The simplified tax system requires many calculations. Borrowed money that the company received into its account is not taxed, but interest accrued for the use of foreign property must be reflected in the reporting. It is important to know whether a loan is considered income under the simplified tax system at the time of repayment.
Issuing and receiving
For many simplified people under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses,” a loan can act as both a means to improve their financial situation and a way to earn money.
Let us recall that as part of a regular loan transaction, one party - the lender - transfers the ownership of money or other things to the other party - the borrower, and the latter is obliged to return one of two things to the lender:
- The same amount of money (loan).
- An equal number of other things he received of the same kind and quality.
Issues related to the loan agreement are regulated by Articles 807 – 814 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Also see “Loan agreement under the simplified tax system”.
There is no direct rule in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation that would regulate the accounting of loans under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses.” Therefore, you need to think logically:
- Loans are not included in expenses (clause 1 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), which are reduced when calculating the single tax on the simplified tax system.
- Loans appear as part of income, which are not taken into account when determining the object for simplified taxation (subclause 1, clause 1.1, article 346.15 and subclause 10, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, issuing a loan under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses,” as well as receiving a loan under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses,” do not in any way affect the tax base for the simplified tax. That is, they do not participate in the calculations. Therefore, whether a loan is an expense under the simplified tax system, the answer will always be negative.
Here, in part, there is a complete analogy with the rules on income tax. With it, loans and credits received also do not form income. Moreover, for tax purposes, it is usually not of fundamental importance how exactly the borrowing is formalized.
Current standards
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation is the main regulatory framework that predetermines the use of the simplified tax system. The specific regulatory framework is contained in Chapter 26, Part 2. A complete list of possible users of the simplified system can be found in Section 346.12.
All main points regarding taxation and inclusion in the list of income received as a result of the loan are subject to consideration. Persons who have a full list of fulfilled conditions can use the simplified option.
Article 346.12. Taxpayers
Each specific case must be considered separately, since even an interest-free loan can be considered as material profit. Everything will depend on the accounting method and tax characteristics.
Most of the disputes between the borrower and the lender are resolved pre-trial, since a court decision can drag on indefinitely, and the requirement for a tax accounting system can interfere with the commerce of an enterprise or individual entrepreneur.
The standards for interest rates, which are not taxed under the simplified tax system, are prescribed in the legislation, but the size of the fixed interest rate may vary by region, therefore, when drawing up contracts and acts, it is necessary to take into account not only federal standards, but also regional values.
Income from the sale of real estate and “simplified” tax
ᐈ If the real estate is not used in commercial activities and was acquired before the status of individual entrepreneur was obtained, the income from the sale may not be taken into account within the framework of the simplified tax system.
If the property was purchased for personal use, its sale is not a business activity.
Commercial real estate, the purchase costs of which were not taken into account under the simplified tax system, and if at the time of sale it is not used in business, can also be excluded from taxation under the simplified tax system. This is what the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service think. In this case, the income from the sale will be subject to personal income tax, and it will be possible to take advantage of personal income tax benefits (if any).
You should be on your guard when it comes to benefits. In judicial practice, there are cases when, during the sale of commercial space that was recently used in business, the application of personal income tax and benefits was refused, charging the simplified tax system. However, there are also opposing court decisions.
If, on the contrary, it is beneficial for you that the proceeds from the sale be taken into account in income under the simplified tax system, then the real estate should be used in business. It is also better to enter the corresponding type of activity into the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs (for the sale of real estate and for the income that real estate brings). In addition, check in advance: proceeds from the sale may cause the loss of the right to apply the simplified tax system if they exceed the limit established for the special regime.
The procedure for accounting for loans and borrowings
Neither the funds received as borrowed nor the funds issued are considered either income or expenses of the taxpayer working on the simplified tax system. Accordingly, the return of these funds will not be regarded as either income or expense. Regarding income, this conclusion follows from the content of Art. 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, referring to Art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in which sub. 10 clause 1 directly indicates that such funds should not be considered income. And as part of the expenses, the closed list of which contains Art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, borrowed funds are not specified.
However, the fee for the use of borrowed funds (interest), if provided for in the agreement, must be taken into account as part of:
- income from the party that issued the loan (clause 1 of Article 346.15, clause 1 of Article 248, subclause 6 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- expenses of the party who received the loan (subclause 9, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Both parties have the right to reflect interest in its full amount when determining the base for the simplified tax system (clause 2 of Article 346.16, Article 269, clauses 1 and 2 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- the party issuing the loan - in income at the time of receipt;
- the borrower is included in the expenses at the time of transfer.
The need to focus on restrictions for both income and expenses arises only in relation to transactions recognized as controlled (clause 1 of Article 269 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For more information about interest arising from controlled transactions, read the article “Loan interest accepted for taxation - 2018”.
Fresh materials
- Clarification on 4 FSS When it is necessary to adjust 4-FSS The calculation presented in the FSS in form 4-FSS does not need adjustments if...
- Social tax 2021 Tax accrualIn accounting, the amounts of advance tax payments are reflected in the credit of account 69 (68)…
- Tax planning Tax planning in an organization Tax planning can significantly affect the formation of the financial results of an organization,…
- Why do they buy gold? Selling gold competently is a process that will require you to spend some free time. It will be necessary to find out...
What other income is not considered income under the simplified tax system?
View the list: income not taken into account under the simplified tax system (return of funds under the simplified tax system, VAT, etc.)
Receipts that are not subject to tax under the simplified tax system under the special regime:
- income of individual entrepreneurs, subject to personal income tax at a rate of 35% (according to paragraph 2 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- winnings and prizes worth over 4,000 rubles received in events held for advertising purposes;
- interest received from the budget or extra-budgetary fund, which is due to the taxpayer in cases of unlawful write-off of taxes and other incorrect actions of the Federal Tax Service and government agencies (full list - Articles 78, 79, 176, 176.1 and 203 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- funds from the Social Insurance Fund - sick leave, maternity and other social insurance payments to individual entrepreneurs and employees;
- proceeds from the return of defective goods;
- funds incorrectly returned or credited by the counterparty or bank;
- refund:
- by a bank or counterparty due to incorrect details;
- overpaid taxes, VAT refund;
- advances and prepayments (for the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” - only if these amounts were not previously taken into account in expenses);
- deposit after participation in the auction;
if the individual entrepreneur - the seller, using the simplified tax system, issued an invoice to the buyer and allocated VAT:
- the amount of VAT by the seller must be transferred to the budget, but it is not taken into account in income under the simplified tax system;
if the individual entrepreneur is an agent or commission agent:
- receipts from agency agreements and commission agreements that do not relate to agency or commission fees;
if an individual entrepreneur combines several tax regimes:
- proceeds from activities subject to UTII or transferred to the patent taxation system;
if the individual entrepreneur is a lessor using the simplified tax system, the tenant has made major repairs to the property:
- income in the form of capital investments in the form of inseparable improvements to the leased property made by the lessee
- if the improvements made are received free of charge, the Federal Tax Service may consider the overhaul as income received, but the situation is controversial. If this is your difficult case, you can read in great detail on Garant.Ru
Borrower – individual
If the borrower is not a company, but an individual (for example, an employee of the lending organization), then he may have income in the form of material benefits from savings on interest, subject to personal income tax. Why can it? Yes, because it all depends on the purpose for which the loan is issued. If a loan is issued for the purchase (construction) of housing or land, then, subject to confirmation by the tax inspectorate of the right of the citizen-borrower to use the property tax deduction, the material benefit is exempt from taxation (paragraph 3, 5 paragraph 1 paragraph 1 of Article 212 of the Tax Code RF).
- notification in the form approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 14, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/3, issued by the tax office for submission to the employer (tax agent);
- a certificate in the form given in letter No. BS-4-11/329 dated January 15, 2016, which can be issued by the tax office for presentation to other tax agents (other than employers).
In this case, the document must contain details of the loan agreement, on the basis of which the funds spent on the purchase of real estate, in respect of which a property deduction was provided, were provided. In the absence of relevant details, such a document cannot be the basis for tax exemption. This conclusion was made, in particular, in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 21, 2016 No. 03-04-07/55231. It also states that a one-time submission of a supporting document is sufficient, that is, it is not necessary to submit a notification (certificate) annually in order to be exempt from personal income tax in subsequent years when repaying the issued loan.
But if the supporting document is issued not to the borrower directly, but to the spouse, then the exemption from personal income tax can no longer be applied. Officials from the Federal Tax Service of Russia drew attention to this in their letter dated June 23, 2016 No. BS-4-11/1120.
Now let’s talk about how to determine income in the form of material benefits from saving on interest. From 2021, such income is determined on the last day of each month in which the loan (credit) agreement was valid, regardless of the date of receipt of such a loan (clause 7, clause 1, article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The income itself is calculated based on 2/3 of the Bank of Russia refinancing rate established on the date of receipt of income (clause 1, clause 2, article 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, personal income tax is calculated at a rate of 35 percent (clause 2 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Are subsidies subject to tax under the simplified tax system?
ᐈ Income under the simplified tax system does not include property received within the framework of targeted financing, but the list of what exactly is classified as targeted financing in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is very limited.
For the most part, this item does not include subsidies received by individual entrepreneurs (an exception in some cases may be for targeted funding for scientific development and innovation activities).
At the same time, preferential rules for accounting for income and expenses can be applied to subsidies, which can, in some cases, reduce tax costs. Detailed material, for example, on subsidies for starting a business from the Employment Center can be read on the website subsidies-on-credits.rf.
Fominykh Natalya Vladimirovna
Is a loan under an agreement considered income when calculating the simplified tax system?
Good day, Natalia.
I answer your question - a loan under an agreement is not income when calculating the simplified tax system. Under a loan agreement, one party (the lender) transfers into the ownership of the other party (borrower) money or other things determined by generic characteristics, and the borrower undertakes to return to the lender the same amount of money (loan amount) or an equal number of other things received by him of the same kind and quality (Article 807 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
In accordance with Art. 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Code), when applying the simplified taxation system, taxpayers must include income from sales and non-operating income as part of the income taken into account when determining the object of taxation. These incomes are determined accordingly based on the provisions of Art. Art. 249 and 250 of the Code. At the same time, the income provided for in Art. 251 of the Code are not taken into account as income.
According to paragraphs. 10 p. 1 art. 251 of the Code, funds received by the taxpayer under
credit or loan agreements, regardless of the form of borrowing, as well as
funds received to repay such borrowings are classified as income, not
taken into account for tax purposes.
Thus, the loan amount returned to the taxpayer-lender, his tax
does not increase the base. The taxpayer-borrower received the loan amount in income in
For tax purposes it is also not taken into account. Due to the fact that Art. 250 of the Code
provision is made for the inclusion in non-operating income of taxpayers of amounts
material benefits under interest-free loan agreements, organizations and individual
entrepreneurs applying a simplified taxation system, the amount of material
benefits under such agreements should not be determined.
Sincerely, Larisa Alexandrovna
What it is
Before dealing with the question of whether a loan is income under the simplified tax system, you need to understand what this taxation system is.
For the first time, a simplified taxation system appeared in Russia after the adoption of Federal Law No. 104 in 2002. It is a simplified tax system (or simply “simplified”), a special tax regime for small businesses that simplifies tax and accounting reporting, as well as reducing the tax burden on companies and individual entrepreneurs, those using it.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
8
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FREE !
Simplification can only be used by representatives of small businesses, and it is necessary that the organization or individual entrepreneur meets the following restrictions:
- income no more than 120 million rubles;
- 100 or fewer employees;
- the total cost of fixed assets does not exceed 150 million rubles;
- lack of branches;
- share in other organizations is no more than 25%.
Important! The restrictions for the application of the simplified tax system established for 2021 are given. Specific indicators change annually, usually the income limit for a business entity increases
The simplified taxation system frees the enterprise from the need to pay VAT, income and property taxes. At the same time, an organization or individual entrepreneur must still transfer personal income tax, insurance contributions for pension insurance, and also from industrial accidents to the state budget.
Characteristics of the transaction regulating financial transactions
A mandatory condition for formalizing credit relations between the parties, one of which is a business entity, is the signing of a paper agreement.
Legal norms determine the need to include mandatory sections in a document, without which it is considered invalid.
Signing a loan agreement means the lender transfers funds or property to the borrower for temporary use.
The main features of a loan agreement are:
- Compensation, which implies the need to return the money received within a predetermined period.
- A unilateral obligation, conditioned by the emergence of obligations after the execution of documents by only one party.
- A reality that presupposes the validity of the contract from the moment of transfer of its subject. The fact of the event must be documented.
A loan transaction is characterized by parameters that determine its general characteristics:
- The results of a financial transaction are characterized by an increase in the assets of the subject, which did not occur due to the conduct of production activities.
- Borrowed funds become the property of the borrower.
- Money can be issued at interest or free of charge.
- The loan can only be repaid by agreement.
- Property registered for temporary use cannot be returned in cash.
Loan against rent
Under a lease agreement (property lease), the lessor (lessor) undertakes to provide the lessee (tenant) with property for a fee for temporary possession and use or for temporary use (Article 606 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The tenant is obliged to promptly pay fees for the use of property (rent), the procedure, conditions and terms of payment of which are determined by the lease agreement (Clause 1, Article 614 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Lease payments are the income of the lessor and the expense of the tenant (if the tenant applies the simplified tax system with the object of taxation “income”, then expenses in the form of rent are not taken into account for taxation). When rental payments are accrued (if such payments are accrued but not paid), the tenant develops a monetary debt to the lessor for the payment of rental payments.
If at the same time the lessor has a monetary debt to the lessee under some other obligation (for example, under a loan agreement), the parties have the opportunity to offset counterclaims. In general, the rules of offset are established in Art. 410 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, according to which “an obligation is terminated in whole or in part by offsetting a counterclaim of a similar nature, the due date of which has come or the due date of which has not been specified or is determined by the moment of demand. A statement from one party is sufficient for offset.”
In the case under consideration, the lender (who is also the tenant under the lease agreement) has the right to declare the termination of his monthly obligations to the borrower for rent by offsetting the counterclaim against the borrower arising from the loan agreement.
Moreover, on the basis of the provisions of Art. 319 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (in the absence of another agreement), first of all, existing and emerging claims for the payment of interest are repaid by offset, and then - for the payment of the principal amount of the debt on account of the rent.
In the event of an agreement to offset mutual obligations, borrowed funds received by the borrowing organization are considered as payment (partial payment) towards the rent; interest under the loan agreement (as noted above) will be income for the lender.
Thus, in order to correctly reflect in the accounting of borrowed obligations and lease payments, when drawing up an agreement on the offset of mutual claims, the agreement should separately reflect the amount of debt and the interest due and the amount of rent to repay the debt under the loan agreement, and also draw up a monthly act on offsetting mutual claims.
For tax purposes, interest under a loan agreement will be recognized as part of the non-operating income of the lender organization (clause 1 of Article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) on the date of offset of counterclaims (clause 1 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation <3>). At the same time, the lessor (individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system) is also obliged to recognize rental income (clause 1 of article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Nuances of the transaction that may affect the tax base
The transfer of temporary use of the property of the lender to the borrower can be implemented for a specific purpose, which determines a specific or unlimited scope of application.
In the case of a targeted loan, the lender has the right to demand from the borrower a report on the condition of the borrowed assets and their intended use. Legally, he has the right to visit his partner with an audit at any time.
A loan with unlimited obligations can be invested in any area of your own business.
If, as a result of an oral agreement, the parties agreed on the interest-free status of the loan, but this decision was not reflected in the agreement, then the lender has the right to demand deductions to its current account for the use of its own assets in the form of interest.
The refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation will be taken into account as a calculation criterion in such a situation.
When the borrower decides to fulfill obligations early, he must notify the lender of this event 30 days before it occurs. If the exact repayment period of the debt is difficult to specify, then the requirements of the contract should be adhered to.
To ensure the lender’s confidence in the return of the provided property or funds, he may require the following as security:
- property as collateral;
- an additional order agreement, in which the solvent entity undertakes to repay the debt to the creditor in the event that the borrower does not comply with the terms of the loan agreement.
Important points when returning
What a founder needs to know who intends to borrow money from a company:
- the lender (founder) has the right, in the absence of an established payment schedule, to return the funds borrowed to the company on demand within 1 calendar month, unless the agreement establishes other repayment terms;
- funds received by the enterprise from the lender in foreign currency must be returned in the national monetary unit of the Russian Federation - rubles (according to Article 317, Civil Code of the Russian Federation), at the current exchange rate at the time of repayment of the loan;
- repayment of a short-term (less than 12 months) loan is reflected in the accounting book under account 66 (settlement of short-term loans), repayment of a long-term loan (more than 12 months) is reflected in account 67 (settlement of long-term loans);
- the amount difference when repaying a cash loan if it was received in foreign currency in the accounting book is shown in account D91/K66 (reflecting the difference in funds for a cash loan issued);
- The loan agreement is protected by the State Property Fund.
- B.! Funds received from the lender are not considered income of the enterprise; accordingly, their return is not an expense. The company's expenses are accrued interest for the use of borrowed funds!
Accounting for expenses of a financial transaction
When formalizing a credit relationship between the parties, the question often arises as to whether a loan is income under the simplified tax system.
The principal loan amount is not included in the category of enterprise expenses when calculating the tax base. Accrued interest is included in the accounting expense item.
Both quantities are subject to reflection in financial statements in accordance with the rules:
- Interest accrued at the actual rate is taken into account if the transaction is classified as ordinary rather than controlled.
- The interest rates are regulated by the maximum values reflected in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The criterion determines the degree of riskiness of the transaction.
A loan issued in the national currency of the Russian Federation is legally regulated in accordance with the standards reflected in the table, which also shows, for comparison, the parameters of uncontrolled transactions based on the results of 2015 and 2021.
The time period for which credit interest is calculated.
Controlled transactions, key rates of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation
More stringent rules for attributing interest to expenses are applied in situations where the financial and credit relations of the parties contain such foreign elements as:
- the founders of one of the parties are non-residents of Russia;
- registration of a business entity not on the territory of the Russian state;
- participation in foreign capital of one of the company's managers.
Step-by-step instruction
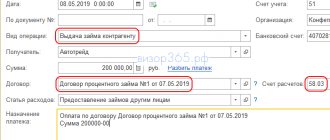
On June 01, the Organization transferred a loan in the amount of 100,000 rubles to the counterparty. According to the terms of the agreement:
- loan term - 1 month;
- rate - 10% per annum;
- interest payment - at the end of the term.
On June 30, the loan amount and interest were credited to the current account.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C |
| KUDiR | ||||||
| Issuing a loan to a counterparty | ||||||
| June 1st | 58.03 | 51 | 100 000 | Issuing a loan to a counterparty | Debiting from the current account - Issuing a loan to a counterparty | |
| Reflection in accounting of accrued interest on a loan | ||||||
| 30 June | 76.09 | 91.01 | 794,60 | Interest accrual | Manual entry - Operation | |
| Receipt of loan principal | ||||||
| 30 June | 51 | 58.03 | 100 000 | Receipt of principal | Receipt to the current account - Repayment of the loan by the counterparty | |
| Receipt of interest on the loan | ||||||
| 30 June | 51 | 76.09 | 794,60 | Payment of principal and interest included therein | Receipt to current account - Other settlements with counterparties | |
| — | — | — | 794,60 | Income. Interest | Report Book of Income and Expenses of the simplified tax system | |
Nuances and features
Despite the preferential position in terms of taxation of business entities operating on the simplified tax system, the Tax Code has prepared some unpleasant surprises for them, ignorance of which can lead to the accrual of huge penalties.
- There is a limit on issuing a cash loan of 100,000 rubles. Responsibility in the form of a fine of 50,000 rubles for non-compliance with the requirements rests with the creditor. The borrower in this situation is considered innocent.
- No expenses are charged to the person who issued the loan.
- Obligations are assigned to the entity that received funds for use.
- The returned funds, which are the principal amount of the loan and are classified as income according to accounting, are not subject to taxation.
- Interest charges for the use of assets belong to the category of non-operating income, subject to taxes that must be paid to the budget.
- Accounting involves reflecting interest accrual at the end of each month.
- If the borrower is an employee of an organization operating under a simplified taxation system, then he repays the debt independently. By agreement of the parties and documentation, the debt can be written off from his wages.
- If the loan agreement does not provide for interest charges for the use of the asset, or their amount is less than two-thirds of the refinancing rate, then it is considered that the borrower has received a benefit, on the first payment of which it is necessary to pay tax at a rate of 35 percent.
How to apply for a cash loan online? The answer is in the link.
Alfa Bank issues cash loans without proof of income, find out the conditions below.
Borrowed funds are received by the enterprise for temporary use. They are characterized by the absence of signs of profitability, which allows them not to be taken into account as part of the tax base under the simplified tax system. To prevent claims from tax authorities, it is necessary to correctly draw up contractual documentation, which should reflect the terms of cooperation between the parties.
Simplified taxation is the most popular taxation system today, since thanks to it you can significantly reduce the tax base. It must be remembered that not all incoming money is profit. For example, all kinds of loans issued to an individual entrepreneur or a legal entity.
How to reflect in accounting policies: then and now
To avoid difficulties in taking into account the deductible fee to the lender, previously documents on the enterprise’s accounting policy had to contain data on the method by which the maximum amount of interest is calculated on a loan issued on comparable terms. If the document did not contain these points, it was extremely difficult to prove comparability to the inspectors.
Attention! Today, there is no longer any need to prescribe these provisions in the accounting policy, since the entire amount of interest in fact is allowed to be included as expenses by default. Therefore, remove the relevant items from the accounting policy. Otherwise, tax authorities may find fault, pointing out that you do not comply with your main accounting document.
Amount of benefits
The system under consideration for paying various government fees is positioned in itself as a benefit. Since the amount of mandatory payments is extremely small.
That is why enterprises, organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplification are no longer entitled to benefits in any form. This point is fixed by the legislation in force on the territory of the Russian Federation.
One of the most diverse sections of legislation affecting this topic is liability for various types of violations.
The following sanctions apply to those who evade payment:
- operations on accounts can be suspended if the filing of a declaration is delayed by more than 10 days (regulated by Article No. 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - the procedure for freezing an account);
- imposition of a fine in the amount of 5 to 30% - if there is a delay in submitting reports (the amount of the fine is not less than 1000 rubles);
- if payments are made with delays, a penalty is imposed - 1/300 of the refinancing rate;
- if there is non-payment of tax, a fine of 20-40% is imposed.
If possible, you should definitely avoid violations. Otherwise, not only may a fine be imposed and a penalty collected, but also a desk audit by the Federal Tax Service may be ordered. This procedure can become quite unpleasant for the individual entrepreneur himself or the head of the enterprise.
Another important point that must be taken into account is regional legislation. According to Government resolutions, the authorities of republics, territories, regions and other entities may, within certain limits established by law, change rates for certain types of activities.
Return of an interest-free loan to the founder
The easiest way for its founder to provide financial support to an enterprise is an interest-free loan (the information below applies to LLCs whose founders are individuals!).
It is recommended to formalize an interest-free loan of funds in the form of an agreement signed between the loan participants (example No. 1 can be viewed here). The loan agreement must clearly indicate the purposes for which the funds can be spent.
The contract is drawn up in free form, the Law does not regulate its content, however, there are several points that must be in the contract:
- indication of the exact loan amount;
- determining the terms of use of an interest-free cash loan;
- determining the intended purpose of funds;
- description of the loan repayment scheme (lump sum/in parts);
- loan repayment guarantees.
If the agreement does not clearly indicate that the loan is provided on an interest-free basis, it will automatically be considered repayable at a rate of 2/3 of the refinancing rate current on the day the loan is repaid!
The amount of the interest-free loan can be returned to the founder in accordance with the relevant clause of the signed agreement, or the parties to the agreement can draw up an agreement on debt forgiveness (example No. 2 can be viewed here).
If the lender forgives the debt and if its share in the authorized capital of the enterprise is 50% or more, the enterprise does not pay any income taxes (according to subparagraph 11 clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Otherwise, the enterprise pays tax in accordance with the general procedure in accordance with clause 8, article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Are loan funds considered income under the simplified tax system?
Today, the answer to the question of whether loan funds are profit is unambiguous and is determined by a number of confirmations in various legislative acts.
Heads of organizations, as well as individual entrepreneurs, must be guided by:
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
So, according to a special loan agreement, funds are transferred from one party to the other. At the same time, any material benefits received on credit (money or something else) are determined by gender.
The bank client must return the funds received by him of the same quality and relatedness. This point is reflected in Article No. 807 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
According to Article No. 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, all persons applying the simplified regime are required to include in income the profit received:
- from selling something;
- non-realization type.
This profit is determined in accordance with the provisions outlined in Articles No. 240, 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, all profits listed in Article No. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not taken into account. It is this article that gives the most accurate and concise answer as to why all kinds of borrowed funds cannot be recognized as income.
Subclause 10, clause 1, Article No. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determines that funds received under special agreements in debt, as well as used to repay debts and interest, cannot be classified as profit. Therefore, they are never taken into account when calculating the tax base. That is why there is no need to add the loan amount to profit.
Also, according to Article No. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, non-operating income should not include the entire amount received under interest-free loan agreements. Thus, individual entrepreneurs and organizations using the simplification should not calculate material benefits in this case. All the points mentioned above must be reflected accordingly in the financial statements.
When conducting accounting, if an organization receives money or other material assets as a loan, it is necessary to follow the following guidelines:
Also, quite detailed explanations on this matter are given in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 07-02-18/01 dated January 28, 2010. The tax return should be formed based on the provisions of Article No. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. You should not forget to indicate the type of loan received by the company/individual entrepreneur; it can be long-term or short-term (more than 12 months or less than this period).
Today, one of the easiest ways to increase the amount of working capital and improve the position of your enterprise is to take out a sufficiently large credit loan. But it is necessary to remember all the features of receiving funds in this way. Since they must be reflected accordingly in the reporting.
Find out everything about loans from Money. Read the article, Money loan.
What types of loans are there? See the answer on the page.
A loan from Zanachka will help you until your payday. It is explained further.
If any errors occur, there is a high probability of imposing sanctions from the tax authorities. Funds borrowed on the basis of an appropriate agreement are not necessarily recognized as profit. That is why there is no need to pay taxes on them. Moreover, this rule applies not only when using simplification.
Not all assets are included in income and objects of taxation.
Borrowed funds are not revenue and are not subject to single tax.
Tax on interest that does not exist
Can the founder, if necessary, give an interest-free loan to his organization? Of course, it can, but the situation of refusing interest has its own peculiarities. For example, if a loan is issued to the founder of his company without receiving interest, does he have income?
From an everyday point of view, of course not, because the founder did not receive any financial benefit from this. But the Tax Code interprets this situation differently - I didn’t receive it because I didn’t want to, but I could have made money from it. Accordingly, he could have income, and where there is income, there is taxation. And it’s okay that this income is only estimated, the tax will be real (letter from the Ministry of Finance dated May 25, 2015 No. 03-01-18/29936).
Fortunately, such a specific point of view extends to a rather rare situation - if a transaction has been concluded between related parties that can be considered controlled.
Let's figure it out. According to Article 105.1 (2) of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, interdependent persons are recognized as an individual and an organization if the share of participation of this person is more than 25%. That is, if your share in the company is more than 25%, then you are dependent on it and can act to the detriment of your personal interests.
Now we need to make sure that the transaction concluded between related parties is controlled in accordance with the provisions of Article 105.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. To do this, the amount of income from transactions concluded by such persons during the year must exceed 1 billion rubles. So, if the owner with a share of more than 25% lent his company a smaller amount, he can rest easy; he will not face additional tax on the income lost from interest.
But what about the organization that received an interest-free loan from the founder? Does she have income if she does not pay interest for using the money of the owner of the company? Here the Ministry of Finance answers as follows: there is a material benefit here, but since the procedure for determining the benefit from an organization receiving an interest-free loan is not established by Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax base does not increase (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 02/09/2015 No. 03-03-06/1/5149 ).
It is interesting that in the opposite situation, when a loan is issued to the founder from an LLC, the individual receives a material benefit in the form of interest that is not charged, and it is subject to personal income tax. True, the tax amount is still significantly less than when receiving the most favorable loan from a bank. For example, if a participant borrowed 100,000 rubles from his company for three months, then the personal income tax on material benefits will be just over 600 rubles. At the bank, for such a loan, at the lowest annual rate, you would have to pay about 3,000 rubles.
General information
Loan – receipt of funds not related to the turnover of goods, works or services. The loan is processed through a separate agreement. The composition of the clauses and the order of the terms of the agreement are regulated by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Attracting borrowed funds to the assets of an enterprise may be associated with the need to increase working capital and expand production.
Receipts are temporary in nature and are subject to return according to the terms of the contract. The lender can be the founders, third-party individuals, individual entrepreneurs or organizations.
When returning borrowed funds or things transferred for temporary use, the amount or monetary value of the property does not increase the tax base of the lender.
The borrower's expenses do not take into account the issuance of a cash loan and the cost of the returned property.
Definitions
The loan agreement obliges the borrower to transfer funds or other things for temporary use.
The signs of a contract that determine its nature have been established:
In the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, interest on borrowed funds is classified as non-operating expenses.
Make a deal
A borrowing agreement, in which one of the parties is an enterprise (organization or individual entrepreneur), is concluded in simple written form.
The document is subject to standard requirements for the inclusion of mandatory items and information. The absence of a number of data leads to the possibility of classifying a document as invalid or void.
When drawing up a contract, the following must be included:
- Date and place of conclusion of the agreement.
- Validity period or return procedure.
- Names of the parties, their representatives and proxies.
- Details of the parties. Organizations indicate the certificate number, location, TIN, checkpoint and, if desired, the current account number and bank. The individual entrepreneur enters the registration address, certificate number, TIN. For individuals, a sufficient condition is passport data.
- Contact phone numbers.
- Subject of the agreement, procedure for transferring funds or property.
- Interest accrued under the agreement. If there is no fee for using the subject of the loan, it is necessary to indicate this in a separate paragraph with the wording: “without charging a fee for using the subject of the agreement.”
- Penalties for violation of return deadlines.
Photo: reporting composition
The agreement must be signed by representatives of the parties. The signature must be deciphered. Responsible persons indicate the position, authorized persons indicate the document number.
Legal grounds
The concept of a loan is established in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. According to Art. 807 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a loan in the form of cash or material assets received by the borrower from the lender is subject to repayment in full quantity and condition determined by the agreement.
In case of transfer of property, the return of equivalent items of similar quality is allowed.
Borrower-individual entrepreneur
Does the situation change if the borrower is an individual registered as an individual entrepreneur? It all depends on the tax regime used by the individual entrepreneur.
However, local tax authorities may not think so. And the courts mostly support them. For example, the Arbitration Court of the Volga-Vyatka District, in its resolution dated December 8, 2014 No. F01-5102/2014, noted that the circumstances excluding taxation of this type of material benefit are given in Article 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and their list is exhaustive. The use of borrowed funds in activities subject to UTII is not such. By ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated April 16, 2015 No. 301-KG15-2401, it was refused to transfer this case to the Judicial Collegium for Economic Disputes of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation for review.
The minimum authorized capital for registering an LLC is only 10,000 rubles. This amount is only enough to organize an intermediary business within the walls of your own apartment. What to do if you need money to develop your business, but you don’t want to increase the authorized capital? Let's take a closer look at an interest-free loan from the founder: the tax consequences of 2021.
Is a loan taken into account as income under the simplified tax system?
The procedure for taxation of funds received in the form of a loan is defined in paragraphs. 10 p. 1 art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The types of income listed in the article are not subject to taxation.
An explanation of the position on whether a loan received is income under the simplified tax system is given in a letter from the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated May 19, 2010. for No. ШС-37-3/ [email protected]
The Tax Service points out that funds and property received in the form of loans and other similar types of obligations do not meet the income criterion.
Keeping records of an enterprise on the simplified tax system according to the taxation scheme in the form of “income” consists of determining the object of taxation in the amount of revenue received.
Read all about the simplified tax system Income here.
Accounting for non-operating income does not include repayable loan amounts. Funds received for temporary use are not revenue of the enterprise.
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system do not reflect funds or the valuation of the loan in KUDiR. When paying off obligations, the company also does not record the transaction in the ledger.
Income minus expenses
The procedure for determining the taxable base under the simplified tax system according to the “income minus expenses” scheme differs from the “income” scheme in the case of concluding an interest-bearing loan.
After paying the lender the interest accrued under the agreement, the amount is entered into the KUDiR and is included in expenses.
The loan is used at the discretion of the enterprise using the simplified tax system. The company has the right to pay from the amounts received for the purchase of materials and fixed assets.
Assets purchased with loan funds can be included in expenses in accordance with the provisions of clause 2 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Short-term loan
The list of short-term contracts includes contracts whose validity period is less than one year. However, the number of clauses in these contracts coincides with the number of sections of long-term contracts.
The organization acting as the borrower is obliged to perform the following actions:
- draw up an agreement that includes all important terms;
- draw up a confirming document on the transfer of funds and property;
- fulfill obligations to pay the debt - keep track of active objects, carry out accruals and transfers of interest on time, fulfill other requirements of the contract;
- repay the loan in full within the specified period of time.
Important! In the absence of documentary evidence, the credited money can be considered an advance payment for further supplies of goods, and the property can be considered a freely accepted value.
Features regarding the type of loan
The variety of loan forms for enterprises using the simplified tax system allows us to group them according to the following criteria:
Short-term and long-term types of contracts are used.
From the founder
The founder, as well as another individual, has the right to conclude a loan agreement with the enterprise and transfer the subject of the agreement for temporary use.
When concluding a loan agreement with the founder, a situation arises in which the parties are represented by one person. In a number of companies, the founder and director are the same person.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Article 53) finds contradictions in the representation of the interests of the parties by one person. The position is based on different representatives' grounds.
- on the basis of the Charter to represent the interests of organizations or a Certificate in the form of an enterprise in the form of an individual entrepreneur.
- independently as an individual.
When concluding a loan agreement and its implementation, there are no interdependent parties. Additional tax conditions for related parties arise only upon receipt of revenue.
Table: paying taxes and submitting reports if there is a separate division
The receipt of funds for temporary use does not entail the generation of income, regardless of the existence of conditions for payment for the use of the subject of the contract.
Is it considered interest-free?
An interest-free loan is such only if there is an indication in the contract that there is no fee charged.
When keeping records, the question arises whether material benefits are included in income. The concept of material benefit does not apply to enterprises under loan agreements.
In Art. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not establish the need to include material benefits from interest-free loans as part of non-operating income.
An organization or individual entrepreneur who received funds or property without additional payment does not accrue benefits in accounting for income.
If short term
The category of short-term contracts includes agreements whose duration is less than a year. The composition of the clauses of the document does not differ from the paragraphs of long-term agreements.
The borrowing company must take the following actions:
- Conclude an agreement including mandatory conditions.
- Document the receipt of funds and property.
- Bear responsibilities for servicing the loan - record the asset, timely accrue and transfer interest, and fulfill other terms of the agreement.
- Return the loan item within the specified period.
In the absence of documentary evidence, the funds received can be interpreted as an advance for subsequent deliveries, and the property - received free of charge.
Characteristics of the loan agreement
Quite often it happens that an organization or entrepreneur does not have free money, but urgently needs to pay off debts or not miss the opportunity to develop a business and invest, for example, in new equipment.
In this case, you can borrow money, that is, draw up a loan agreement. This option for receiving money is much easier and faster than applying for a loan. The main differences between a loan and a loan:
The loan agreement must clearly state its terms:
- parties to the contract and on what basis they act;
- subject of the contract (amount and currency for funds and detailed description for property);
- the moment when the loan is considered transferred and the method of transfer of the subject of the agreement;
- whether the loan is targeted (specify the purpose of the loan) or non-targeted;
- whether the loan is interest-bearing (specify the amount of interest, which can be calculated in a fixed amount or in the form of an interest rate and the period for their payment) or interest-free;
- term and method of loan repayment;
- terms of termination of the contract;
- responsibility of the parties.
When receiving a loan, a natural question arises as to what tax consequences this entails. Let's consider the operations of obtaining and issuing a loan from the point of view of tax accounting for organizations and individual entrepreneurs in a simplified manner for both options for calculating the tax base.
Frequently asked questions
The documentation of the loan agreement and the procedures for interaction between the parties raise a number of questions.
Along with the main question about whether a loan agreement under the simplified tax system should be classified as income or not, the most frequently arising doubts are: repayment of a loan with property, the need to indicate sanctions in the agreement, determining the characteristics and value of the property of the item.
A special case is the repayment of a loan in the form of compensation property
Legislation in Art. 409 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation defines the possibility of repaying a cash loan with the property of the enterprise.
The transferred assets may include fixed assets, finished products, materials and other inventory items.
When repaying obligations, the amount of assets must correspond to the amount of the contract.
The transfer of tangible assets to repay the contract is expressed in the form of revenue received from the transfer of fixed assets and inventory items.
When transferring compensation property in the form of a fixed asset, simplified enterprises must take into account the inability to reduce income by the residual value of the property.
The limitation is determined by law. In paragraph 1 of Art. 346 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes a closed list of expenses when maintaining a simplified taxation system.
If the subject of the agreement changes, the Federal Tax Service has the opportunity to present the loan funds as an advance received and charge penalties and fines.
A company can be insured against sanctions by expressly specifying in the contract the possibility of repaying the loan with property.
A change in the subject of the contract with compensation property can be formalized by an additional agreement during the validity of the main document.
Sanctions under the treaty
The loan agreement must indicate the sanctions that may arise if the terms of return of the transferred item are violated. This item is mandatory and is monitored by Federal Tax Service inspectors during inspection.
To limit the possibility of additional charges under the agreement, you can introduce the wording “at the initiative of the lender.” Such terminology will exclude claims from the inspection.
Description and value of the transferred property
The subject of borrowing may be property in respect of which property rights apply. The transferred item must have generic characteristics that allow it to be identified.
The legislation does not clearly indicate the need to determine the value of property in the contract.
Acceptance of the loan subject by an organization or individual entrepreneur obliges to establish the value in an agreement or other document.
The monetary value of the property can be determined by the conclusion of an independent assessment or an accountant’s certificate based on the inventory of the asset.
Reflection in accounting (postings)
Maintaining full accounting records under the simplified tax system is a voluntary decision of enterprises. Reflection of loans is possible when accounting for all transactions.
The company issues postings:
Only interest on the loan agreement is included in expenses.
How to calculate interest on loans?
Interest on debt obligations of any kind is included in the company's expenses for the simplified tax system. The need to determine the expenditure portion arises only for persons using the “income minus expenses” accounting scheme.
Is interest recognized as a non-operating expense for the simplified tax system? 25 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The possibility of accounting for interest on a loan as an expense is established in paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 265 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The fee for using the loan subject can be set as a percentage or a fixed amount specified in accordance with the time period - for the entire term of the agreement, month, quarter or other.
How to fill out a statement of financial results under the simplified tax system, read here.
How to keep a book of expenses and income under the simplified tax system, see here.
Costs are recognized only for the actual use of borrowed funds or property.
The company must determine the method of normalizing interest to write off expenses - according to comparable contracts or at the refinancing rate multiplied by the coefficient. The method is approved in the accounting policy of the enterprise.
Loan repayment
Contractual relations establish a period for the return of funds (property) received for temporary use.
There are options for determining the validity period of the agreement in the form:
- fixed loan repayment date.
- conditions for repayment of obligations at the request of the lender. Termination of the agreement occurs upon written instructions sent to the borrower. Refunds are made within 30 days from the date of receipt of the request.
Early repayment of obligations is allowed. The borrower must notify the lender of the planned return of funds and property 30 days before termination of obligations.
Early repayment of interest agreements is made only with the written consent of the lender.
The deadlines established by law in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation can be reduced or increased by introducing additional clauses into the contract.
Borrowed funds are provided to the company for temporary use. The absence of indicators of income makes it possible not to take into account sums of money or property as part of income under the simplified tax system.
Proper drafting of a loan agreement can prevent claims from tax authorities.
The document must clearly state the repayment procedure, interest or fees for using the loan item, and additional conditions.
Entries for accounting for interest on a loan
The party receiving the loan accrues interest on it monthly, unless a different frequency of accrual is provided for in the agreement, recording this by posting:
Dt 91 Kt 66 (67).
The fact of payment of interest will be displayed as:
Dt 66 (67) Kt 51.
The party that issued the loan will accrue interest at the same frequency as the borrower, and will take this into account by posting:
Dt 76 Kt 91.
She will reflect the receipt of interest as:
Dt 51 Kt 76.
Read about the main points that determine the differences between a loan and a loan in the material “Accounting for loans and borrowings in accounting .