Is a business trip possible under a GPC agreement? The answer to this question must be sought in the provisions of the Labor and Civil Codes. In Art. 166 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that business trips can be issued in relation to hired employees on the basis of an internal order of the manager. A business trip is recognized as such only if the daily performance of work functions does not require the person to be constantly on the road. The purpose of business trips is to carry out the employer’s instructions not at the main place of work, but at a territorial distance from it.
What is included in the list of travel expenses
The following employee expenses are subject to reimbursement of expenses related to business trips:
- daily expenses (you can read more about daily allowances in the article “The amount of daily allowances for business trips and their calculation”);
- fare;
- housing expenses;
- payment for a visa and fee for obtaining a foreign passport;
- consular fees;
- exit/entry fees;
- toll road fees;
- registration of compulsory insurance;
- mandatory fees and payments;
- other expenses incurred by an employee on a business trip with the consent of management.
This list was compiled taking into account the norms of labor legislation (Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and the Regulations on business trips approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Calculating and processing travel expenses abroad has its own characteristics, which you can familiarize yourself with in the article “How to calculate daily allowances when traveling abroad.”
Lawyers Services ->
if during a tourist trip it turns out that the volume and quality of the tourist services provided do not comply with the terms of this agreement and the requirements of the law, replace the tourist services provided during the tourist trip with tourist services of similar or higher quality without additional costs for the Customer , and with the consent of the Customer or tourist - tourist services of lower quality with compensation to the Customer for the difference between the cost of tourist services specified in this agreement and the cost of actually provided tourist services;
4.4. If a trip is canceled at the initiative of the Customer, regardless of the reasons, more than ______ days before departure (departure), the Customer is refunded the cost of the trip minus ______% of the cost. If a trip is canceled at the Customer's initiative, regardless of the reasons, less than _______ days before departure (departure), the trip fee is not refunded.
25 Jul 2021 jurist7sib 94
Share this post
Related Posts
Payment of travel expenses
In order for an employee to travel to perform a job assignment, he must be paid an advance for travel expenses.
The deadline for paying travel expenses is before the start of the trip. It can be established in the organizational and administrative document of the company.
To receive an advance, an order is made for a business trip (you can read more about this topic in the material “How to properly arrange a business trip”).
Also, the employer can establish in the internal regulations the need to submit a preliminary calculation, memo, application for travel expenses or the development of an estimate of travel expenses, samples of which should preferably be fixed in a local act.
You can learn how to calculate travel allowances in the article “How to calculate travel allowances (expenses).”
In addition to daily allowance and payment of other travel expenses, the employee retains an average salary.
There are certain nuances when it comes to paying for business trip days that fall on weekends or holidays. You can find them in the article “Payment for business trips on weekends and holidays: features.”
Each company sets its own travel expense standards, taking into account its financial capabilities. At the same time, the daily allowance should cover the cost of food and household expenses during a business trip.
In what cases personal income tax is withheld from the amount of travel expenses, you can find out in the article “How to reflect daily allowances in tax accounting.”
Important Details
There are no marks on the travel certificate: what to do?
This situation may arise when the business trip was not associated with a visit to an organization, but with a conversation or negotiations with another individual who does not have his own seal or stamp.
To protect yourself during a tax audit of travel documents, it is recommended that an enterprise sending an employee on such a business trip draw up and collect the following documents:
- issue an order to send an employee on a business trip;
- keep the employee’s travel documents in both directions;
- draw up a job assignment;
- provide an employee report on the work done;
- keep documents confirming the employee’s stay in a certain city at a specific time.
If this list of supporting documents is available, the organization’s expenses will not be transferred to profit.
Visit abroad
A mandatory condition for an employee to be on a business trip abroad is to independently declare their expenses and income related to their stay in another country. The responsibility of a tax agent is removed from the legal entity.
Compensation of expenses to the contractor
According to the contract concluded with the counterparty, it may be stipulated that the customer is obliged to compensate the contractor for all expenses, including those related to business trips.
Article 702 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation determines that under a work contract, the contractor has the obligation to fulfill the customer’s task specified in the document within the specified period, and the latter, in turn, must pay for the work. Unless the contract provides for a different state of affairs, the contractor performs the work with his own resources, resources and using his own materials.
Article 709 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation indicates that the document concluded by the parties must indicate the cost of the work performed or the methods by which it will be determined in the future. Compensation payments for business trips can be immediately taken into account in the price or set additionally.
When handing over the work, the contractor must provide a complete set of documentation related to the business trip and subject to reimbursement.
When hiring, a probationary period is often established. Is it possible to extend the probationary period? Dismissal at one's own request without service is possible. Read more here.
Even after dismissal, you can get paid sick leave. See how.
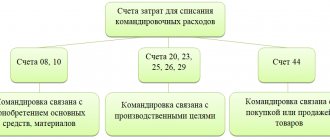
Accounting for travel expenses
Let's consider the reflection of travel expenses in accounting. To reflect them, account 71 “Settlements with accountables” is provided:
- by debit – take into account all funds issued for travel and entertainment expenses;
- on credit - reflect transactions when travel expenses are written off.
An advance for business trip expenses can be issued from the company's cash desk, transferred from a current account to an employee's bank card, or it can be transferred to a special corporate card.
Here are examples of wiring:
- Dt 71 – Kt 50: issued for travel expenses. If before this money was received at the cash desk for travel expenses, then the posting is as follows: Dt 50 - Kt 51 ;
- Dt 71 – Kt 51 : an advance was transferred against the report from the company’s current account;
- Dt 55 – Kt 51: transfer to a special account was made.
Subsequently - when the employee pays by card (for example, for a hotel) - the accountant will reflect the following transaction: Dt 71 - Kt 55 .
If an employee withdraws money from a corporate card (for example, for food), the posting is as follows: Dt 71 – Kt 55.
In accounting, travel expenses are charged to expense accounts (in most cases).
At the end of the business trip, the employee must submit to the accounting department a correctly completed advance report for travel expenses. In this case, the accountant will reflect the following entries in accounting: Dt 26 – Kt 71 (travel expenses written off).
You can read how to correctly draw up an advance report and report for an advance on travel expenses in the article “What should a business trip report be?”
Free legal advice online
Legal advice is provided free of charge online around the clock, regardless of weekends and holidays. The response time from specialists on the website is up to 15 minutes.
There is no need to register on the Internet portal and you can send a personal appeal anonymously. Attention! The online lawyer provides answers to questions and continues to support the client in the event of further difficulties.
Legal advice can be obtained in the following ways:
- call the hotline.
- use the online chat service;
- draw up a contact form for the feedback service;
Online legal consultation can also be carried out via email. The advantages of the services of our law firm are due to the professional attitude of our specialists to their work, the receipt of regular training courses, as well as participation in official forums.
Other expenses of an employee on a business trip with the consent of management
An employee has the right to claim compensation for additional travel expenses if they are provided for in company regulations or labor legislation.
Additionally, in addition to daily allowance and accommodation, an employee may have expenses for a taxi on a business trip.
How to arrange this payment of travel expenses can be found in detail in the article “Payment for a taxi on a business trip: taxes and supporting documents.”
The company may also include other expenses in travel expenses. So, if an employee goes on a long trip, then packing luggage may be included in travel expenses.
Service fees and fines for returning/exchanging tickets (if the traveler is not at fault) are also included in travel expenses.
Payment of travel expenses on a business trip may take into account the standards established for categories of employees. For example, in a local act, an employer can stipulate that the company’s management, including deputy directors, have the right to travel in first class in a railway carriage and fly in business class. For all other employees - reserved seat and economy class, respectively. And this will not be a violation of paying expenses for business trips.
When auditing travel expenses, it is necessary to check first of all the existence of an internal regulation on business trips, which should specify all the norms for additional reimbursement. expenses.
Contract for paid legal services: download
- According to this agreement, the Contractor undertakes, on the instructions of the Customer (Appendix No. 1), to provide the following services: representation of the interests of a legal entity in the Arbitration Court, and the Customer undertakes to pay for these services.
- The Contractor undertakes to provide services personally.
- The cost of the services provided is: 60,000 (sixty thousand) rubles 00 kopecks, including VAT 18% - 10,800 (ten thousand eight hundred) rubles 00 kopecks.
- Services are paid within the following terms and in the following order: advance payment in the amount of 40% within 2 days after signing the contract and the remaining amount after the provision of services in the amount of 60%.
- In case of impossibility of performance due to the fault of the Customer, services are subject to payment in full.
- The Customer has the right to refuse to fulfill this contract, subject to payment to the Contractor for the expenses actually incurred by him.
- The Contractor has the right to refuse to fulfill this contract, subject to full compensation for losses to the Customer.
- The general provisions on contracts (Articles 702 - 729 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) apply to this agreement, unless this contradicts Art. Art. 779 – 782 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, regulating issues of paid services.
- Validity period of this agreement: beginning: September 15, 2021; End: February 02, 2021.
- Neither Party is liable to the other Party for failure to fulfill obligations caused by force majeure circumstances that arose against the will and desire of the Parties and which cannot be foreseen or avoided, including declared or actual war, civil unrest, epidemics, blockade, embargo, earthquakes, floods , fires and other natural disasters, etc.
- A Party that cannot fulfill its obligation due to force majeure circumstances must notify the other Party of the existing obstacles and their impact on the fulfillment of obligations under this Agreement.
- The Agreement is concluded in 2 copies having equal legal force, one copy for each Party.
- Any agreement between the Parties entailing new obligations that do not arise from the Agreement must be confirmed by the Parties in the form of additional agreements to the Agreement. All changes and additions to the Agreement are considered valid if they are in writing and signed by appropriate authorized representatives of the Parties.
- A Party does not have the right to transfer its rights and obligations under the Agreement to third parties without the prior written consent of the other Party.
- References in the Agreement to a word or term in the singular include references to that word or term in the plural. References to a word or term in the plural include references to that word or term in the singular. This rule is applicable unless otherwise follows from the text of the Agreement.
- The Parties agree that, with the exception of information that, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, cannot constitute a trade secret of a legal entity, the contents of the Agreement, as well as all documents transferred by the Parties to each other in connection with the Agreement, are considered confidential and relate to the trade secret of the Parties, which shall not be disclosed without the written consent of the other Party.
- For purposes of convenience, in the Agreement the Parties also mean their authorized persons, as well as their possible successors.
- Notifications and documents transferred under the Agreement are sent in writing to the following addresses: for the Customer: Moscow, Moiki St., 12; for the Contractor: Moscow, Dzerzhinsky St. 53.
- Any messages are valid from the date of delivery to the appropriate correspondence address.
- In the event of a change in the addresses specified in clause 18 of the Agreement and other details of the legal entity of one of the Parties, it is obliged to notify the other Party about this within 10 (ten) calendar days, provided that such a new address for correspondence can only be the address in Moscow, Russian Federation. Otherwise, the Party’s fulfillment of obligations under the previous details will be considered proper fulfillment of obligations under the Agreement.
- All disputes and disagreements that may arise between the Parties and arising from this Agreement or in connection with it will be resolved through negotiations. If it is impossible to reach an agreement on controversial issues through negotiations within 15 (fifteen) calendar days from the receipt of a written claim, the disputes are resolved in the Moscow Arbitration Court in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
- The Parties declare that their official seals on documents drawn up in connection with the execution of this Agreement are unconditional confirmation that an official of the signatory Party has been duly authorized by that Party to sign this document.
- The terms of the Agreement are binding on the legal successors of the Parties.
OJSC "___________", hereinafter referred to as the "Contractor", represented by General Director _______________, acting on the basis of the Charter, on the one hand, and LLC "___________", hereinafter referred to as the "Customer", represented by General Director _________________, acting on the basis of the Charter , on the other hand, have entered into this agreement (hereinafter referred to as the “Agreement”) as follows:
Payment of travel expenses according to the agreement
The contractor very often wants to be reimbursed for additional costs under the contract. In the general case (clause 2 of Article 709 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), the price of the contract already includes compensation for all costs of the contractor and his remuneration. However, the parties may include a provision for reimbursement of travel expenses in the contract. How to pay travel expenses to the contractor in this case?
The provision for compensation for travel expenses makes sense when the contractor does not know in advance how many visits he will make to the site. However, you can:
- in the contract , limit the amount of reimbursement of travel expenses by the customer and set a limit;
- include the amount for travel expenses in the summary estimate.
It also makes sense to indicate in the contract what applies to travel expenses, as well as the deadline for reporting them. These clauses of the agreement will help justify the amount of travel expenses in tax accounting.
How to pay travel expenses under an audit agreement? Similarly: include in the contract a provision for compensation of travel expenses by the customer.
Reimbursable Expenses for Business Travel Under the Agreement for the Provision of Legal Services
There is no clear position on income tax. According to the courts, the amount of reimbursable costs is not recognized as the contractor’s revenue for income tax purposes (Resolutions of the North Caucasian Federal Antimonopoly Service of February 11, 2021 N F08-8206/07-3204A, East Siberian Federal Antimonopoly Service of March 21, 2021 N A74-3165/06-F02 -1481/07 and dated July 14, 2021 N A33-23362/04-С3-Ф02-3274/05-С1 districts). Accordingly, it does not take into account the amount of the expenses themselves, which are compensated by the customer.
Maximum control over the actions of the contractor is provided by the option when the customer pays expenses to third parties. In this case, the documents are issued in the name of the customer, the contractor is not even mentioned in them.
Agreement with the entrepreneur
Now let’s look at the tax consequences for a situation where a company enters into a civil contract with an individual entrepreneur.
Personal income tax and insurance premiums
According to sub. 1 and sub. 2 p. 1 art. 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, individuals registered as individual entrepreneurs calculate and pay personal income tax on the amounts of income received from such activities independently. Therefore, when entrepreneurs receive income from a company within the framework of a civil contract, it is not recognized as a tax agent.
Please note: in order to confirm the fact that an individual receives income specifically from his entrepreneurial activity, the company should indicate in the contract for the performance of work or the provision of services that the contract is concluded specifically with an individual entrepreneur. To do this, the contract should provide the number and date of the individual entrepreneur’s certificate of state registration, the body that issued the document and the TIN (letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 03/21/2011 No. 03-04-06/3-52 and dated 05/07/2007 No. 03-04-06 -01/139, resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated 04/03/2014 in case No. A72-6849/2013).
As for insurance premiums, in paragraph 1 of Art. 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation clearly states that when concluding civil contracts with entrepreneurs, the customer does not accrue mandatory insurance contributions. According to sub. 2 p. 1 art. 419 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, entrepreneurs pay contributions for themselves.
Income tax
If the customer compensates the contractor-entrepreneur for travel and accommodation and this is a condition for concluding a contract, then such costs are recognized as economically justified. The courts also confirm this. An example is the resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated April 30, 2009 No. F09-2594/09-S3 in case No. A76-15564/2008-39-356, which was supported by the Ruling of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 31, 2009 No. VAS-9188/09.
The court found it lawful for the company to include payment for hotel accommodation for the contractor's employees as expenses, since it was made under the contract. Let us note that the above court decision dealt with the employees of the contractor company. But the conclusions made by the arbitrators are applicable to our situation. After all, an individual entrepreneur acts both as a contractor and as an employee of the contractor in one person.