Microenterprises, along with small and medium-sized enterprises, constitute a special category of economic entities of the Russian Federation. In the field of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), simplified accounting rules apply; in addition, such enterprises are legally exempt from inspections by regulatory authorities until the end of this year. The criteria characterizing an enterprise as “micro” are established by law. In particular, the income limit is indicated in Government Decree No. 265 of 04/04/16.
The status of a microenterprise can be assigned to a commercial organization: partnership, society, cooperative, peasant farm. Individual entrepreneurs can also be classified in this category (Federal Law No. 209 dated 07/24/07, Art. 3).
Microenterprise concept
A microenterprise is one of the actively developing forms of small business.
It is understood as a business company (JSC, LLC), cooperative, peasant farm (peasant farm) or individual entrepreneur (IP), which meet certain criteria prescribed in the federal law on small business.
Based on these criteria, on August 1 of each year, existing businesses are entered into a special register.
There is no need to confirm this status with any documents; this happens automatically based on the submitted tax and statistical reports.
In 2021, Rosstat registered over 2.5 million such organizations.
You can find out whether any company is on this list on the Federal Tax Service website by searching by TIN, OGRN or initials of an individual entrepreneur.
Large enterprises: pros and cons
Compared to SMEs, large enterprises have a serious impact on the national economy. They work much more efficiently.
Positive aspects of large enterprises:
- Availability of a huge resource base. It is through large enterprises that the main financial flows pass.
- Large production scales make it possible to reduce the cost of manufacturing a unit of product, that is, reduce the cost. This makes enterprises competitive not only in the domestic but also in the foreign market.
- Availability of cheap loans. Banks are more willing to work with large firms rather than small or medium-sized ones.
- Significant cash flows allow you to withstand periods of crises or other financial shocks.
- The ability to attract highly qualified personnel and provide them with decent wages.
- High level of social security.
- Developed infrastructure.
- Access to the markets of developing countries and the opportunity to influence their economic system.
- Accessibility to the international market and the use of relatively inexpensive resources provided by the global economy.
Weak sides:
- Significant concentration.
- Excessive localization of economic relations.
- A high level of bureaucracy and slowness can ruin any initiative. Any changes are possible only upon instructions from the very top. They take root slowly and with difficulty.
- Opposition to any horizontal economic ties. Their exit beyond the company's boundaries is blocked.
The basis for the success of large enterprises is their business models. They were invented a long time ago and are so effective that they continue to function successfully and generate profit. Of course, the models are slightly improved and updated to suit modern conditions.
Microenterprise criteria
To be included in the micro-enterprise register in 2021, the enterprise must meet the following criteria:
- the share of the state, regions or municipalities in the authorized capital should not exceed 25%, and the share of foreign and large Russian companies should not exceed 49%;
- number of employees up to 15 people;
- financial income from business activities should not “exceed” the bar of 120 million rubles.
Income now includes not only sales revenue, but also income from other types of activities.
The amount of income is determined from income tax returns or special tax regimes, if any.
If one or more indicators are not achieved within three calendar years, the company will be excluded from the list of microenterprises, but not earlier than 08/10/2019.
Functions of large enterprises
Large companies perform the following functions:
- Manufacturing of products and their sale to consumers.
- Providing raw materials, materials, equipment.
- Accounting for business and financial transactions.
- Management of all components of the production process and personnel.
Large companies also have additional functions:
- Scientific work and research.
- Close relations with the media and the public.
- Entrepreneurship support.
Large enterprises are presented in the following basic forms:
| Forms of large business | Characteristic |
| 1. Independent enterprise | An indivisible economic entity with a unified production structure. May consist of several legal entities, but the division is only nominal |
| 2. Company | 1) Several companies are united together. 2) They are connected by a similar type of activity. 3) Company:
4) Each component company is an independent unit. She has the right, if necessary, to work independently |
| 3. Integrated business group | Several companies with common owners. Businesses often belong to different industries |
Important! Large enterprises function not just as an element of the economic system. They have the power to change the surrounding space. Such enterprises influence the economic situation in the industry to which they belong.
Accounting statements of micro-enterprises
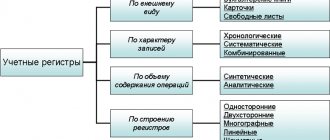
The management of a micro-enterprise has a lot of legal opportunities to optimize accounting. Its features depend on the chosen form of accounting.
There are several types of simplified accounting for small businesses.
[A]. In the full form, an organization uses many registers and accounts to maintain records. Records of liabilities and assets are kept in accordance with recommended forms.
This type of accounting makes sense to use if the organization carries out many different transactions.
To determine the tax base, it is advisable to use the accrual method.
[B]. Short form . If the company's operations are of a uniform nature, then there is no need to use a large number of accounts, and some homogeneous accounts can be combined into one.
For example, you can take into account on the twentieth account expenses not only for the main, but also for auxiliary production and general business expenses, and so on.
All transactions are recorded in one journal in chronological order by double entry.
It is recommended to use the K-1MP book for recording the facts of economic life as this journal.
It will also be useful to use the payroll slip (8MP).
To calculate the tax base, it is better to use the cash method.
[IN]. Simple form . Double entry does not apply.
Transactions are entered in chronological order into a single journal - “K-2MP” or “KUDiR” (book of income and expenses), if this is an individual entrepreneur or a simplified enterprise.
The chosen accounting method is fixed in the accounting policy, as well as the forms of the corresponding registers with the required details (name, name of the organization, dates, persons responsible for maintaining, etc.).
Benefits for small businesses
At the state level, a number of benefits are provided for organizations and individual entrepreneurs that meet the criteria of a micro-enterprise.
- Possibility of using simplified accounting.
- Priority when participating in government procurement (microenterprises must account for at least 15% of the total annual volume of government procurement).
- Simplified procedure for cash transactions.
- Minimum personnel documentation.
- Right to subsidies and grants.
- Soft sanctions. For the first violation, microenterprises get off with a warning rather than a fine. This approach is applied only if there is no damage to property, citizens, or the environment.
- Application of reduced tax rates. Since 2021, local authorities have been given the right to reduce rates for special regime residents. For the simplified tax system “Income without expenses” – 7.5% (up to 2 times), simplified tax system “Income” 1% (6 times).
- Financial support from the state. Micro-enterprises can count on free subsidies to compensate for part of the expenses under the leasing agreement, to secure a loan and expenses incurred in connection with participation in specialized and thematic events (conferences, exhibitions, etc.).
Features of accounting for micro-enterprises
The accounting regulations (PBU) and other regulations provide for a number of relaxations for small businesses. Thus, a microenterprise has the right:
- recognize income and expenses based on the actual receipt or write-off of funds (cash method);
- to level out the difference between tax and accounting accounting when calculating income tax and not to create deferred tax assets and liabilities;
- do not use estimated liabilities (do not create reserves);
- do not correct errors retrospectively; you can do this in the month in which they were discovered; the resulting profit or loss is reflected in 91 accounts;
- take into account all borrowing costs as part of other expenses (account 91);
- make depreciation payments once a year (for other enterprises once a month);
- do not set a cash limit.
For reporting purposes, it is sufficient to submit a balance sheet and financial statements.
It is allowed to use simplified forms of these documents, in which individual articles are grouped into larger groups.
For example, only 5 indicators remain on the balance sheet assets, instead of 15 in full form: tangible and intangible assets, inventories, monetary and financial assets.
Personnel records for micro-enterprises
From 01/01/2017 you can use simplified personnel document flow.
This means that the company is freed from the obligation to draw up local regulations, such as shift schedules, bonus provisions and others.
These points must be spelled out individually in a standard employment contract with each employee.
Instructions on labor protection at a micro-enterprise can be carried out by its manager.
Certification of workplaces is still required, except for remote and home workers.
If there is a need, employment contracts can be concluded for a period of up to 5 years; in general, such contracts are indefinite.
Video about personnel document flow of micro-enterprises:
mb.jpg
Related publications
The criteria for classifying an enterprise as a small enterprise are regulated by law. Compliance with the entire set of mandatory requirements will allow a small business entity to take advantage of a wide range of benefits. The main regulatory act in regulating the work of small businesses is the Law on the Development of Small and Medium Businesses dated November 27, 2017 No. 209-FZ.
Read more: Statement from Sberbank on a card from three years ago
Statistical reporting of micro-enterprises
Rosstat can conduct continuous and selective collection of data on companies.
In the first case, standard reporting is usually submitted:
- for individual entrepreneurs falling under the concept of a micro-enterprise, a report on the activities of 1 individual entrepreneur is submitted;
- information on key performance indicators - MP (micro);
- data on manufactured products - MP (micro)-nature;
From 2021, the TORG (micro) form has been abolished in retail trade, and form 1-alcohol has been abolished for those selling alcohol.
Rosstat may organize random checks and then you will have to submit additional reports.
You can find out whether any microenterprise is in the sample on the website of the State Statistics Service.
For violation of delivery deadlines, a fine of 20 to 70 thousand is provided for organizations, and for managers - from 10 to 20 thousand rubles.
Occupational Safety and Health
Responsibility for labor protection in a micro-enterprise rests entirely with the employer. He needs to take special courses and receive a certificate. Only after this he has the right to conduct classes with employees on the topic of labor protection and fire safety. His responsibilities also include the responsibility for preparing the briefing log.
The set of occupational safety measures at a micro-enterprise includes:
- ensuring the safety of work premises;
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic requirements in the workplace;
- conducting training and its written execution;
- recording and tracking accidents;
- registration and monitoring of employees with occupational diseases;
- compulsory social insurance of hired personnel;
- provision of PPE;
- payment of compensation provided by law.
In some cases, a medical examination is necessary. This applies to hazardous production and drivers.
For such small organizations, it is legally permissible to hire specialized companies to implement the labor protection function. They take upon themselves the preparation of all documents, conducting training events with the manager and staff.