Important components of a leasing agreement
The leasing agreement is always drawn up in writing. It reflects all the terms of the transaction, including:
- Name of the parties involved.
- Detailed description of the leased item.
- Cost of the leasing agreement.
- The period of validity of the transaction.
- Procedure and terms for making payments.
- Conditions for the return or redemption of property into the client's ownership.
- The amount of the redemption price.
In addition, the leasing agreement specifies the amount of the advance payment (down payment), if the agreement is drawn up taking into account its payment.
The down payment performs several functions simultaneously. Payment of an advance is one of the confirmations of the borrower’s reliability and solvency. Additionally, such a contribution allows you to reduce the financial burden of further payments.
The larger the down payment, the smaller your monthly payments will be.
Results
When providing or receiving property on lease, the simplifier must take into account restrictions on the amount of income and the amount of residual value of fixed assets. Recognition of the value of leased fixed assets as expenses depends on whether the contract provides for the redemption value of this property, and on whose balance sheet it is located.
How leasing transactions are reflected in the accounting accounts, read the article “Leasing under the simplified tax system, income minus expenses - transactions.”
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Advance payment under a leasing agreement
Payment under leasing transactions is used by the lender to ensure the fulfillment of all obligations by the lessee.
The amount of the down payment varies from 5 to 50%, depending on the requirements set by the leasing company.
The advance payment is made by the borrower immediately after execution of the contract. The down payment can be paid in one lump sum or in installments, as previously agreed upon by the parties involved. In the case of gradual payment, a schedule for offset of such payments is drawn up, which is displayed in the agreement itself or is provided in a separate application.
The advance payment can be credited in several ways:
- The full agreed amount when paying the first installment of the lease payment.
- One-time in the process of making the last part of the payment under the leasing agreement.
- In equal parts during the validity period of the transaction itself.
If the down payment is made in one payment, then the lender immediately after receiving it pays the full cost of the property to the seller. Next, the necessary documents are completed, after which the subject of the transaction is placed at the disposal of the borrower.
Important nuances of accounting for advance payments
An advance payment is provided for in most leasing agreements, and its offset can be made in any of the provided ways. For example, against the starting payment, against several starting payments until the advance amount is fully repaid, evenly during the repayment of the main debt, against the last payment under the leasing agreement, etc.
The lender, in the process of transferring the property to the lessor, provides an invoice for the entire amount of the advance payment. In this case, this amount, excluding VAT in tax reports, can be taken into account as expenses when taxing profits.
As part of leasing transactions, services are provided until the end of the agreement, so tax structures do not need to compare such payments with the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. And you don’t have to worry about how to reflect the down payment in the leasing company’s turnover.
As for the partial payment of the advance, borrowers often have a question about whether these payments can be immediately attributed to expenses. The answer will be negative, since in this case the amount of the down payment will be counted as an expense in accounting for income taxation. Similar conditions are met if the lessor accepted the advance payment not according to the current schedule.
Ways to save on taxes
Sometimes when comparing leasing and credit, users take into account only interest rates and the ratio of payment terms. However, these factors are far from decisive when it comes to the benefits of one type of investment over another. Leasing provides an opportunity to significantly save on taxes, and this effect will persist for some time after all payments to the leasing company have been completed. Let's consider how the tax burden will be reduced when concluding a property leasing agreement.
Income tax
There is a significant saving in income tax when leasing. The benefit can be calculated using a conditional example. Company A makes a one-time advance payment, this will be 20% of the amount of the entire transaction, and the contract establishes a fixed amount of payments for the entire period. All these indicators, with the exception of VAT, will be considered expenses.
Accounting for advance payments from the lessee
The down payment for a leasing transaction in the borrower's accounting (transfer and offset) is made in the agreed amount and the period for offset of the advance by the lender, as part of the amount of leasing payments. The transfer of the advance is recorded as follows: to the debit of account 76 to the subaccount of advances issued from the credit of account 51.
VAT on the advance payment under the leasing agreement is taken into account by the lessee as follows:
| Debit | Credit |
| 68 (VAT subaccount) | 76 |
The borrower records the amount of the advance as follows:
| Debit | Credit |
| 76 (sub-account of debt for leasing payments) | 76 (sub-account of advances issued) |
Advance payments are an important condition of any contract, including leasing agreements. Therefore, a detailed description and, in general, recording of its terms in the document will help to avoid controversial and unforeseen situations, including fraudulent actions.
Features of VAT calculation
The regulatory framework governing the accounting of VAT on advance payments for leasing: Chapter 21 of the Tax Code, Letter of the Ministry of Finance numbered 03-07-03/34 dated 03/19/07.
Article navigation
- Important terms of the leasing agreement
- Is it possible to recover VAT on an advance payment?
- Accounting for VAT on advance payments in accounting entries
- Additional conditions for receiving a deduction
To provide themselves with guarantees regarding the reliability and solvency of the counterparty, lessors use a special form of prepayment - advance payments. The legislation does not set limits regarding their size, and the amount can be any, but more often - from 10 to 50%.
Lessees have the right to reduce VAT payments to the budget by the amount of tax they paid to the lessor as part of the advance payment. But in order to receive this deduction, taxpayers must take into account the specifics of the procedure in terms of documentation, and correctly draw up VAT entries for the advance payment.
The regulatory framework governing the accounting of VAT on advance payments for leasing: Chapter 21 of the Tax Code, Letter of the Ministry of Finance numbered 03-07-03/34 dated 03/19/07.
Civil law basics
One of the forms of rental relations is leasing.
The subject of leasing can be any non-consumable things, except for land plots and other natural objects (Article 666 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
According to Art. 607 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, non-consumable things are, for example, enterprises and other property complexes, buildings, structures, equipment, vehicles and other things that do not lose their natural properties during their use. In addition to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, leasing relations are also regulated by Federal Law No. 164-FZ of October 29, 1998 “On financial rent (leasing)” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 164-FZ).
Under a leasing agreement, the lessor undertakes to acquire ownership of certain property from a certain seller in order to transfer it for a fee for a certain period as a leased asset to the lessee (Article 2, paragraph 4 of Article 15 of the Federal Law of October 29, 1998 N 164-FZ “On Financial rent (leasing)”, Article 665 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The size, method of implementation and frequency of leasing payments are determined by the leasing agreement (clause 2 of article 28 of Federal Law N 164-FZ).
Property transferred for temporary possession and use to the lessee is the property of the lessor (Clause 1, Article 11 of Law No. 164-FZ). In this case, by mutual agreement of the parties, leased property can be recorded on the balance sheet of the lessee or on the balance sheet of the lessor (Clause 1, Article 31 of Law No. 164-FZ).
Upon expiration of the leasing agreement, the lessee may acquire ownership of the leased asset if this is provided for in the leasing agreement (Clause 5, Article 15 of Federal Law No. 164-FZ). In this case, the total amount of the leasing agreement may include the redemption price of the leased asset (Clause 1, Article 28 of Federal Law No. 164-FZ).
Accounting for leasing transactions must be carried out in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 17, 1997 N 15, which approved the Instructions on the reflection in accounting of transactions under a leasing agreement (hereinafter referred to as the Instructions).
Leased item on the lessee's balance sheet
Accounting
If, according to the terms of the agreement, the leased property is accounted for on the balance sheet of the lessee, then the lessee accounts for leasing transactions as follows.
Receipt of leased property
The cost of received leased property is reflected in the debit of account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”, subaccount “Purchase of individual fixed assets under a leasing agreement”, in correspondence with the credit of account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”, subaccount “Lease obligations”.
Then the costs associated with obtaining leased property and the cost of the object itself are written off from the credit of account 08 to the debit of account 01 “Fixed assets”, sub-account “Leased property” (paragraph 2, clause 8 of the Instructions).
From the provisions of clauses 4, 7, 8 PBU 6/01 and para. 2 clause 8 of the Instructions it follows that if the leased property is accounted for on the balance sheet of the lessee, then the leased item is accepted by the lessee for balance sheet accounting as part of fixed assets at its original cost, which is equal to the total amount of debt to the lessor under the leasing agreement excluding VAT.
Costs incurred by the lessee for delivery, bringing the leased asset to a state in which it is suitable for operation (including design, installation and commissioning work) are not subject to inclusion in the initial cost of the leased asset, accounted for under the financial lease (leasing) agreement on the balance sheet lessee (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western Territory dated November 19, 2010 in case No. A26-11541/2009, Resolution of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated April 12, 2011 No. VAS-251/11 refused to reconsider this case).
Leasing payments
The accrual of lease payments due to the lessor is reflected in the debit of account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”, sub-account “Lease obligations”, in correspondence with account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”, sub-account “Debt on leasing payments” (paragraph 2 clause 9 of the Instructions). That is, the amounts of lease payments due to the lessor from the lessee in this case are not recognized as an expense.
Accounting and tax accounting of leasing from the lessee
Accounting for transactions under a leasing agreement is regulated by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 15 dated February 17, 1997.
Leasing entries depend on whose balance sheet the leased property is reflected on: the lessor or the lessee. The party on whose balance sheet the leased property is accounted for must be indicated in the leasing agreement.
Accounting for leasing when reflecting property on the lessor’s balance sheet
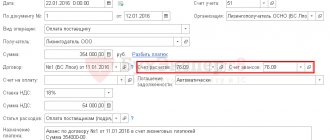
Leasing transactions correspond to the payment schedule located at the link.
If the leasing agreement provides for the reflection of the leased asset on the lessor’s balance sheet, the lessee reflects the leased property on off-balance sheet account 001 “Leased fixed assets”.
The accrual of leasing payments is reflected in the credit of account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” in correspondence with cost accounts: 20, 23, 25, 26, 29 - when accounting for leasing payments on property that is used in production activities, 44 - on property used in the activities of a trade organization, 91.2 - for property that is used for non-production purposes. Further, for simplicity, in the leasing accounting examples, only entries for the 20th account will be given.
Postings upon receipt of the leased asset
Dt 001 - 1,000,000
(the leased asset is accepted for accounting at cost excluding VAT)
Postings for current lease payments
Dt 60 - Kt 51 - 236,000
(advance payment (down payment) under the leasing agreement has been paid)
It is necessary to take into account that the advance payment under the leasing agreement can be charged as expenses (offset of the advance payment) not immediately, but throughout the entire agreement. In the above payment schedule, the advance payment under the contract is offset evenly (RUB 6,555.56 each) over 36 months.
Dt 20 - Kt 76 - 29,276.27
(accrued leasing payment No. 1 - 34,546 minus VAT - 5,269.73)
Dt 19 - Kt 76 - 5,269.73
(VAT charged on lease payment No. 1)
Dt 20 - Kt 60 - 5,555.56
(part of the advance payment under the leasing agreement is credited - 6,555.56 minus VAT 1,000)
Dt 19 - Kt 60 - 1,000
(VAT is calculated based on the advance payment)
Dt 68 - Kt 19 - 6,269.73
(VAT submitted to the budget)
Dt 76 - Kt 51 - 34 546
(listed leasing payment No. 1)
The commission that is paid at the beginning of the leasing transaction (commission for concluding the transaction) is charged in accounting to the same expense accounts as current leasing payments.
Postings for the redemption of the leased asset
If there is a buyout price in the leasing agreement (this amount is not included in the leasing payment schedule, for example, let’s take it equal to 1,180 rubles including VAT), the following entries are made in accounting:
Dt 08 - Kt 76 - 1,000
(reflects the costs of repurchasing the leased asset upon transfer of ownership to the lessee)
Dt 19 - Kt 76 - 180
(VAT is charged when purchasing the leased asset)
Dt 68 - Kt 19 - 180
(VAT submitted to the budget)
Dt 76 - Kt 51 - 1 180
(the amount of redemption of the leased asset has been paid)
Dt 01 - Kt 08 - 1 000
(the leased asset was accepted for accounting as part of its own fixed assets)
Accounting for leasing when reflecting property on the lessee’s balance sheet
The legislation regulating leasing accounting does not contain unambiguous instructions on the reflection of transactions under a leasing agreement if the lessee is the balance holder of the property.
Currently, the practice of communication between lessees and leasing companies with auditors and inspection bodies has developed, and a certain scheme of leasing transactions has been formed.
Accounting for leasing when reflecting property on the lessee’s balance sheet
If, under the terms of the leasing agreement, the property is taken into account on the lessee’s balance sheet, upon receipt of the leased asset in the lessee’s accounting, the value of the property minus VAT is reflected in the debit of account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” in correspondence with the credit of account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”.
When a leased asset is accepted for accounting as part of fixed assets, its value is written off from credit 08 of account to debit 01 of account “Fixed Assets”.
The accrual of leasing payments is reflected in the debit of account 76, subaccount, for example, “Settlements with the lessor” in correspondence with account 76, subaccount, for example, “Settlements for leasing payments”.
Depreciation on the leased asset is calculated by the lessee. The amount of depreciation of the leased asset is recognized as an expense for ordinary activities and is reflected in the debit of account 20 “Main production” in correspondence with the credit of account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets, subaccount for depreciation of leased property.
Tax accounting of leasing when reflecting property on the lessee’s balance sheet
In the tax accounting of the lessee, leased property is recognized as depreciable property.
The initial cost of the leased asset is determined as the amount of the lessor's expenses for its acquisition.
For profit tax purposes, the monthly depreciation amount is determined based on the product of the original cost of the leased asset and the depreciation rate, which is determined based on the useful life of the leased property (taking into account the classification of fixed assets included in depreciation groups). In this case, the lessee has the right to apply a coefficient of up to 3 to the depreciation rate. The specific size of the increasing coefficient is determined by the lessee in the range from 1 to 3. This coefficient does not apply to leased property belonging to the first to third depreciation groups.
Leasing payments minus the amount of depreciation on leased property are expenses associated with production and sales.
An example of accounting for leasing when reflecting property on the lessee’s balance sheet
Leasing transactions correspond to the payment schedule for property leasing located at the link
The lessee received a passenger car under a leasing agreement, payment schedule parameters:
- leasing agreement term - 3 years (36 months)
- the total amount of payments under the leasing agreement is 1,479,655.10 rubles, incl. VAT — 225,710.10 rubles
- advance payment (down payment) - 20%, 236,000 rubles, incl. VAT — 36,000 rubles
- The cost of the car is 1,180,000 rubles, incl. VAT - 180,000 rubles
The expected period of use of the leased property is four years (48 months). The car belongs to the third depreciation group (property with a useful life of 3 to 5 years). Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method.
Let's determine the amount of monthly depreciation in accounting. Because the cost of the property (including the leasing company's remuneration) is equal to 1,253,945 rubles (1,479,655.10 - 225,710.10), monthly depreciation will be 1,253,945: 48 = 26,123.85 rubles.
A passenger car belongs to the third depreciation group, therefore, a period of 48 months can be established in tax accounting. The monthly depreciation rate is 2.0833% (1: 48 months x 100%), the monthly depreciation amount is 1,000,000? 2.0833% = 20,833.33 rubles.
In accordance with paragraph 10, paragraph 1 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of the lease payment recognized monthly as an expense for profit tax purposes is 8,442.94 rubles (34,546 (lease payment) - 5,269.73 (VAT as part of the lease payment) — 20,833.33 (monthly depreciation in tax accounting)).
Expenses under the leasing agreement are formed monthly in accounting due to depreciation (26,123.85 rubles), in tax accounting - due to depreciation (20,833.33 rubles) and leasing payment (8,442.94 rubles), a total of 29,276 ,27 rubles.
Because in accounting, the amount of expenses over 36 months (the term of the leasing agreement) is less than in tax accounting, this leads to the emergence of taxable temporary differences and deferred tax liabilities.
During the term of the leasing agreement, the lessee has a monthly taxable temporary difference in the amount of 3,152.42 rubles (29,276.27 - 26,123.85) and a corresponding deferred tax liability arises in the amount of 630.48 rubles (3,152.42?20% ).
Separately, it is necessary to say about accounting for the advance payment (down payment under the contract)
. The following situations are possible:
1. When transferring property for leasing, the lessor provides an invoice for the full amount of the advance
(in the given schedule of leasing payments - by 236,000 rubles). In this case, the entire amount of the advance payment minus VAT in tax accounting is recognized as an expense for profit tax purposes.
I would like to note that under the leasing agreement, services are provided throughout the entire contract and the fiscal authorities have no reason to assess compliance with the criteria of paragraph 4, paragraph 2 of Article 40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on the comparability of leasing payments, because individual payments cannot be considered as separate transactions, and the price under a leasing agreement must be analyzed in aggregate for all payments in the agreement.
2. The advance payment under the leasing agreement is offset in equal payments throughout the entire leasing term.
In this case, the offset portion of the advance payment is recognized as an expense in tax accounting for profit tax purposes.
In the given example of a leasing payment schedule, it is assumed that an advance invoice is issued to the lessee when the property is leased, i.e. In tax accounting, when transferring property into leasing, expenses in the amount of 200,000 rubles are reflected (the advance payment, which is a leasing payment, is not deducted, since in the first month when transferring property into leasing, it is not yet accrued). At the same time, a taxable temporary difference in the amount of 200,000 rubles and a corresponding deferred tax liability in the amount of 40,000 rubles (200,000 rubles x 20%) arise.
At the end of the leasing agreement, the lessee will continue to accrue monthly depreciation in accounting in the amount of 26,123.85 rubles. There will be no expenses in tax accounting. This will lead to a monthly decrease in deferred tax liabilities in the amount of 5,224.77 rubles (26,123.85 rubles x 20%).
Thus, based on the results of the agreement, the total amount of deferred tax liabilities will be equal to zero:
40,000 (deferred tax liability for the advance payment) + 22,697 (630.48? 36 - deferred tax liability for current lease payments) - 62,697 (5,224.77? 12 - reduction of deferred tax liabilities for 12 months of depreciation in the accounting accounting after the end of the leasing agreement).
Postings upon receipt of the leased asset
Dt 60 - Kt 51 - 236,000
(advance paid under the leasing agreement)
Dt 08 - Kt 76 (Settlements with the lessor) - 1,253,945
(debt under the leasing agreement is reflected without VAT)
Dt 19 - Kt 76 (Settlements with the lessor) - 225,710.10
(VAT reflected under the leasing agreement)
Dt 01 - Kt 08 - 1 253 945
(a car received under a leasing agreement is accepted for registration)
Dt 76 - Kt 60 - 236,000
(advance payment paid upon concluding the leasing agreement is included)
Dt 68 (Income tax) - Kt 77 - 40,000
(deferred tax liability reflected)
Dt 68 (VAT) - Kt 19 - 36,000
(VAT submitted on advance payment)
Postings for current lease payments
Dt 20 - Kt 02 - 26,123.85
(depreciation has been calculated on the car)
Dt 76 (Settlements with the lessor) - Kt 76 (Settlements for leasing payments) - 34,546
(leasing debt has been reduced by the amount of the lease payment)
Dt 76 “Calculations for leasing payments” - Kt 51 - 34,546
(leasing payment transferred)
Dt 68 (VAT) - Kt 19 - 5,269.73
(VAT is presented on the current lease payment)
Dt 68 (Income tax) - Kt 77 - 630.48
(deferred tax liability reflected)
Postings at the end of the leasing agreement
Dt 01 (Own fixed assets) - Kt 01 (Fixed assets received under leasing) - 1,253,945
(reflects the receipt of the car into ownership)
Dt 02 (Depreciation of leased property) - Kt 02 (Depreciation of own fixed assets) - 940,458.60
(accrued depreciation on the car is reflected)
Postings within 12 months after the end of the leasing agreement
Dt 20 - Kt 02 (Depreciation of own fixed assets) - 26,123.85
(depreciation has been calculated on the car)
Dt 77 - Kt 68 (Income tax) - 5,224.77
(reflects a decrease in deferred tax liability)
There is also a method in which the initial cost of the leased asset in accounting is equal to the cost of purchasing a car from the lessor, i.e. coincides with the value in tax accounting. In this case, on account 76, when the property is accepted for accounting, only the debt for the value of the property is reflected.
Leasing payments are accrued monthly on credit 20 of account in correspondence with account 76 in the amount of the difference between accrued depreciation and the amount of the monthly lease payment.
Selecting the most reasonable option for reflecting leased property on the balance sheet of the lessor or lessee, as well as agreeing with the leasing company on the optimal scheme for reflecting leasing payments, is a very complex task that requires good knowledge of the specifics of accounting for leasing operations and the peculiarities of the wording in the leasing agreement and primary documents.
The essence of leasing
A leasing agreement is concluded between two interested parties. The subject of the contract is buildings, equipment, cars and other types of property. The lessee can become the legal owner of the leased property by purchasing it.
For the subject of leasing, you need to draw up a transfer and acceptance certificate. Depreciation is calculated by the party whose property is recorded on its balance sheet.
Fill out and send reports to the Federal Tax Service on time and without errors with Kontur.Extern. 3 months of service are free for you!
Try it
Accounting and tax accounting of leasing from the lessee
In order to correctly reflect the leased item on the accounting accounts, you need to know on whose balance sheet it is listed.
Accounting for leased property on the lessor's balance sheet
If the object is accounted for on the lessor's balance sheet, the lessee uses accounting account 001. It is from this account that all leasing operations begin. Using the example of Tekhnik LLC and Spusk LLC, we will analyze all the nuances of accounting. You will find not only postings, but also detailed calculations.
Tekhnik LLC received from Spusk LLC under agreement No. 25 dated January 1, 2019, a lease of the A187 hydroelectric power station worth 1,296,000 rubles, including VAT 216,000 rubles. The total rental period is 36 months. The monthly payment is 36,000 rubles, including VAT (20%) 6,000 rubles. After three years, the equipment is purchased by Tekhnik LLC, the redemption price is already included in the monthly payments.
In the accounting of Tekhnik LLC, the accountant will make the following entries under the leasing agreement:
Debit 001 - 1,296,000 - equipment is put on off-balance sheet accounting
Debit (20, 26, 44 - depending on the purposes for which the leased asset is used) Credit 76 - 30,000 - monthly lease payment accrued (the accountant of Tekhnik LLC will make this entry monthly for three years)
Debit 19 Credit 76 - 6,000 - VAT on the lease payment is reflected (Tekhnik LLC will make this entry once a month)
Debit 68 Credit 19 - 6,000 - VAT accepted for deduction (Tekhnik LLC will make this entry monthly)
Debit 76 Credit 51 - 36,000 - the lease payment was transferred to the account of Spusk LLC (Tekhnik LLC will make this posting monthly)
Loan 001 - 1,296,000 - equipment was written off from the register of Tekhnik LLC, since all obligations under agreement No. 25 dated 01/01/2019 were fulfilled
Debit 01 Credit 02 - 1,080,000 (1,296,000 - 216,000) - the cost of the purchased hydroelectric power station A187 is reflected in the fixed assets of Tekhnik LLC
Redemption value of leased property: transactions with the lessee
If Tekhnik LLC bought the equipment for a fee, the following entries would be made in accounting:
Credit 001 - equipment was written off from the register of Tekhnik LLC due to the expiration of contract No. 25 dated 01/01/2019
Debit 60 Credit 51 - redemption price for hydroelectric power station A187 is transferred
Debit 08 Credit 76 - leased equipment purchased (hydroelectric power station A187)
Debit 19 Credit 76 - VAT included
Debit 01 Credit 08 - the accountant of Tekhnik LLC included hydroelectric power station A187 in fixed assets
Debit 68 Credit 19 - VAT on hydroelectric power station A187 accepted for deduction
Early repurchase of leased property: postings from the lessee
Debit 97 Credit 76 - the amount of remaining lease payments excluding VAT
Debit 19 Credit 76 - VAT allocated
Debit 68 Credit 19 - VAT is accepted for deduction.
Debit 76 Credit 51 - the remaining lease payments are listed
Debit 20 Credit 97 - the accrued amount of payments is written off ahead of schedule (monthly for the remaining term under the agreement)
Accounting for leased property on the lessee's balance sheet: entries
Tekhnik LLC received from Spusk LLC under agreement No. 25 dated January 1, 2019, a lease of the A187 hydroelectric power station worth 1,296,000 rubles, including VAT 216,000 rubles. The total rental period is 36 months. The monthly payment is 36,000 rubles, including VAT of 6,000 rubles. After three years, the equipment is purchased by the lessee for 20,000 rubles.
In this case, Tekhnik LLC will need to open sub-accounts to account 76, for example:
- "Rental obligations";
- "Debt on leasing payments."
The following entries will be made in the accounting of Tekhnik LLC under the leasing agreement:
Debit 08 Credit 76 (sub-account “Rental obligations”) - 1,096,666.67 (1,296,000 + 20,000) / 1.20) - hydroelectric power station A187 accepted for accounting
Debit 19 Credit 76 (sub-account “Rental obligations”) - 219,333.33 - VAT allocated
Debit 01 Credit 08 - 1,096,666.67 - equipment classified as fixed assets for further accounting
Debit 76 Credit 51 - 36,000 - the lease payment was transferred to the account of Spusk LLC (Tekhnik LLC will make this entry monthly for three years)
Debit 76 (sub-account “Lease obligations”) Credit 76 (sub-account “Debt on leasing payments”) - 30,000 - monthly lease payment accrued (the accountant of Tekhnik LLC will make this entry monthly for three years)
Debit 68 Credit 19 - 6,000 - VAT accepted for deduction (Tekhnik LLC will make this entry monthly)
Debit 20 (26, 44 - depending on the purposes for which the leased asset is used) Credit 02 - 30,462.96 (1,096,666.67 / 36) - depreciation accrued (Tekhnik LLC will make this entry monthly)
Debit 76 (sub-account “Lease obligations”) Credit 76 (sub-account “Debt on leasing payments”) - 20,000 - the debt on the redemption value of the leased property is reflected (the accountant of Tekhnik LLC will make this entry monthly for three years)
Debit 76 Credit 51 - 20,000 - transferred to the account of Spusk LLC, redemption price
Debit 01 Credit 01 - 1,096,666.67 - hydroelectric power station A187 transferred to the category of own funds after three years
Debit 02 Credit 02 - 1,096,666.67 - depreciation reflected
Accounting for VAT on advance payments in accounting entries
Entries for an advance payment under a leasing agreement, which the accountant must use to reflect transactions related to accounting, restoration and refund of VAT:
| Contents of operation | Dt | CT |
| The advance payment from the leasing recipient (first transfer, then offset) is carried out simultaneously with the offset of this advance from the lessor. The prepayment is a component of the amount of leasing payments (according to the conditions specified in the contract). | 76, subaccount for advances issued | 51 |
| Reflection in the balance sheet of the amount of VAT on the transaction | 68, subaccount for VAT accounting | 76, subaccount where VAT on advances issued is taken into account |
| After receiving the leased object (according to the invoice, acceptance certificate, etc.), the previously allocated VAT is subject to restoration | 76, subaccount for accounting for VAT on advances issued | 68, subaccount for VAT accounting |
| An advance payment loses its prepayment status at the time of official purchase of the goods. Basis – transfer and acceptance act, invoice | 76, subaccount for accounting for rental obligations | 76, subaccount for accounting for advances issued |
| According to the invoice, invoice or acceptance certificate, the accountant charges VAT | 19 | 76, subaccount for accounting for rental obligations |
| The amount is to be deducted | 68 | 19 |
Upon receipt of an advance payment to the current account, the lessor is obliged to issue an invoice within 5 days (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code). Until that moment, the recipient organization has no basis for accepting the VAT amount for reimbursement as part of the advance payment (clause 12 of Article 171 and clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code).
The amount of the advance issued is reflected in the balance sheet minus VAT. After receiving the invoice, the accountant will be able to reflect it as follows:
| Contents of operation | Dt | CT |
| Fixed assets are reflected upon receipt on the balance sheet (using the acquisition subaccount under a leasing agreement) | 08 | 76 |
| Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting as property acquired on lease | 01 | 08 |
Accounting with the lessor
Let's take a closer look at leasing in transactions with the lessor.
Spusk LLC leased hydroelectric power station A187 to Tekhnik LLC under agreement No. 25 dated January 1, 2019, with an initial cost of 1,296,000 rubles, including VAT of 216,000 rubles. The total rental period is 36 months. The monthly payment is 36,000 rubles, including VAT of 6,000 rubles. After three years, the equipment is purchased by the lessee for 20,000 rubles. The redemption price is included in the monthly payments of Tekhnik LLC.
Leasing: accounting features for legal entities
Currently, both individuals and legal entities can lease a car. But the obligation to record transactions with such a car in accounting and tax accounting arises only for legal entities.
At the same time, legal entities can take advantage of certain preferences that individuals do not have, in particular, reduce the tax base for profits on leasing payments and deduct VAT paid to the lessor. It is important to remember that these preferences are applicable under the general taxation system. The use of special modes by legal entities is characterized by its own nuances, for example:
- when applying the simplified tax system “income”, leasing expenses cannot be written off as a reduction in the tax base in the same way as other expenses for conducting business;
- when applying UTII, the calculation of tax payable is also carried out according to certain principles, which do not include the deduction from the tax base of the costs of payments under the leasing agreement.
Further in the material we will talk about accounting for car leasing from legal entities located on OSNO. We will not touch upon tax accounting issues, since there are some discrepancies in the professional literature and publications due to the fact that the legal issues of leasing accounting in the Russian Federation are not fully regulated.
The issues of distinguishing between accounting and tax entries are presented in detail in the articles: