Delay of wages in Russia, as well as other payments, is a serious violation of labor rights. Employers sometimes ignore payment deadlines in pursuit of their own personal gain. Such violations should not go unpunished, especially if the delay is significant.
Do they have the right to delay, how to achieve timely payments, receive a penalty and bring the violator to justice, and much more will be discussed in the article.
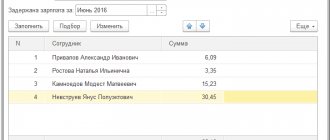
- Case 1. Payment delay for more than 15 days
Rights of an employee who has not received his salary on time
An employee who has not received his salary within the prescribed period has the opportunity to file a complaint with the State Labor Inspectorate (Rostrud) or file an application in court. Both authorities are contacted at the location of the employer.
The employee may not show up for work during the period of suspension. Moreover, the employer is obliged to pay him for this entire period, based on the employee’s average earnings.
However, not every situation, place of work or position allows an employee to take advantage of such a measure.
Documents attached to the application
The statement of claim will need to be accompanied by documents indicating, firstly, that you have an employment relationship with the employer, and secondly, documents confirming your claims.
Thus, in general terms, the list of attached documents should look like this:
- An extract from the work book, which can be obtained from the personnel service or from the accounting department of the enterprise.
- Employment contract.
- Interest calculations that you can do using the calculator.
- Optional documents, for example, indicating that you missed a deadline for a good reason or the costs of a lawyer that you are asking to recover from the employer.
- Copies of statements of claim at the rate of “one for the court, one for the defendant.”
When submitting an application, it would be useful to have an additional copy with you, on which the court employee will put a mark of acceptance.
Employer's liability in case of delayed wages
The liability arising from the employer in connection with delays in salary payments may turn out to be:
- material - it is provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- administrative - in accordance with both the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation and the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- criminal - according to the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
The first type of liability obliges the employer to pay compensation to the employee for late payment and compensate for moral damages, if such compensation is provided for in the employment agreement.
The decision to impose liability of the second type is made by the inspector of Rostrud. Moreover, such responsibility can be expressed not only in the requirement that the employer and its officials pay an administrative fine.
Since December 13, 2019, Rostrud has the right to make a decision on collecting wage debts out of court through the FSSP if the employer does not comply with its instructions to repay such debt.
Criminal liability concerns only managers and is associated with their personal interest in non-payment. If such a crime is committed for the first time, they can be released from criminal liability if they pay back wages and compensation for delayed payments within 2 months from the date of initiation of the criminal case.
The amounts of sanctions arising from each type of liability are given in the table.
Is it possible to delay wages without issuing compensation?
Some documents contain information that allows for a legal delay in wages of up to two weeks. But this is an incorrect interpretation of Article 142 of the Labor Code.
Paragraph 2 of this article is devoted to the fact that employees are prohibited from suspending their duties if the following circumstances are present:
- Work is related to the maintenance of life.
- Responsibilities include maintaining hazardous facilities.
- An employee in the state or military service.
But the employer, even in such cases, is not exempt from delays in wages and payment of compensation.
Let's sum it up
- Regarding the timing of salary payments, the rules enshrined in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation apply, obliging the employer to make such payments twice a month and adhere to the dates established for this.
- A delay in payment allows an employee not only to appeal to Rostrud or the courts, but also to suspend work if wages are not paid within 15 days. The employer is obliged to pay for the period of suspension if all the conditions accompanying this procedure are met.
- For an employer, untimely payment of wages results in liability, which has 3 types - material, administrative, criminal. The first boils down to the need to pay compensation for the delay, but may also require compensation for moral damage. Involvement in the second is carried out by an inspector of Rostrud, and it may concern both the employer and its officials. The third arises only for managers and only if they have a personal financial interest in delaying payments.
The permissible intervals for making payments to personnel, as well as the maximum possible time that should pass between the performance of work and its payment, are established by law (Articles 136, 140, 141 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Any deviation from these standards is unacceptable, however, the duration of the delay in wages directly affects the severity of the sanctions applied to the employer.
- What are the acceptable deadlines for salary payments?
- Can an employer withhold wages without consequences?
- What does an employer face for delaying wages?
Salary advance: calculation rules
Its value is now equal to the value of the Central Bank key rate.
The algorithm for calculating compensation is as follows:
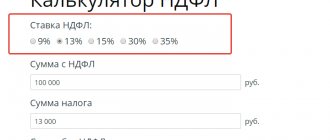
DK = ZP X (1: 300) X KST X DP
where DK is compensation for late payment of monetary reward;
ZP – the total amount to be paid to the employee;
KST – key rate fixed by the Central Bank;
DP – number of days of delay in payment of earnings.
Example of compensation calculation:
The LLC has drawn up a collective agreement, which stipulates the terms for payment of wages: the first part - on the 21st of the current month; the second part – on the 6th of the next billing period.
For the second half of March 2021, the employee was credited 22,000 rubles, taking into account the withheld personal income tax. In fact, the money was transferred to the bank card only on April 25, the delay was 18 calendar days.
Cash compensation is calculated using the formula:
DK = 22000 x 1/300 x 11 x 18 = 145.20 rubles.
According to the above procedure, the minimum amount of compensation fixed in labor law is calculated. The workforce, together with the trade union, may propose to the employer that a different calculation algorithm or an increased amount of compensation be established in the collective agreement.
For the legislator, the absence or presence of the employer’s fault in case of delay in payment of the due remuneration is not significant; in any case, he is obliged to compensate the employee’s monetary losses.
Accounting and taxation of compensation
Guaranteed compensation for delays in official payments to an employee, like all other types of compensation, are not subject to personal income tax.
For the employer, the calculation of compensation involves additional tax and mandatory payments:
• accrued compensation does not reduce the tax base for income tax;
• from the compensation amounts it is necessary to pay contributions to extra-budgetary funds - Social Insurance Fund, Pension Fund, Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
For employers using the “simplified” tax system according to the “income minus expenses” scheme, the annual income tax cannot be adjusted downwards for compensation expenses.
If the employer’s delays in payment of wages become a system, and the delays exceed half a month (15 days), then employees are given the right to take measures to normalize the situation:
• payment can be accelerated by a written request from employees to the labor inspectorate with a mandatory indication of the violated right (non-payment of wages), the number of days of delay and the amount due for payment;
• refuse to perform duties and suspend work until the labor remuneration is fully paid. All days of forced downtime at work must be paid according to average earnings;
• resort to the help of the judiciary, police and prosecutor's office - illegal actions of the administration for non-payment of wages are punishable by administrative and criminal penalties.
Keep in mind: suspension of work is impossible for workers in areas related to the vital support of the population or with dangerous working conditions - military personnel, police officers, public utility employees, and doctors.
When filing a claim in court, members of the labor collective can add to the amount of debt not only the amount of compensation, but also the inflation rate established in the country. If the employer recognizes the workers' claims, then a writ of execution for the entire amount is issued without a court hearing.
What does an employer face for violating the terms of payment of salary?
Violation of labor legislation, expressed in non-compliance with the salary payment schedule, is an administrative offense recorded in Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offences. For such an offense, a fine is imposed on both the manager and the enterprise - up to 5 and 50 thousand rubles, respectively.
If a similar offense is repeated, the head of the company may lose his position for a period of 1 to 3 years.
Criminal prosecution may occur in case of long delays in the payment of required types of remuneration or benefits, if the delays are associated with the manager’s selfish or personal motives. If at least 50% of the due remuneration remains unpaid on time, then the punishment may range from a fine of 120,000 rubles to two years in prison.
What are the acceptable deadlines for salary payments?
Expert opinion
Gusev Pavel Petrovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in defense in court.
The entire list of restrictions on the dates of transfer of payment for work done is enshrined in Art. 136, 140, 141 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, the timing of salary payment depends on the specific circumstances of its accrual:
- For amounts for work performed, both systematic and one-time, the following parameters must be adhered to: Payment occurs every half month;
- The transfer of money is carried out no later than 15 days after the end of the time period for which the accrual was carried out.
There are no provisions in legislative acts allowing for delays in employee salaries.
Consequences of missing a deadline
If the statute of limitations is missed, the case will not be considered and the judge will make a decision to reject the claim without examining the circumstances of the case.
Therefore, if it happens that you missed the deadline out of laziness or ignorance of the law, then before filing a claim in court, take care of several things:
- Think about how you might motivate missing a deadline. To extend the period, the reason must be valid - illness, caring for a sick family member, funeral, wedding, administrative arrest, etc. But the reason will have to be confirmed. As an option, think about your chronic illnesses, run to the doctor, tell him that you have been feeling bad for two months now, but you have been patient, and let him write it all down in your chart.
- Indicate in the statement of claim that you are asking to reinstate the missed deadline for a valid reason.
- Attach to the claim documents confirming valid reasons for missing the deadline. Perhaps the court will believe you.
If you could not come up with a good reason, then there will be little chance of winning the case. However, you can still file a claim. And at the same time hope that the employer will not come to court and the decision will be made in his absence or that the employer will simply admit your claim.
Can an employer withhold wages without consequences?
In general, an unpunished delay in the payment of wages, as noted above, is impossible. According to the provisions of Art. 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer in any case charges the employee a penalty for each day of delay in the amount of 1/150 of the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation calculated from the amount of debt.
But it is also necessary to take into account the provisions of Art. 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which regulates the procedure for self-defense of workers.
It gives the employee the right to temporarily suspend work only in the event of non-payment of wages in full or in part for more than 15 days. Based on this, an employee can initiate complaints to inspection authorities, the court or the prosecutor's office only after the expiration of the specified period, or in the event of non-payment of the above penalty, since this would be a direct violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, if the employer paid the salary with due penalties within 15 days after the date of accrual established by local regulations, most likely he will not suffer any more severe punishment.
In what ways can you receive compensation?
An employee has several solutions if the manager himself refuses to fulfill his duties.
| Where to go | A comment |
| Labour Inspectorate | Already on the first day of violation of deadlines, you can contact representatives of this body. But maximum - after three months. The three-month period is counted from the moment the debt is repaid by the employer. But - if at the time of application the debt has not yet been repaid. |
| Prosecutor's office | It is better to contact the prosecutor if the delay exceeds two months. Otherwise, the application will still be forwarded to labor inspectors |
| Court | This method is used if the solutions do not produce results. A statement of claim is drawn up, and the employer is appointed as the defendant. The main thing is to present the essence of the problem in detail and use as much evidence as possible. Among the evidence we can highlight the following papers:
|
What does an employer face for delaying wages?
For those who violate the deadlines for settlements with personnel, the legislation provides for several types of liability. Each of them depends on certain parameters, including the delay period:
- Financial liability, in the form of a penalty, occurs in any case, even if the deadline is not met by only 1 day;
- Administrative liability, ranging from fines to disqualification, will be applied if the delay is more than 15 days, and the employee contacts the authorized bodies;
- Criminal punishment is applied if there is personal intent of the manager in the following cases: Complete non-payment for more than 2 months;
- Partial (less than half the amount) non-payment for more than 3 months;
- Payment less than the minimum wage issued for more than 2 months.
In this regard, the employer should think about whether it is worth delaying wages at all.
One of the mandatory conditions that must be included in the employment contract of every worker is the timing of payment of wages. And the employer is obliged to comply with them and pay the money due to the workers on time.
- Salary payment terms
- How to determine the payday and delay period
- Compensation for delayed wages
- Formula and example of calculating compensation for 1 day salary delay
- When must an employer pay compensation amounts?
- What to do if the company management refuses to pay compensation
- Responsibility of the enterprise for delays in wages and non-payment of compensation
Procedure for collecting monetary compensation
After the expiration of the last period during which the employer is obliged to pay wages, interested parties:
- Establish the debt at the time of application.
- Calculate compensation.
- Draw up and send an application demanding the necessary payments and compensation.
The application can be individual or collective. In the latter case, all interested parties sign. The appeal is submitted officially through the office of the head, by mail.
The sender must keep documents confirming the fact of the application - checks, receipts, an internal inventory of the postal item or the signature (and date) of the secretary on receipt of the application.
What payment is due (calculation)
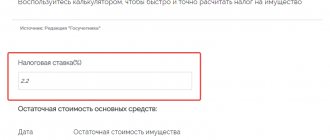
To carry out the calculations, use the formula K=Сзд×Кдзд×Ксрф/150, where :
- K – amount of compensation;
- Szd – amount of salary debt;
- Kdzd – the number of days during which the debt to the labor collective is valid;
- Ksrf is the key refinancing rate.
The debt amount is taken without personal income tax. This is explained by the fact that wages are issued with the deduction of tax, which means that the actual debt is taken without it.
The number of days is calculated taking into account the fact that the delay period:
- Begins to be calculated from the next day after the final date of payment of wages;
- All days are taken into account, including weekends and holidays, as well as the day of actual payment, which is the last day of delay.
The key rate refers to the interest rate adopted by the Central Bank for issuing loans to commercial credit institutions (or accepting deposits from them) for a period of 1 week. Affects size :
- Inflation.
- Interest on deposits in banks.
For calculations, the value is taken in tenths or thousandths (0.1 if 10% or 0.09 if 9%) or in the formula it is further divided by 100. The terms of the employment contract may establish a different percentage for late payments. In this case, the parameters specified in the agreement are used.
If you are interested in using the interest calculator for late payment of wages, we recommend that you read this article.
Calculation example
30 days have passed from the first day of overdue payment to the full repayment of the debt to the labor collective. Ten employees were not paid 42 thousand rubles each. The key rate is 9%.
The required compensation for each of the 10 employees is K = 42 × 30 × 0.09/150 = 756 rubles. Each employee is entitled to pay 42 thousand 756 rubles.
Deadlines
If previously the employer set the payment period independently, it could be vague, but from October 2021 the Legislator has introduced strict dates that are mandatory for everyone :
- For the issuance of basic wages - no later than the 15th day of the next month;
- For advance payment - no later than the 30th day of the current month.
The day following these dates is the beginning of the calculation of the period of delay. But there are payments that are regulated by the internal regulations of the enterprise. These include bonuses: quarterly, annual, one-time.
Vacation pay must be transferred no later than three days before the start of the vacation. Severance pay and compensation for unused vacation are paid on the day the employee is dismissed.
Also on the day the salary is transferred, benefits are paid:
- For pregnancy and childbirth;
- For child care;
- Due to illness (sick leave).
The benefit in connection with the birth of children is paid within 10 days from the date of submission to the employer of documents that are the basis for the accrual. On the day the documents are submitted, a funeral benefit is issued.
These deadlines are the starting point for calculating the number of days overdue. But interested parties should take into account that the time to go to court is limited. The statute of limitations for compensation for delayed wages is 1 year.
Salary payment terms
The timing of the payment of wages is regulated by Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, according to which it is paid:
- By issuing cash or transferring money to a person’s account.
- At least every 15 days, respectively, at least twice a month.
- Wages for a particular month must be issued to the worker no later than 15 days after the end of the month.
- Salary amounts are paid personally to the person (transferred to his account), unless otherwise provided by law.
All other issues related to wages can be decided by the head of the company at his own discretion, provided that he does not violate the above rules. Thus, the employer has the responsibility to:
- Determining the place for issuing funds.
- Determining the frequency of issuance (payments can be made more often than twice, for example, every week).
- Determining specific dates for the employee to receive advance payments and wages.
One of the common mistakes made by employers is to set a period rather than a specific date of issue. For example, wages will be issued from the 5th to the 10th. This is incorrect, the above article says that a specific date for the payment of salaries must be determined.
Fixed rate or payment of compensation at the Central Bank rate?
Many novice entrepreneurs are concerned about the question: what is the best course of action: indicate the rate in the contract or charge at the minimum established by law? Both options have their pros and cons. If you specify a fixed rate in the contract, you can significantly simplify the calculations, calculate the amount of compensation for 1 day in advance, and then simply multiply this number by the number of days if delays occur. But on the other hand, the amount of payments will always be greater than if compensation is paid at the Central Bank rate. But if you decide to pay at the Central Bank rate, you will need to constantly monitor changes in the refinancing rate and make calculations using a new one each time.
However, if previously this really took time, now the process has been significantly simplified. There are many online calculators on the Internet. However, they need to be checked. Sometimes the Central Bank rate changes, but the indicators on the websites do not have time to change. As a result, you get the wrong number.
In any case, a fixed rate simplifies the calculation process somewhat. But what to choose is up to you.
How to determine the payday and delay period
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation indicates that if the day designated as the date of transfer of advance payment or wages falls on a weekend, then the issuance of funds is carried out on the last day of work before it.
The table below shows several situations when you need to pay wages in advance and how this can affect the delay period.
| Date of payment of wages (advance) | Date to which payment must be postponed | Delay period |
| The date of payment of wages is determined on the 2nd of the month. May 2, 2021, according to the production calendar, will be a public holiday. | In this case, the salary must be paid no later than April 28, 2021, since all subsequent days will be days off. | Even if the employer pays wages on May 3, that is, tomorrow after the due date, the delay period will be 5 days. |
| The salary transfer date is set on the 9th day of the month. May 9, 2021 will be a public holiday. | In this case, salary payment must be made on May 8, 2021 | If it is paid on May 10, then the delay period will be 2 days, since in this case the payment is automatically postponed to May 8. |
Calculation examples
Let’s say that in regulatory documents the organization has established the following payment period:
- The advance is paid on the 20th of the current month.
- 4th day of the month after the payroll month - regular salary.
Let’s take an employee who received an advance of 5 thousand with a salary of 10 thousand. The latter is listed not on the 4th, but on the 22nd. Because of this, there was an 18-day delay. For the period of delay, the refinancing rate is 8.25%. In fractions of one it is 0.0825. The compensation calculation will look like this:
K = 10,000 x 18 x 1/150 x 0.0825 = 99.
99 – final salary increase on the day of issue.
Compensation for delayed wages
Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the following rules for the payment of compensation amounts for late wages:
- The amount of compensation must be no less than 1/150 of the approved key rate.
- Compensation is calculated on the overdue amount, and not on the entire salary;
- Compensation is issued immediately, along with your salary.
The legislation regulates only the minimum threshold of compensation; an organization can increase it by stipulating this in local regulations.
The employer needs not only to pay compensation to the employee, but also to accrue all insurance premiums, as stated in the letter of the Ministry of Labor dated April 28, 2016, No. 17-3/OOG-692.
Accounting and taxation of compensation
Guaranteed compensation for delays in official payments to an employee, like all other types of compensation, are not subject to personal income tax. For the employer, the calculation of compensation involves additional tax and mandatory payments:
- the accrued compensation does not reduce the tax base for income tax;
- From the compensation amounts, contributions must be paid to extra-budgetary funds - Social Insurance Fund, Pension Fund, Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
For employers using the “simplified” tax system according to the “income minus expenses” scheme, the annual income tax cannot be adjusted downwards for compensation expenses.
When must an employer pay compensation amounts?
The employer must provide compensation immediately with wages, reflecting it as a separate line on the payslip.
Example: May LLC was supposed to issue wages on the 5th, but delayed them by 1 day, and they were paid only on the 6th. In this case, compensation must be calculated and paid along with earnings on the 6th.
When should compensation be given for an overdue advance, when paying an advance or salary? Payment of compensation amounts for delayed advance payments is made on the day it is transferred to employees, and is not postponed until the date of wages.
Do I need to make an order?
There is a need to issue an order in case of delays in wages. The design form is arbitrary. The main thing is that current standards and local rules applied at the enterprise are not violated.
The text of the accrual order must contain the following information:
- Reason for calculating compensation.
- Payment amount.
- The period for which the salary was initially delayed.
The order is given to the employee for study, against signature.
What to do if the company management refuses to pay compensation
In most cases, the employer does not charge compensation for late wages by default, especially if the delay was only one day. The amount to be paid with such a delay will be very small, but in this case, workers must still defend their rights.
Expert opinion
Gusev Pavel Petrovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in defense in court.
To begin with, you can contact the management of the enterprise in writing with a request to accrue the compensation due. The application is drawn up in free form.
If management refuses to calculate compensation, the employee can appeal the violation of his rights to the relevant organizations.
In the table below you can see where a person whose rights have been violated can turn:
| Name of company | Application procedure | Complaint consideration period |
| State Labor Inspectorate | The employee writes a statement listing all the facts of what happened. | Within 7 days |
| Prosecutor's office | The employee writes a statement (complaint) in which he indicates all the facts of what happened | Within 30 days |
| Judicial authorities | The employee files a statement of claim, which must contain the specific demand of the plaintiff, in this case the calculation of compensation | In the order of consideration of cases by the court |
Case practice
The Moscow District Court considered the claim of the labor collective against a private entrepreneur. The applicants' demands were for payment :
- Delayed wages in the total amount of 1.5 million rubles.
- Compensation of 30 tr. (2 tr each).
- Compensation for moral damage – 100 rubles. (10 tr each).
In addition, the applicants demanded payment of legal costs. The court reviewed the case and found the delay compensation calculations to be incorrect. Thus, the total debt period was 45 days, of which the Central Bank refinancing rate was:
- 23 days – 9%;
- 22 days – 9.5%.
The total amount of compensation was K=1500000×23×0.09/150+1500000×22×0.095/150=20700+20900=41.6 tr. or 4160 rub. to each. The rest of the claims were satisfied, with the exception of moral damages. The court reduced the requirements to 30 thousand rubles. based on 3 tr. to each.
Responsibility of the enterprise for delays in wages and non-payment of compensation
An administrative penalty may also be imposed on the employer for delaying wages. As well as for refusal to voluntarily accrue compensation for late payments. There is no separate article in the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation for delayed payments, therefore the punishment is imposed in accordance with paragraph 6 of Article 5.27.
In this situation, the penalty is:
- From 1 thousand to 5 thousand rubles for individuals who are individual entrepreneurs;
- From 10 thousand to 20 thousand rubles for responsible employees of the company;
- From 30 thousand to 50 thousand rubles in relation to a legal entity.
This administrative penalty can be imposed on the employer even if the salary is delayed by 1 day.
If wages are delayed, the employer is obliged to pay compensation to employees, even if the delay is only one day. Compensation must be accrued by the employer on a voluntary basis; moreover, he must inform employees that they are entitled to compensation. As a rule, this information is included on payslips.
Information updated and current as of December 2021
- What is delayed wages from a legal point of view in 2021?
- Legal regulation of the issue in 2021
- How many days can an employer legally withhold wages?
- What can an employee do if his salary is delayed?
- How to receive monetary compensation from an employer without conflict
- What to do if wages have been delayed for half a month
- What to do if the problem is not resolved between the parties within the team
- Labor Dispute Commission
- Labour Inspectorate
- Prosecutor's office
- District Court
- Magistrate's Court
- Important nuances and features of filing a complaint about the lack of salary in 2021
- What are the consequences for an employer if they delay an employee’s salary in 2021?
- Penalties for delayed salary payments in 2021
- Financial compensation
- Court and employer
- Bottom line
What consequences does a delay in paying wages have for an employer and what rights employees have to legally defend their rights and resolve the issue as quickly as possible - today one of the regular authors of the column on labor law in the Russian Federation, a practicing lawyer, Oleg Ustinov, will tell you.
Let us immediately note that the terms and procedure for paying wages to employees are clearly regulated by regulations, the rules of which must be complied with, regardless of the legal form and type of employers.
Unfortunately, every year, more and more employers violate the norms established by the legislator, ignoring the legal demands of their employees to pay the latter wages in full.
The size of debts in the Russian Federation
According to Rosstat, as of October 1, 2021, in the Russian Federation, the amount of overdue wages for employees who are not small businesses amounted to 2.5 billion rubles. Monitoring the monthly situation shows that the figure generally remains around this level, occasionally increasing in some months to 3 billion rubles.
According to experts, today the largest volume of overdue wages is recorded in Moscow. True, if we take into account the scale of this region and the overall share of the economically active population, then even such figures will look very modest.
What is delayed wages from a legal point of view in 2021?
According to the standards established in the labor legislation of the Russian Federation, wages must be paid twice a month (that is, every 15 days), and a delay in payments is considered to be any deviation by the employer from these terms.
At the same time, specific dates for the payment of remuneration to employees for work are prescribed individually in the employment contract drawn up upon hiring.
Such violations of employee rights can lead to negative consequences not only for management, but for the company as a whole.
Legal regulation of the issue in 2021
As we mentioned above, according to the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to pay wages 2 times a month. As an exception, an employee may perform any work under a previously executed civil law agreement.
In this situation, the employer has the right to pay the remuneration in question within a timeframe that suits both parties.
In the event of a delay in wages for a period exceeding the standards established by the legislator, the employee has the legal right to complain (in writing) about the employer to the relevant authorities that control this field of activity.
How many days can an employer legally withhold wages?
Based on the information contained in the Labor Code, the period of delay by the employer of wages should not exceed 15 days. In the event that remuneration for work is not paid to the employee within a given period, he can defend his rights by taking established measures.
According to the provisions of the Labor Code, all employed residents of the country must receive wages on time, twice a month. Otherwise, the negligent employer will have to answer before the law. The legal aspects of payments are regulated by the law on delayed wages in 2021.
Delay of wages: legislative framework
All legal issues relating to the payment and delays of wages are regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The bill was adopted in the first reading by State Duma deputies in 2001.
The main basis for the formation of a strong working relationship between employer and employee is considered to be a correctly drawn up employment contract. The document protects the rights of the worker and guarantees that the court will side with him if the fact of a delay in payment of wages is recorded.
Main provisions of the bill
According to current regulations, delays in cash payments are not permitted. If such a violation occurs and lasts longer than 2 weeks, the employee has the right to stop performing official duties until he receives the due funds.
You just need to inform the employer about this. In some cases, it is not permitted to cease operations.
So, representatives of certain professions cannot do this:
- military personnel;
- social workers;
- employees of the Ministry of Emergency Situations;
- civil servants;
- representatives of the medical field.
If an employee goes on strike due to non-payment of wages, he has the right not to come to work. Moreover, the employer will be obliged to pay him even for those days when professional activities were not carried out.
It is prohibited to impose penalties for failure to fulfill work duties if the employee does not show up for work due to late payments.
The official text of the Labor Code states that the employer is obliged to pay compensation to the employee for each day of delay. It is calculated as a percentage of the amount of payment not received on time. The bill also determines that administrative proceedings may be initiated against an unscrupulous employer.
In the most difficult cases, the head of a company in which wages are withheld may be held criminally liable. This usually happens in cases where funds have not been transferred for at least 2 months.
Criminal liability is provided if it is proven that the manager deliberately initiated the bankruptcy procedure of the company.
Changes to the Labor Code
The latest amendments made to the bill concerned the establishment of compensation for delayed wages. The parliamentarians determined that the employer is obliged not only to pay the due amount in full, but also to pay the employee a percentage for each day of delay.
According to current regulations, the payment should be 1.5% of the average monthly salary per day.
This percentage can be increased if specialists identify violations on a large scale, i.e. if the number of victims from the actions of an unscrupulous employer reaches several people. You can recover compensation from the employer through a complaint to the labor inspectorate or by contacting other competent authorities.
Changes were also adopted regulating payment transfers twice a month.