Kontur.Accounting - 14 days free!
Friendly, simple and functional online service for small businesses.
Clear for the director, convenient for the accountant! Try it
In recent years, some innovations have appeared in the rules for paying property taxes. The form of the declaration has changed, the procedure for calculating tax based on cadastral value has been adjusted, and new grounds have emerged on which it can be changed. We will cover tax rates, exemptions, reporting and penalties for property taxes in 2020 and 2021.
How property tax will change in 2021
In 2021, several laws were adopted that affected the procedure for property taxation. Among the changes are the following:
- We have updated the property tax declaration form - the new form must be used for reporting for 2021 (Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 28, 2020 No. ED-7-21 / [email protected] ). The new form takes into account coronavirus benefits, and also adds special arrangements for organizations that have entered into an agreement to protect and encourage investment.
- New codes for federal and regional benefits related to coronavirus have appeared.
- It no longer matters whether real estate is accounted for as a fixed asset; tax will still have to be paid unless the region decides otherwise.
- The list of real estate that is taxed at cadastral value has been increased. Now these are all objects that are subject to personal property tax. Residential premises, garages, parking spaces, unfinished construction projects, residential buildings, garden houses, utility buildings or structures on plots for personal households or individual housing construction were added to the old objects.
- Accountants no longer need to submit advance tax calculations; they have been canceled as of January 1, 2021.
- The tax return can be submitted centrally. If a taxpayer is registered simultaneously with several tax authorities at the location of his property, then he has the right to submit a declaration to one of the inspectorates of his choice.
Material assets of the company in accounting
According to the current Russian legislation, the property of each individual organization exists separately from the property of other organizations and owners.
Property accounting is regulated by Russian PBU. Property assets of organizations are divided into categories:
- fixed assets - include real estate, transport, technological equipment;
- intangible property assets - intangible objects that bring income to the organization (inventions, computer programs);
- cash, non-cash funds of the organization in any currency;
- investments in valuable assets, authorized capital of other organizations;
- inventories for production (raw materials, goods, finished products, etc.);
- accounts receivable - finances that are the debt of counterparties.
The reporting of property assets of companies is based on the strictest principle: the company's property in money is equivalent to the sources of its formation. The increase in sources is recorded on credit accounts. Expenses are shown by account debits.
Which properties pay property tax in 2021?
What property do organizations pay tax on? The main feature of such property is that it belongs to real estate. The list of real estate includes:
- buildings, structures, structures, garden houses, utility structures;
- unfinished construction projects;
- garages, parking spaces;
- residential and non-residential premises with inseparable improvements;
- enterprise, a single real estate complex;
- aircraft, sea vessels and inland navigation vessels registered in accordance with the established procedure.
Since 2021, officials have abolished the taxation of movable property. To understand which property is classified as movable and which is not, read Article 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. All objects that are not classified as real estate are recognized as movable property, including money and securities. In addition, the Ministry of Finance draws attention to the fact that the property must be recorded in the Unified State Register or there must be grounds confirming the impossibility of moving the object without significant damage. At the same time, there may not be an entry in the Unified State Register of Real Estate; the courts recognize even unregistered objects as real estate.
Another sign is that it is recorded on the balance sheet as fixed assets. This applies to real estate objects taxed at the average annual value, and is stated in paragraph 1 of Art. 374 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The fixed asset must meet a number of conditions:
- they plan to use it in production, rent it out or use it for management purposes;
- it is planned to be used for more than a year;
- they do not plan to resell it for profit;
- the object can generate economic income.
Such property is transferred to accounting account 01 “Fixed Assets” and is subject to taxation, even if the object is in temporary or joint use. Companies also pay tax at cadastral value on residential premises and houses that are not reflected in fixed assets (for this, additional conditions must be met, which we will discuss below). Real estate recorded on account 03 “Income-generating investments in tangible assets” is also subject to tax.
The rules for paying property taxes have their own subtleties: if a fixed asset is used, its value is included in the tax base. This is done even if the facility has not yet been put into operation, has not been transferred to account 01, and the rights to the object have not been registered. It is important that the tax base is determined as the cadastral value. Equipment for installation reflected on account 07 is not subject to tax.
In addition, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation now establishes a tax on cadastral value in relation to objects that are subject to property tax for individuals. This also applies to organizations in special regimes.
The property listed in clause 4 of Art. is not subject to the tax. 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: land plots, cultural objects, icebreakers, spaceships and objects included in the first and second depreciation groups according to the OS Classifier.
Maintaining accounting records of sources of property formation
The company's property is not created out of thin air - assets are acquired through sources of property formation. Economists identify three such sources:
- Own capital - this concept includes both the authorized capital formed at the time of creation of the enterprise, and additional and reserve capital - these funds accumulate during the operation of the company. Equity also includes profit received and targeted financing.
For more information about what can be included in a company’s equity capital, read the material “Equity on the balance sheet is...”.
- Borrowed funds - this includes bank loans and loans from counterparties.
Find out more in the article “What is debt capital (nuances)?”
- Liabilities - that is, accounts payable: money that the company owes to counterparties.
See also “Basic rules for managing accounts payable.”
Accounting for the sources of formation of an organization's property is based on the basic accounting rule: the company's property in monetary value and the sources of its formation are equal. An increase in the sources of the company's property is reflected in the credit of accounts 60, 66, 67, 76 and capital and reserve accounts (Section VII of the Chart of Accounts, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). The expenditure of sources is reflected in the debit of the listed accounts.
When forming the balance sheet, the property of the enterprise is reflected in the asset, and the sources of the company's property are its liabilities.
For more information on how to fill out a balance sheet, read the article “Procedure for drawing up a balance sheet (example).”
Benefits for paying property taxes in 2021
For some types of organizations, benefits are applied that exempt from paying property tax (see Article 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- the organization is part of a free economic zone, belongs to the religious sphere or the penal system;
- "Skolkovo", prosthetic and orthopedic enterprises, advocacy and legal consultations, state research centers, management companies of innovative scientific and technological centers;
- management companies, participants, residents of various economic zones;
- manufacturers of pharmaceutical products, public organizations of disabled people.
Also, some types of real estate are exempt from tax: federal public roads, used energy-efficient real estate, real estate for hydrocarbon production.
Regions can establish their own benefits, reduce rates and exempt from paying taxes (clause 2 of Article 372 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In 2021, landlords who deferred rent payments to their tenants could receive additional benefits. The benefit is to reduce the amount of tax. Check the information on benefits and rates in your region on the official website of the tax service.
Due to the spread of COVID-19, a number of organizations have been exempted from paying taxes and advance payments for the period of real estate ownership from April 1 to June 30, 2021.
The system will calculate the tax and prepare a payment invoice
“Accounting is a convenient program. Thanks to the developers. I have been working with Kontur for a long time. And it’s convenient to manage personnel; you’ll never miss anything in payroll. Taxes are calculated on their own. All reports reach the recipient on time. Everything is updated with the times. I really like it, everything is convenient. And when something is unclear, you can call - and they will always come to your aid. Thanks again to the developers."
Natalia Abbasova, accountant, senior Veshenskaya, Rostov region.
Results
The property of an enterprise and the sources of its formation are the two most important categories of accounting.
Property includes fixed assets, intangible assets, inventories, cash and non-cash money of the company, accounts receivable, financial investments and a number of other assets. Sources of property formation are capital and reserves, loans, credits, accounts payable, profit. The company's assets and liabilities must be equal. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How to calculate property taxes in 2021
The tax service calculates the tax for entrepreneurs and sends them a notice for payment. Organizations must calculate the tax themselves. In the accounting web service Kontur.Accounting, you can do this automatically.
- First you need to figure out which of your existing assets is subject to tax.
- Next, you should check whether the organization is entitled to benefits - data on benefits is contained in regional laws.
- Find out the basis for calculating tax.
- Find out the tax rates established in the region.
- Calculate the tax payable to the budget.
The basis for calculating property tax can be the average annual value of real estate or the cadastral value. Let's look at why this depends further.
We determine the volume of collection to retain it
Algorithm for determining the fee amount:
H = monetary value of all funds * fee rate/100%
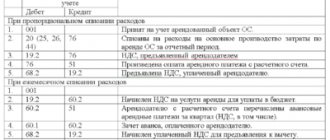
To calculate the amount of property tax in monetary terms for its further withholding, it is necessary to determine the average annual value of fixed assets registered with the enterprise.
The basis for tax calculation will be:
(sum of all funds on the first day of the month + sum of all funds on the last day of the month) / 13
As a result, property tax is calculated 4 times a year, quarterly. But it is withheld only once a year; on the remaining 3 dates an advance payment is charged to it. Please note that some property may be exempt from this fee and is therefore not included in the calculation.
Which OS are not subject to taxation:
- Property enjoying benefits.
- Fixed assets that are not taxable property: land plots, property of law enforcement agencies, natural resources.
Property with benefits should be excluded from the tax base, and those that were not taxable should not be included in it.
At average annual cost
Real estate that:
- not taxed at cadastral value in accordance with regional legislation;
- belongs to the organization by right of ownership, economic management or operational management;
- accepted for accounting as part of fixed assets and reflected in accounts 01 or 03.
Real estate that was received under a concession agreement and reflected in off-balance sheet accounts is also taxed at the average annual cost.
Advance tax payments are made quarterly. Calculation for the quarter is carried out according to the following formula:
Property tax at average annual value = Average value of fixed assets for the reporting period × Tax rate / 4
For example, to calculate the down payment for the first quarter, you need to add up the residual value of the property on January 1, February 1, March 1 and April 1. The result obtained is divided by 4. For the calculation at the end of the year, the procedure is similar.
Separate divisions pay tax at the rate of the region where the division is registered. If the property is not located at the place of registration of the parent organization or division, then the tax is calculated at the rate of the region where the property is located.
Example of calculating property tax based on average annual value
The tax base is calculated by adding the residual value of each object on the first day of each month and on the last day of the billing period. The tax base of depreciated objects is zero, but the objects are included in the report.
Residual value of fixed asset:
- January 1 - 150,000 rubles
- February 1 - 145,000 rubles
- March 1 — 140,000 rubles
- April 1 — 135,000 rubles
- May 1 - 130,000 rubles
- June 1 - 125,000 rubles
- July 1 - 120,000 rubles
- August 1 - 115,000 rubles
- September 1 - 110,000 rubles
- October 1 - 105,000 rubles
- November 1 - 100,000 rubles
- December 1 — 95,000 rubles
- December 31 — 90,000 rubles
Advance payment for 1st quarter
Tax base = (150,000 + 145,000 + 140,000 + 135,000) / 4 = 142,500 rubles Payment = 142,500 × 2.2% / 4 = 783.75 rubles
Advance payment for half a year
Tax base = (150,000 + … +125,000 + 120,000) / 7 = 135,000 rubles Payment = 135,000 × 2.2% / 4 = 742.5 rubles
Advance payment for 9 months
Tax base = (150,000 + … + 105,000) / 10 = 127,500 rubles Payment = 127,500 × 2.2% / 4 = 701.25 rubles
Additional tax payment for the year
Tax base = (150,000 + … + 90,000) / 13 = 120,000 rubles Payment = 120,000 × 2.2% – (783.75 + 742.5 + 701.25) = 412.5 rubles
Tax calculation
Tax on the property of organizations (taxable base) is calculated by the taxpayer independently .
The tax base for calculating tax includes all real estate and movable property . accepted for accounting as part of the operating system until 2013. Movable property will be taken into account in the tax base until it is fully depreciated or disposed of. Movable property objects accepted for accounting from January 1, 2013 are not taken into account in the base for calculating property tax for enterprises.
The amount of property tax is calculated . based on the average value of property (PV) for the reporting period.
If in 2013 there are no real estate assets on the balance sheet of an enterprise, and only movable property is listed that was accepted for accounting from the beginning of 2013, then such property is not included in the calculation and report, and the report itself is not submitted . since there is no obligation to pay property tax.
For clarification on issues of calculation and accounting of property taxation, please contact specialized organizations. Qualified employees will answer your questions and help you choose an accounting method .
According to cadastral value
Many companies calculate tax based on cadastral value. The authorities must warn organizations and publish a list of property for payment of tax at cadastral value before January 1 on the region’s official website. A closed list of real estate objects taxed at cadastral value is given in Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
There are four mandatory conditions for taxing real estate at cadastral value:
- the property is located on the territory of the Russian Federation;
- real estate belongs to the organization under the right of ownership, economic management or received under a concession agreement;
- the cadastral value of real estate is determined by the region;
- in the region, the procedure for taxation of real estate has been approved and the specific types of property from Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation to which it applies are specified.
If an object is not specified in the law, then it is taxed at the average annual cost. If the type of objects is specified in the law, but the cadastral value is not determined according to it, then the tax is also paid on the average annual value.
The procedure for real estate accounting for cadastral tax does not matter. It can be listed both as part of the fixed assets and as part of current assets or off the balance sheet.
The tax base in this case is the cadastral value of the property indicated in the Unified State Register of Real Estate as of January 1 of the year for which the payment is calculated. For each object, the base is determined separately.
The reporting periods for property tax calculated based on cadastral value are 1st quarter, 2nd quarter and 3rd quarter. Calculate the tax using the formula:
Property tax by cadastral value = Cadastral value of property as of January 1 × Tax rate
If your region provides advance payments, then the quarterly payment is equal to a quarter of the tax amount. When calculating the final payment for the year, simply subtract the listed advance payments from the amount received.
An example of calculating property tax based on cadastral value
Vozdushny Shar LLC owns a shopping center, which is subject to property tax at cadastral value. As of January 1, 2021, its cadastral value was 120,000,000 rubles. The property tax rate in the region is 2%.
Advance payment for the first quarter = 120,000,000 × 2% / 4 = 600,000 rubles;
Advance payment for the second quarter = 120,000,000 × 2% / 4 = 600,000 rubles;
Advance payment for the third quarter = 120,000,000 × 2% / 4 = 600,000 rubles;
Tax payable at the end of the year = 120,000,000 × 2% – 1,800,0000 = 600,000 rubles.
Features of tax calculation and advance payments
In some cases, the formula for calculating tax changes. Features may arise when receiving benefits, having data on the cadastral value only for the entire building, buying or selling real estate in the middle of the year, or changing the cadastral value. Let's look at them all:
1. Real estate is subject to benefits. The benefit can be provided in the form of a non-taxable part of the cadastral value or a tax reduction. In the first case, you need to subtract the non-taxable part of the cadastral value from the cadastral value approved as of January 1 in the Unified State Register of Real Estate and calculate the tax on the remainder. In the second case, subtract the amount of the benefit from the tax calculated using the standard formula.
2. The cadastral value is determined only for the building, and you own the premises. Calculate your tax for the year and advance payments as usual. To determine the tax base, find the cadastral value of your premises in proportion to its area in the entire building.
3. The property was bought or sold in the middle of the year. Use the ownership coefficient (clause 5 of Article 382 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It shows the ratio of the number of months you owned the property to the total number of months in a year or quarter.
4. The cadastral value was revised in the middle of the year . If the characteristics of the object have changed and its value has been revised, adjust the tax and advance payments (clause 5.1 of Article 382 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The adjustment coefficient shows the ratio of the number of months in which the old cost was in effect to the total number of months.
5. In the middle of the year, the authorities excluded the property from the list of property for payment of tax at cadastral value . Recalculate the tax from the beginning of the year at the average annual cost.
What does the equity capital of an LLC consist of?
Any company has certain material assets on its balance sheet.
But they are not always paid for by it, that is, some of the organization’s property is accounted for in accounting as acquired with borrowed funds. To determine the equity capital of an LLC from the price of real estate/movable property, it is necessary to subtract debt obligations. The organization's equity capital includes:
- Authorized capital is the investment of the founders. It is created at the initial stage of company formation. The amount and percentage of investors' investments are not established by current legislation, but the authorized capital should not be less than 10 thousand rubles, otherwise the owners of the organization will not be able to register it.
- Additional capital represents a unit formed after periodic additional assessment of non-current assets, carried out as part of accounting for the company's property assets.
- Reserve capital is funds accrued by reserve funds intended to cover shortfalls and repurchase own shares. An LLC can create such a fund if this provision is specified in the constituent documentation. The fund is replenished with funds from net profits. Often, LLCs specifically create reserve funds to pay annual bonuses, carry out repairs, and other activities.
- Profit is the finances that remain after calculating the necessary expenses and taxation from income. Profit, as a rule, accumulates during the operation of the enterprise. Therefore, in accounting there is the concept of profit for the period of the current year (January 1 is the date of calculations), profit for previous years (accumulations from the moment the enterprise began operating until December 31 of the previous annual period).
- Targeted financing is money intended for established events, coming from special funds, companies, and authorities. It is possible to allocate budget money, for example: for scientific research, organization of an international conference, construction of a socially important facility, and other needs. Targeted financing is possible in the form of subsidies and other income from third parties and government agencies.
- Borrowed capital is credit funds that are used for the development of a company in the event of a lack of own funds. The company's liabilities are also borrowed funds.
Important! According to accounting, property assets acquired through borrowed funds also include property acquired by the company on terms of deferred payment by installments. That is, when the counterparty credited the enterprise for the amount of the cost of services provided or items of property.
It is quite difficult to engage in entrepreneurial activity without attracting third-party funding. In practice, there are no companies that would not use borrowed funds for their own development and expansion of production lines.
Tax and reporting periods
For the property tax of organizations, the Tax Code provides for reporting and tax periods.
The reporting period is intended to ensure that organizations, based on the results of the stipulated period, prepare and draw up a report on the cost changes of property and its movement. When determining property tax, the calculation methodology should be such that it is carried out in the following reporting periods: first quarter, six months, nine months. Subjects of the Russian Federation, represented by their representative bodies, are allowed not to set reporting periods.
The tax period is set to be the year following which the organization will have to make a final tax calculation and pay it to the budget.
Privileges
This type of tax provides many benefits. Moreover, they can be established by both the federal center and the regions. The fact that there is no need to calculate property tax for individual entrepreneurs can also be regarded as a benefit, since individual entrepreneurs are individuals, and they have their own rules for paying this tax.
According to federal decisions, benefits are provided to organizations specified in Article 381 of the Tax Code. It identifies 17 categories of organizations that have preferences. These are, in particular, enterprises for people with disabilities, pharmaceuticals, scientific associations, organizations operating in special economic zones, and other legal entities that have properties valuable to the state.
Some tips
When paying property tax, legal entities have several subtleties, without taking them into account, the calculation of property tax can be done in such a way that claims from the tax authorities will be received. So, tips:
- You should always submit zero declarations, even if the organization enjoys benefits or the property has gone through the full depreciation cycle. Otherwise, the organization will be fined for violating reporting deadlines.
- When calculating the tax on rental property, inseparable improvements to the property should be included. However, the property that was accepted onto the balance sheet after 01/01/2013 should not be included, as well as land plots.
- It is mandatory to indicate in the calculations the property sold during the year before the end of the tax period. Just in those months that follow the month of write-off, you should indicate zero information. The same should be done if the property is accepted on the balance sheet in the middle of the year. Then zero data will be all the months that passed before this property was registered.
- Before sending it to the inspectorate, you should use the control ratios available on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia to check for errors by drawing up your own property tax calculation form. Tax service specialists have placed here special formulas that will allow you to determine online whether there are errors in the declaration.