: 1. The supplier's debt has been accrued in the amount of the penalty: Debit 2.209.40.560 Credit 2.401.10.140 2.
The supplier transferred the penalty to the institution's personal account (personal account statement): debit 2.201.11.510 Credit 2.209.40.660 Increase in off-balance sheet account 17 (analytics code 140, KOSGU 140) How to offset the penalty against payment under the contract is given in the justification for the answer. Rationale How to reflect in accounting the return of money excessively transferred to a counterparty in the current year, or a return from the bank. An error was made in the payment. Reflect the return of excessively transferred money from the supplier, contractor, or performer in accounting as a restoration of cash expenses.
Do the same if you indicated incorrect details in the payment document and the bank returns the funds. Reflect the amount received according to the same CVR for which the payment was made. This conclusion follows from paragraph 11 of the Procedure, approved by order of the Treasury of Russia dated July 19, 2013 No. 11n, paragraph 2.5.4 of the Procedure approved by order of the Treasury of Russia dated October 10, 2008 No. 8n.
The procedure for recording the return of money from a counterparty or bank in accounting depends on the type of institution. In the accounting of budgetary institutions: Reflect the return of money as follows: No. Contents of the transaction Account debit Account credit 1.
Receipt reflected
Accounting for the return of overpayments of income tax for previous years
In 2012, according to a reconciliation with the tax office, an overpayment of income tax for previous years was revealed. At the same time, in accounting there is no difference between the debit and credit balances in account 68, the subaccount “Income Tax Calculations”. The organization submitted an application for a refund of the amount of overpaid tax to the tax office. In 2012, the tax inspectorate refunded her the amount of overpaid income tax. The organization applies PBU 18/02.
How to reflect this situation in accounting and tax accounting? An error of the previous reporting year, which is not significant, discovered after the date of signing the financial statements for this year, is corrected by entries in the corresponding accounting accounts in the month of the reporting year in which the error was identified. Profit or loss arising as a result of correcting this error is reflected as part of other income or expenses of the current reporting period (clause 14 of PBU 22/2010). In the situation under consideration, in 2012, based on the results of a reconciliation with the tax office, an overpayment of income tax for previous tax periods was revealed.
At the same time, in accounting there is no difference between the debit and credit balances of account 68, the subaccount “Calculations for income tax”, which apparently indicates that in case of overpayment of income tax based on the results of tax periods, there were no entries were made to adjust the income tax (Debit 68, subaccount “Calculations for income tax” Credit 99). According to the Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 N 94n (hereinafter referred to as the Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts), it is intended to summarize information on settlements with budgets for taxes and fees paid by the organization account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees.” In this case, account 68 is credited for the tax amounts due on tax returns (calculations) for contributions to budgets, in correspondence with account 99 “Profits and losses”, and the debit of account 68 reflects the amounts actually transferred to the budget.
For an organization, the discovered and returned amount of income tax overpaid for previous years is an unexpected gift, but for an accountant it is an unpleasant surprise if this overpayment was not taken into account at the end of the tax period. Olga Podvolokina and Svetlana Myagkova, experts from the Legal Consulting Service GARANT, talk about accounting and tax accounting, as well as how to correct a mistake in this situation. Thus, since in accounting, income tax is accrued based on the results of reporting periods, then, accordingly, the organization, based on the tax return data, calculates the amounts subject to accrual in accounting and reflects the accrual (additional accrual) of tax for the first quarter, first half of the year , nine months on the debit of account 99 “Profits and losses” in correspondence with the credit of account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”.
Payment of advance payments for income tax is reflected in the generally established procedure - by the debit of account 68 in correspondence with the credit of account 51 “Current accounts”.
Results
- Excess accruals and wage payments can be returned to the organization without any problems only with the written consent of the employee in respect of whom the overpayment was made, and only if the one-month period is observed after the one set for the employee to voluntarily repay.
- In other cases, the return may be contested, including in court, despite the legally established possibility of debt repayment. A detected error in payments must be recorded in an act signed by the organization’s internal commission. The employee must be familiarized with the act.
- An accountant who makes a mistake bears financial responsibility for it in accordance with the law.
- Correspondence accounts used to account for overpayments of wages are reversal entries of previously made entries. The excess amount paid in hand is reflected in Dt 73 account. Its repayment by the employee is reflected in the Dt of the corresponding accounts, depending on the method of repayment. If the loss cannot be recovered, it is transferred to Dt 76 and then recorded according to Dt 91/2.