The concept of revenue in accounting
Based on PBU 9/99 “Income of the organization”, revenue in accounting can be recognized only if: (click to expand)
- the enterprise has the right to receive this revenue, that is, this right must be confirmed either by a concluded agreement or in another way;
- the amount of revenue can be determined;
- after receiving the proceeds, the organization will receive economic benefits;
- the goods have been transferred to the buyer, or the service has been provided (work accepted);
- It is possible to determine the expenses that an organization incurred to obtain specific revenue.
Determine the financial result
Accounting errors
If you find accounting errors, correct them before you carry out the reformation. Prepare an accounting statement and make adjusting entries for December 31.
At the second stage of the reformation, it is necessary to close account 99 “Profits and losses”. To do this, enter a separate subaccount, for example, “Profit and Loss Balance,” and write off all other subaccounts to it. The final balance on account 99 must be transferred to account 84. If at the end of the year you made a profit, the posting is as follows:
DEBIT 99 subaccount “Profit and Loss Balance” CREDIT 84 subaccount “Retained Earnings (Uncovered Loss)”, profit was written off based on the results of the year.
Did you make a loss? Make the wiring:
DEBIT 84 subaccount “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” CREDIT 99 subaccount “Balance of profits and losses”, the loss was written off based on the results of the year.
As a result of the balance reform, the balance in account 99 “Profits and losses” as of January 1, 2021 will become zero. Now you can begin compiling accounting reports and distributing profits.
Reflection of revenue in accounting
In order to reflect revenue in accounting, you need to rely on supporting documents. That is, on such documents that can confirm that the right to the goods has transferred to the buyer, for example, a deed or invoice, as well as other primary documents. There are a certain number of requirements for these primary documents. They, for example, must be drawn up either according to standard forms of accounting documentation, or according to a form approved by the organization.
The procedure for determining revenue, according to PBU 9/99, revenue is taken to be those amounts that are equal to receipts of money and property in monetary terms, as well as accounts receivable. At the same time, revenue is recognized in accounting taking into account VAT and excise duties, but they are not revenue.
In cases where the buyer does not fully pay his debt to the company, revenue should be recognized in the accounting of the supplier organization as the amount of payment received, as well as receivables from this buyer.
Calculate simplified tax
Before you begin closing entries, calculate the total amount of the “simplified” tax. After all, this is also an expense, and without it it will not be possible to sum up the correct results of the year. Although you consider the tax already in 2021, it must be reflected by posting on December 31, 2021. When you have calculated the additional tax at the end of the year, make the following entry:
DEBIT 99 subaccount “Tax under simplification” CREDIT 68 subaccount “Calculations for tax under simplification” tax was accrued under simplification based on the results of 2021.
If you have calculated the final tax to be reduced, reverse the excess accrued amounts using the same transaction. Likewise, consider the minimum tax. But first, create a separate sub-account for him. Then reverse the accruals for the year and make an entry to calculate the minimum tax:
DEBIT 99 subaccount “Tax under simplification” CREDIT 68 subaccount “Calculations for the minimum tax under simplification” the minimum tax was calculated at the end of the year.
Methods of revenue recognition in accounting
There are two methods for recording revenue in accounting:
- Accrual method - is a generally accepted method, revenue is recorded as shipment;
- Cash method - revenue with this method is taken into account when payment is received.
The accrual method is used by all organizations to account for all revenue, with the exception of revenue under contracts with a special right to transfer ownership.
By the way, small businesses are given the right to choose; they can use both the accrual method and the cash method. This possibility is provided for in clause 20 of the Standard Accounting Recommendations. But when using the cash accrual method, the following requirement must be taken into account: expenses are recognized only after the debt is repaid.
The chosen method of revenue recognition is necessarily recorded in the accounting policies of the organization. The cash method is more convenient to use only for those small businesses that do not have many business transactions. Since, under the cash method, a company recognizes expenses only after they have been paid, then with a large number of such expenses, it is very difficult to track which of them are reflected in accounting and which are not yet.
When the cash method is used, costs that are related to the sale of products should be reflected in account 20 “Main production”.
Close accounts
Simplified tax
Before you start reforming your balance sheet, calculate the total tax amount for the year.
Balance sheet reformation is a write-off of the company’s financial results for the past year. It is carried out in two stages. The first step is to close accounts 90 and 91.
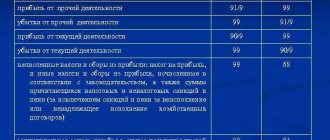
During the year, you recorded all the organization’s income and expenses for its main activities in account 90 “Sales”. The difference between revenue and costs was attributed to the subaccount “Profit (loss) from sales.” Profit or loss was written off on the last day of the month. If revenue exceeded costs, profit was reflected by posting:
DEBIT 90 subaccount “Profit (loss) from sales” CREDIT 99 reflected the profit for the month.
If costs exceed the amount of revenue, then the organization suffered a loss. Then the wiring was like this:
DEBIT 99 CREDIT 90 subaccount “Profit (loss) from sales” reflected the loss at the end of the month.
In this case, at the end of the year you will have a zero balance in account 90. But the balances will be on sub-accounts to account 90. They need to be reset to zero. To do this, make the following entries in your accounting as of December 31:
DEBIT 90 subaccount “Revenue” CREDIT 90 subaccount “Profit (loss) from sales” closed the subaccount “Revenue” of account 90 at the end of the year;
DEBIT 90 subaccount “Profit (loss) from sales” CREDIT 90 subaccount “Cost of sales” subaccount “Cost of sales” of account 90 was closed at the end of the year.
Reformation date
Reform the balance sheet as of December 31, after you have reflected the last business transaction for the reporting year in the accounting records.
Every month you collected income from other types of credit activities and debit expenses in account 91 “Other income and expenses.” The financial result for other income and expenses was reflected by the following entries:
DEBIT 91 subaccount “Balance of other income and expenses” CREDIT 99 reflected profit from other activities;
DEBIT 99 CREDIT 91 subaccount “Balance of other income and expenses” reflected the loss from other activities.
The balance of 91 accounts at the end of the year will be zero, and the amounts accumulated during the year will remain in the subaccounts. Close subaccounts with transactions:
DEBIT 91 subaccount “Other income” CREDIT 91 subaccount “Balance of other income and expenses” closed the subaccount “Other income” of account 91 at the end of the year;
DEBIT 91 subaccount “Balance of other income and expenses” CREDIT 91 subaccount “Other expenses” closed the subaccount “Other expenses” of account 91 at the end of the year.
As a result of the entries, the debit and credit turnovers on the subaccounts will be equal on both account 90 and account 91. On January 1, 2021, there will be no balance on either the synthetic accounts themselves or the subaccounts to them. This means that the first stage of the reformation has been completed.
Features that arise when determining revenue
- When the price is not determined. Sales of products, provision of services and other activities for which the company receives revenue occur on the basis of an agreement between the buyer and the customer. In this case, the contract, as a rule, provides for the establishment of a price. However, there are also contracts where the price is not provided and is determined based on the prices charged for similar types of goods. Revenue in this case is also determined by the price of similar goods.
- Transfer of ownership after receipt of funds. Revenue under this type of contract is determined on the date of receipt of money.
- When providing a commercial loan. When the buyer is granted a deferred payment, the proceeds are accepted in the full amount of the debt. The term of the so-called loan does not matter.
- When paying not in cash. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation allows the option of non-monetary payment only under an exchange agreement. Revenue under such contracts is taken into account at the cost of the goods that the organization receives. In this case, the cost of the goods is determined based on the cost of similar goods (works, services). When the cost of the goods received cannot be determined for some reason, the organization will determine revenue based on the cost of the goods transferred in exchange. The cost of your goods should be similar to the cost of usually shipped goods.
- When the obligation under the contract changes, when a discount is provided. There are situations when the price changes after the contract has been concluded. For example, it is possible to provide a discount. If the goods are transferred to the buyer already taking into account the discount, then there will be no need to adjust the revenue in this case. And if the discount is provided after the shipment has taken place and after the relevant documents have been issued, then the selling company will need to adjust the revenue by creating the posting: D62 K90-1 – REVERSE! Sales revenue is adjusted by the discount amount.
- When returning an item. If a situation arises when the buyer returns the goods, then an adjustment must be made in accounting for revenue, otherwise at the end of the period it will reflect an incorrect result. When the sale of goods and the return of goods occur in the same tax period, then it is necessary to adjust the 90 “Sales” account. But if the return occurs only next year, then the cost of this product will be reflected in non-operating expenses in the form of a loss from previous years and taken into account in account 91 “Other income and expenses.”
- When setting the price in USD There are also situations when settlement under an agreement occurs in rubles, but is equivalent to an amount in the currency of another country or in conventionally accepted units. In this case, the parties to the contract set the date for recalculating the price either from the foreign exchange rate at the time of payment or on the day of shipment. The peculiarity of such an agreement is that the final price is formed only after calculation. That is, the final cost of goods in Russian currency is determined at the time of final settlement and consists of partial payment for future deliveries, as well as other amounts transferred for the goods. The moment of determining revenue will be an earlier date, either the date of shipment or the moment of payment.
- When creating a reserve for doubtful debts. When creating a reserve for debts, the amount of revenue should not change.
Revenue recognition example
Continent LLC ships goods to the Counterparty on prepayment. On the date of transfer of the goods, ownership rights also pass. Revenue is accordingly recognized on the date of shipment. Let's reflect these transactions in accounting with the appropriate entries:
- D51 K62 – Prepayment received for future shipment
- D62 K68 – VAT accrued (as of the date the tax base was determined)
- D62 K90-1 – Products shipped
- D90-3 K68 – VAT charged
- D68 K62 – VAT calculated at the time of shipment is accepted for deduction
Profit received from sales of products posting
Business lawyer > Accounting > Accounting and reporting > Profit from sales: posting and other nuances of accounting science
The ability to correctly systematize costs, receipts of funds into an account, and accounting is a concept for professional economists and ordinary people. Basic concepts in the field will directly affect the correct distribution of financial flows and further well-being. The natural result of the activities of production structures over a certain period of time is the receipt of stable profits.
The profit factor is the most powerful driver of the growth and development of an enterprise, from procurement to the salary fund. Based on indicators and profit margins, management and investors evaluate development prospects and formulate tasks for the future.
Sales profit concept
Profit from sales is the difference between the cost of producing a product and gross income (total annual income of the structure).
Profit shows the financial result of the company's work for the reporting period. The task of the enterprise is to make a profit with a minimum of invested funds. Business efficiency is proportional to the profit reflected in the financial statements.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=043gmLHUn1A
The size and scale of revenue from goods or services sold directly affect:
Revenue from sales
The head of the structure or individual entrepreneur (individual entrepreneur) is interested in maximum income, for this it is necessary to know and study the points on which it depends:
- formation
- factors
- calculation
Formation
Profit from sales shows and evaluates the component of the company's functioning. The benefit should be exactly enough to ensure the normal operation of the enterprise.
The success of economic activity can be tracked through a comparative analysis of the reporting period of work with past values. Accordingly, subject to income growth, the commercial structure reaches a new level.
The values are formed from the difference between gross income and funds spent on sales and look as follows:
profit = gross income – cost of selling manufactured goods – expense for carrying out management functions
Factors
Revenue growth is the result of the relationship between two factors.
Interior:
- earnings
- price
- volume
- costs
- implementation
Higher sales volume, along with product profitability, contributes to increased profits and natural financial success at the end of the year. An increase in profits results from a reduction in the costs of producing a product and an increase in the selling price.
Volume of sales
Factor analytics ensures increased sales quality and optimizes management.
External:
- depreciation
- cost of raw materials
- set of economic indicators of the market at the current moment
- taxes, fines
- various natural disasters (accidents)
External circumstances, although they do not directly affect changes in profit, do have an impact on costs and fluctuations in the volume of products sold.
Calculation
The option helps at the planning stage of accounting for estimated profits. It is important to know the following parameters:
- Name of product
- price
- sales volume
A simple way is to calculate using profitability. An analysis of past performance in the books allows one to calculate expected future profits.
Sales profit postings
Accounting entries are the documentation and entry into a journal or PC of data about changes in accounts.
Reflection in accounting
Accounting account 90 is responsible for posting profits or expenses from sales - a specialized calculation system used to display and analytically characterize the total indicators of profits and expenses received by the enterprise for the reporting period. Based on the account, the financial and economic result of the company’s activities is formed.
https://www..com/watch?v=n1rkL-mJPys
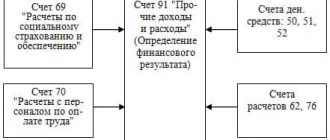
Accounting account 91 is a special calculation system that shows and analyzes information about non-core profits or expenses.
Account 99 – closing the results of profit and loss for the reporting period.
Reforming the balance sheet means writing off profits and losses at the end of the year and resetting balances to zero using account 90/91. The goal is to obtain a financial result based on the results. For this, indicators are taken into account: main production and other operations.
The financial result of the year has a cumulative system, therefore, its final result is summed up with data for previous periods.
The reformation procedure includes the following stages:
- write-off of expenses spent on production and sales
- resetting account balance 90/91
- determination of loss/profit and subsequent write-off on account 99
Features of account 90
The account generates and analyzes the total profit and scale of products sold for key sections of work:
- non-industrial and industrial
- construction, research, design
- rental costs
- sale of products, including our own production
- intellectual property
Posting diagram for account 90
Score 90
A key feature of the account is that it is completely closed at the end of the year. During the entire period, monthly, the difference (balance) accumulates in the subaccounts. In the final record, the subaccounts are closed and the overall financial total is added up.
Subaccounts
The algorithm and procedure for posting to account 90 is carried out using a number of sub-accounts:
- 90.01.1 - profit from production with basic taxes
- 90.01.2 - profit on individual positions with individual taxation
- 90.02.1 - calculation of the cost of trade turnover with the main tax
- 90.02.2 - calculation of cost of sales for items with personal taxes
- 90.03 - value added taxation
- 90.04 - excise taxes
- 90.05 - duty
- 90.07.1 - sales costs for working with taxes
- 90.07.2 - sales costs for individual items with individual taxes
- 90.08.1 - management costs with taxes
- 90.08.2 - management costs for certain items with individual taxes
- 90.09 - income and loss from sales
The credit chapter displays the profit from the sale, the debit chapter records the cost and displays the VAT on the sale. At the end of the month, the results and calculation of the financial achievements of the products sold during the month are summed up: profit on debit and loss on credit.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ng4Ifp0Mgog
The final result of the accountant's reconciliation of account 90/91 will determine the financial outcome of the company and reflect the presence of profit or loss.
Examples of display in the balance sheet
Displaying profit in the accountant’s balance sheet is the last link in the final activities of the enterprise.
Reflection in the balance
Generalized information on income and expenses for the year is analyzed. The result is recorded on the account: 99 (profit/loss).
We determine the result of the company’s activities using account 90.5 (sales profit). It is important to remember that revenue (our amount) is reflected in the credit of subaccount 90.1 (revenue), and expenses and costs are reflected in the debit of subaccounts 90.2, 90.3 and 90.4.
Next, we calculate the revenue and expenses of other income/expenses and enter the data in subaccounts 91 (other income and expenses).
The next step is balance sheet reform. At the end of the year, we close the subaccounts completely using internal postings. To do this, we write off the turnover of subaccounts 90.1 (debit) and 90.2, 90.3, 90.4, 90.5 (credit) to account 90.9. Non-main income (debit) and loss (credit) are sent to the account balance/difference 91.9 (balance).
We indicate in the report the income of the structure on the debit of subaccounts 90.9 and 91.9 in the posting from the credits of account 99.
We analyze the obtained values and if the result is unsatisfactory, we post it to debit account 99.
The next step is to display the net income of account 99 in a transaction with the credit of account 84 (retained income).
As a result of the posting, the management of the enterprise makes a conclusion about the allocation of net profit to needs and consolidates the decision with the appropriate order.
Accounting is a component of the functioning of enterprises. Financial literacy in the preparation of accounting documents will help to avoid problems with the legislation of the Russian Federation and will allow a commercial structure or state enterprise to develop to the fullest.
Source: https://sudar-buh.com/poluchena-pribyl-ot-realizatsii-produktsii-provodka/
Answers to common questions
Question No. 1. “To recognize revenue for the sale of goods, is a contract sufficient, or are some other documents required?”
In order to recognize revenue in accounting, one contract is not enough. Since we are dealing with the sale of goods, in addition to the contract, a TORG-12 invoice must be issued.
Question No. 2. “The date of recognition of revenue and the date of recognition of the tax base are the same?” (click to expand)
No, the tax base can be determined on the day of shipment, and revenue recognized on the day of payment. These dates may be the same or different. In any case, the moment of recognition of the tax base and the moment of recognition of revenue must be fixed in the company's accounting policies.