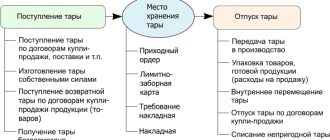
To replenish a company's budget, a legal entity can borrow money through bonds. They are securities with a certain denomination that provide interest payments to the holder. By purchasing them, a person pays only a nominal amount, which he will receive back after a certain period. Considering that all transactions with securities must be reflected in the accounting department, this raises the question of how bonds are accounted for. The correctness of this process is verified by regulatory authorities, and if the standards are not followed, a fine may be imposed.
Types of bonds in circulation and by form of income
In circulation there are state (federal, regional, municipal) securities and corporate ones - issued by legal entities. The date of transaction with bonds for their acquisition or disposal is the day of transfer of ownership.
According to the categories of income generation, there is a division into 2 types of securities - coupon and zero-coupon. Depending on the type of security, forms of income are established: (click to expand)
- In the form of interest with a specified payment period for coupon bonds. Payment control is carried out using cut-off coupons.
- In the form of a discount - the difference between the face value and the purchase price.
Securities, the market value of which is not determined, must reach the par value of the book value by maturity. The difference is taken into account evenly as part of other income or expenses throughout the entire period of use.
Carrying out accounting with the issuer
The parties that issue bonds carry out operations with them to place them, provide legal income, and also pay the value of the securities to their holders. The enterprise that sold the bonds makes entries in the accounts that account for long- and short-term loans, these are 67 and 66, respectively. Detailed accounting is carried out according to IFRS standards and chronological norms, taking into account the issue, all acquirers, as well as the price. When the issuer pays income, the following rules apply:
- interest charges and discounts are included in the list of other expenses;
- debts should be written off evenly across reporting periods, or done simultaneously if the process occurs during the period of time when expenses occur;
- the order in which funds move is approved and prescribed in the company's accounting policy, but bankruptcy in any case will not be confirmed if the issuer has not paid off its debts.
Securities must be recorded
When the issuer needs to reflect the placement at a nominal price, the accounting of bonds in accounting will have entries Dt 51 Kt 66 or 67. The provision of interest for a one-time write-off is expressed in accounting notations for accounts 91/2-66 (67). In the case of calculating profit according to the scheme of uniform return over periods when it was decided to amortize the debt, reflections are used:
- 97-66 or 67;
- 91/2-97.
When taking into account the positive difference, when bonds were purchased at a price higher than their face value, an accounting entry is made. For this purpose, the designations Dt 51 Kt 98 are used, and with a uniform and periodic write-off of income, when bonds are placed at a price above their face value, entry 98-91/1 is made.
Documentary form of securities
A security in the form of a bond is a document containing information about the details that allow it to be identified. The data contained on the document ensures the rights of the owner. The bond certifies only the material rights of the investor and does not affect non-property rights, for example, participation in the activities of the enterprise that issued the securities.
The form presented on paper or other media permitted by law is used. The placement of bonds into circulation is carried out through an issue that has a state registration number, and, if there is no need to register the issue, an identification number.
Bonds have pricing characteristics that allow holders to determine the costs and income received. Initially, the bond is assigned a par value - the price indicated on the document. When sold on the secondary circulation market, the bond acquires a market value - a market price that fluctuates during the circulation period.
At maturity, the bond primarily has a value equal to its par value.
Partial repayment
Working according to this scheme is a fairly common practice.
The decision on early partial termination of the bond occurs within the framework of the offer agreement, if the issuer has appropriate reserves. In the standard mode, a payment of half the face value is usually scheduled in the middle of the cycle.
For the accounting department of enterprises that hold exchange assets, appropriate entries should be made. Partial disposal of financial investments is reflected in the amount of funds received. At the same time, a record is made of a decrease in the quotes of the acquired assets, with the noted difference being attributed to the company’s expenses.
Accounting for bonds with coupon income
The cost of bonds with accumulated coupon income differs from the nominal value either down or up. The value of a bond is the sum of the market price and the amount that has changed the value of the security. Bonds with accrued coupon income are purchased on the secondary market.
Example No. 2 for determining the amount to write off the difference in excess of the actual purchase amount over the nominal amount
The LLC Kontakt enterprise purchased a bond of OJSC Kedr with a par value of 50,000 rubles at a price of 55,000 rubles. According to the terms of the agreement, the income from the investment will be 10% of the value of the bond with payment twice a year and maturity 5 years after purchase. The amount of costs exceeding the nominal value must be written off in equal parts over the reporting periods - 500 rubles per six months. In the accounting of Contact LLC, entries are made, accompanied by the following entries:
| Operation | Wiring | Amount, rub. |
| Payment has been made for the purchased asset | Dt 76 Kt 51 | 55 000 |
| The bond is taken into account in the amount of actual expenses | Dt 58/2 Kt 76 | 55 000 |
| Part of the excess of actual costs over nominal costs was written off | Dt 91/2 Kt 58/2 | 500 |
| Interest accrued on the bond | Dt 76 Kt 91/1 | 2 500 |
| Interest income received | Dt 51 Kt 76 | 2 500 |
A uniform write-off of the excess amount over the par value of the bonds as part of other expenses will allow you to obtain the par value by the maturity date. If the purchase amount (actual expenses) is less than the nominal value, the difference is accrued in equal parts as part of other income.
Reflection of receipts and repayment process
Expenses for the purchase of bonds are reflected in account number 58, which stipulates the availability of financial investments and allows for tax accounting of bonds. To increase the detail of the information, the buyer indicates it with a reflection of the companies and costs, while entries are made in the chronological order indicated in the table.
| Operation | Specified wiring, Dt-Kt |
| Issuer received cash | 76-50 |
| Payment was made by bank transfer | 76-51 |
| The papers have been registered | 58/2-76 |
| Interest accrual for the reporting period | 76-91/1 |
| Receiving income as a percentage | 51-76 |
| Determining the amount that will allow you to repay the document | 76-91/1 |
| Payment of nominal price | 51-76 |
| Removing a bond from the balance sheet | 91/2-58/2 |
Additional amounts are not added to the original cost of the paper, and accounting provides that the profit that is provided to the holder is defined as receivables. If the issuer revaluates bonds, they continue to be accounted for by purchase, and subsequent changes in accounting are not made and the result from the redemption of bonds in the same amount is reflected in the account Dt 51 Kt 76. But at the same time, they must be reflected by institutions that have the right to revaluate, to for example, a brokerage center.
Accounting for transactions on federal loan bonds (OFZ)
The issue and circulation of OFZ are determined by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. The transfer of a security is carried out in the order of transfer of ownership rights with the conclusion of an agreement and sale at auction. The conditions for treatment are determined:
- Nominal purchase price.
- The value of the bond on each day of circulation. Published monthly on the official website of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
- Start, end and maturity dates.
- Release form (documentary).
- Circle of potential owners.
The nominal value of OFZ in circulation is determined taking into account the consumer price index. In addition to the changed value on the maturity date, the owner of the OFZ receives coupon income. Depending on the conditions of issue, a constant or variable coupon income is used in the calculation.
The amount of variable income is added up over individual payment periods. Accounting for OFZs must be taken into account separately from other types of securities. Detailed accounting is maintained for each bond, with data grouped according to the chronology of registration and price.
OFZs are not used to cover the cost of goods, work, services or other types of expenses within the framework of commercial activities.
Conditions and rules for withdrawal from circulation
The company that initiated the inclusion of a valuable form in the exchange listing attracts financing and, along with it, creditors.
In fact, the condition of mandatory urgent redemption attracts investors who calculate their income taking into account other characteristics of the bond. The specified data is usually published in the information prospectus of the financial instrument and other official sources.
Until the bond matures, the value of the asset may change relative to the value at the time of issue. When entering the market, the bond is adjusted to take into account the discount. The relationship between yield and bond value also remains. At the same time, at the moment of closing the bond, the issuer uses the par value as a repurchase standard. Therefore, in order to earn money, it is advisable to purchase it below the initial placement.
During the closing period of the issue, the due amount of remuneration is paid. In the example of a federal loan, the transfer of funds occurs on the day of withdrawal from circulation. When withdrawing corporate financial instruments from the market, there may be a delay in payments, usually no more than 2 weeks. The delay is explained by the fact that it takes a certain time to transfer the required amount to the broker’s accounts. Moreover, on the day of withdrawal, the bonds are no longer in the investor’s account. To avoid panic, the issuer's creditors can clarify information about the reasons for closing the issue.
Redemption of bonds from broker clients
Security holders most often acquire assets through professional market participants. Only large companies with the appropriate status can afford to carry out direct acquisition transactions from the issuer’s organization. Closing of the issue for the broker's clients is carried out automatically. Information on the formed portfolio is updated in the market participant’s personal account. At the same time, the period for crediting funds directly depends on the level of the company. Refusal to transfer premiums within the prescribed period is not allowed due to the fact that the process of borrowing through bonds is regulated by the norms of current legislation.
Mortgage coverage with bonds
Property can serve as collateral for the bond. Collateral is provided to reduce the risk of the acquirer (investor). The essence and types of bonds do not change depending on the presence of mortgage collateral. Operations and document flow are similar to the circulation of bonds without collateral. In the event of loss of property serving as collateral, the investor receives the insured amount.
The circulation of covered securities is carried out by credit institutions or mortgage agents. Issuers of bonds must provide detailed information about the securities. Organizations registered as LLC or JSC act as mortgage agents. The enterprise must fulfill the following conditions:
- Clearly state in the Charter the procedure for issuing bonds and follow it throughout the entire period of activity.
- Determine the maximum number of bonds allowed for issue and limit the issue to the constituent documents and is included in the Charter.
- Do not hire employees.
Record keeping is transferred to a specialized organization. Voluntary termination of the existence of an organization is permitted upon full repayment of obligations.
Taxes upon redemption
Investors who include bonds in their portfolio should be aware of mandatory fees.
A personal income tax of 13% is paid on the amount of profit received. Starting from January 1, 2021, this requirement will apply to securities regardless of the date of their issue. There is no tax on municipal issues.
Buyback refers to a financial relationship. By attracting borrowed funds, enterprises receive significant reserves for conducting their core activities. At the same time, issuers retain the obligation to return their funds to investors within the framework of the requirements of the law and rules established in the decision to attract investments.
Article read: 150
Securities reporting
Issuers issuing bonds are required to disclose information in reports published quarterly. Reporting begins from the first quarter after the issue of bonds and is carried out until the obligations are repaid, the issue is determined to be invalid, and the documents are declared invalid.
The reporting is presented in the form established in the document approved by the Bank of Russia on December 30, 2014 No. 454-P “Regulations on the disclosure of information by issuers of equity securities.” The reporting contains information about the issuer, its activities, liabilities, liquidity of securities, and investments made.
The issuer must submit a complete package of financial statements including all forms. The following information is subject to disclosure in the issuer's financial statements:
- Availability and change in the amount of debt on loans issued by bonds.
- Amounts, maturity dates of bonds.
- The amount of expenses incurred during the issue and circulation of bonds.
How does a bond repay?
Upon expiration of the securities circulation period, the issuer must make a repurchase.
During this time, the list of holders is updated, coupon income payments are received, and investors await scheduled payments.
Cash in the amount of par value is transferred by the issuer to the sites used for placement. Assets are transferred to broker accounts or individual investment accounts of holders. There is no need to fill out separate applications or provide additional details. Given that the bond circulation period is set in months, planning an exact date for the return of funds is impractical. Enrollment period is from 1 day to two weeks.